User login
A 45-year-old woman is referred to dermatology for a “fungal infection” that has failed to respond to the following treatments: topical clotrimazole cream, topical miconazole cream, a 30-day course of oral terbinafine (250 mg/d), and a 2-month course of oral griseofulvin (unknown dose). The lesions are completely asymptomatic but quite worrisome to the patient since they manifested 6 months ago.
She has consulted at least 6 different providers—none of whom was a dermatologist but all of whom were certain of the diagnosis and thus felt no need to refer the patient. However, the passage of time and trail of ineffective treatments finally prompts the (albeit reluctant) decision to send the patient to dermatology.
On questioning, she denies any serious health problems, such as diabetes or immunosuppression. She has had no contact with any animals or children.
EXAMINATION
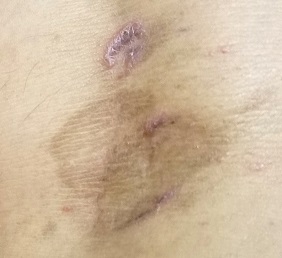
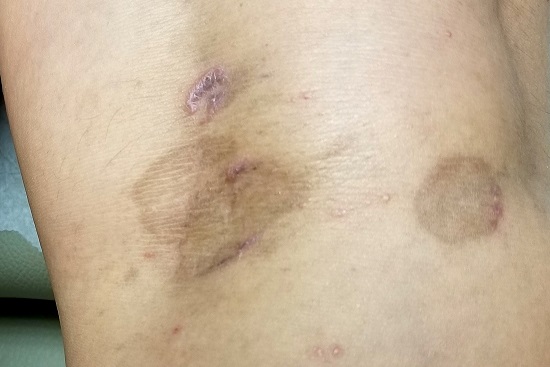
The lesions in question total 6; all are uniformly purplish brown, round, and macular, and they range from 5 mm to more than 3 cm. Most are located on the bilateral popliteal areas. The lesions have sharp, well-defined margins. Several have faintly raised papular margins that give the centers a slightly concave appearance.
Palpation reveals the complete absence of any surface disturbance, such as scaling or erosion. Thus, no KOH prep can be performed to check for fungal elements. Instead, a shave biopsy is performed, the results of which show a sawtooth-patterned lymphocytic infiltrate obliterating the normally smooth undulating dermoepidermal junction.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
This case effectively demonstrates the principle that, when confronted with round or annular lesions, some providers will rely on the diagnosis of “fungal” even when evidence (eg, failed treatment attempts) suggests otherwise. What that nonresponse should do is signal the need for an expanded differential—that is, a consideration of other diagnostic possibilities. This is a bedrock principle in every medical specialty, not just in dermatology.
In this case, the biopsy results clearly pointed to the correct diagnosis of lichen planus (LP), a common dermatosis well known to present in annular morphology. LP is a benign process, albeit one that is occasionally quite bothersome (eg, itching) and, rarely, widespread. LP’s more typical distribution is on volar wrists, in the sacral areas, and occasionally on genitals, so the inability to make a visual diagnosis in this case is forgivable.
Although LP’s etiology is unfortunately unknown, what is known is how to treat it: with topical steroids when necessary or “tincture of time,” as in this patient’s asymptomatic case. LP typically resolves on its own, and it has no worrisome import or connections to more serious disease.
But as always, the first step to correct diagnosis is to consider letting go of the old diagnosis—fungal infection—which was clearly incorrect given the lack of response to numerous antifungals. The second step is to consider other possibilities, which would include lichen planus, psoriasis, granuloma annulare, tinea versicolor, and necrobiosis. The third step is to perform a biopsy, which would establish the correct diagnosis with certainty and in turn, dictate correct treatment.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- There is an extensive differential for round or annular skin lesions that includes many nonfungal causes.
- When antifungals fail to help, consider other diagnostic possibilities.
- Perform a biopsy when a visual diagnosis is not possible.
- Lichen planus (LP) is a common benign inflammatory skin condition that can present with annular lesions.
A 45-year-old woman is referred to dermatology for a “fungal infection” that has failed to respond to the following treatments: topical clotrimazole cream, topical miconazole cream, a 30-day course of oral terbinafine (250 mg/d), and a 2-month course of oral griseofulvin (unknown dose). The lesions are completely asymptomatic but quite worrisome to the patient since they manifested 6 months ago.
She has consulted at least 6 different providers—none of whom was a dermatologist but all of whom were certain of the diagnosis and thus felt no need to refer the patient. However, the passage of time and trail of ineffective treatments finally prompts the (albeit reluctant) decision to send the patient to dermatology.
On questioning, she denies any serious health problems, such as diabetes or immunosuppression. She has had no contact with any animals or children.

EXAMINATION
The lesions in question total 6; all are uniformly purplish brown, round, and macular, and they range from 5 mm to more than 3 cm. Most are located on the bilateral popliteal areas. The lesions have sharp, well-defined margins. Several have faintly raised papular margins that give the centers a slightly concave appearance.
Palpation reveals the complete absence of any surface disturbance, such as scaling or erosion. Thus, no KOH prep can be performed to check for fungal elements. Instead, a shave biopsy is performed, the results of which show a sawtooth-patterned lymphocytic infiltrate obliterating the normally smooth undulating dermoepidermal junction.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
This case effectively demonstrates the principle that, when confronted with round or annular lesions, some providers will rely on the diagnosis of “fungal” even when evidence (eg, failed treatment attempts) suggests otherwise. What that nonresponse should do is signal the need for an expanded differential—that is, a consideration of other diagnostic possibilities. This is a bedrock principle in every medical specialty, not just in dermatology.
In this case, the biopsy results clearly pointed to the correct diagnosis of lichen planus (LP), a common dermatosis well known to present in annular morphology. LP is a benign process, albeit one that is occasionally quite bothersome (eg, itching) and, rarely, widespread. LP’s more typical distribution is on volar wrists, in the sacral areas, and occasionally on genitals, so the inability to make a visual diagnosis in this case is forgivable.
Although LP’s etiology is unfortunately unknown, what is known is how to treat it: with topical steroids when necessary or “tincture of time,” as in this patient’s asymptomatic case. LP typically resolves on its own, and it has no worrisome import or connections to more serious disease.
But as always, the first step to correct diagnosis is to consider letting go of the old diagnosis—fungal infection—which was clearly incorrect given the lack of response to numerous antifungals. The second step is to consider other possibilities, which would include lichen planus, psoriasis, granuloma annulare, tinea versicolor, and necrobiosis. The third step is to perform a biopsy, which would establish the correct diagnosis with certainty and in turn, dictate correct treatment.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- There is an extensive differential for round or annular skin lesions that includes many nonfungal causes.
- When antifungals fail to help, consider other diagnostic possibilities.
- Perform a biopsy when a visual diagnosis is not possible.
- Lichen planus (LP) is a common benign inflammatory skin condition that can present with annular lesions.
A 45-year-old woman is referred to dermatology for a “fungal infection” that has failed to respond to the following treatments: topical clotrimazole cream, topical miconazole cream, a 30-day course of oral terbinafine (250 mg/d), and a 2-month course of oral griseofulvin (unknown dose). The lesions are completely asymptomatic but quite worrisome to the patient since they manifested 6 months ago.
She has consulted at least 6 different providers—none of whom was a dermatologist but all of whom were certain of the diagnosis and thus felt no need to refer the patient. However, the passage of time and trail of ineffective treatments finally prompts the (albeit reluctant) decision to send the patient to dermatology.
On questioning, she denies any serious health problems, such as diabetes or immunosuppression. She has had no contact with any animals or children.

EXAMINATION
The lesions in question total 6; all are uniformly purplish brown, round, and macular, and they range from 5 mm to more than 3 cm. Most are located on the bilateral popliteal areas. The lesions have sharp, well-defined margins. Several have faintly raised papular margins that give the centers a slightly concave appearance.
Palpation reveals the complete absence of any surface disturbance, such as scaling or erosion. Thus, no KOH prep can be performed to check for fungal elements. Instead, a shave biopsy is performed, the results of which show a sawtooth-patterned lymphocytic infiltrate obliterating the normally smooth undulating dermoepidermal junction.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
This case effectively demonstrates the principle that, when confronted with round or annular lesions, some providers will rely on the diagnosis of “fungal” even when evidence (eg, failed treatment attempts) suggests otherwise. What that nonresponse should do is signal the need for an expanded differential—that is, a consideration of other diagnostic possibilities. This is a bedrock principle in every medical specialty, not just in dermatology.
In this case, the biopsy results clearly pointed to the correct diagnosis of lichen planus (LP), a common dermatosis well known to present in annular morphology. LP is a benign process, albeit one that is occasionally quite bothersome (eg, itching) and, rarely, widespread. LP’s more typical distribution is on volar wrists, in the sacral areas, and occasionally on genitals, so the inability to make a visual diagnosis in this case is forgivable.
Although LP’s etiology is unfortunately unknown, what is known is how to treat it: with topical steroids when necessary or “tincture of time,” as in this patient’s asymptomatic case. LP typically resolves on its own, and it has no worrisome import or connections to more serious disease.
But as always, the first step to correct diagnosis is to consider letting go of the old diagnosis—fungal infection—which was clearly incorrect given the lack of response to numerous antifungals. The second step is to consider other possibilities, which would include lichen planus, psoriasis, granuloma annulare, tinea versicolor, and necrobiosis. The third step is to perform a biopsy, which would establish the correct diagnosis with certainty and in turn, dictate correct treatment.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- There is an extensive differential for round or annular skin lesions that includes many nonfungal causes.
- When antifungals fail to help, consider other diagnostic possibilities.
- Perform a biopsy when a visual diagnosis is not possible.
- Lichen planus (LP) is a common benign inflammatory skin condition that can present with annular lesions.