Gallbladder duplication is a congenital abnormality of the hepatobiliary system and often is not considered in the evaluation of a patient with right upper quadrant pain. Accuracy of the most commonly used imaging study to assess for biliary disease, abdominal ultrasound, is highly dependent on the skills of the ultrasonographer, and given its relative rarity, this condition is often not considered prior to planned cholecystectomy.1 Small case reviews found that < 50% of gallbladder duplications are diagnosed preoperatively despite use of ultrasound or computed tomography (CT) scan.2-4 Failure to recognize duplicate gallbladder anatomy in symptomatic patients may result in incomplete surgical management, an increase in perioperative complications, and years of morbidity due to unresolved symptoms. Once a patient has had a cholecystectomy, symptoms are presumed to be due to a nonbiliary etiology and an extensive, often repetitive, workup is pursued before “repeat cholecystectomy” is considered.5
Case Presentation
A 63-year-old man was referred to gastroenterology for recurrent episodic right upper quadrant pain. He reported intermittent both right and left upper abdominal pain that was variable in quality. At times it was associated with an empty stomach prior to meals; at other times, onset was 30 to 60 minutes after meals. The patient also reported significant flatulence and bloating and intermittent loose stools. Sixteen years before, he underwent a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. He reported that the pain he experienced before the cholecystectomy never resolved after surgery but occurred less frequently. For the next 16 years, the patient did not seek evaluation of his ongoing but infrequent symptoms until his pain became a daily occurrence. The patient’s surgical history included a remote open vagotomy and antrectomy for peptic ulcer disease, laparoscopic appendectomy, and a laparoscopic cholecystectomy for reported biliary colic.
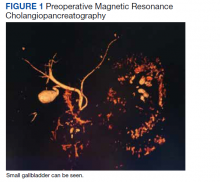
The gastroenterology evaluation included a colonoscopy and esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD); both were benign and without findings specific to identify the etiology for the patient’s pain. The patient was given a course of rifaximin 1200 mg daily for 7 days for possible bacterial overgrowth and placed on a proton pump inhibitor twice daily. Neither of these interventions helped resolve the patient’s symptoms. Further workup was pursued by gastroenterology to include a right upper quadrant ultrasound that showed a structure most consistent with a small gallbladder containing a small polyp vs stone. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) also was performed and showed the presence of a small gallbladder with a small 2-mm filling defect and an otherwise benign biliary tree. MRCP images and EGD documented a Billroth 1 reconstruction at the time of his remote antrectomy and vagotomy (Figure 1).
The patient was referred to general surgery for consideration of a repeat cholecystectomy. He confirmed the history of intermittent upper abdominal pain for the past 16 years, which was similar to the symptoms he had experienced before his original laparoscopic cholecystectomy. On examination, the patient had a body mass index of 38, had a large upper midline incision from his prior antrectomy and vagotomy procedure, and several scars presumed to be port incision scars to the right lateral abdominal wall. Hospital records were obtained from the patient’s prior workup for biliary colic and cholecystectomy 16 years before. The preoperative abdominal ultrasound examination showed a mildly distended gallbladder but was notably described as “quite limited due to patient’s body habitus and liver is not well seen.” No additional imaging was documented in his presurgical evaluation notes and imaging records.
The operative report described a gallbladder that was densely adherent to adjacent fat and omental tissue with significant adhesions secondary to the prior vagotomy and antrectomy procedure. The cystic duct and artery were dissected free at the level of their junction with the gallbladder infundibulum. The cystic artery was divided with a harmonic scalpel. Following this the gallbladder body was dissected free from the liver bed in top-down fashion. A 0 Vicryl Endoloop suture was placed over the gallbladder and secured just past the origin of the cystic duct on the gallbladder infundibulum and the cystic duct divided above this suture. No surgical clips were used, which corresponded with the lack of surgical clips seen in imaging in his recent gastroenterology workup. No documentation of an intraoperative cholangiogram existed or was considered in the operative report.
The pathology report from this first cholecystectomy procedure noted the removed specimen to be an unopened 6-cm gallbladder containing 2 small yellow stones that otherwise were benign. At the time of this patient’s re-presentation to general surgery, there was suspicion that the patient’s prior surgical procedure had not been a cholecystectomy but rather a subtotal cholecystectomy. However, after appropriate workup and review of prior records, the patient had, indeed, previously undergone cholecystectomy and represented a rare case of gallbladder duplication resulting in abdominal pain for 16 years after his index operation.
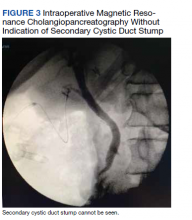
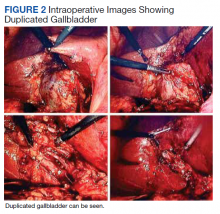
The patient was consented for repeat cholecystectomy and underwent a laparoscopic lysis of adhesions, cholecystectomy, and intraoperative cholangiogram. Significant scarring was found at the liver undersurface that would have been exposed during the original laparoscopic resection of the gallbladder from its liver bed. Deeper to this, a small saccular structure was identified as the duplicate gallbladder (Figure 2). Though the visualized gallbladder was small with a deep intrahepatic lie, the critical view of safety was achieved and was without additional variation. An intraoperative cholangiogram was performed to determine whether residual ductal stumps or other additional evidence of the previously removed gallbladder could be identified. The cholangiogram showed clear visualization of the cystic duct, common bile duct, right and left hepatic ducts, and contrast into the duodenum without abnormal variants. There was no visualized accessory or secondary cystic duct stump seen on the cholangiogram (Figure 3). Pathology of the repeat cholecystectomy specimen confirmed a 3-cm gallbladder with a distinct duct leading out of the gallbladder and the presence of several gallstones. The patient had an uneventful recovery after the repeat laparoscopic cholecystectomy with complete resolution of his upper abdominal pain.