User login
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
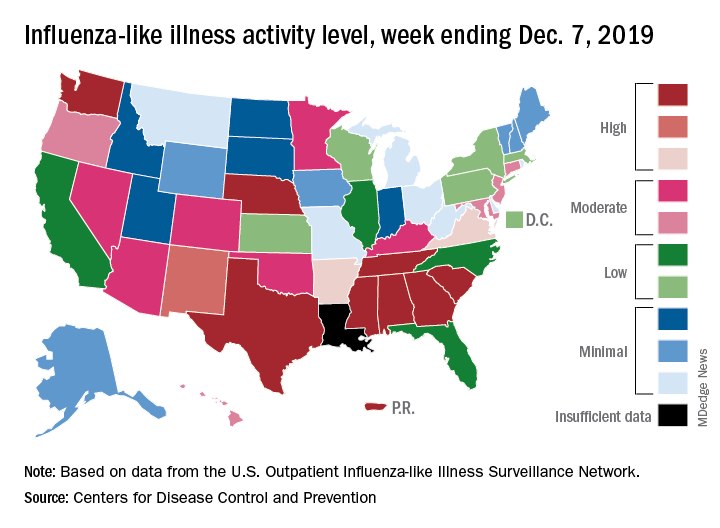
Nationally, 3.2% of outpatient visits were for influenza-like illness (ILI) during the week of Dec. 1-7, the CDC reported. That is down from 3.4% the week before, which was the highest November rate in 10 years. The national baseline rate is 2.4%, and the current 3.2% marks the fifth consecutive week that the outpatient ILI rate has been at or above the baseline level, the CDC report noted.
The drop in activity “may be influenced in part by a reduction in routine healthcare visits surrounding the Thanksgiving holiday. … as has occurred during previous seasons,” the CDC influenza division said Dec. 13 in its weekly flu report.
The early spike in “activity is being caused mostly by influenza B/Victoria viruses, which is unusual for this time of year,” the report said. Since the beginning of the 2019-2020 season a little over 2 months ago, almost 70% of specimens that have been positive for influenza have been identified as type B.
The nationwide decline in activity doesn’t, however, show up at the state level. For the week ending Dec. 7, there were eight states along with Puerto Rico at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of flu activity, as there were the previous week. Washington state moved up from 9 to 10, but Louisiana, which was at level 10 last week, had insufficient data to be included this week, the CDC data show.
There were four flu-related pediatric deaths reported to the CDC during the week ending Dec. 7, all occurring in previous weeks, which brings the total to 10 for the season. In 2018-2019, there were 143 pediatric deaths caused by influenza, the CDC said.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Nationally, 3.2% of outpatient visits were for influenza-like illness (ILI) during the week of Dec. 1-7, the CDC reported. That is down from 3.4% the week before, which was the highest November rate in 10 years. The national baseline rate is 2.4%, and the current 3.2% marks the fifth consecutive week that the outpatient ILI rate has been at or above the baseline level, the CDC report noted.
The drop in activity “may be influenced in part by a reduction in routine healthcare visits surrounding the Thanksgiving holiday. … as has occurred during previous seasons,” the CDC influenza division said Dec. 13 in its weekly flu report.
The early spike in “activity is being caused mostly by influenza B/Victoria viruses, which is unusual for this time of year,” the report said. Since the beginning of the 2019-2020 season a little over 2 months ago, almost 70% of specimens that have been positive for influenza have been identified as type B.
The nationwide decline in activity doesn’t, however, show up at the state level. For the week ending Dec. 7, there were eight states along with Puerto Rico at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of flu activity, as there were the previous week. Washington state moved up from 9 to 10, but Louisiana, which was at level 10 last week, had insufficient data to be included this week, the CDC data show.
There were four flu-related pediatric deaths reported to the CDC during the week ending Dec. 7, all occurring in previous weeks, which brings the total to 10 for the season. In 2018-2019, there were 143 pediatric deaths caused by influenza, the CDC said.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Nationally, 3.2% of outpatient visits were for influenza-like illness (ILI) during the week of Dec. 1-7, the CDC reported. That is down from 3.4% the week before, which was the highest November rate in 10 years. The national baseline rate is 2.4%, and the current 3.2% marks the fifth consecutive week that the outpatient ILI rate has been at or above the baseline level, the CDC report noted.
The drop in activity “may be influenced in part by a reduction in routine healthcare visits surrounding the Thanksgiving holiday. … as has occurred during previous seasons,” the CDC influenza division said Dec. 13 in its weekly flu report.
The early spike in “activity is being caused mostly by influenza B/Victoria viruses, which is unusual for this time of year,” the report said. Since the beginning of the 2019-2020 season a little over 2 months ago, almost 70% of specimens that have been positive for influenza have been identified as type B.
The nationwide decline in activity doesn’t, however, show up at the state level. For the week ending Dec. 7, there were eight states along with Puerto Rico at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of flu activity, as there were the previous week. Washington state moved up from 9 to 10, but Louisiana, which was at level 10 last week, had insufficient data to be included this week, the CDC data show.
There were four flu-related pediatric deaths reported to the CDC during the week ending Dec. 7, all occurring in previous weeks, which brings the total to 10 for the season. In 2018-2019, there were 143 pediatric deaths caused by influenza, the CDC said.