A cute colonic pseudo-obstruction, or Ogilvie syndrome, is dilatation of the colon without mechanical obstruction. It is often seen postoperatively after cesarean section , pelvic , spinal, or other orthopedic surgery, such as knee arthroplasty. 1 One study demonstrated an incidence of acute colonic pseudo-obstruction of 1.3% following hip replacement surgery. 2
The most common symptoms are abdominal distension, pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation, or diarrhea. Bowel sounds are present in the majority of cases.3 It is important to recognize the varied presentations of ileus in the postoperative setting. The most serious complications of acute colonic pseudo-obstruction are colonic ischemia and bowel perforation.
Case Presentation
An 84-year-old man underwent a total left hip arthroplasty revision. The evening after his surgery, his blood pressure (BP) decreased from 93/54 to 71/47 mm Hg, and his heart rate was 73 beats per minute. He was awake, in no acute distress, but reported loose stools. Results of cardiac and pulmonary examinations were normal, showing a regular rate and rhythm with no murmurs and clear lungs. There was normal jugular venous pressure and chronic pitting edema of the lower extremities bilaterally.
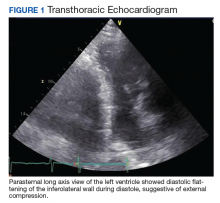
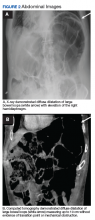
An abdominal examination revealed positive bowel sounds, a large ventral hernia, which was easily reducible, and a distended abdomen. His BP remained unchanged after IV normal saline 4 L, and urine output was 200 cc over 4 hours, which the care team determined represented adequate resuscitation. An infection workup, including chest X-ray, urinalysis, and blood and urine cultures, was unrevealing. Hemoglobin was stable at 8.5 g/dL (normal range 14-18), and creatinine level 0.66 mg/dL (normal range 0.7-1.2) at baseline. A transthoracic echocardiogram showed impaired diastolic filling suggestive of extrinsic compression of the left ventricle by mediastinal contents (Figure 1). An abdominal X-ray revealed diffuse dilatation of large bowel loops up to 10 cm, causing elevation and rightward shift of the heart (Figure 2A). A computed tomography scan of the abdomen showed total colonic dilatation without obstruction (Figure 2B).
The patient was diagnosed with postoperative ileus and acute colonic pseudo-obstruction. Nasogastric and rectal tubes were placed for decompression, and the patient was placed on nothing by mouth status. By postoperative day 3, his hypotension had resolved and his BP had improved to 111/58 mm Hg. The patient was able to resume a regular diet.