User login
An 8-year-old boy is brought in for evaluation of a collection of blisters on his finger, near the nail. The problem manifested about 6 days ago. The affected area is tender to touch. The child reportedly feels well, with no fever or malaise.
The patient has an extensive personal and family history of atopy. Since birth, he has had dry, sensitive skin and has experienced episodes of eczema, seasonal allergies, and asthma. Three months ago, he was admitted to the hospital with eczema herpeticum and successfully treated with IV acyclovir.
EXAMINATION
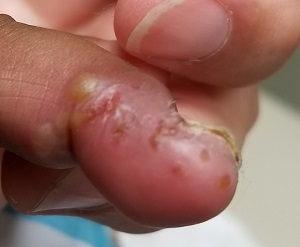
A cluster of vesicles is seen in the lateral perionychial area of the left third finger. Very modest erythema surrounds the vesicles, which contain cloudy yellow fluid suggestive of pus. There is a palpable lymph node in the left epitrochlear area.
The child is afebrile and in no distress. Patches of mild eczema are seen on the extremities and trunk.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
The lesion on this child’s finger is a herpetic whitlow. Patients with atopy are often susceptible to all types of skin infections: bacterial, fungal, and viral. In fact, human papillomavirus infection manifesting as multiple warts is not uncommon in this population. Nor is herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection, of which this case represents 1 manifestation.
A culture could have been done to confirm the diagnosis, but that would entail opening a vesicle to collect the fluid and then waiting at least 2 weeks for the results. By then, this whitlow would have long since resolved.
As with all HSV infections in the immunocompetent, treatment with acyclovir must be started in the first 2 to 3 days to have any effect—so such treatment in this case would be useless. If the herpetic whitlow were to recur in the same location, prompt treatment could be initiated, which would likely shorten the disease course and reduce symptoms.
Another HSV infection seen almost exclusively in atopic patients is eczema herpeticum (also known as Kaposi varicelliform eruption). This diffuse infection comprises dozens of tiny papulovesicular lesions, mostly concentrated on the face but often spilling down onto the chest. Patients with Darier disease or seborrheic dermatitis can also acquire it.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Patients with atopy, especially children, are susceptible to all kinds of skin infections—fungal, bacterial, and viral.
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV) can appear in almost any location, including on fingers, but can also manifest as diffuse papulovesicular lesions on the face and chest of atopic patients.
- The blisters/vesicles of HSV are often pus-filled and usually provoke regional adenopathy.
- If diagnosed early enough, herpetic whitlows can be successfully treated with oral acyclovir; this doesn’t provide a cure but does stop the particular episode.
An 8-year-old boy is brought in for evaluation of a collection of blisters on his finger, near the nail. The problem manifested about 6 days ago. The affected area is tender to touch. The child reportedly feels well, with no fever or malaise.
The patient has an extensive personal and family history of atopy. Since birth, he has had dry, sensitive skin and has experienced episodes of eczema, seasonal allergies, and asthma. Three months ago, he was admitted to the hospital with eczema herpeticum and successfully treated with IV acyclovir.

EXAMINATION
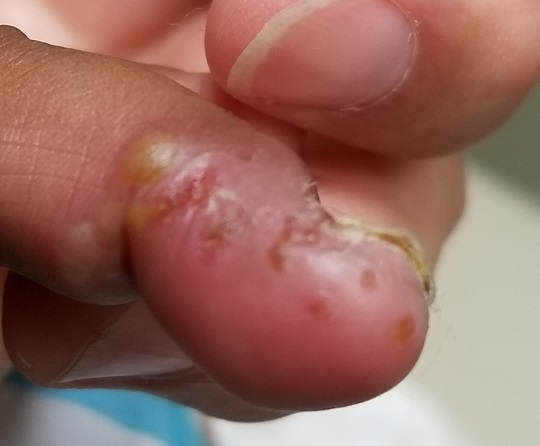
A cluster of vesicles is seen in the lateral perionychial area of the left third finger. Very modest erythema surrounds the vesicles, which contain cloudy yellow fluid suggestive of pus. There is a palpable lymph node in the left epitrochlear area.
The child is afebrile and in no distress. Patches of mild eczema are seen on the extremities and trunk.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
The lesion on this child’s finger is a herpetic whitlow. Patients with atopy are often susceptible to all types of skin infections: bacterial, fungal, and viral. In fact, human papillomavirus infection manifesting as multiple warts is not uncommon in this population. Nor is herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection, of which this case represents 1 manifestation.
A culture could have been done to confirm the diagnosis, but that would entail opening a vesicle to collect the fluid and then waiting at least 2 weeks for the results. By then, this whitlow would have long since resolved.
As with all HSV infections in the immunocompetent, treatment with acyclovir must be started in the first 2 to 3 days to have any effect—so such treatment in this case would be useless. If the herpetic whitlow were to recur in the same location, prompt treatment could be initiated, which would likely shorten the disease course and reduce symptoms.
Another HSV infection seen almost exclusively in atopic patients is eczema herpeticum (also known as Kaposi varicelliform eruption). This diffuse infection comprises dozens of tiny papulovesicular lesions, mostly concentrated on the face but often spilling down onto the chest. Patients with Darier disease or seborrheic dermatitis can also acquire it.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Patients with atopy, especially children, are susceptible to all kinds of skin infections—fungal, bacterial, and viral.
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV) can appear in almost any location, including on fingers, but can also manifest as diffuse papulovesicular lesions on the face and chest of atopic patients.
- The blisters/vesicles of HSV are often pus-filled and usually provoke regional adenopathy.
- If diagnosed early enough, herpetic whitlows can be successfully treated with oral acyclovir; this doesn’t provide a cure but does stop the particular episode.
An 8-year-old boy is brought in for evaluation of a collection of blisters on his finger, near the nail. The problem manifested about 6 days ago. The affected area is tender to touch. The child reportedly feels well, with no fever or malaise.
The patient has an extensive personal and family history of atopy. Since birth, he has had dry, sensitive skin and has experienced episodes of eczema, seasonal allergies, and asthma. Three months ago, he was admitted to the hospital with eczema herpeticum and successfully treated with IV acyclovir.

EXAMINATION
A cluster of vesicles is seen in the lateral perionychial area of the left third finger. Very modest erythema surrounds the vesicles, which contain cloudy yellow fluid suggestive of pus. There is a palpable lymph node in the left epitrochlear area.
The child is afebrile and in no distress. Patches of mild eczema are seen on the extremities and trunk.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
The lesion on this child’s finger is a herpetic whitlow. Patients with atopy are often susceptible to all types of skin infections: bacterial, fungal, and viral. In fact, human papillomavirus infection manifesting as multiple warts is not uncommon in this population. Nor is herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection, of which this case represents 1 manifestation.
A culture could have been done to confirm the diagnosis, but that would entail opening a vesicle to collect the fluid and then waiting at least 2 weeks for the results. By then, this whitlow would have long since resolved.
As with all HSV infections in the immunocompetent, treatment with acyclovir must be started in the first 2 to 3 days to have any effect—so such treatment in this case would be useless. If the herpetic whitlow were to recur in the same location, prompt treatment could be initiated, which would likely shorten the disease course and reduce symptoms.
Another HSV infection seen almost exclusively in atopic patients is eczema herpeticum (also known as Kaposi varicelliform eruption). This diffuse infection comprises dozens of tiny papulovesicular lesions, mostly concentrated on the face but often spilling down onto the chest. Patients with Darier disease or seborrheic dermatitis can also acquire it.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Patients with atopy, especially children, are susceptible to all kinds of skin infections—fungal, bacterial, and viral.
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV) can appear in almost any location, including on fingers, but can also manifest as diffuse papulovesicular lesions on the face and chest of atopic patients.
- The blisters/vesicles of HSV are often pus-filled and usually provoke regional adenopathy.
- If diagnosed early enough, herpetic whitlows can be successfully treated with oral acyclovir; this doesn’t provide a cure but does stop the particular episode.