Cancer Data Trends 2024: Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Reviewed by Cynthia Moylan, MD, MHS
Associate Professor of Medicine
GI Clinical Research Unite Co-Director
Duke University Health System
Durham VA Health System
Durham, NC
Dr. Moylan has no relevant financial relationships to disclose.

1
-
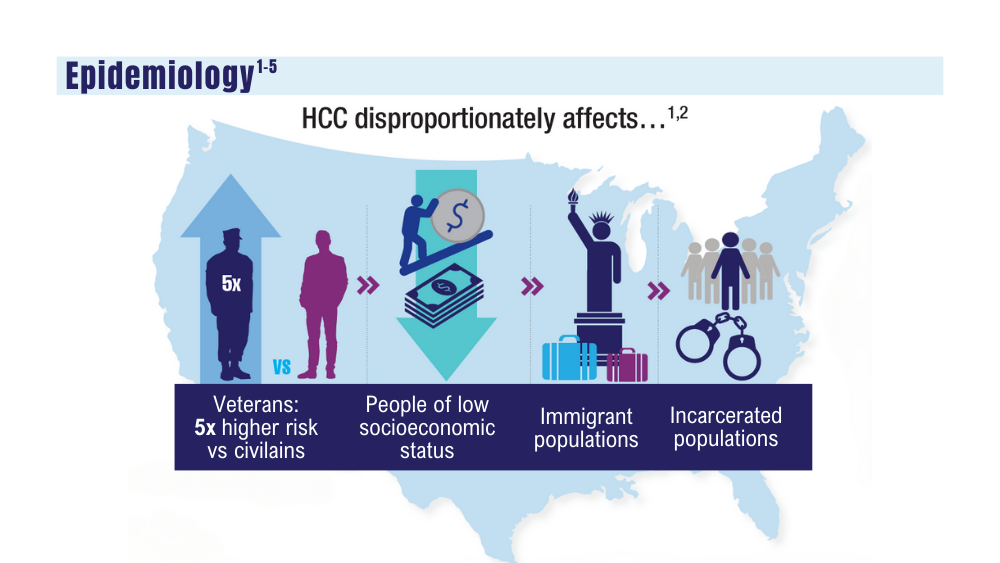
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of primary liver cancer, has tripled in incidence since 1990, and is the fastest-growing cause of cancer-related death in the United States.3 In 2021, 2000 veterans were diagnosed with HCC.4 HCC is fatal if left untreated, with a 5-year survival rate of < 10%. Most veterans with HCC present at advanced stages.5
-
-
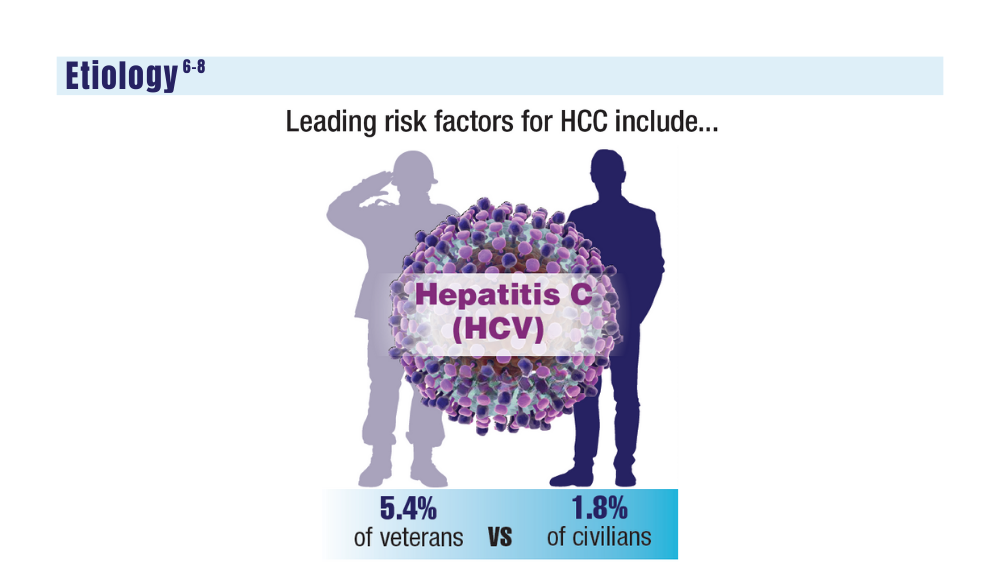
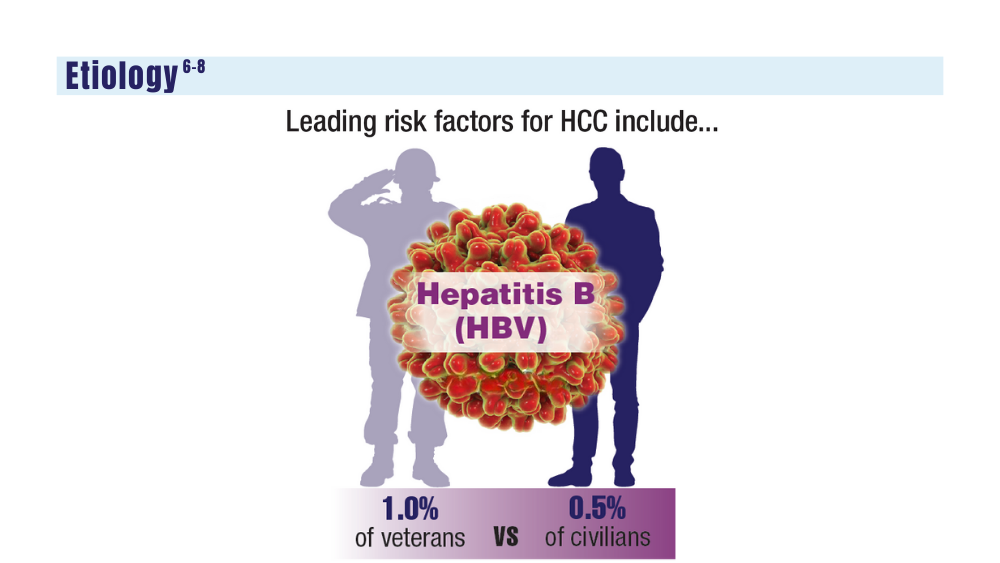
Direct-acting antiviral drugs have slowed rates of HCV-HCC.
-

Although this has offset recent increases in alcoholic liver disease- and MASLD-HCC, those with MASLD are known to have a lower survival rate than those with viral hepatitis-related HCC.
-

A study of 149 veterans diagnosed with HCC evaluated the benefits of individualizing care as well as aiding with travel and lodging and found a marked prevalence of psychosocial barriers in the veteran population that can negatively affect veterans in need of cancer care.5
-

-
-
-
atezo-bev, atezolizumab in combination with bevacizumab
-
-

-
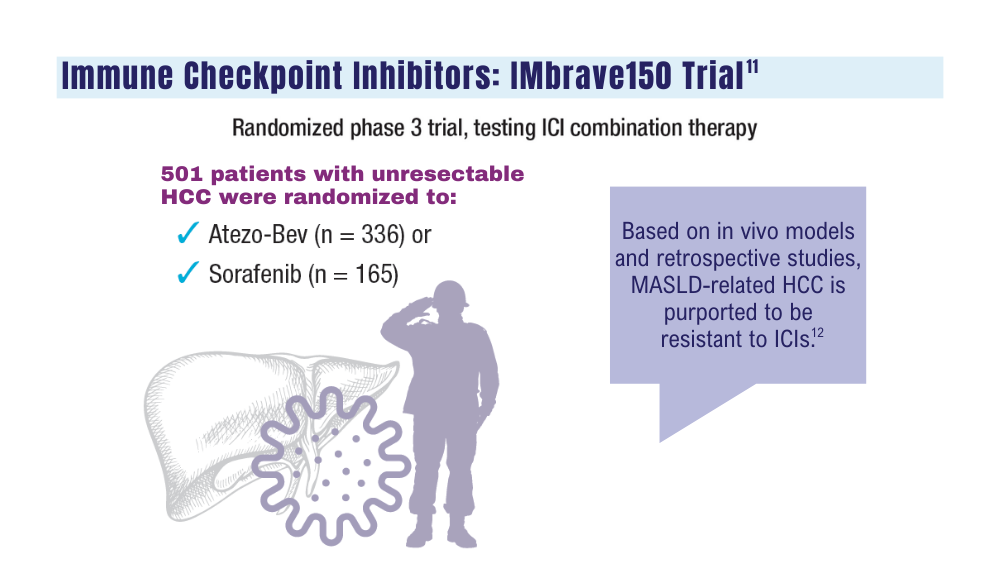
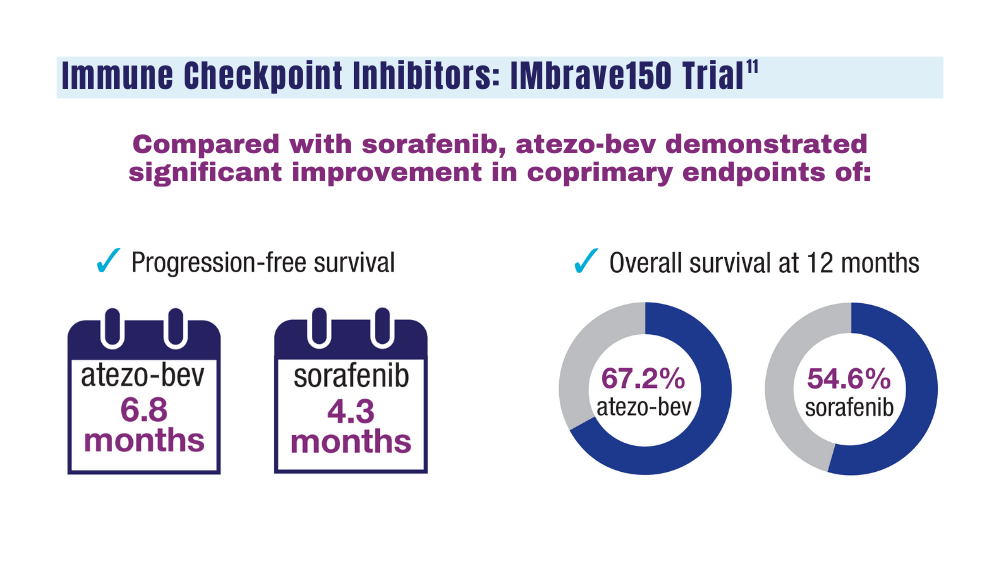
IMbrave150 led to the FDA approval of atezo-bev for patients with unresectable HCC who have not received prior systemic therapy, establishing this regimen as a standard of care.11
-
In addition to targeting PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4, an increasing number of ICIs, such as LAG-3, TIM-3, and GITR, are gradually demonstrating their efficacy.12
GITR, glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein; ICI, immune checkpoint inhibitor; LAG-3, lymphocyte-associated gene 3; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand 1; TIM-3, T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3
-
-
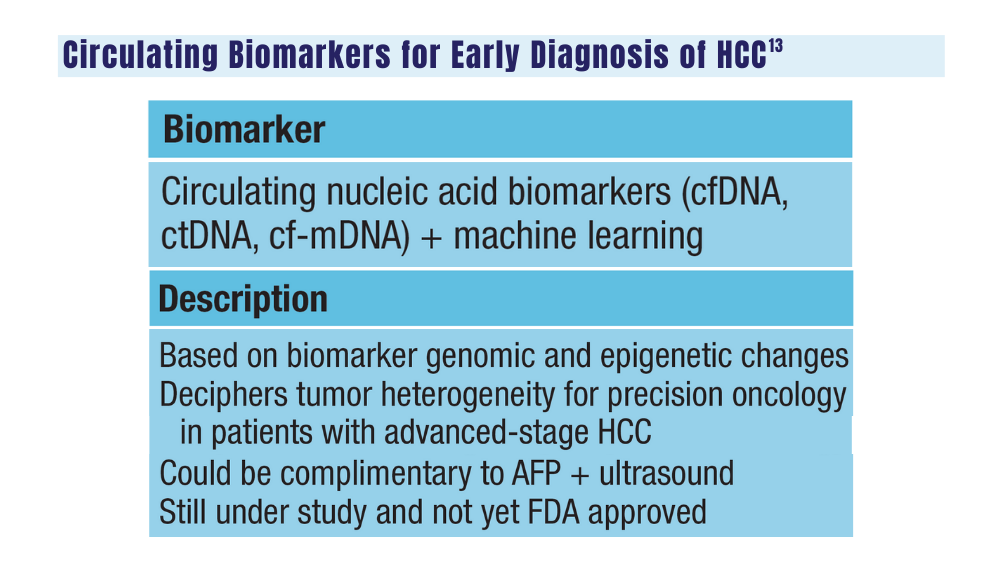
cfDNA, cell-free DNA; ctDNA, circulating tumor DNA; cf-mDNA, cell-free mitochondrial NDA.; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4
-
-
-
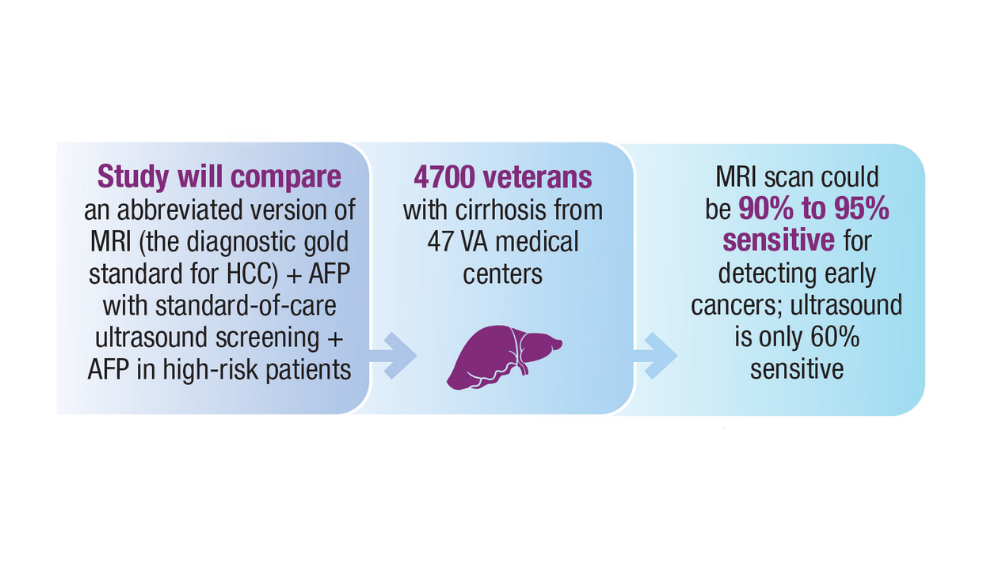
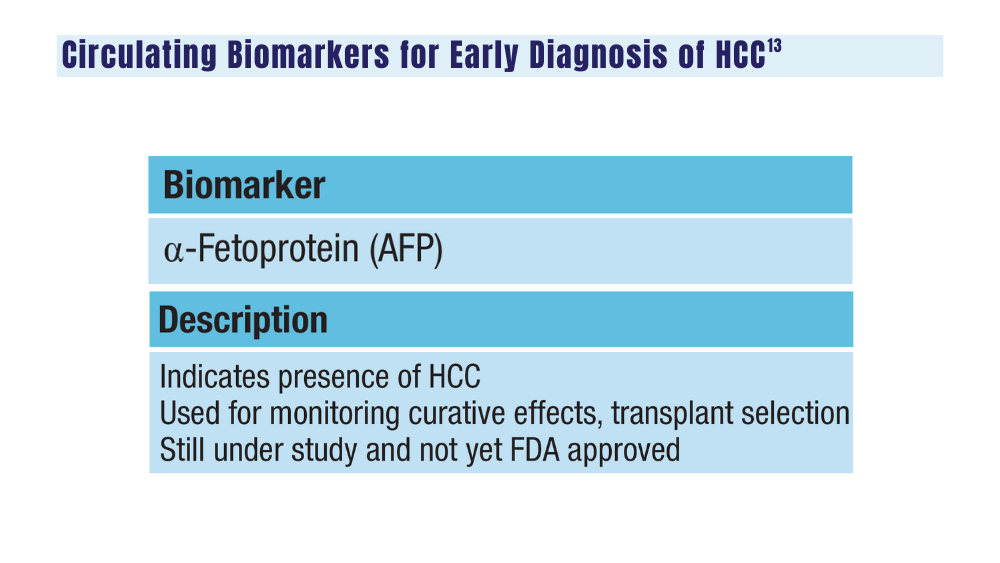
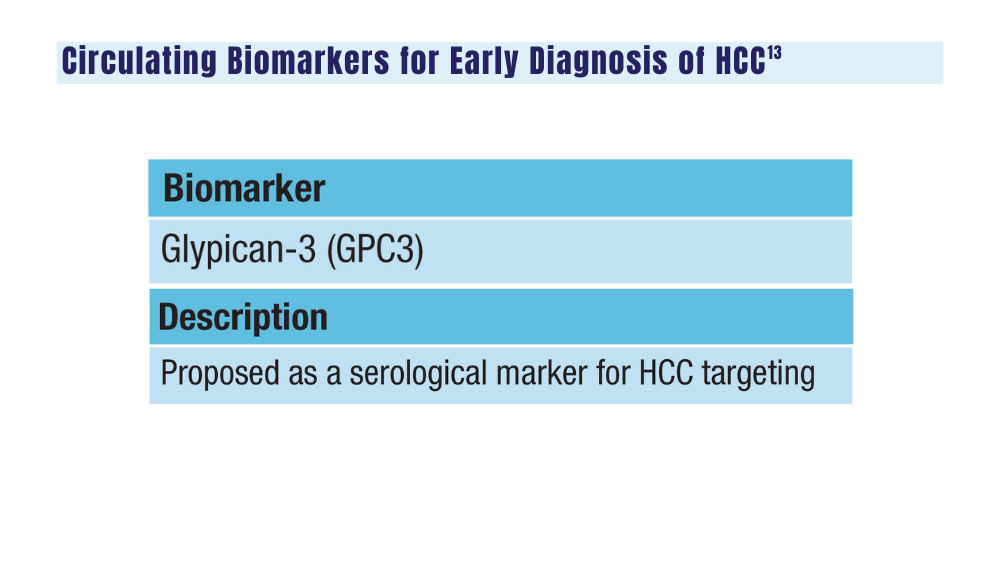
Surveillance of high-risk HCC groups using ultrasound, with or without serum analysis of AFP, can help detect early, potentially curable tumors, but is limited by its insensitivity, especially in patients who have obesity. To date, there are still no FDA-approved liquid biopsy assays for HCC.
