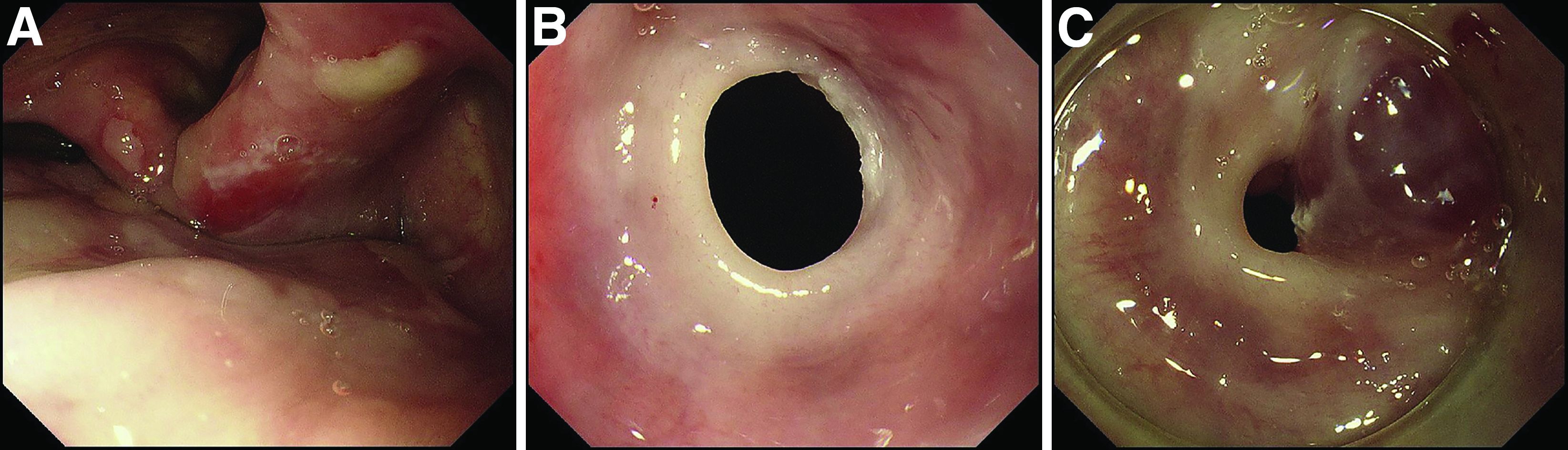
Mucous membrane pemphigoid with esophageal web stricture.
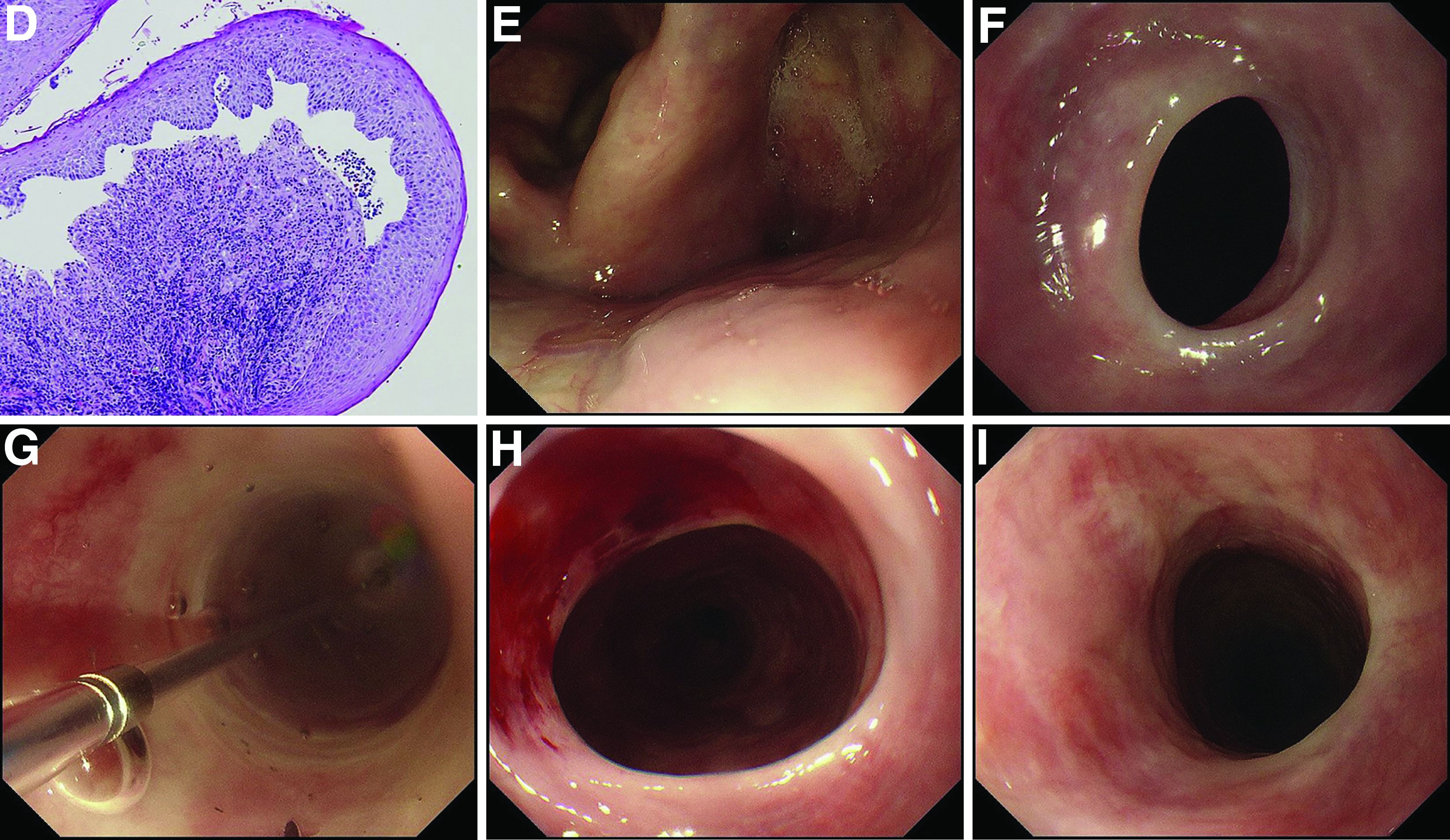
Additional laboratory examination showed that his serum anti-BP180 antibody level was high (11.7 U/mL; normal range, <9.0 U/mL). Biopsy specimens taken from the laryngopharyngeal erosion showed subepithelial blister formation and it was consistent with pemphigoid pathologically (Figure D). He did not have cutaneous lesions and was diagnosed with mucous membrane pemphigoid (MMP). After performing endoscopic dilation, prednisolone (20 mg/d) was administered orally. Three months after starting the prednisolone treatment, follow-up endoscopy showed improvements of the laryngopharyngeal erosions (Figure E) and esophageal blister on the web. However, esophageal narrowing remained, and thus endoscopic balloon dilation was performed (Figure F-H). Three months after the dilation, the narrowing improved (Figure I).
MMP is an autoimmune blistering disease that induces the formation of mucous membrane subepithelial bullae. Basement membrane zone components such as collagen XVII (also known as BP180) are targets of autoantibodies in MMP. Symptomatic esophageal involvement affects 5.4% of patients with MMP and dysphagia is the most frequent symptom. 1 Endoscopic findings include erosion, web stricture, subepithelial hematomas, and scars. 2,3 Endoscopic dilation is sometimes necessary for the treatment of severe esophageal strictures. 1
References
1. Zehou O et al. Br J Dermatol. 2017 Oct;177(4):1074-85.
2. Sallout H et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000 Sep;52(3):429-33.
3. Gaspar R et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017 Aug;86(2):400-2.