Finding new liver lesions on imaging during a febrile illness may indicate hepatic abscesses or malignancy. These can be difficult to diagnose with imaging alone. Differentiating between infectious and neoplastic etiologies may require additional images and/or tissue samples.
Hepatic abscesses are more commonly seen with other abdominal or biliary infections while metastatic disease usually presents in patients with active cancer or on surveillance imaging. While renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common malignant neoplasm of the kidney, chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (chRCC) is a rare subtype that comprises only 5% of RCC cases.1 We present a case of a patient with numerous new liver lesions and fever, initially thought to be hepatic abscesses, who was found to have metastatic chRCC.
CASE PRESENTATION
A 53 year-old male with a history of stage 2 chRCC and right radical nephrectomy 2 years prior presented to the emergency department following 1 week of drenching night sweats, fatigue, and subjective fevers. In addition, the patient reported gradually progressive, dull, right upper-quadrant abdominal pain. He noted no other acute medical complaints at the time of presentation. His history was notable for hyperlipidemia. His only surgery was the nephrectomy 2 years earlier. The patient reported no alcohol, tobacco, or drug use, any recent travel, or pet or animal exposure. On admission, he was afebrile with normal heart rate and was normotensive. His physical examination was remarkable for hepatomegaly with right upper-quadrant abdominal tenderness to palpation with a negative Murphy sign. There were otherwise no abnormal cardiovascular, respiratory, or skin findings.
Laboratory tests during initial evaluation were notable for hemoglobin of 10.0 g/dL, white blood cell count of 16.7×103 μL, alkaline phosphatase of 213 U/L, aspartate aminotransferase of 185 U/L, and alanine aminotransferase of 36 U/L. Screening tests for viral hepatitis A, B, and C were negative. Additional tests for HIV, rapid plasma reagin, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and toxoplasma were negative. Tests for antimitochondrial, antismooth muscle, and serum antinuclear antibodies were negative.
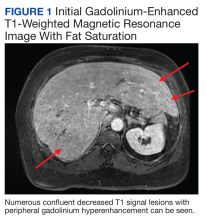
Chest X-ray did not reveal any acute cardiopulmonary process. Computed tomography with contrast of the abdomen and pelvis demonstrated numerous hypodensities within the right hepatic lobe. Right upper-quadrant ultrasound demonstrated multiple hyperechoic foci throughout the liver. confluent decreased T1 signal lesions with peripheral gadolinium hyperenhancement were evident on Gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with fat saturation demonstrated numerous (Figure 1).
Liver biopsy and tissue cultures demonstrated normal hepatic tissue and no organism growth. Blood cultures demonstrated no growth. The patient was empirically treated with IV ceftriaxone 1 g daily and metronidazole 500 mg every 8 hours for suspected hepatic abscesses after he was admitted to the hospital.
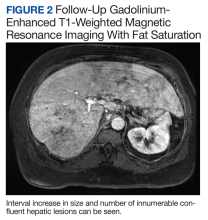
The patient’s symptoms initially improved following antibiotic treatment; however, he reported recurrence of the initial symptoms2 months later at a follow-up appointment with gastroenterology. Liver-associated enzymes also remained elevated despite 4 weeks of antibiotic treatment. Repeat gadolinium-enhanced T1 fat-saturated MRI demonstrated an interval increase in size and number of confluent hepatic lesions throughout the liver (Figure 2).
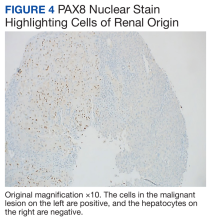
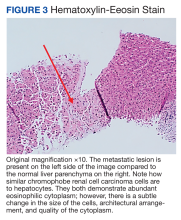
A repeat liver biopsy revealed metastatic chRCC (Figures 3 and 4) that was both morphologically and immunohistochemically similar to the first pathologic diagnosis made following nephrectomy. The first liver biopsy likely did not sample the metastatic lesions that were present but instead sampled the surrounding normal liver. The patient was initiated on lenvatinib and everolimus therapy with oncology, a recommended regimen per the National Comprehensive Cancer Network for patients with nonclear cell RCC.1