The primary objectives were to compare the incidence of AKI and persistent bacteremia and assess rates of AUC target attainment (400-600 mcg*h/mL) in the AUC-based and trough-based dosing groups. 6 Data for both groups included anthropomorphic measurements, serum creatinine, amputation status, vancomycin dosing, and infection characteristics. The X2 test was used for categorical data and the t test was used for continuous data. A 2-tailed α of 0.05 was used to determine significance. Each site sequentially reviewed all patients receiving ≥ 48 hours of intravenous vancomycin over a 3-month period and contributed up to 50 patients for each group. Due to staggered implementation, the study periods for sites spanned 2018 to 2023. A minimum 6-month washout period was observed between the trough and AUC groups at each site. Patients were excluded if pregnant, receiving renal replacement therapy, or presenting with AKI at the time of vancomycin initiation.
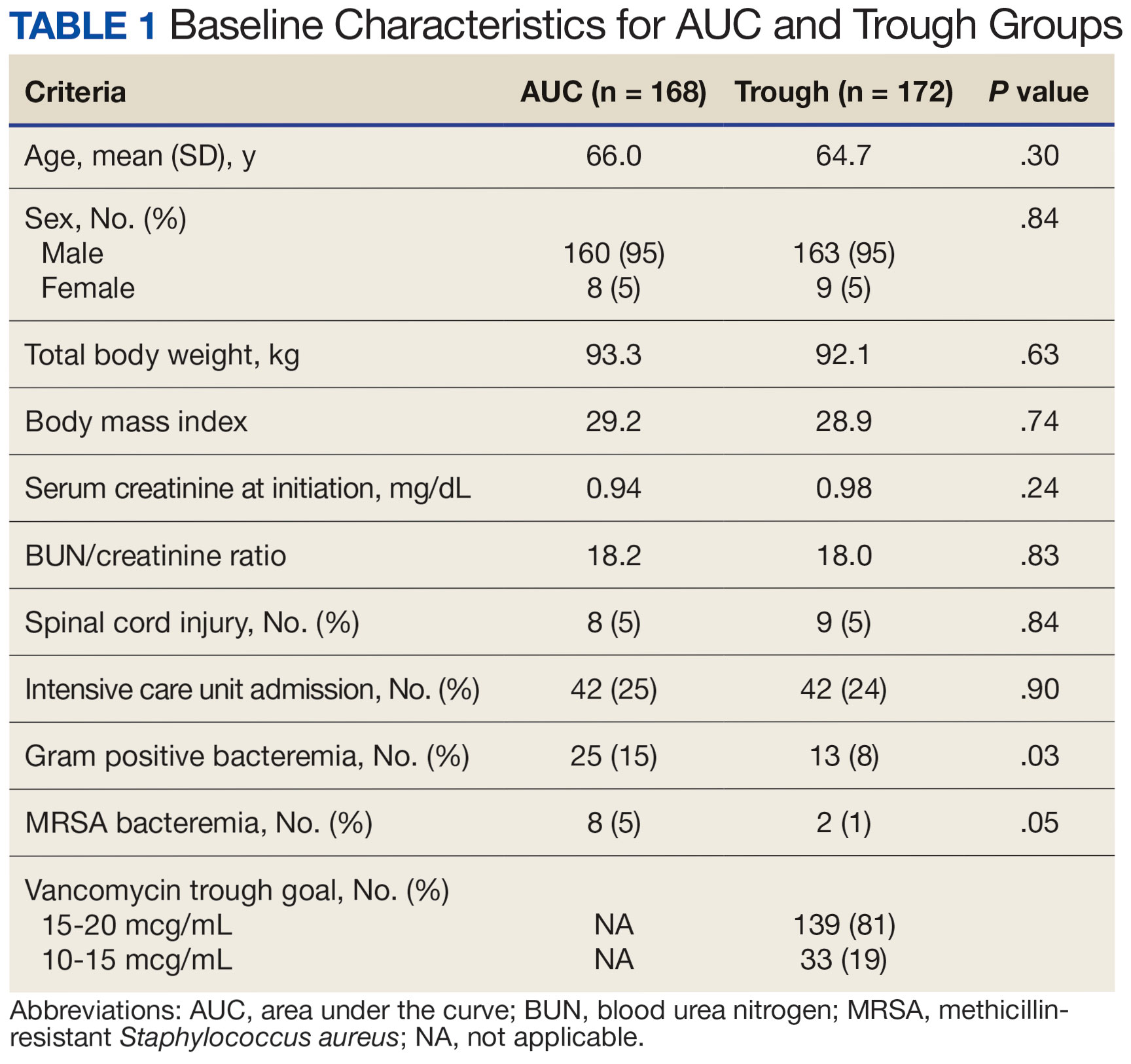
There were 168 patients in the AUC group and 172 patients in the trough group (Table 1). The rate of AUC target attainment with the initial dosing regimen varied across sites from 18% to 69% (mean, 48%). Total daily vancomycin exposure was lower in the AUC group compared with the trough group (2402 mg vs 2605 mg, respectively), with AUC-dosed patients being less likely to experience troughs level ≥ 15 or 20 mcg/mL (Table 2). There was a statistically significant lower rate of AKI in the AUC group: 2.4% in the AUC group (range, 2%-3%) vs 10.4% (range 7%-12%) in the trough group (P = .002). Rates of AKI were comparable to those observed in previous interventions. 6 There was no statistical difference in length of stay, time to blood culture clearance, or rate of persistent bacteremia in the 2 groups, but these assessments were limited by sample size.
We did not anticipate such variability in initial target attainment across sites. The multisite quality assurance design allowed for qualitative evaluation of variability in dosing practices, which likely arose from sites and individual pharmacists having some flexibility in adjusting dosing tool parameters. Further analysis revealed that the facility with low initial target attainment was not routinely utilizing vancomycin loading doses. Sites routinely use robust loading doses achieved earlier and more consistent target attainment. Some sites used a narrower AUC target range in certain clinical scenarios (eg, > 500 mcg*h/mL for septic patients and < 500 mcg*h/mL for patients with less severe infections) rather than the 400 to 550 mcg*h/mL range for all patients. Sites targeting broader AUC ranges for all patients had higher rates of target attainment. Reviewing differences among sites allowed the ASPWG to identify best practices to optimize future care.
CONCLUSIONS
VHA ASPs must meet the standards outlined in VHA Directive 1031, including the new requirement for each VISN to develop an ASP collaborative. The VISN 8 ASPWG demonstrates how ASP champions can collaborate to solve common issues, complete tasks, explore new infectious diseases concepts, and impact large veteran populations. Furthermore, ASP collaboratives can harness their collective size to complete robust quality assurance evaluations that might otherwise be underpowered if completed at a single center. A limitation of the collaborative model is that a site with a robust ASP may already have specific practices in place. Expanding the ASP collaborative model further highlights the VHA role as a nationwide leader in ASP best practices.