User login
ANSWER
The correct answer is inclusion cyst (choice “c”).
DISCUSSION
Inclusion cysts are also called traumatic inclusion cysts or implantation cysts and are quite distinct from “sebaceous,” epidermal, or epidermoid cysts. An inclusion cyst results from traumatic implantation of surface adnexal structures (eg, sebaceous glands) that continue to function, eventuating in the formation of an organized sac whose wall is composed of stratified squamous epithelium with a granular layer, no significant atypia, and surrounding pasty lamellated acellular keratin.
Hands are the most commonly affected area, although the precipitating puncture wound doesn’t have to be as impressive as this patient’s was. Nails and sewing needles can produce the same result.
The patient’s lesion was removed, at which point its pasty contents (a diagnostic clue) were revealed, and the wound closed. Although the absence of redness or tenderness helped to rule out some items in the differential (eg, felon, abscess), and the lesion demonstrated clear cystic features, the specimen was sent for pathologic examination for confirmation, since cancer would also belong in the differential for such a lesion.
ANSWER
The correct answer is inclusion cyst (choice “c”).
DISCUSSION
Inclusion cysts are also called traumatic inclusion cysts or implantation cysts and are quite distinct from “sebaceous,” epidermal, or epidermoid cysts. An inclusion cyst results from traumatic implantation of surface adnexal structures (eg, sebaceous glands) that continue to function, eventuating in the formation of an organized sac whose wall is composed of stratified squamous epithelium with a granular layer, no significant atypia, and surrounding pasty lamellated acellular keratin.
Hands are the most commonly affected area, although the precipitating puncture wound doesn’t have to be as impressive as this patient’s was. Nails and sewing needles can produce the same result.
The patient’s lesion was removed, at which point its pasty contents (a diagnostic clue) were revealed, and the wound closed. Although the absence of redness or tenderness helped to rule out some items in the differential (eg, felon, abscess), and the lesion demonstrated clear cystic features, the specimen was sent for pathologic examination for confirmation, since cancer would also belong in the differential for such a lesion.
ANSWER
The correct answer is inclusion cyst (choice “c”).
DISCUSSION
Inclusion cysts are also called traumatic inclusion cysts or implantation cysts and are quite distinct from “sebaceous,” epidermal, or epidermoid cysts. An inclusion cyst results from traumatic implantation of surface adnexal structures (eg, sebaceous glands) that continue to function, eventuating in the formation of an organized sac whose wall is composed of stratified squamous epithelium with a granular layer, no significant atypia, and surrounding pasty lamellated acellular keratin.
Hands are the most commonly affected area, although the precipitating puncture wound doesn’t have to be as impressive as this patient’s was. Nails and sewing needles can produce the same result.
The patient’s lesion was removed, at which point its pasty contents (a diagnostic clue) were revealed, and the wound closed. Although the absence of redness or tenderness helped to rule out some items in the differential (eg, felon, abscess), and the lesion demonstrated clear cystic features, the specimen was sent for pathologic examination for confirmation, since cancer would also belong in the differential for such a lesion.
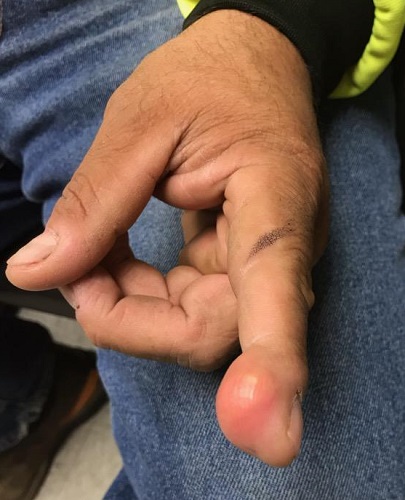
A 38-year-old man sustained an on-the-job injury to his finger, which was punctured by a tiny drill bit. He was promptly seen by a clinician, who administered a tetanus injection and prescribed a 2-week course of an antibiotic. However, within a few weeks, the patient noticed a lesion on the affected finger. It caused little to no pain but grew steadily, until it interfered with his functioning and prompted a return to the clinic.
The patient was in good health, despite being a long-term smoker. X-rays of the finger showed no bony changes or evidence of a foreign body. A referral to dermatology was provided.
Examination revealed a firm, painless, 2-cm subcutaneous mass in the pad of his left index finger. The surface felt quite tense, but there was no disruption nor any redness. Palpation of relevant nodal locations failed to reveal any palpable masses.