User login
ANSWER
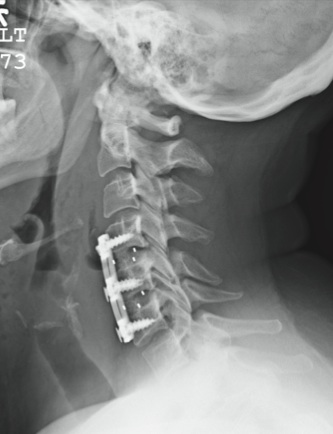
The patient is status post two-level anterior cervical diskectomy and fusion, with interbody grafts and hardware appearing intact. The radiograph demonstrates significant prevertebral soft-tissue swelling greater than 2 cm over several levels. This results in significant posterior compression of the oropharynx. Such findings are typically seen in patients who develop retropharyngeal hematomas.
This patient was urgently returned to the operating room, where she underwent successful evacuation of a hematoma that was under a moderate amount of pressure. No specific source was identified, which is not uncommon.
The patient made a full recovery.
ANSWER
The patient is status post two-level anterior cervical diskectomy and fusion, with interbody grafts and hardware appearing intact. The radiograph demonstrates significant prevertebral soft-tissue swelling greater than 2 cm over several levels. This results in significant posterior compression of the oropharynx. Such findings are typically seen in patients who develop retropharyngeal hematomas.
This patient was urgently returned to the operating room, where she underwent successful evacuation of a hematoma that was under a moderate amount of pressure. No specific source was identified, which is not uncommon.
The patient made a full recovery.
ANSWER
The patient is status post two-level anterior cervical diskectomy and fusion, with interbody grafts and hardware appearing intact. The radiograph demonstrates significant prevertebral soft-tissue swelling greater than 2 cm over several levels. This results in significant posterior compression of the oropharynx. Such findings are typically seen in patients who develop retropharyngeal hematomas.
This patient was urgently returned to the operating room, where she underwent successful evacuation of a hematoma that was under a moderate amount of pressure. No specific source was identified, which is not uncommon.
The patient made a full recovery.
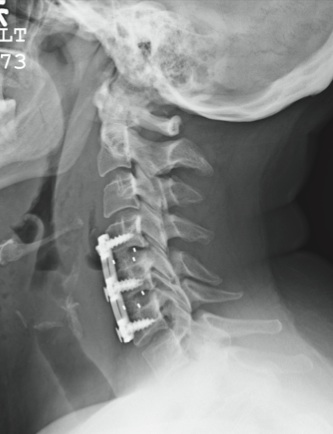
You receive a call from the nursing staff stating that a postoperative patient is experiencing respiratory distress. The patient is a 41-year-old woman who underwent a two-level anterior cervical diskectomy and fusion yesterday. There were no problems during the surgery. Earlier this morning, when the patient was examined during rounds, she was experiencing mild dysphagia, and steroids were ordered. Now, the patient says she cannot breathe well unless she is sitting upright. Her vital signs are stable, with an O2 saturation of 93%. Her incision is swollen and appears full. Stat radiograph of the cervical spine is obtained (shown). What is your impression?