User login
Cesarean scar defect: What is it and how should it be treated?
Cesarean delivery is one of the most common surgical procedures in women, with rates of 30% or more in the United States.1 As a result, the rate is rising for cesarean scar defect—the presence of a “niche” at the site of cesarean delivery scar—with the reported prevalence between 24% and 70% in a random population of women with at least one cesarean delivery.2 Other terms for cesarean scar defect include a niche, isthmocele, uteroperitoneal fistula, and diverticulum.1–9
Formation of cesarean scar defect
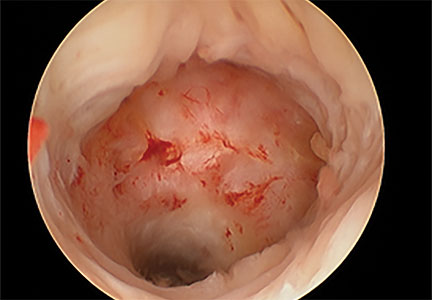
Cesarean scar defect forms after cesarean delivery, at the site of hysterotomy, on the anterior wall of the uterine isthmus (FIGURE 1). While this is the typical location, the defect has also been found at the endocervical canal and mid-uterine body. Improper healing of the cesarean incision leads to thinning of the anterior uterine wall, which creates an indentation and fluid-filled pouch at the cesarean scar site. The exact reason why a niche develops has not yet been determined; however, there are several hypotheses, broken down by pregnancy-related and patient-related factors. Surgical techniques that may increase the chance of niche development include low (cervical) hysterotomy, single-layer uterine wall closure, use of locking sutures, closure of hysterotomy with endometrial-sparing technique, and multiple cesarean deliveries.3,4 Patients with medical conditions that may impact wound healing (such as diabetes and smoking) may be at increased risk for niche formation.

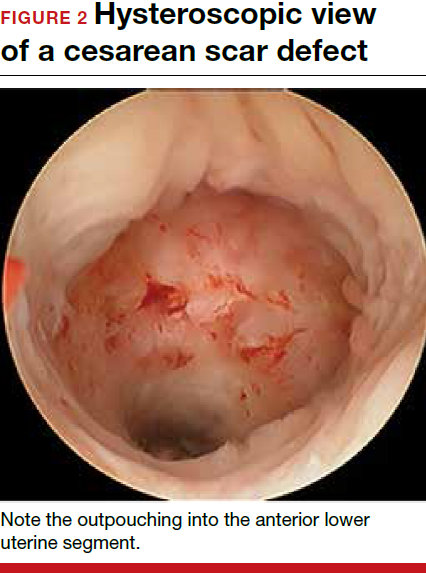
Viewed hysteroscopically, the defect appears as a concave shape in the anterior uterine wall; to the inexperienced eye, it may resemble a second cavity (FIGURE 2).
Pelvic pain and other serious consequences
The presence of fibrotic tissue in the niche acts like a valve, leading to the accumulation of blood in this reservoir-like area. A niche thus can cause delayed menstruation through the cervix, resulting in abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain, vaginal discharge, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, and infertility. Accumulated blood in this area can ultimately degrade cervical mucus and sperm quality, as well as inhibit sperm transport, a proposed mechanism of infertility.5,6 Women with a niche who conceive are at potential risk for cesarean scar ectopic pregnancy, with the embryo implanting in the pouch and subsequently growing and developing improperly.
Read about evaluation and treatment.
Evaluation and treatment
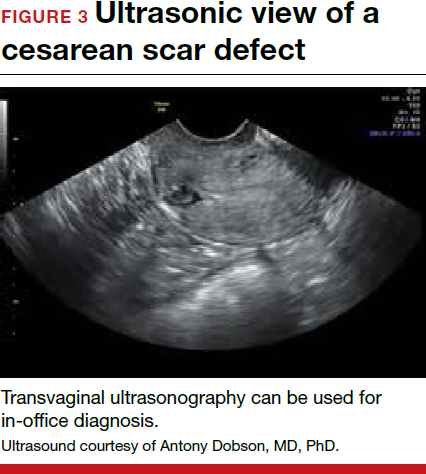
Patients presenting with the symptoms de-scribed above who have had a prior cesarean delivery should be evaluated for a cesarean scar defect.9 The best time to assess for the abnormality is after the patient’s menstrual cycle, when the endometrial lining is at its thinnest and recently menstruated blood has collected in the defect (this can highlight the niche on imaging). Transvaginal ultrasonography (FIGURE 3) or saline-infusion sonohysterogram serve as a first-line test for in-office diagnosis.7 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), 3-D ultrasonography, and hysteroscopy are additional useful imaging modalities that can aid in the diagnosis.
Treatments for cesarean scar defect vary dramatically and include hormonal therapy, hysteroscopic resection, vaginal or laparoscopic repair, and hysterectomy. Nonsurgical treatment should be reserved for women who desire a noninvasive approach, as the evidence for symptom resolution is limited.8
To promote fertility and decrease symptoms, the abnormal, fibrotic tissue must be removed. In our experience, since 2003, we have found that use of a laparoscopic approach is best for women desiring future fertility and that hysteroscopic resection is best for women whose childbearing is completed.9 Our management is dictated by the patient’s fertility plans, since there is concern that cesarean scar defect in a gravid uterus presents a risk for uterine rupture. The laparoscopic approach allows the defect to be repaired and the integrity of the myometrium restored.9
What are the coding options for cesarean scar defect repair?
Melanie Witt, RN, CPC, COBGC, MA
As the accompanying article discusses, the primary treatment for a cesarean scar defect depends on whether the patient wishes to preserve fertility, but assigning a procedure code for either surgical option will entail reporting an unlisted procedure code.
Under Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) guidelines (which are developed and copyrighted by the American Medical Association), procedure code selected must accurately describe the service/procedure performed rather than just approximate the service. This means that when a procedure-specific code does not exist, an unlisted procedure code that represents the type of surgery, the approach, and the anatomic site needs to be selected.
When an unlisted CPT code is reported, payment is based on the complexity of the surgery, and one way to communicate this to a payer is to provide additional documentation that not only includes the operative report but also suggests one or more existing CPT codes that have a published relative value unit (RVU) that approximates the work involved for the unlisted procedure.
The coding options for hysteroscopic and laparoscopic treatment options are listed below. The comparison codes offered will give the surgeon a range to look at, but the ultimate decision to use one of those suggested, or to choose an entirely different comparison code, is entirely within the control of the physician.
ICD-10-CM diagnostic coding
While the cesarean scar defect is a sequela of cesarean delivery, which is always reported as a secondary code, the choice of a primary diagnosis code can be either a gynecologic and/or an obstetric complication code. The choice may be determined by payer policy, as the use of an obstetric complication may not be accepted with a gynecologic procedure code. From a coding perspective, however, use of all 3 of these codes from the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) paints the most accurate description of the defect and its cause:
- N85.8 Other specified noninflammatory disorders of uterus versus
- O34.21 Maternal care for scar from previous cesarean delivery plus
- O94 Sequelae of complication of pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium.
Hysteroscopic resection codes:
- 58579 Unlisted hysteroscopy procedure, uterus
- The codes that may most closely approximate the physician work include 58561 (Hysteroscopy, surgical; with removal of leiomyomata) with 15.48 RVUs or 58560 (Hysteroscopy, surgical; with division or resection of intrauterine septum [any method]) with 10.92 RVUs.
Laparoscopic repair codes:
- 58578 Unlisted laparoscopy procedure, uterus
- The codes that may most closely approximate the physician work include 58520 (Hysterorrhaphy, repair of ruptured uterus [nonobstetrical] 24.25 RVUs or 58662 (Laparoscopy, surgical; with fulguration or excision of lesions of the ovary, pelvic viscera, or peritoneal surface by any method) with 20.14 RVUs.
You may also want to report a diagnostic hysteroscopy (code 58555), but keep in mind that payment will depend on documentation that clearly indicates that the use of the hysteroscope was for diagnostic purposes. Use of the hysteroscope to simply identify the surgical site to be repaired via the laparoscope will usually not be reimbursed separately.
Ms. Witt is an independent coding and documentation consultant and former program manager, department of coding and nomenclature, American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
The author reports no financial relationships relevant to this article.
Read about techniques for repair.
Techniques for repairing cesarean scar defect
For hysteroscopic resection of a niche, the uterus is distended and the intrauterine defect is visualized hysteroscopically, as seen in FIGURE 2. Using a bipolar or unipolar resectoscope, resect the fibrotic tissue of the defect and endometrial-like glands present within the niche. The goal of this relatively quick procedure is to open up the reservoir and facilitate the complete drainage of menstrual blood, thus alleviating the patient’s symptoms.Postoperatively, follow the patient for symptom resolution, and evaluate for defect resolution with transvaginal ultrasonography.
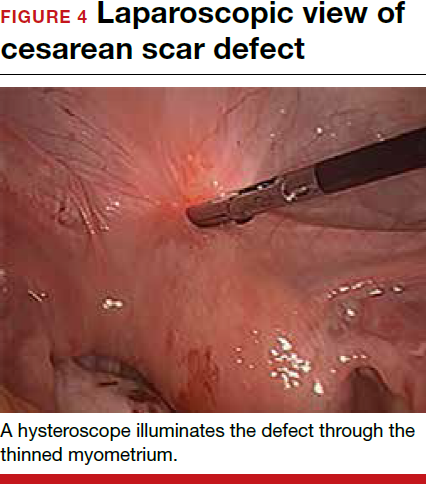
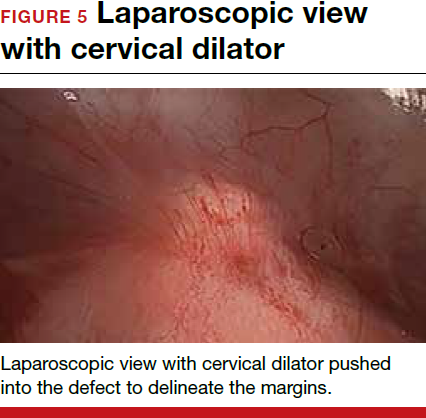
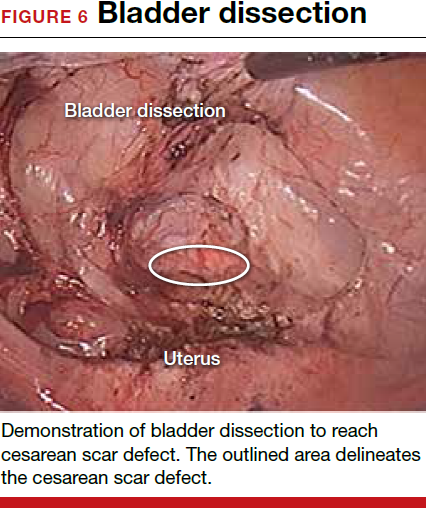
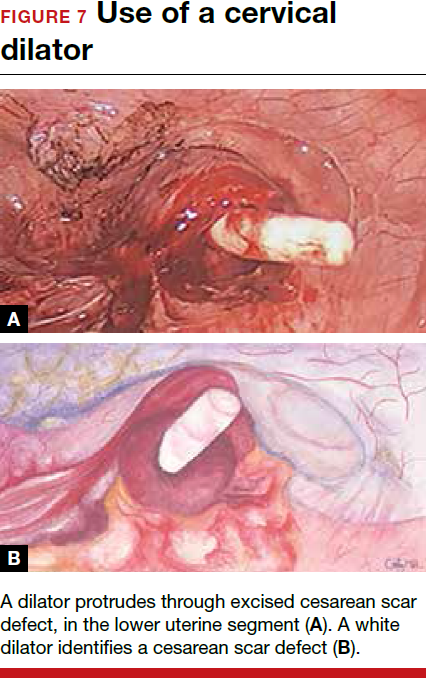
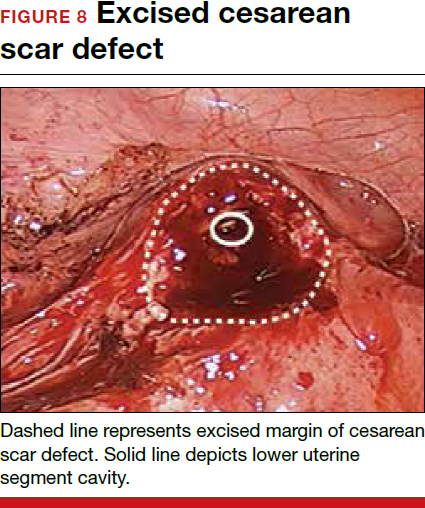
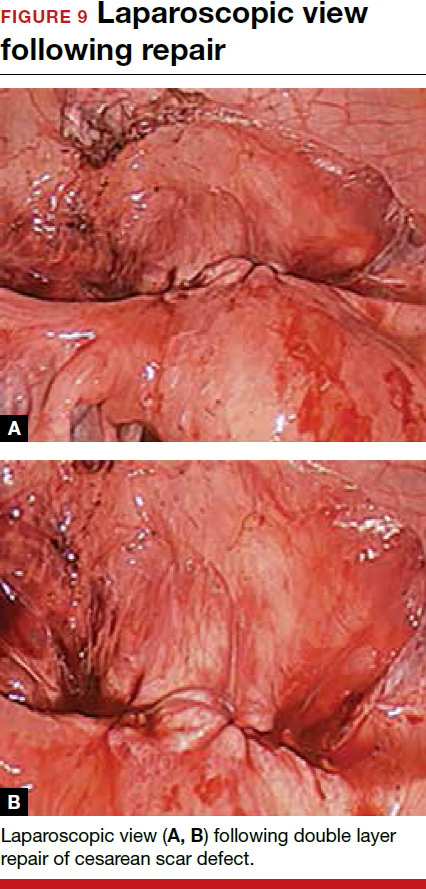
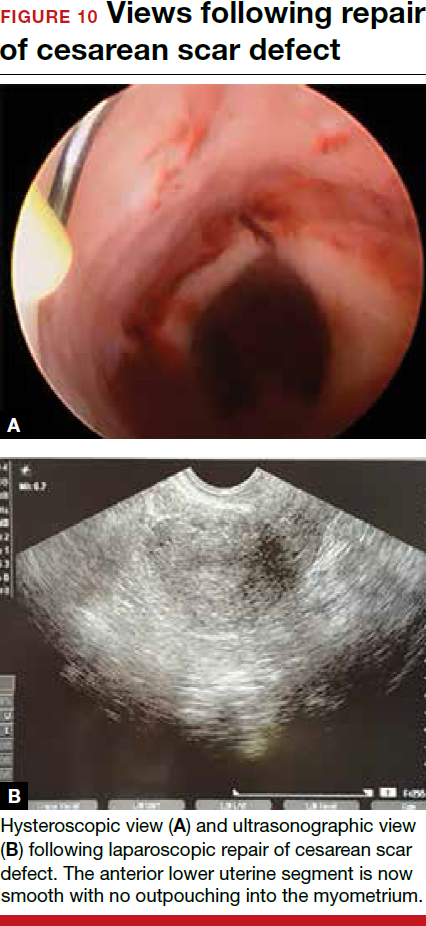
For a laparoscopic repair, first identify the niche hysteroscopically. At the same time as hysteroscopic examination of the cavity, the defect can be evaluated laparoscopically (FIGURE 4). The light from the hysteroscope can be visualized easily laparoscopically because of the thinned myometrium in the area of the defect. Map out the niche by transvaginally passing a cervical dilator into the defect in the uterine cavity (FIGURE 5). Again, given the thinning of this segment of the uterus, the dilator can be easily visualized laparoscopically. Be cautious when placing this dilator, as there is often overlying bladder. Prevent incidental cystotomy by gently advancing the dilator into the defect only until the niche can be adequately detected.9At this point, develop a bladder flap by opening the vesicovaginal and vesicocervical space, mobilizing the bladder inferiorly (FIGURE 6). With the guide of the dilator mapping out the defect (FIGURE 7), excise the fibrotic edges of the niche with thermal energy (monopolar cautery or CO2 laser) or sharp dissection (FIGURE 8). This leaves healthy myometrial tissue margins. Reapproximate these margins with absorbable suture (2-0 polyglactin 910 [Vicryl]) in an interrupted or running fashion, in 2 layers9 (FIGURE 9). Following the laparoscopic repair, perform hysteroscopic evaluation of the uterine cavity to assure complete resolution of the defect (FIGURE 10). With the hysteroscope in place, perform concurrent laparoscopic assessment of the repair. Check for impermeability by assuring no hysteroscopic fluid escapes at the site of repaired hysterotomy.9
Postoperative care requires following the patient for symptom resolution and counseling regarding future fertility plans. We recommend that patients wait 6 months following the procedure before attempting conception.
When it comes to recommendations regarding preventing cesarean scar defects, additional randomized controlled trials need to be performed to evaluate various surgical techniques. At this time, there is no conclusive evidence that one method of hysterotomy closure is superior to another in preventing cesarean scar defect.
Symptoms often resolve with repair
When a patient with a prior cesarean delivery presents with symptoms of abnormal uterine bleeding, vaginal discharge, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, pelvic pain, or infertility that remain unexplained, consider cesarean scar defect as the culprit. Once a diagnosis of niche has been confirmed, the treatment approach should be dictated by the patient’s plans for future fertility. Hysteroscopic resection has been reported to have a 92% to 100% success rate for resolving symptoms of pain and bleeding, while 75% of patients undergoing laparoscopic niche repair for infertility achieved pregnancy.10,11 In our practice, a majority of patients experience symptom relief and go on to carry healthy pregnancies.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
Cesarean delivery is one of the most common surgical procedures in women, with rates of 30% or more in the United States.1 As a result, the rate is rising for cesarean scar defect—the presence of a “niche” at the site of cesarean delivery scar—with the reported prevalence between 24% and 70% in a random population of women with at least one cesarean delivery.2 Other terms for cesarean scar defect include a niche, isthmocele, uteroperitoneal fistula, and diverticulum.1–9
Formation of cesarean scar defect
Cesarean scar defect forms after cesarean delivery, at the site of hysterotomy, on the anterior wall of the uterine isthmus (FIGURE 1). While this is the typical location, the defect has also been found at the endocervical canal and mid-uterine body. Improper healing of the cesarean incision leads to thinning of the anterior uterine wall, which creates an indentation and fluid-filled pouch at the cesarean scar site. The exact reason why a niche develops has not yet been determined; however, there are several hypotheses, broken down by pregnancy-related and patient-related factors. Surgical techniques that may increase the chance of niche development include low (cervical) hysterotomy, single-layer uterine wall closure, use of locking sutures, closure of hysterotomy with endometrial-sparing technique, and multiple cesarean deliveries.3,4 Patients with medical conditions that may impact wound healing (such as diabetes and smoking) may be at increased risk for niche formation.

Viewed hysteroscopically, the defect appears as a concave shape in the anterior uterine wall; to the inexperienced eye, it may resemble a second cavity (FIGURE 2).

Pelvic pain and other serious consequences
The presence of fibrotic tissue in the niche acts like a valve, leading to the accumulation of blood in this reservoir-like area. A niche thus can cause delayed menstruation through the cervix, resulting in abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain, vaginal discharge, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, and infertility. Accumulated blood in this area can ultimately degrade cervical mucus and sperm quality, as well as inhibit sperm transport, a proposed mechanism of infertility.5,6 Women with a niche who conceive are at potential risk for cesarean scar ectopic pregnancy, with the embryo implanting in the pouch and subsequently growing and developing improperly.
Read about evaluation and treatment.
Evaluation and treatment
Patients presenting with the symptoms de-scribed above who have had a prior cesarean delivery should be evaluated for a cesarean scar defect.9 The best time to assess for the abnormality is after the patient’s menstrual cycle, when the endometrial lining is at its thinnest and recently menstruated blood has collected in the defect (this can highlight the niche on imaging). Transvaginal ultrasonography (FIGURE 3) or saline-infusion sonohysterogram serve as a first-line test for in-office diagnosis.7 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), 3-D ultrasonography, and hysteroscopy are additional useful imaging modalities that can aid in the diagnosis.

Treatments for cesarean scar defect vary dramatically and include hormonal therapy, hysteroscopic resection, vaginal or laparoscopic repair, and hysterectomy. Nonsurgical treatment should be reserved for women who desire a noninvasive approach, as the evidence for symptom resolution is limited.8
To promote fertility and decrease symptoms, the abnormal, fibrotic tissue must be removed. In our experience, since 2003, we have found that use of a laparoscopic approach is best for women desiring future fertility and that hysteroscopic resection is best for women whose childbearing is completed.9 Our management is dictated by the patient’s fertility plans, since there is concern that cesarean scar defect in a gravid uterus presents a risk for uterine rupture. The laparoscopic approach allows the defect to be repaired and the integrity of the myometrium restored.9
What are the coding options for cesarean scar defect repair?
Melanie Witt, RN, CPC, COBGC, MA
As the accompanying article discusses, the primary treatment for a cesarean scar defect depends on whether the patient wishes to preserve fertility, but assigning a procedure code for either surgical option will entail reporting an unlisted procedure code.
Under Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) guidelines (which are developed and copyrighted by the American Medical Association), procedure code selected must accurately describe the service/procedure performed rather than just approximate the service. This means that when a procedure-specific code does not exist, an unlisted procedure code that represents the type of surgery, the approach, and the anatomic site needs to be selected.
When an unlisted CPT code is reported, payment is based on the complexity of the surgery, and one way to communicate this to a payer is to provide additional documentation that not only includes the operative report but also suggests one or more existing CPT codes that have a published relative value unit (RVU) that approximates the work involved for the unlisted procedure.
The coding options for hysteroscopic and laparoscopic treatment options are listed below. The comparison codes offered will give the surgeon a range to look at, but the ultimate decision to use one of those suggested, or to choose an entirely different comparison code, is entirely within the control of the physician.
ICD-10-CM diagnostic coding
While the cesarean scar defect is a sequela of cesarean delivery, which is always reported as a secondary code, the choice of a primary diagnosis code can be either a gynecologic and/or an obstetric complication code. The choice may be determined by payer policy, as the use of an obstetric complication may not be accepted with a gynecologic procedure code. From a coding perspective, however, use of all 3 of these codes from the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) paints the most accurate description of the defect and its cause:
- N85.8 Other specified noninflammatory disorders of uterus versus
- O34.21 Maternal care for scar from previous cesarean delivery plus
- O94 Sequelae of complication of pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium.
Hysteroscopic resection codes:
- 58579 Unlisted hysteroscopy procedure, uterus
- The codes that may most closely approximate the physician work include 58561 (Hysteroscopy, surgical; with removal of leiomyomata) with 15.48 RVUs or 58560 (Hysteroscopy, surgical; with division or resection of intrauterine septum [any method]) with 10.92 RVUs.
Laparoscopic repair codes:
- 58578 Unlisted laparoscopy procedure, uterus
- The codes that may most closely approximate the physician work include 58520 (Hysterorrhaphy, repair of ruptured uterus [nonobstetrical] 24.25 RVUs or 58662 (Laparoscopy, surgical; with fulguration or excision of lesions of the ovary, pelvic viscera, or peritoneal surface by any method) with 20.14 RVUs.
You may also want to report a diagnostic hysteroscopy (code 58555), but keep in mind that payment will depend on documentation that clearly indicates that the use of the hysteroscope was for diagnostic purposes. Use of the hysteroscope to simply identify the surgical site to be repaired via the laparoscope will usually not be reimbursed separately.
Ms. Witt is an independent coding and documentation consultant and former program manager, department of coding and nomenclature, American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
The author reports no financial relationships relevant to this article.
Read about techniques for repair.
Techniques for repairing cesarean scar defect
For hysteroscopic resection of a niche, the uterus is distended and the intrauterine defect is visualized hysteroscopically, as seen in FIGURE 2. Using a bipolar or unipolar resectoscope, resect the fibrotic tissue of the defect and endometrial-like glands present within the niche. The goal of this relatively quick procedure is to open up the reservoir and facilitate the complete drainage of menstrual blood, thus alleviating the patient’s symptoms.Postoperatively, follow the patient for symptom resolution, and evaluate for defect resolution with transvaginal ultrasonography.
For a laparoscopic repair, first identify the niche hysteroscopically. At the same time as hysteroscopic examination of the cavity, the defect can be evaluated laparoscopically (FIGURE 4). The light from the hysteroscope can be visualized easily laparoscopically because of the thinned myometrium in the area of the defect. Map out the niche by transvaginally passing a cervical dilator into the defect in the uterine cavity (FIGURE 5). Again, given the thinning of this segment of the uterus, the dilator can be easily visualized laparoscopically. Be cautious when placing this dilator, as there is often overlying bladder. Prevent incidental cystotomy by gently advancing the dilator into the defect only until the niche can be adequately detected.9At this point, develop a bladder flap by opening the vesicovaginal and vesicocervical space, mobilizing the bladder inferiorly (FIGURE 6). With the guide of the dilator mapping out the defect (FIGURE 7), excise the fibrotic edges of the niche with thermal energy (monopolar cautery or CO2 laser) or sharp dissection (FIGURE 8). This leaves healthy myometrial tissue margins. Reapproximate these margins with absorbable suture (2-0 polyglactin 910 [Vicryl]) in an interrupted or running fashion, in 2 layers9 (FIGURE 9). Following the laparoscopic repair, perform hysteroscopic evaluation of the uterine cavity to assure complete resolution of the defect (FIGURE 10). With the hysteroscope in place, perform concurrent laparoscopic assessment of the repair. Check for impermeability by assuring no hysteroscopic fluid escapes at the site of repaired hysterotomy.9







Postoperative care requires following the patient for symptom resolution and counseling regarding future fertility plans. We recommend that patients wait 6 months following the procedure before attempting conception.
When it comes to recommendations regarding preventing cesarean scar defects, additional randomized controlled trials need to be performed to evaluate various surgical techniques. At this time, there is no conclusive evidence that one method of hysterotomy closure is superior to another in preventing cesarean scar defect.
Symptoms often resolve with repair
When a patient with a prior cesarean delivery presents with symptoms of abnormal uterine bleeding, vaginal discharge, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, pelvic pain, or infertility that remain unexplained, consider cesarean scar defect as the culprit. Once a diagnosis of niche has been confirmed, the treatment approach should be dictated by the patient’s plans for future fertility. Hysteroscopic resection has been reported to have a 92% to 100% success rate for resolving symptoms of pain and bleeding, while 75% of patients undergoing laparoscopic niche repair for infertility achieved pregnancy.10,11 In our practice, a majority of patients experience symptom relief and go on to carry healthy pregnancies.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
Cesarean delivery is one of the most common surgical procedures in women, with rates of 30% or more in the United States.1 As a result, the rate is rising for cesarean scar defect—the presence of a “niche” at the site of cesarean delivery scar—with the reported prevalence between 24% and 70% in a random population of women with at least one cesarean delivery.2 Other terms for cesarean scar defect include a niche, isthmocele, uteroperitoneal fistula, and diverticulum.1–9
Formation of cesarean scar defect
Cesarean scar defect forms after cesarean delivery, at the site of hysterotomy, on the anterior wall of the uterine isthmus (FIGURE 1). While this is the typical location, the defect has also been found at the endocervical canal and mid-uterine body. Improper healing of the cesarean incision leads to thinning of the anterior uterine wall, which creates an indentation and fluid-filled pouch at the cesarean scar site. The exact reason why a niche develops has not yet been determined; however, there are several hypotheses, broken down by pregnancy-related and patient-related factors. Surgical techniques that may increase the chance of niche development include low (cervical) hysterotomy, single-layer uterine wall closure, use of locking sutures, closure of hysterotomy with endometrial-sparing technique, and multiple cesarean deliveries.3,4 Patients with medical conditions that may impact wound healing (such as diabetes and smoking) may be at increased risk for niche formation.

Viewed hysteroscopically, the defect appears as a concave shape in the anterior uterine wall; to the inexperienced eye, it may resemble a second cavity (FIGURE 2).

Pelvic pain and other serious consequences
The presence of fibrotic tissue in the niche acts like a valve, leading to the accumulation of blood in this reservoir-like area. A niche thus can cause delayed menstruation through the cervix, resulting in abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain, vaginal discharge, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, and infertility. Accumulated blood in this area can ultimately degrade cervical mucus and sperm quality, as well as inhibit sperm transport, a proposed mechanism of infertility.5,6 Women with a niche who conceive are at potential risk for cesarean scar ectopic pregnancy, with the embryo implanting in the pouch and subsequently growing and developing improperly.
Read about evaluation and treatment.
Evaluation and treatment
Patients presenting with the symptoms de-scribed above who have had a prior cesarean delivery should be evaluated for a cesarean scar defect.9 The best time to assess for the abnormality is after the patient’s menstrual cycle, when the endometrial lining is at its thinnest and recently menstruated blood has collected in the defect (this can highlight the niche on imaging). Transvaginal ultrasonography (FIGURE 3) or saline-infusion sonohysterogram serve as a first-line test for in-office diagnosis.7 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), 3-D ultrasonography, and hysteroscopy are additional useful imaging modalities that can aid in the diagnosis.

Treatments for cesarean scar defect vary dramatically and include hormonal therapy, hysteroscopic resection, vaginal or laparoscopic repair, and hysterectomy. Nonsurgical treatment should be reserved for women who desire a noninvasive approach, as the evidence for symptom resolution is limited.8
To promote fertility and decrease symptoms, the abnormal, fibrotic tissue must be removed. In our experience, since 2003, we have found that use of a laparoscopic approach is best for women desiring future fertility and that hysteroscopic resection is best for women whose childbearing is completed.9 Our management is dictated by the patient’s fertility plans, since there is concern that cesarean scar defect in a gravid uterus presents a risk for uterine rupture. The laparoscopic approach allows the defect to be repaired and the integrity of the myometrium restored.9
What are the coding options for cesarean scar defect repair?
Melanie Witt, RN, CPC, COBGC, MA
As the accompanying article discusses, the primary treatment for a cesarean scar defect depends on whether the patient wishes to preserve fertility, but assigning a procedure code for either surgical option will entail reporting an unlisted procedure code.
Under Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) guidelines (which are developed and copyrighted by the American Medical Association), procedure code selected must accurately describe the service/procedure performed rather than just approximate the service. This means that when a procedure-specific code does not exist, an unlisted procedure code that represents the type of surgery, the approach, and the anatomic site needs to be selected.
When an unlisted CPT code is reported, payment is based on the complexity of the surgery, and one way to communicate this to a payer is to provide additional documentation that not only includes the operative report but also suggests one or more existing CPT codes that have a published relative value unit (RVU) that approximates the work involved for the unlisted procedure.
The coding options for hysteroscopic and laparoscopic treatment options are listed below. The comparison codes offered will give the surgeon a range to look at, but the ultimate decision to use one of those suggested, or to choose an entirely different comparison code, is entirely within the control of the physician.
ICD-10-CM diagnostic coding
While the cesarean scar defect is a sequela of cesarean delivery, which is always reported as a secondary code, the choice of a primary diagnosis code can be either a gynecologic and/or an obstetric complication code. The choice may be determined by payer policy, as the use of an obstetric complication may not be accepted with a gynecologic procedure code. From a coding perspective, however, use of all 3 of these codes from the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) paints the most accurate description of the defect and its cause:
- N85.8 Other specified noninflammatory disorders of uterus versus
- O34.21 Maternal care for scar from previous cesarean delivery plus
- O94 Sequelae of complication of pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium.
Hysteroscopic resection codes:
- 58579 Unlisted hysteroscopy procedure, uterus
- The codes that may most closely approximate the physician work include 58561 (Hysteroscopy, surgical; with removal of leiomyomata) with 15.48 RVUs or 58560 (Hysteroscopy, surgical; with division or resection of intrauterine septum [any method]) with 10.92 RVUs.
Laparoscopic repair codes:
- 58578 Unlisted laparoscopy procedure, uterus
- The codes that may most closely approximate the physician work include 58520 (Hysterorrhaphy, repair of ruptured uterus [nonobstetrical] 24.25 RVUs or 58662 (Laparoscopy, surgical; with fulguration or excision of lesions of the ovary, pelvic viscera, or peritoneal surface by any method) with 20.14 RVUs.
You may also want to report a diagnostic hysteroscopy (code 58555), but keep in mind that payment will depend on documentation that clearly indicates that the use of the hysteroscope was for diagnostic purposes. Use of the hysteroscope to simply identify the surgical site to be repaired via the laparoscope will usually not be reimbursed separately.
Ms. Witt is an independent coding and documentation consultant and former program manager, department of coding and nomenclature, American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
The author reports no financial relationships relevant to this article.
Read about techniques for repair.
Techniques for repairing cesarean scar defect
For hysteroscopic resection of a niche, the uterus is distended and the intrauterine defect is visualized hysteroscopically, as seen in FIGURE 2. Using a bipolar or unipolar resectoscope, resect the fibrotic tissue of the defect and endometrial-like glands present within the niche. The goal of this relatively quick procedure is to open up the reservoir and facilitate the complete drainage of menstrual blood, thus alleviating the patient’s symptoms.Postoperatively, follow the patient for symptom resolution, and evaluate for defect resolution with transvaginal ultrasonography.
For a laparoscopic repair, first identify the niche hysteroscopically. At the same time as hysteroscopic examination of the cavity, the defect can be evaluated laparoscopically (FIGURE 4). The light from the hysteroscope can be visualized easily laparoscopically because of the thinned myometrium in the area of the defect. Map out the niche by transvaginally passing a cervical dilator into the defect in the uterine cavity (FIGURE 5). Again, given the thinning of this segment of the uterus, the dilator can be easily visualized laparoscopically. Be cautious when placing this dilator, as there is often overlying bladder. Prevent incidental cystotomy by gently advancing the dilator into the defect only until the niche can be adequately detected.9At this point, develop a bladder flap by opening the vesicovaginal and vesicocervical space, mobilizing the bladder inferiorly (FIGURE 6). With the guide of the dilator mapping out the defect (FIGURE 7), excise the fibrotic edges of the niche with thermal energy (monopolar cautery or CO2 laser) or sharp dissection (FIGURE 8). This leaves healthy myometrial tissue margins. Reapproximate these margins with absorbable suture (2-0 polyglactin 910 [Vicryl]) in an interrupted or running fashion, in 2 layers9 (FIGURE 9). Following the laparoscopic repair, perform hysteroscopic evaluation of the uterine cavity to assure complete resolution of the defect (FIGURE 10). With the hysteroscope in place, perform concurrent laparoscopic assessment of the repair. Check for impermeability by assuring no hysteroscopic fluid escapes at the site of repaired hysterotomy.9







Postoperative care requires following the patient for symptom resolution and counseling regarding future fertility plans. We recommend that patients wait 6 months following the procedure before attempting conception.
When it comes to recommendations regarding preventing cesarean scar defects, additional randomized controlled trials need to be performed to evaluate various surgical techniques. At this time, there is no conclusive evidence that one method of hysterotomy closure is superior to another in preventing cesarean scar defect.
Symptoms often resolve with repair
When a patient with a prior cesarean delivery presents with symptoms of abnormal uterine bleeding, vaginal discharge, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, pelvic pain, or infertility that remain unexplained, consider cesarean scar defect as the culprit. Once a diagnosis of niche has been confirmed, the treatment approach should be dictated by the patient’s plans for future fertility. Hysteroscopic resection has been reported to have a 92% to 100% success rate for resolving symptoms of pain and bleeding, while 75% of patients undergoing laparoscopic niche repair for infertility achieved pregnancy.10,11 In our practice, a majority of patients experience symptom relief and go on to carry healthy pregnancies.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
In this Article