User login
ANSWER
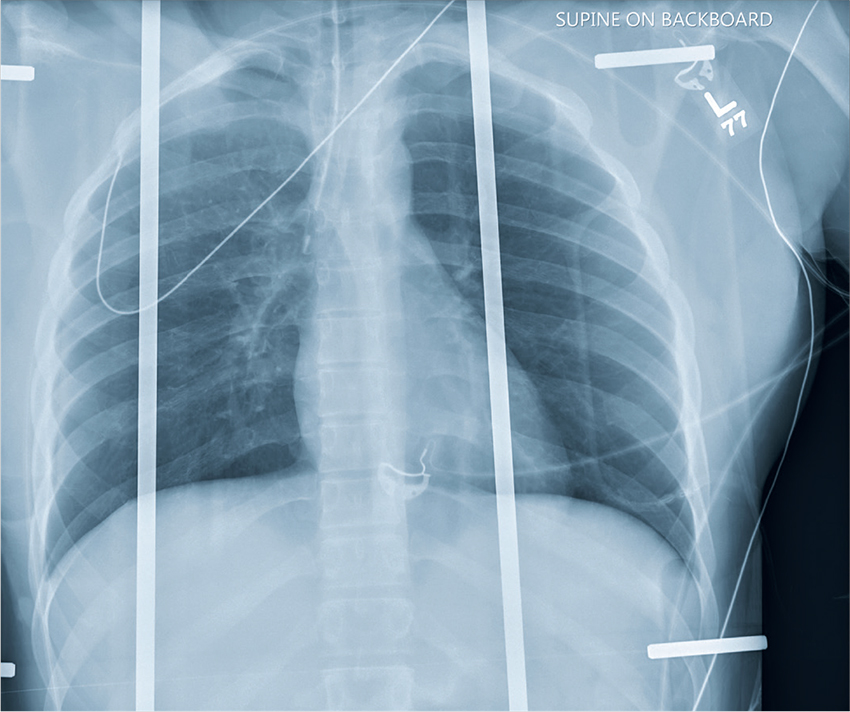
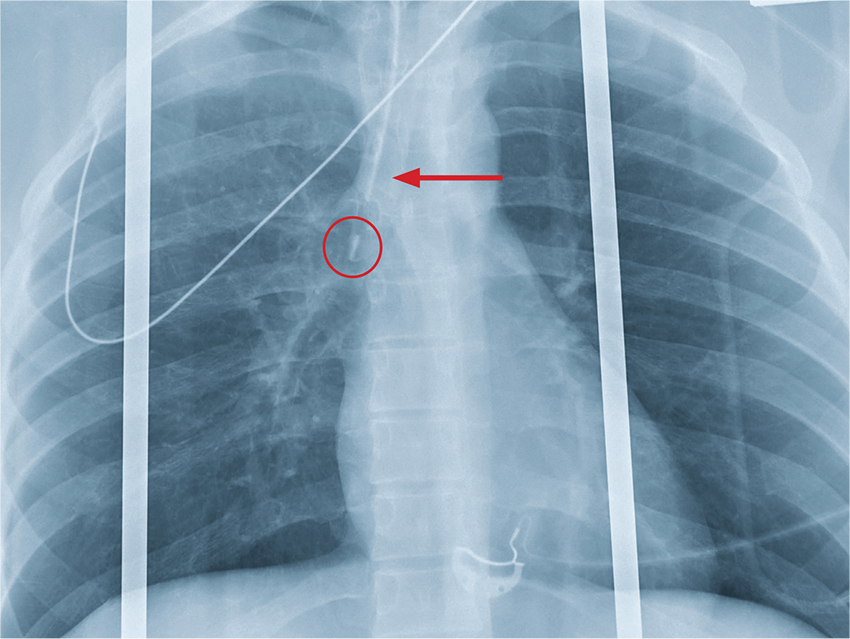
The chest radiograph shows an endotracheal tube within the right main stem bronchus. There is no evidence of any other acute pathology (eg, fracture, contusion, pneumothorax).
The tube needs to be withdrawn so that it sits just above the carina (see arrow). If not promptly addressed, incorrect placement of an endotracheal tube can lead to complications, including hypoxemia, pneumothorax, atelectasis, or complete collapse of the left lung.

ANSWER
The chest radiograph shows an endotracheal tube within the right main stem bronchus. There is no evidence of any other acute pathology (eg, fracture, contusion, pneumothorax).
The tube needs to be withdrawn so that it sits just above the carina (see arrow). If not promptly addressed, incorrect placement of an endotracheal tube can lead to complications, including hypoxemia, pneumothorax, atelectasis, or complete collapse of the left lung.

ANSWER
The chest radiograph shows an endotracheal tube within the right main stem bronchus. There is no evidence of any other acute pathology (eg, fracture, contusion, pneumothorax).
The tube needs to be withdrawn so that it sits just above the carina (see arrow). If not promptly addressed, incorrect placement of an endotracheal tube can lead to complications, including hypoxemia, pneumothorax, atelectasis, or complete collapse of the left lung.
A woman who looks to be 30 years old is brought to your facility as a trauma code following a car accident. She was a restrained driver, traveling at a high speed when she lost control of her vehicle and hit a retaining wall.
When first responders arrived, the patient had extricated herself but demonstrated a decreased level of consciousness, severe respiratory distress, and a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 7. She was intubated at the scene by emergency medical personnel.
On evaluation, you note a young, intubated, unresponsive female. Her blood pressure is 90/50 mm Hg; heart rate, 90 beats/min; and O2 saturation, 100%. Rapid primary survey shows
A portable chest radiograph is obtained (shown). What is your impression?