The 2019-2020 flu season took a big jump in severity during the last full week of 2019, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
For the week ending Dec. 28, 6.9% of all outpatient visits to health care providers were for influenza-like illness (ILI), the CDC’s influenza division reported Jan. 3. That is up from 5.1% the previous week and is the highest rate recorded in December since 2003. During the flu pandemic season of 2009-2010, the rate peaked in October and dropped to relatively normal levels by the end of November, CDC data show.
This marks the eighth consecutive week that the outpatient visit rate has been at or above the nation’s baseline level of 2.4%, but the data for this week “may in part be influenced by changes in healthcare-seeking behavior that can occur during the holidays,” the CDC suggested.
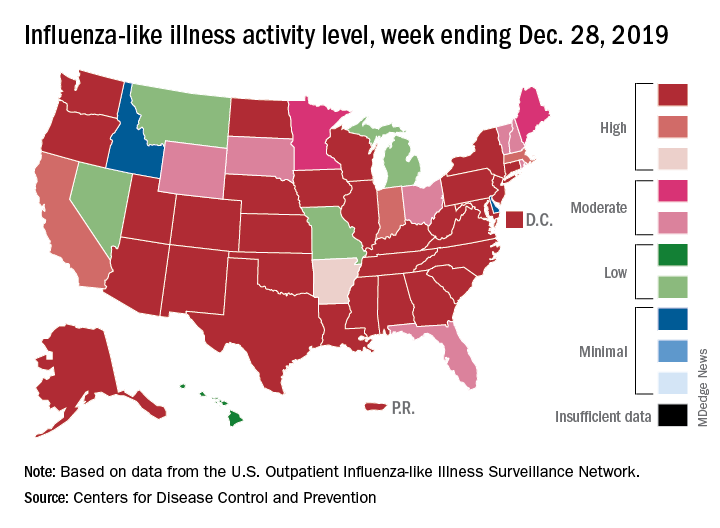
All those outpatient visits mean that the ILI activity map is getting quite red. Thirty states, as well as the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico, were at the highest level on the CDC’s 1-10 activity scale during the week ending Dec. 28, compared with 20 the week before. Four states were categorized in the “high” range with activity levels of 8 and 9.
There have been approximately 6.4 million flu illnesses so far this season, the CDC estimated, along with 55,000 hospitalizations, although the ILI admission rate of 9.2 per 100,000 population is fairly typical for this time of year.
The week of Dec. 28 also brought reports of five more ILI-related pediatric deaths, which all occurred in the two previous weeks. A total of 27 children have died from the flu so far during the 2019-2020 season, the CDC said.