User login
A 17-year-old boy was born with rough skin on his face, arms, legs, thighs, and posterior shoulders. Over the years, his face, especially the posterior lateral aspects, has become progressively redder, while the roughness has increased. The redness is amplified with heat, exertion, anger, or embarrassment. Regarding the latter, mere mention of the condition by his siblings results in worsening of the erythema. Additionally, the skin in his eyebrows is now turning red and scaly.
The patient denies a history of dandruff. His parents, who have accompanied him to the clinic, report a family history of similar skin changes on triceps and thighs, but not on faces. There is no family history of cardiac anomalies or other congenital abnormalities. The boy’s health is otherwise excellent.
EXAMINATION
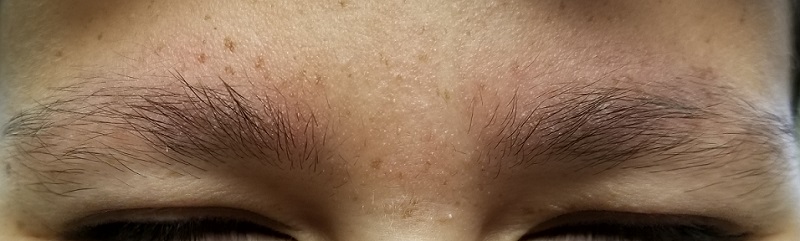
The patient’s bilateral triceps are covered with fine, rough, follicular papules, which create a faintly erythematous look. Similar lesions are visible on his posterior shoulders and anterior thighs. The skin beneath his eyebrows is faintly erythematous and scaly.
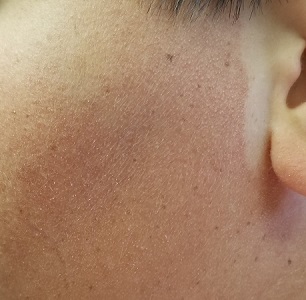
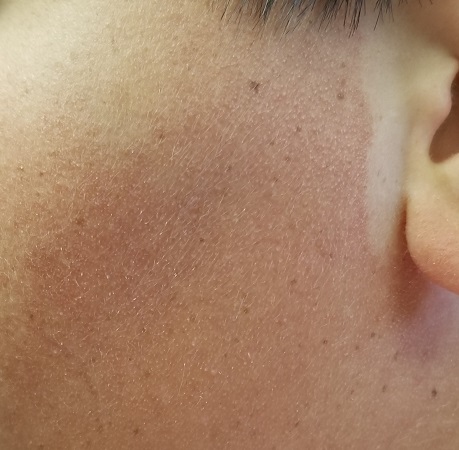
The posterior sides of his face are bright red and covered with the same type of papules. The erythema grows redder as it approaches the immediate preauricular areas, where it ends abruptly, creating a sharp demarcation with the white skin closer to the ears. The visual effect is almost clownish, as if bright red makeup had been applied.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
This young man has all the signs of an extremely rare variant of keratosis pilaris (KP) called ulerythema ophryogenes (UO). In the United States, about 40% of adults have ordinary KP, which usually manifests in childhood (with about 80% of cases occurring in adolescent girls). KP is inherited through autosomal dominance, with highly variable penetrance, though no specific gene has been identified. In this form, KP is considered by most experts to be a minor diagnostic criterion for atopic dermatitis.
However, UO is not merely a variant of KP. Over the decades, it has been connected with more serious conditions, such as cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, and Cornelia de Lange disease. Although these conditions are not common, they should be considered when UO is seen.
For this patient, the main concern was his appearance, especially the pronounced erythema around the periphery of his face. This aspect of the problem was addressed with a referral to a provider who can, using an assortment of lasers, try to even out his skin color and hopefully erase the sharp border at the periphery of the affected area.
For the physical discomfort caused by UO, the patient was instructed either to use general moisturizers to reduce dryness or to consider using moisturizers containing salicylic acid, which should help to reduce the prominence of the papules. For the erythema in his brows, he is using 2.5% hydrocortisone ointment two to three times a week.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Ulerythema ophryogenes is a rarely encountered variant of keratosis pilaris—a condition inherited by autosomal dominance with highly variable penetrance.
- Its main significance, beyond cosmetic concerns, is the possible connection with syndromes that involve heart and structural defects (eg, cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome).
- Treatment options include heavy emollients to soften the scaly papules and laser therapy to reduce the extreme redness seen on the periphery of the face.
A 17-year-old boy was born with rough skin on his face, arms, legs, thighs, and posterior shoulders. Over the years, his face, especially the posterior lateral aspects, has become progressively redder, while the roughness has increased. The redness is amplified with heat, exertion, anger, or embarrassment. Regarding the latter, mere mention of the condition by his siblings results in worsening of the erythema. Additionally, the skin in his eyebrows is now turning red and scaly.
The patient denies a history of dandruff. His parents, who have accompanied him to the clinic, report a family history of similar skin changes on triceps and thighs, but not on faces. There is no family history of cardiac anomalies or other congenital abnormalities. The boy’s health is otherwise excellent.

EXAMINATION
The patient’s bilateral triceps are covered with fine, rough, follicular papules, which create a faintly erythematous look. Similar lesions are visible on his posterior shoulders and anterior thighs. The skin beneath his eyebrows is faintly erythematous and scaly.
The posterior sides of his face are bright red and covered with the same type of papules. The erythema grows redder as it approaches the immediate preauricular areas, where it ends abruptly, creating a sharp demarcation with the white skin closer to the ears. The visual effect is almost clownish, as if bright red makeup had been applied.

What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
This young man has all the signs of an extremely rare variant of keratosis pilaris (KP) called ulerythema ophryogenes (UO). In the United States, about 40% of adults have ordinary KP, which usually manifests in childhood (with about 80% of cases occurring in adolescent girls). KP is inherited through autosomal dominance, with highly variable penetrance, though no specific gene has been identified. In this form, KP is considered by most experts to be a minor diagnostic criterion for atopic dermatitis.
However, UO is not merely a variant of KP. Over the decades, it has been connected with more serious conditions, such as cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, and Cornelia de Lange disease. Although these conditions are not common, they should be considered when UO is seen.
For this patient, the main concern was his appearance, especially the pronounced erythema around the periphery of his face. This aspect of the problem was addressed with a referral to a provider who can, using an assortment of lasers, try to even out his skin color and hopefully erase the sharp border at the periphery of the affected area.
For the physical discomfort caused by UO, the patient was instructed either to use general moisturizers to reduce dryness or to consider using moisturizers containing salicylic acid, which should help to reduce the prominence of the papules. For the erythema in his brows, he is using 2.5% hydrocortisone ointment two to three times a week.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Ulerythema ophryogenes is a rarely encountered variant of keratosis pilaris—a condition inherited by autosomal dominance with highly variable penetrance.
- Its main significance, beyond cosmetic concerns, is the possible connection with syndromes that involve heart and structural defects (eg, cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome).
- Treatment options include heavy emollients to soften the scaly papules and laser therapy to reduce the extreme redness seen on the periphery of the face.
A 17-year-old boy was born with rough skin on his face, arms, legs, thighs, and posterior shoulders. Over the years, his face, especially the posterior lateral aspects, has become progressively redder, while the roughness has increased. The redness is amplified with heat, exertion, anger, or embarrassment. Regarding the latter, mere mention of the condition by his siblings results in worsening of the erythema. Additionally, the skin in his eyebrows is now turning red and scaly.
The patient denies a history of dandruff. His parents, who have accompanied him to the clinic, report a family history of similar skin changes on triceps and thighs, but not on faces. There is no family history of cardiac anomalies or other congenital abnormalities. The boy’s health is otherwise excellent.

EXAMINATION
The patient’s bilateral triceps are covered with fine, rough, follicular papules, which create a faintly erythematous look. Similar lesions are visible on his posterior shoulders and anterior thighs. The skin beneath his eyebrows is faintly erythematous and scaly.
The posterior sides of his face are bright red and covered with the same type of papules. The erythema grows redder as it approaches the immediate preauricular areas, where it ends abruptly, creating a sharp demarcation with the white skin closer to the ears. The visual effect is almost clownish, as if bright red makeup had been applied.

What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
This young man has all the signs of an extremely rare variant of keratosis pilaris (KP) called ulerythema ophryogenes (UO). In the United States, about 40% of adults have ordinary KP, which usually manifests in childhood (with about 80% of cases occurring in adolescent girls). KP is inherited through autosomal dominance, with highly variable penetrance, though no specific gene has been identified. In this form, KP is considered by most experts to be a minor diagnostic criterion for atopic dermatitis.
However, UO is not merely a variant of KP. Over the decades, it has been connected with more serious conditions, such as cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, and Cornelia de Lange disease. Although these conditions are not common, they should be considered when UO is seen.
For this patient, the main concern was his appearance, especially the pronounced erythema around the periphery of his face. This aspect of the problem was addressed with a referral to a provider who can, using an assortment of lasers, try to even out his skin color and hopefully erase the sharp border at the periphery of the affected area.
For the physical discomfort caused by UO, the patient was instructed either to use general moisturizers to reduce dryness or to consider using moisturizers containing salicylic acid, which should help to reduce the prominence of the papules. For the erythema in his brows, he is using 2.5% hydrocortisone ointment two to three times a week.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Ulerythema ophryogenes is a rarely encountered variant of keratosis pilaris—a condition inherited by autosomal dominance with highly variable penetrance.
- Its main significance, beyond cosmetic concerns, is the possible connection with syndromes that involve heart and structural defects (eg, cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome).
- Treatment options include heavy emollients to soften the scaly papules and laser therapy to reduce the extreme redness seen on the periphery of the face.