User login
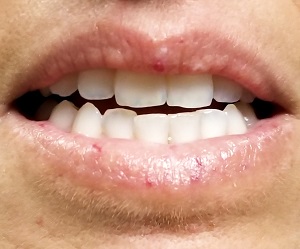
A 39-year-old woman presents with red vascular streaks on her upper and lower lips. They have slowly multiplied and become more prominent since she first noticed them several years ago. Although the lesions are asymptomatic, their effect on her appearance bothers the patient.
Her primary care provider tried to resolve the problem with cryotherapy. But the treatment attempt was unsuccessful.
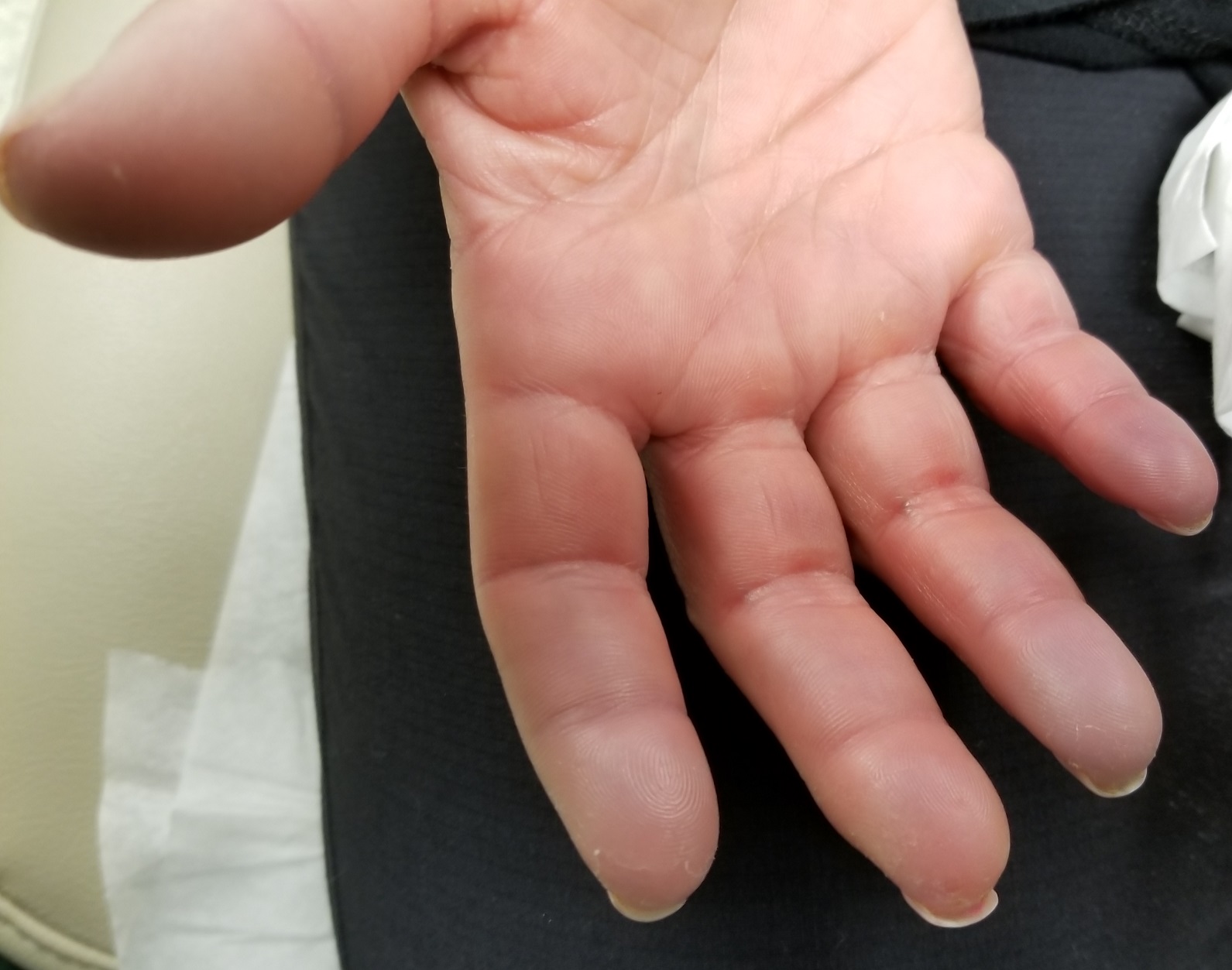
During history-taking, the patient divulges other existing health problems. She has been diagnosed with Raynaud syndrome, which flares several times a year, especially in cold weather or times of exceptional stress. She also has permanent thickening of the skin on her distal fingers, a result of sudden-onset swelling of all 10 fingers several years ago.
She denies any problems with eating, such as heartburn or difficulty swallowing. She also denies any respiratory problems or chronic fatigue.
EXAMINATION
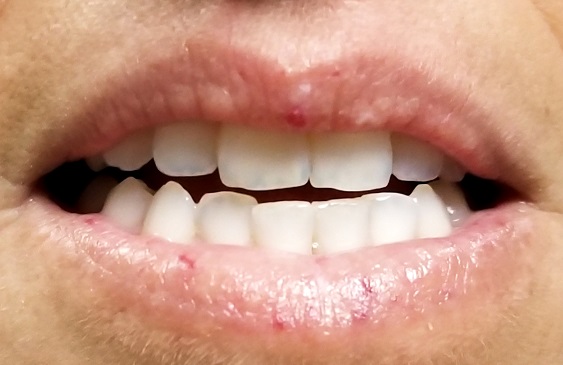
Seven very slender telangiectasias, most aligned vertically, are seen on the upper and lower vermillion surfaces. They range from a pinpoint to 6 mm in length. There are no similar lesions are on the rest of the oral mucosae, the face, or the chest.
The patient’s fingers, from the metacarpals to the tips, are decidedly edematous and firm but not tender. Several fingertips are scarred from past Raynaud episodes.
The patient looks her stated age and is in no distress.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
This patient almost certainly has CREST syndrome, a limited form of systemic sclerosis (or scleroderma). Both represent an autoimmune process in which antibodies attack cell DNA and centromeres (a component of the cell nucleus).
CREST can be difficult to diagnose because it can involve diverse organ systems. The name of the syndrome is an acronym for the symptoms it causes:
Calcinosis is a deposition of calcium triggered by inflammation. It manifests as small subcutaneous nodules, which are usually felt on the hands or seen on radiographs of the hands.
Raynaud syndrome causes intense vasoconstriction of blood vessels, usually in fingertips or toes, which first turn white, then red. The phenomenon is accompanied by pain and can be triggered by cold or stress.
Esophageal dysmotility occurs when atrophy and/or fibrosis of the esophageal lining leads to difficulty swallowing food.
Sclerodactyly is the term for tightening and thickening of the skin on the hands and fingers.
Telangiectasias are dilated capillaries that can worsen with time; they are common on lips, mucosal surfaces, the face, and the chest. They are often associated with vascular disease (eg, pulmonary hypertension).
Any of these signs can be seen with full-blown systemic sclerosis, but CREST is usually much less aggressive and seldom leads to renal or congestive heart failure—the 2 leading causes of death in systemic sclerosis.
Diagnosis is based on recognition of the clinical signs and symptoms, as well as blood work (ie, antinuclear antibody and anti-centromere antibody tests). A skin biopsy is often performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Since there is no effective treatment for the overarching disease, the specific components of CREST are treated separately. For this patient, her lip lesions were treated with light electrodessication. Another option would have been laser treatment.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- CREST syndrome, a limited form of systemic sclerosis, is a rare autoimmune condition caused by antibodies to cellular DNA and nuclear centromeres.
- CREST is an acronym for the symptomatic manifestations of the condition: calcinosis, Raynaud disease, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasias.
- Diagnosis is based on connecting the clinical dots and taking a thorough history, as well as lab results (for antinuclear antibodies and anti-centromere antibodies) and a skin biopsy.
- CREST is usually treated symptomatically, one system at a time, since no definitive treatment exists for the disease itself.
A 39-year-old woman presents with red vascular streaks on her upper and lower lips. They have slowly multiplied and become more prominent since she first noticed them several years ago. Although the lesions are asymptomatic, their effect on her appearance bothers the patient.
Her primary care provider tried to resolve the problem with cryotherapy. But the treatment attempt was unsuccessful.
During history-taking, the patient divulges other existing health problems. She has been diagnosed with Raynaud syndrome, which flares several times a year, especially in cold weather or times of exceptional stress. She also has permanent thickening of the skin on her distal fingers, a result of sudden-onset swelling of all 10 fingers several years ago.
She denies any problems with eating, such as heartburn or difficulty swallowing. She also denies any respiratory problems or chronic fatigue.

EXAMINATION
Seven very slender telangiectasias, most aligned vertically, are seen on the upper and lower vermillion surfaces. They range from a pinpoint to 6 mm in length. There are no similar lesions are on the rest of the oral mucosae, the face, or the chest.
The patient’s fingers, from the metacarpals to the tips, are decidedly edematous and firm but not tender. Several fingertips are scarred from past Raynaud episodes.

The patient looks her stated age and is in no distress.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
This patient almost certainly has CREST syndrome, a limited form of systemic sclerosis (or scleroderma). Both represent an autoimmune process in which antibodies attack cell DNA and centromeres (a component of the cell nucleus).
CREST can be difficult to diagnose because it can involve diverse organ systems. The name of the syndrome is an acronym for the symptoms it causes:
Calcinosis is a deposition of calcium triggered by inflammation. It manifests as small subcutaneous nodules, which are usually felt on the hands or seen on radiographs of the hands.
Raynaud syndrome causes intense vasoconstriction of blood vessels, usually in fingertips or toes, which first turn white, then red. The phenomenon is accompanied by pain and can be triggered by cold or stress.
Esophageal dysmotility occurs when atrophy and/or fibrosis of the esophageal lining leads to difficulty swallowing food.
Sclerodactyly is the term for tightening and thickening of the skin on the hands and fingers.
Telangiectasias are dilated capillaries that can worsen with time; they are common on lips, mucosal surfaces, the face, and the chest. They are often associated with vascular disease (eg, pulmonary hypertension).
Any of these signs can be seen with full-blown systemic sclerosis, but CREST is usually much less aggressive and seldom leads to renal or congestive heart failure—the 2 leading causes of death in systemic sclerosis.
Diagnosis is based on recognition of the clinical signs and symptoms, as well as blood work (ie, antinuclear antibody and anti-centromere antibody tests). A skin biopsy is often performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Since there is no effective treatment for the overarching disease, the specific components of CREST are treated separately. For this patient, her lip lesions were treated with light electrodessication. Another option would have been laser treatment.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- CREST syndrome, a limited form of systemic sclerosis, is a rare autoimmune condition caused by antibodies to cellular DNA and nuclear centromeres.
- CREST is an acronym for the symptomatic manifestations of the condition: calcinosis, Raynaud disease, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasias.
- Diagnosis is based on connecting the clinical dots and taking a thorough history, as well as lab results (for antinuclear antibodies and anti-centromere antibodies) and a skin biopsy.
- CREST is usually treated symptomatically, one system at a time, since no definitive treatment exists for the disease itself.
A 39-year-old woman presents with red vascular streaks on her upper and lower lips. They have slowly multiplied and become more prominent since she first noticed them several years ago. Although the lesions are asymptomatic, their effect on her appearance bothers the patient.
Her primary care provider tried to resolve the problem with cryotherapy. But the treatment attempt was unsuccessful.
During history-taking, the patient divulges other existing health problems. She has been diagnosed with Raynaud syndrome, which flares several times a year, especially in cold weather or times of exceptional stress. She also has permanent thickening of the skin on her distal fingers, a result of sudden-onset swelling of all 10 fingers several years ago.
She denies any problems with eating, such as heartburn or difficulty swallowing. She also denies any respiratory problems or chronic fatigue.

EXAMINATION
Seven very slender telangiectasias, most aligned vertically, are seen on the upper and lower vermillion surfaces. They range from a pinpoint to 6 mm in length. There are no similar lesions are on the rest of the oral mucosae, the face, or the chest.
The patient’s fingers, from the metacarpals to the tips, are decidedly edematous and firm but not tender. Several fingertips are scarred from past Raynaud episodes.

The patient looks her stated age and is in no distress.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
This patient almost certainly has CREST syndrome, a limited form of systemic sclerosis (or scleroderma). Both represent an autoimmune process in which antibodies attack cell DNA and centromeres (a component of the cell nucleus).
CREST can be difficult to diagnose because it can involve diverse organ systems. The name of the syndrome is an acronym for the symptoms it causes:
Calcinosis is a deposition of calcium triggered by inflammation. It manifests as small subcutaneous nodules, which are usually felt on the hands or seen on radiographs of the hands.
Raynaud syndrome causes intense vasoconstriction of blood vessels, usually in fingertips or toes, which first turn white, then red. The phenomenon is accompanied by pain and can be triggered by cold or stress.
Esophageal dysmotility occurs when atrophy and/or fibrosis of the esophageal lining leads to difficulty swallowing food.
Sclerodactyly is the term for tightening and thickening of the skin on the hands and fingers.
Telangiectasias are dilated capillaries that can worsen with time; they are common on lips, mucosal surfaces, the face, and the chest. They are often associated with vascular disease (eg, pulmonary hypertension).
Any of these signs can be seen with full-blown systemic sclerosis, but CREST is usually much less aggressive and seldom leads to renal or congestive heart failure—the 2 leading causes of death in systemic sclerosis.
Diagnosis is based on recognition of the clinical signs and symptoms, as well as blood work (ie, antinuclear antibody and anti-centromere antibody tests). A skin biopsy is often performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Since there is no effective treatment for the overarching disease, the specific components of CREST are treated separately. For this patient, her lip lesions were treated with light electrodessication. Another option would have been laser treatment.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- CREST syndrome, a limited form of systemic sclerosis, is a rare autoimmune condition caused by antibodies to cellular DNA and nuclear centromeres.
- CREST is an acronym for the symptomatic manifestations of the condition: calcinosis, Raynaud disease, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasias.
- Diagnosis is based on connecting the clinical dots and taking a thorough history, as well as lab results (for antinuclear antibodies and anti-centromere antibodies) and a skin biopsy.
- CREST is usually treated symptomatically, one system at a time, since no definitive treatment exists for the disease itself.