User login
On the basis of the patient's medical history and presentation, this is probably a case of uveitis, a common extra-articular manifestation of psoriatic disease. In fact, the presence of uveitis can help distinguish PsA from osteoarthritis. Uveitis is characterized by inflammation of the uvea tract, with the retina, optic nerve, vitreous body, and sclera potentially becoming inflamed as well. Among patients with PsA, the prevalence of uveitis rises with ongoing disease duration, though the condition may also precede the development of PsA in patients with psoriasis, and is common among patients with severe psoriatic disease in Western and Asian populations. Overall, the prevalence of uveitis has been estimated to be 6%-9%. HLA-B27 genotype is strongly associated with uveitis in patients with concomitant PsA.
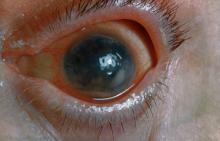
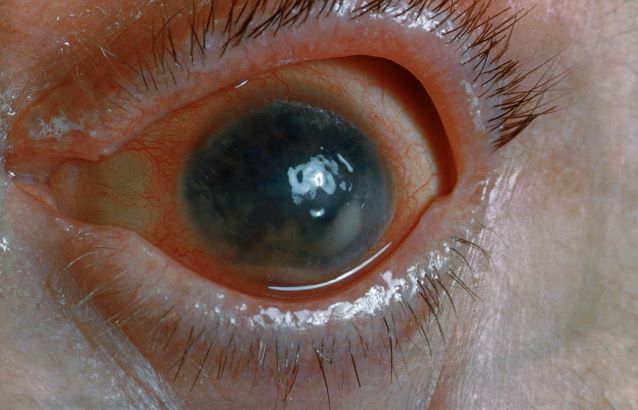
Symptoms of uveitis, as seen in the present case, include blurred vision, photophobia, pain, and ciliary flush. The condition is classified as anterior, intermediate, posterior, or panuveitis, with the majority of cases diagnosed as anterior. In anterior uveitis, the inflamed pupil may become constricted or take on an irregular shape caused by iris adhesions to the anterior lens capsule. Uveitis in PsA is bilateral and has a chronic relapsing course. Onset is typically insidious.
Workup for uveitis should comprise visual acuity testing, slit lamp biomicroscopy, measurement of intraocular pressures, and a dilated eye exam. Conditions in the differential which threaten a patient's sight include retinal vasculitis, vitritis, cystoid macular edema, Behçet disease, and tubulo-interstitial nephritis. Other autoimmune diseases which can cause uveitis with systemic manifestations (multiple sclerosis, sarcoidosis, lupus) should be investigated. Infectious causes must also be eliminated. However, considering this patient's history of psoriatic disease, uveitis should be highly suspected.
Uveitis demands urgent treatment to control ocular inflammation. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors are the recommended first-line and second-line treatment for PsA, including in patients with complications such as uveitis. However, etanercept should not be used as it is less effective than adalimumab or other TNF inhibitors for uveitis. Because uveitis may sometimes respond to MTX therapy, patients with severe PsA may use a biologic agent in combination with MTX if they have had a partial response to current MTX therapy, as recommended by the American College of Rheumatology.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, Professor of Medicine (retired), Temple University School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh; Chairman, Department of Medicine Emeritus, Western Pennsylvania Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
On the basis of the patient's medical history and presentation, this is probably a case of uveitis, a common extra-articular manifestation of psoriatic disease. In fact, the presence of uveitis can help distinguish PsA from osteoarthritis. Uveitis is characterized by inflammation of the uvea tract, with the retina, optic nerve, vitreous body, and sclera potentially becoming inflamed as well. Among patients with PsA, the prevalence of uveitis rises with ongoing disease duration, though the condition may also precede the development of PsA in patients with psoriasis, and is common among patients with severe psoriatic disease in Western and Asian populations. Overall, the prevalence of uveitis has been estimated to be 6%-9%. HLA-B27 genotype is strongly associated with uveitis in patients with concomitant PsA.
Symptoms of uveitis, as seen in the present case, include blurred vision, photophobia, pain, and ciliary flush. The condition is classified as anterior, intermediate, posterior, or panuveitis, with the majority of cases diagnosed as anterior. In anterior uveitis, the inflamed pupil may become constricted or take on an irregular shape caused by iris adhesions to the anterior lens capsule. Uveitis in PsA is bilateral and has a chronic relapsing course. Onset is typically insidious.
Workup for uveitis should comprise visual acuity testing, slit lamp biomicroscopy, measurement of intraocular pressures, and a dilated eye exam. Conditions in the differential which threaten a patient's sight include retinal vasculitis, vitritis, cystoid macular edema, Behçet disease, and tubulo-interstitial nephritis. Other autoimmune diseases which can cause uveitis with systemic manifestations (multiple sclerosis, sarcoidosis, lupus) should be investigated. Infectious causes must also be eliminated. However, considering this patient's history of psoriatic disease, uveitis should be highly suspected.
Uveitis demands urgent treatment to control ocular inflammation. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors are the recommended first-line and second-line treatment for PsA, including in patients with complications such as uveitis. However, etanercept should not be used as it is less effective than adalimumab or other TNF inhibitors for uveitis. Because uveitis may sometimes respond to MTX therapy, patients with severe PsA may use a biologic agent in combination with MTX if they have had a partial response to current MTX therapy, as recommended by the American College of Rheumatology.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, Professor of Medicine (retired), Temple University School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh; Chairman, Department of Medicine Emeritus, Western Pennsylvania Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
On the basis of the patient's medical history and presentation, this is probably a case of uveitis, a common extra-articular manifestation of psoriatic disease. In fact, the presence of uveitis can help distinguish PsA from osteoarthritis. Uveitis is characterized by inflammation of the uvea tract, with the retina, optic nerve, vitreous body, and sclera potentially becoming inflamed as well. Among patients with PsA, the prevalence of uveitis rises with ongoing disease duration, though the condition may also precede the development of PsA in patients with psoriasis, and is common among patients with severe psoriatic disease in Western and Asian populations. Overall, the prevalence of uveitis has been estimated to be 6%-9%. HLA-B27 genotype is strongly associated with uveitis in patients with concomitant PsA.
Symptoms of uveitis, as seen in the present case, include blurred vision, photophobia, pain, and ciliary flush. The condition is classified as anterior, intermediate, posterior, or panuveitis, with the majority of cases diagnosed as anterior. In anterior uveitis, the inflamed pupil may become constricted or take on an irregular shape caused by iris adhesions to the anterior lens capsule. Uveitis in PsA is bilateral and has a chronic relapsing course. Onset is typically insidious.
Workup for uveitis should comprise visual acuity testing, slit lamp biomicroscopy, measurement of intraocular pressures, and a dilated eye exam. Conditions in the differential which threaten a patient's sight include retinal vasculitis, vitritis, cystoid macular edema, Behçet disease, and tubulo-interstitial nephritis. Other autoimmune diseases which can cause uveitis with systemic manifestations (multiple sclerosis, sarcoidosis, lupus) should be investigated. Infectious causes must also be eliminated. However, considering this patient's history of psoriatic disease, uveitis should be highly suspected.
Uveitis demands urgent treatment to control ocular inflammation. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors are the recommended first-line and second-line treatment for PsA, including in patients with complications such as uveitis. However, etanercept should not be used as it is less effective than adalimumab or other TNF inhibitors for uveitis. Because uveitis may sometimes respond to MTX therapy, patients with severe PsA may use a biologic agent in combination with MTX if they have had a partial response to current MTX therapy, as recommended by the American College of Rheumatology.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, Professor of Medicine (retired), Temple University School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh; Chairman, Department of Medicine Emeritus, Western Pennsylvania Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 48-year-old male patient presents with blurred vision, pain, and photophobia. He recently had a routine visit with an ophthalmologist, which was normal. The affected pupil appears irregular in shape. The anterior chamber appears foggy. Local ciliary flush is observed on slit lamp exam. The physical examination is also notable for axial arthropathy. The patient has an 11-year history of moderate to severe psoriatic arthritis (PsA) which he typically manages with methotrexate (MTX) therapy, to which he has had a partial response. He was initially diagnosed when he presented with worsening psoriasis and enthesitis on the insertion sites of the plantar fascia, as well as dactylitis.