Gastroenterology and Climate Change: Assessing and Mitigating Impacts
Associate Professor
Department of Medicine
Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology
West Virginia University
Morgantown, WV
Slideshow below.
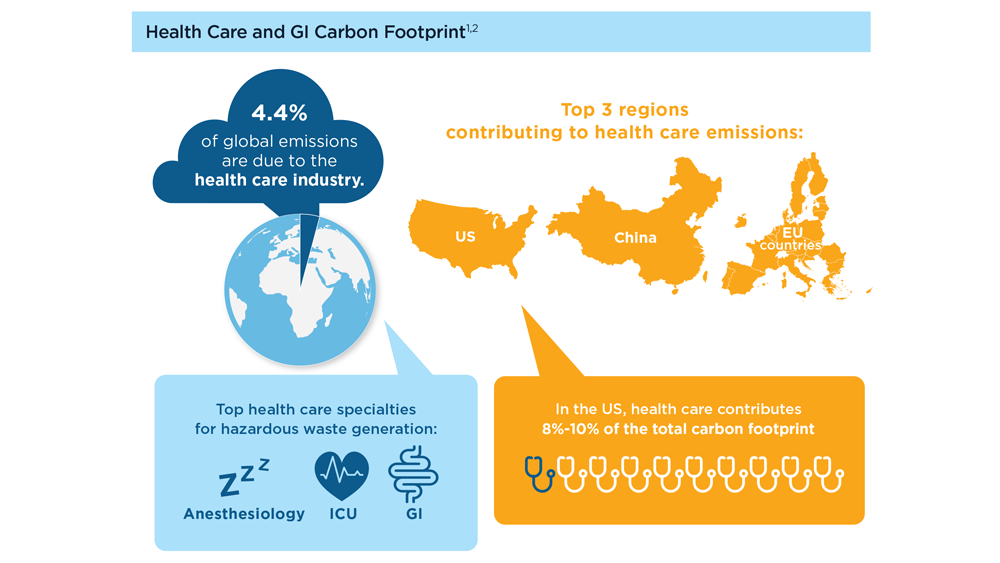
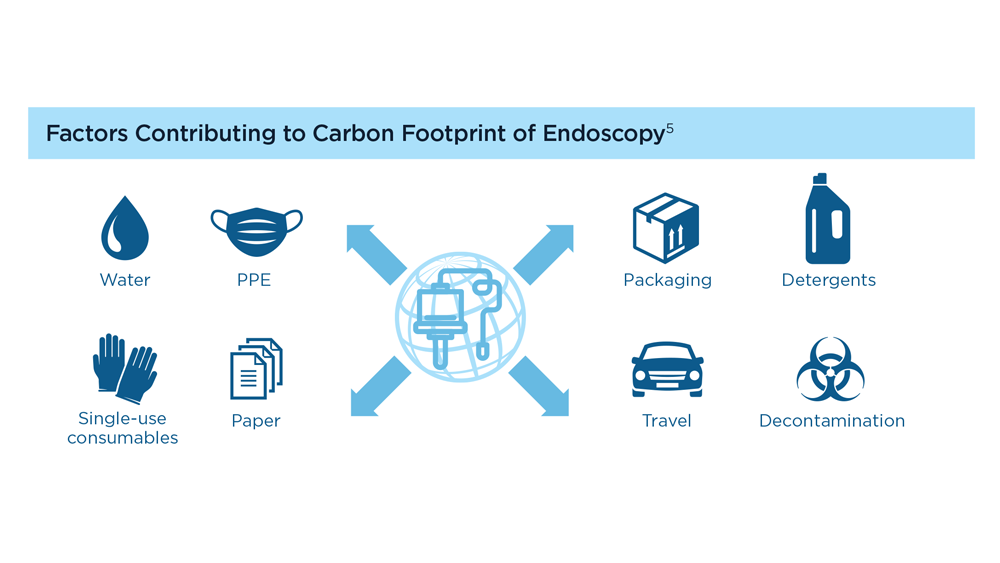
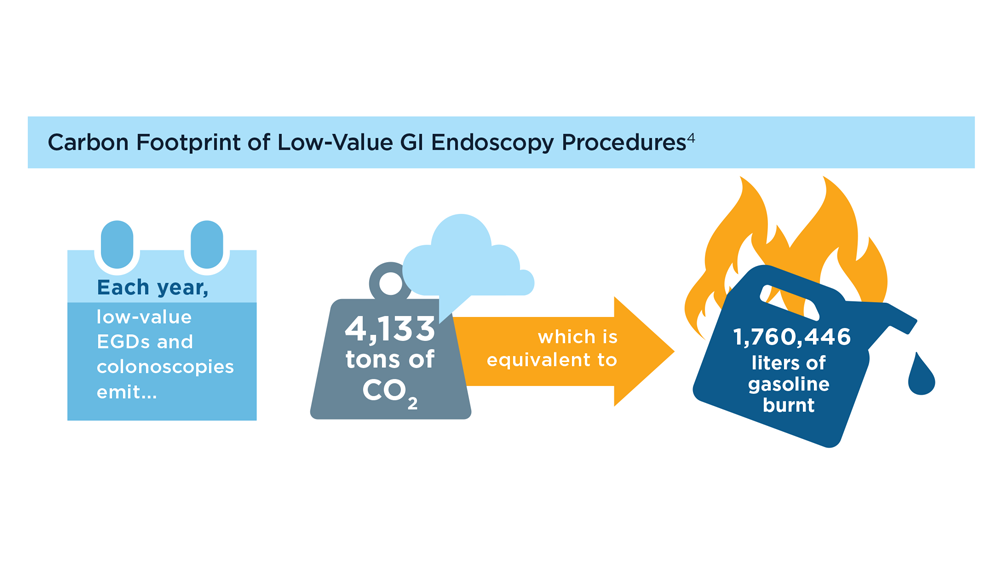
The health care industry, particularly in the United States, is a large contributor to climate change, with the field of GI being one of the top contributors to overall and hazardous waste emissions.1,2 One of the most important components of the carbon footprint of GI is the sheer volume of procedures performed. More than 18 million endoscopic procedures are performed each year in the US alone, and a significant portion are of low-value.3,4 Every endoscopic procedure uses substantial resources, including single-use consumables, water (including sterile water bottles), electricity, paper, and personal protective equipment (PPE), among others.5-7 Within the field of endoscopy, disposable endoscopes are an important area of concern; a complete switch to disposables could increase waste by up to 40%.8 Along with the impact of GI on climate change, there is also a bidirectional effect—climate change affects GI and liver health, worsening symptoms for many.9-11
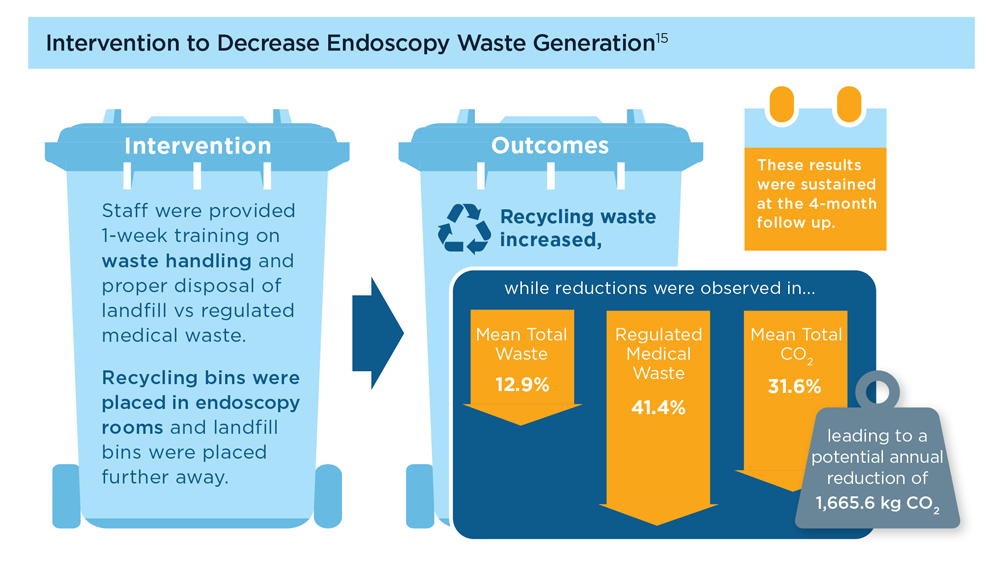
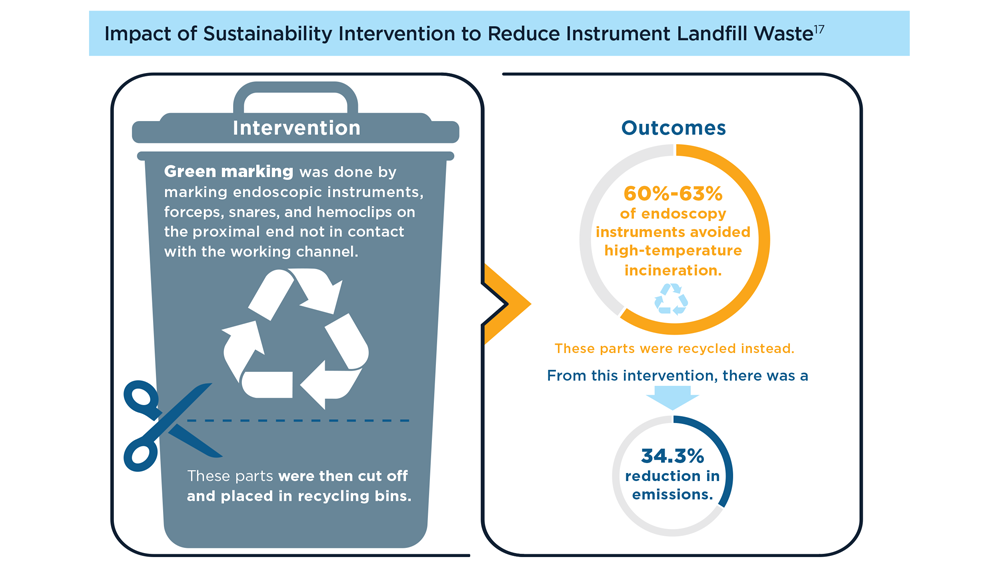
To combat the contribution of GI to climate change, a GI multisociety task force was formed comprising members from 4 major US societies, including the AGA.12 A strategic plan was proposed to decrease the carbon footprint of GI, similar to a plan proposed by European and British societies.13,14 Multiple recent studies have shown positive effects of interventions such as waste segregation in reducing overall endoscopic waste and increasing recycled waste.15 Such measures also have been shown to have financial benefits, with estimated cost savings of around $5.4 billion dollars in 5 years.16
1
More Endoscopy News
- Liquid Fasting Mitigates Negative Pre-Surgery Impact of Semaglutide
- GLP-1 RAs Safe in the Perioperative Period: New Guidance
- AI-Assisted Colonoscopy Linked to Higher Rate of Benign Lesion Removal
- Short-Course Vasoconstrictors After EVL: Time for a New Standard of Care?
- Weight Loss Surgery, Obesity Drugs Achieve Similar Results but Have Different Safety Profiles
- Medical, Endoscopic, and Surgical Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- Low-Volume Bowel Prep Easier, as Effective as Standard Prep in Hospitalized Patients
- AI Tool Helps Detect, Differentiate Pancreatic Lesions During Endoscopic Ultrasound
USMSTF Recommendations: When to surgically manage colorectal polyps