User login
The growing NP and PA workforce in hospital medicine
High rate of turnover among NPs, PAs
If you were a physician hospitalist in a group serving adults in 2017 you probably worked with nurse practitioners (NPs) and/or physician assistants (PAs). Seventy-seven percent of hospital medicine groups (HMGs) employed NPs and PAs that year.
In addition, the larger the group, the more likely the group was to have NPs and PAs as part of their practice model – 89% of hospital medicine groups with more than 30 physician had NPs and/or PAs as partners. In addition, the mean number of physicians for adult hospital medicine groups was 17.9. The same practices employed an average of 3.5 NPs, and 2.6 PAs.
Based on these numbers, there are just under three physicians per NP and PA in the typical HMG serving adults. This is all according to data from the 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) report that was published in 2019 by the Society of Hospital Medicine.
These observations lead to a number of questions. One thing that is not clear from the SoHM is why NPs and PAs are becoming a larger part of the hospital medicine workforce, but there are some insights and conjecture that can be drawn from the data. The first is economics. Over 6 years, the median incomes of NPs and PAs have risen a relatively modest 10%; over the same period physician hospitalists have seen a whopping 23.6% median pay increase.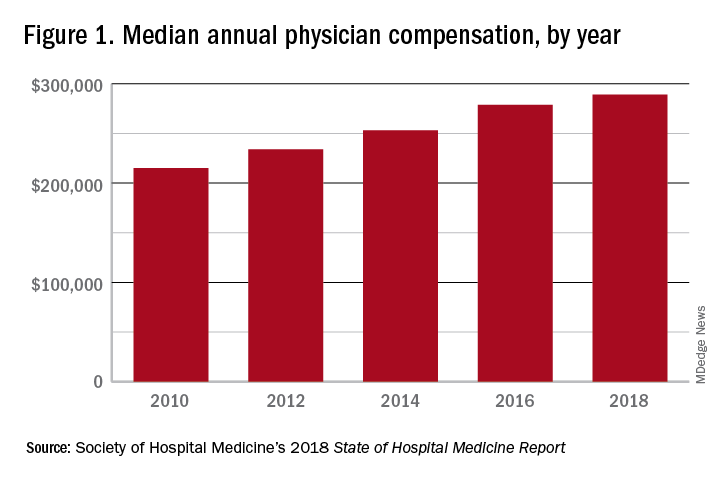
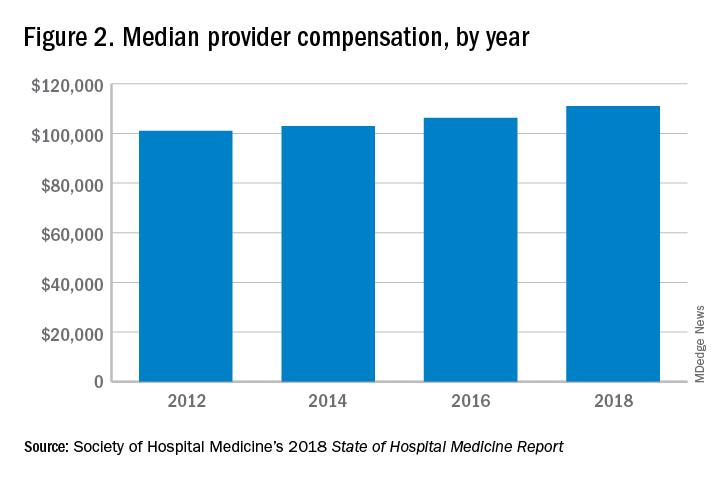
One argument against economics as a driving force behind greater use of NPs and PAs in the hospital medicine workforce is the billing patterns of HMGs that use NPs and PAs. Ten percent of HMGs do not have their NPs and PAs bill at all. The distribution of HMGs that predominantly bill NP and PA services as shared visits, versus having NPs and PAs bill independently, has also not changed much over the years, with 22% of HMGs having NPs and PAs bill independently as a predominant model. This would seem to suggest that some HMGs may not have learned how to deploy NPs and PAs effectively.
While inefficiency can be due to hospital bylaws, the culture of the hospital medicine group, or the skill set of the NPs and PAs working in HMGs – it would seem that if the driving force for the increase in the utilization of NPs and PAs in HMGs was financial, then that would also result in more of these providers billing independently, or alternatively, an increase in hospitalist physician productivity, which the data do not show. However, multistate HMGs may have this figured out better than some of the rest of us – 78% of these HMGs have NPs and PAs billing independently! All other categories of HMGs together are around 13%, with the next highest being hospital or health system integrated delivery systems, where NPs/PAs bill independently about 15% of the time.
In the last 2 years of the survey, there have been marked increases in the number of NPs and PAs at HMGs performing “nontraditional” services. For example, outpatient work has increased from 11% to 17%, and work in the postacute space has increased from 13% to 25%. Work in behavioral health and alcohol and drug rehab facilities has also increased, from 17% to 26%. As HMGs seek to rationalize their workforce while expanding, it is possible that decision makers have felt that it was either more economical to place NPs and PAs in positions where they are seeing these patients, or it was more aligned with the NP/PA skill set, or both. In any event, as the scope of hospital medicine broadens, the use of PAs and NPs has also increased – which is probably not coincidental.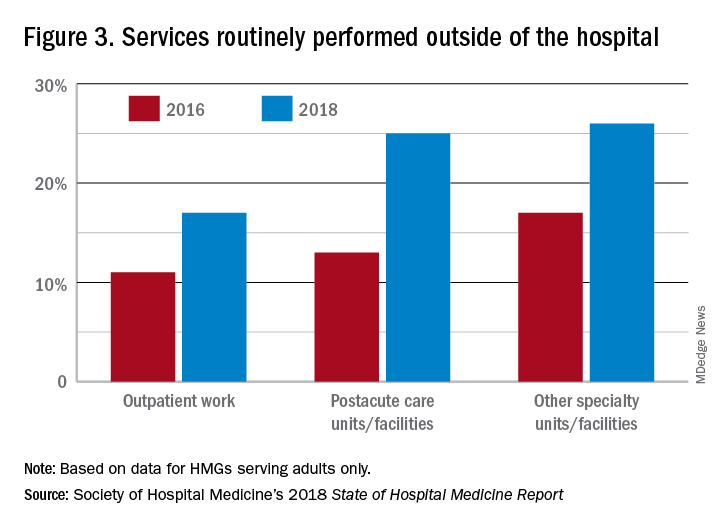
The average hospital medicine group continues to have staff openings. Workforce shortages may be leading to what in the past may have been considered physician openings being filled by NPs and PAs. Only 33% of HMGs reported having all their physician openings filled. Median physician shortage was 12% of total approved staffing. Given concerns in hospital medicine about provider burnout, the number of hospital medicine openings is no doubt a concern to HMG leaders and hospitalists. And necessity being the mother of invention, HMG leadership must be thinking differently than in the past about open positions and the skill mix needed to fill them. I believe this is leading to NPs and PAs being considered more often for a role that would have been open only to a physician in the past.
Just as open positions are a concern, so is turnover. One striking finding in the SoHM is the very high rate of turnover among NPs and PAs – a whopping 19.1% per year. For physicians, the same rate was 7.4% and has been declining every survey for many years. While NPs and PAs may be intended to stabilize the workforce, because of how this is being done in some groups, NPs and PAs may instead be a destabilizing factor. Rapid growth can lead to haphazard onboarding and less than clearly defined roles. NPs and PAs may often be placed into roles for which they are not yet prepared. In addition, the pay disparity between NPs and PAs and physicians has increased. As a new field, and with many HMGs still rapidly growing, increased thoughtfulness and maturity about how NPs and PAs are integrated into hospital medicine practices should lead to less turnover and better HMG stability in the future.
These observations could mark a future that includes higher pay for hospital medicine PAs and NPs (and potentially a slowdown in salary growth for physicians); HMGs taking steps to make the financial model more attractive by having NPs and PAs bill independently more often; and HMGs and their leaders engaging NPs and PAs by more clearly defining roles, shoring up onboarding and mentoring programs, and other measures that decrease turnover. This would help to make hospital medicine a career destination, rather than a stopping off point for NPs and PAs, much as it has become for internists over the past 20 years.
Dr. Frederickson is medical director, hospital medicine and palliative care, at CHI Health, Omaha, Neb., and assistant professor at Creighton University, Omaha.
High rate of turnover among NPs, PAs
High rate of turnover among NPs, PAs
If you were a physician hospitalist in a group serving adults in 2017 you probably worked with nurse practitioners (NPs) and/or physician assistants (PAs). Seventy-seven percent of hospital medicine groups (HMGs) employed NPs and PAs that year.
In addition, the larger the group, the more likely the group was to have NPs and PAs as part of their practice model – 89% of hospital medicine groups with more than 30 physician had NPs and/or PAs as partners. In addition, the mean number of physicians for adult hospital medicine groups was 17.9. The same practices employed an average of 3.5 NPs, and 2.6 PAs.
Based on these numbers, there are just under three physicians per NP and PA in the typical HMG serving adults. This is all according to data from the 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) report that was published in 2019 by the Society of Hospital Medicine.
These observations lead to a number of questions. One thing that is not clear from the SoHM is why NPs and PAs are becoming a larger part of the hospital medicine workforce, but there are some insights and conjecture that can be drawn from the data. The first is economics. Over 6 years, the median incomes of NPs and PAs have risen a relatively modest 10%; over the same period physician hospitalists have seen a whopping 23.6% median pay increase.

One argument against economics as a driving force behind greater use of NPs and PAs in the hospital medicine workforce is the billing patterns of HMGs that use NPs and PAs. Ten percent of HMGs do not have their NPs and PAs bill at all. The distribution of HMGs that predominantly bill NP and PA services as shared visits, versus having NPs and PAs bill independently, has also not changed much over the years, with 22% of HMGs having NPs and PAs bill independently as a predominant model. This would seem to suggest that some HMGs may not have learned how to deploy NPs and PAs effectively.
While inefficiency can be due to hospital bylaws, the culture of the hospital medicine group, or the skill set of the NPs and PAs working in HMGs – it would seem that if the driving force for the increase in the utilization of NPs and PAs in HMGs was financial, then that would also result in more of these providers billing independently, or alternatively, an increase in hospitalist physician productivity, which the data do not show. However, multistate HMGs may have this figured out better than some of the rest of us – 78% of these HMGs have NPs and PAs billing independently! All other categories of HMGs together are around 13%, with the next highest being hospital or health system integrated delivery systems, where NPs/PAs bill independently about 15% of the time.
In the last 2 years of the survey, there have been marked increases in the number of NPs and PAs at HMGs performing “nontraditional” services. For example, outpatient work has increased from 11% to 17%, and work in the postacute space has increased from 13% to 25%. Work in behavioral health and alcohol and drug rehab facilities has also increased, from 17% to 26%. As HMGs seek to rationalize their workforce while expanding, it is possible that decision makers have felt that it was either more economical to place NPs and PAs in positions where they are seeing these patients, or it was more aligned with the NP/PA skill set, or both. In any event, as the scope of hospital medicine broadens, the use of PAs and NPs has also increased – which is probably not coincidental.
The average hospital medicine group continues to have staff openings. Workforce shortages may be leading to what in the past may have been considered physician openings being filled by NPs and PAs. Only 33% of HMGs reported having all their physician openings filled. Median physician shortage was 12% of total approved staffing. Given concerns in hospital medicine about provider burnout, the number of hospital medicine openings is no doubt a concern to HMG leaders and hospitalists. And necessity being the mother of invention, HMG leadership must be thinking differently than in the past about open positions and the skill mix needed to fill them. I believe this is leading to NPs and PAs being considered more often for a role that would have been open only to a physician in the past.
Just as open positions are a concern, so is turnover. One striking finding in the SoHM is the very high rate of turnover among NPs and PAs – a whopping 19.1% per year. For physicians, the same rate was 7.4% and has been declining every survey for many years. While NPs and PAs may be intended to stabilize the workforce, because of how this is being done in some groups, NPs and PAs may instead be a destabilizing factor. Rapid growth can lead to haphazard onboarding and less than clearly defined roles. NPs and PAs may often be placed into roles for which they are not yet prepared. In addition, the pay disparity between NPs and PAs and physicians has increased. As a new field, and with many HMGs still rapidly growing, increased thoughtfulness and maturity about how NPs and PAs are integrated into hospital medicine practices should lead to less turnover and better HMG stability in the future.
These observations could mark a future that includes higher pay for hospital medicine PAs and NPs (and potentially a slowdown in salary growth for physicians); HMGs taking steps to make the financial model more attractive by having NPs and PAs bill independently more often; and HMGs and their leaders engaging NPs and PAs by more clearly defining roles, shoring up onboarding and mentoring programs, and other measures that decrease turnover. This would help to make hospital medicine a career destination, rather than a stopping off point for NPs and PAs, much as it has become for internists over the past 20 years.
Dr. Frederickson is medical director, hospital medicine and palliative care, at CHI Health, Omaha, Neb., and assistant professor at Creighton University, Omaha.
If you were a physician hospitalist in a group serving adults in 2017 you probably worked with nurse practitioners (NPs) and/or physician assistants (PAs). Seventy-seven percent of hospital medicine groups (HMGs) employed NPs and PAs that year.
In addition, the larger the group, the more likely the group was to have NPs and PAs as part of their practice model – 89% of hospital medicine groups with more than 30 physician had NPs and/or PAs as partners. In addition, the mean number of physicians for adult hospital medicine groups was 17.9. The same practices employed an average of 3.5 NPs, and 2.6 PAs.
Based on these numbers, there are just under three physicians per NP and PA in the typical HMG serving adults. This is all according to data from the 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) report that was published in 2019 by the Society of Hospital Medicine.
These observations lead to a number of questions. One thing that is not clear from the SoHM is why NPs and PAs are becoming a larger part of the hospital medicine workforce, but there are some insights and conjecture that can be drawn from the data. The first is economics. Over 6 years, the median incomes of NPs and PAs have risen a relatively modest 10%; over the same period physician hospitalists have seen a whopping 23.6% median pay increase.

One argument against economics as a driving force behind greater use of NPs and PAs in the hospital medicine workforce is the billing patterns of HMGs that use NPs and PAs. Ten percent of HMGs do not have their NPs and PAs bill at all. The distribution of HMGs that predominantly bill NP and PA services as shared visits, versus having NPs and PAs bill independently, has also not changed much over the years, with 22% of HMGs having NPs and PAs bill independently as a predominant model. This would seem to suggest that some HMGs may not have learned how to deploy NPs and PAs effectively.
While inefficiency can be due to hospital bylaws, the culture of the hospital medicine group, or the skill set of the NPs and PAs working in HMGs – it would seem that if the driving force for the increase in the utilization of NPs and PAs in HMGs was financial, then that would also result in more of these providers billing independently, or alternatively, an increase in hospitalist physician productivity, which the data do not show. However, multistate HMGs may have this figured out better than some of the rest of us – 78% of these HMGs have NPs and PAs billing independently! All other categories of HMGs together are around 13%, with the next highest being hospital or health system integrated delivery systems, where NPs/PAs bill independently about 15% of the time.
In the last 2 years of the survey, there have been marked increases in the number of NPs and PAs at HMGs performing “nontraditional” services. For example, outpatient work has increased from 11% to 17%, and work in the postacute space has increased from 13% to 25%. Work in behavioral health and alcohol and drug rehab facilities has also increased, from 17% to 26%. As HMGs seek to rationalize their workforce while expanding, it is possible that decision makers have felt that it was either more economical to place NPs and PAs in positions where they are seeing these patients, or it was more aligned with the NP/PA skill set, or both. In any event, as the scope of hospital medicine broadens, the use of PAs and NPs has also increased – which is probably not coincidental.
The average hospital medicine group continues to have staff openings. Workforce shortages may be leading to what in the past may have been considered physician openings being filled by NPs and PAs. Only 33% of HMGs reported having all their physician openings filled. Median physician shortage was 12% of total approved staffing. Given concerns in hospital medicine about provider burnout, the number of hospital medicine openings is no doubt a concern to HMG leaders and hospitalists. And necessity being the mother of invention, HMG leadership must be thinking differently than in the past about open positions and the skill mix needed to fill them. I believe this is leading to NPs and PAs being considered more often for a role that would have been open only to a physician in the past.
Just as open positions are a concern, so is turnover. One striking finding in the SoHM is the very high rate of turnover among NPs and PAs – a whopping 19.1% per year. For physicians, the same rate was 7.4% and has been declining every survey for many years. While NPs and PAs may be intended to stabilize the workforce, because of how this is being done in some groups, NPs and PAs may instead be a destabilizing factor. Rapid growth can lead to haphazard onboarding and less than clearly defined roles. NPs and PAs may often be placed into roles for which they are not yet prepared. In addition, the pay disparity between NPs and PAs and physicians has increased. As a new field, and with many HMGs still rapidly growing, increased thoughtfulness and maturity about how NPs and PAs are integrated into hospital medicine practices should lead to less turnover and better HMG stability in the future.
These observations could mark a future that includes higher pay for hospital medicine PAs and NPs (and potentially a slowdown in salary growth for physicians); HMGs taking steps to make the financial model more attractive by having NPs and PAs bill independently more often; and HMGs and their leaders engaging NPs and PAs by more clearly defining roles, shoring up onboarding and mentoring programs, and other measures that decrease turnover. This would help to make hospital medicine a career destination, rather than a stopping off point for NPs and PAs, much as it has become for internists over the past 20 years.
Dr. Frederickson is medical director, hospital medicine and palliative care, at CHI Health, Omaha, Neb., and assistant professor at Creighton University, Omaha.

