Click here to view more from Gastroenterology Data Trends 2024
Role of Non-invasive Biomarkers in the Evaluation and Management of MASLD
Julia J. Wattacheril, MD, MPH
Associate Professor
Department of Medicine
Director, MASLD Program
Division of Digestive and Liver Disease
Center for Liver Disease and Transplantation
Columbia University Irving Medical Center
New York Presbyterian Hospital
New York, New York
Disclosures:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for:
AlphaSights, GlaxoSmithKline
Received research grant from: Galectin Therapeutics; Intercept Pharmaceuticals; AMRA Medical

Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), previously known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD),1 refers to a range of liver conditions characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver due to metabolic factors. MASLD affects nearly 30% of the global population and is a prevalent cause of advanced liver disease.2 This disease can progress from simple steatosis to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), which involves inflammation and liver cell damage—and unmitigated can lead to liver cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer.
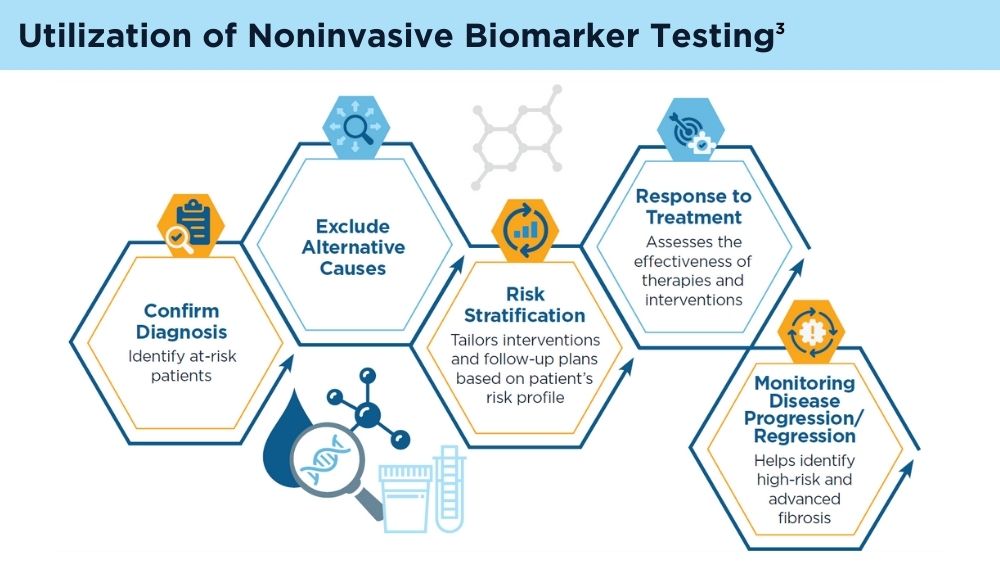
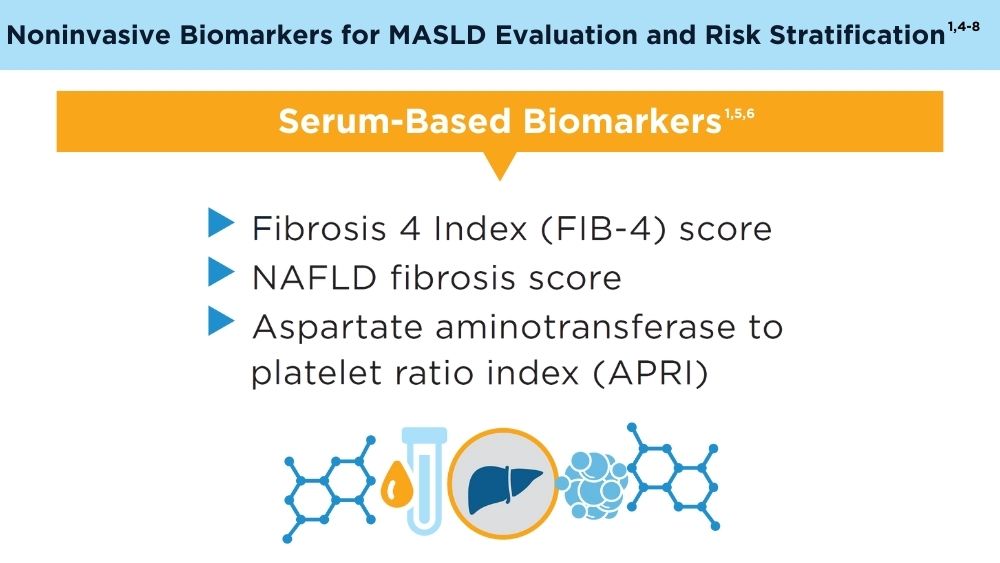
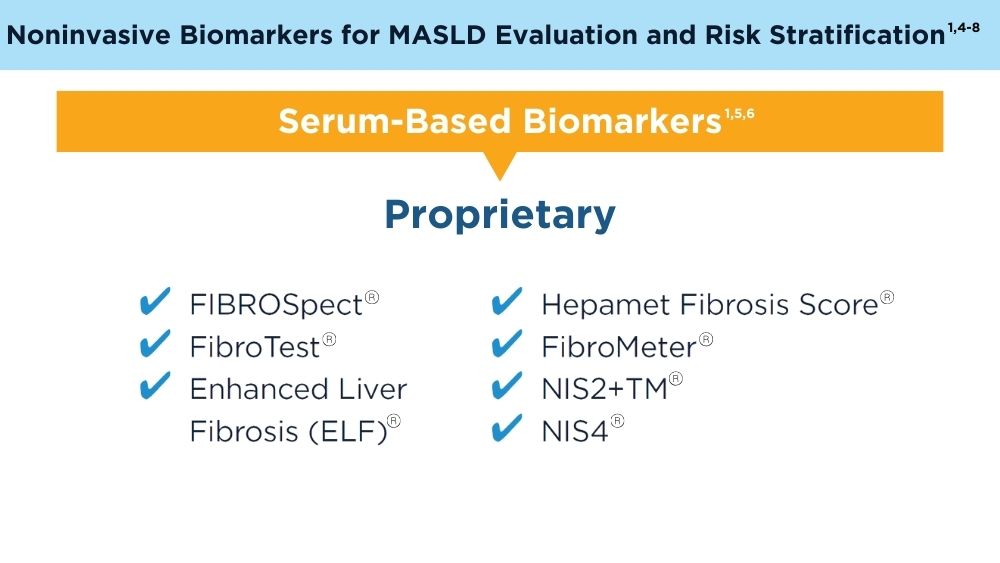
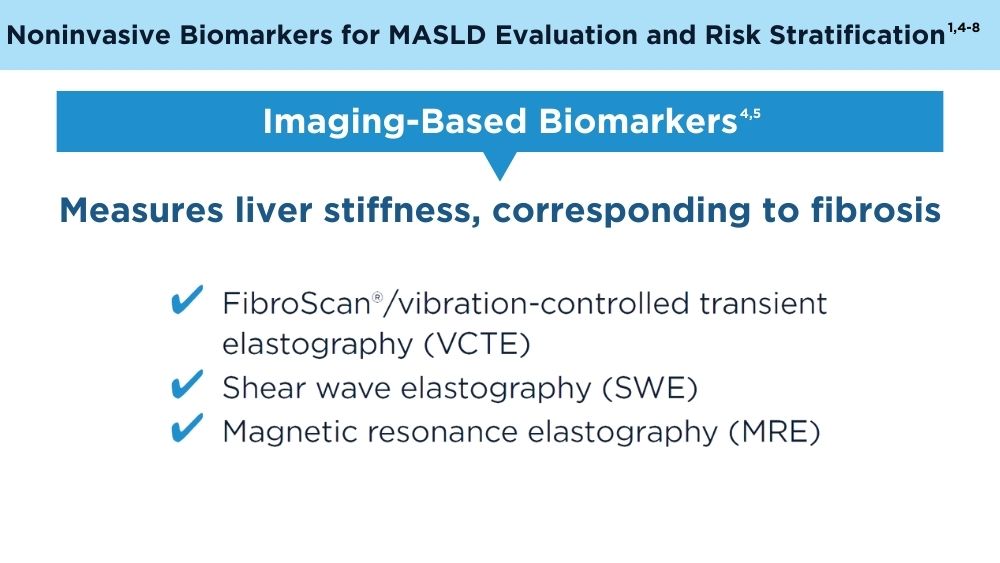
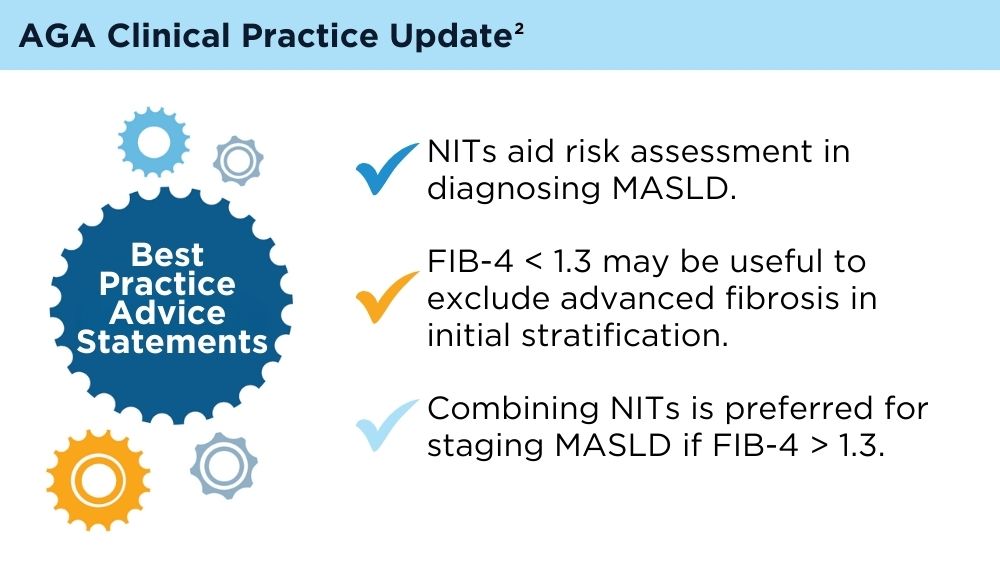
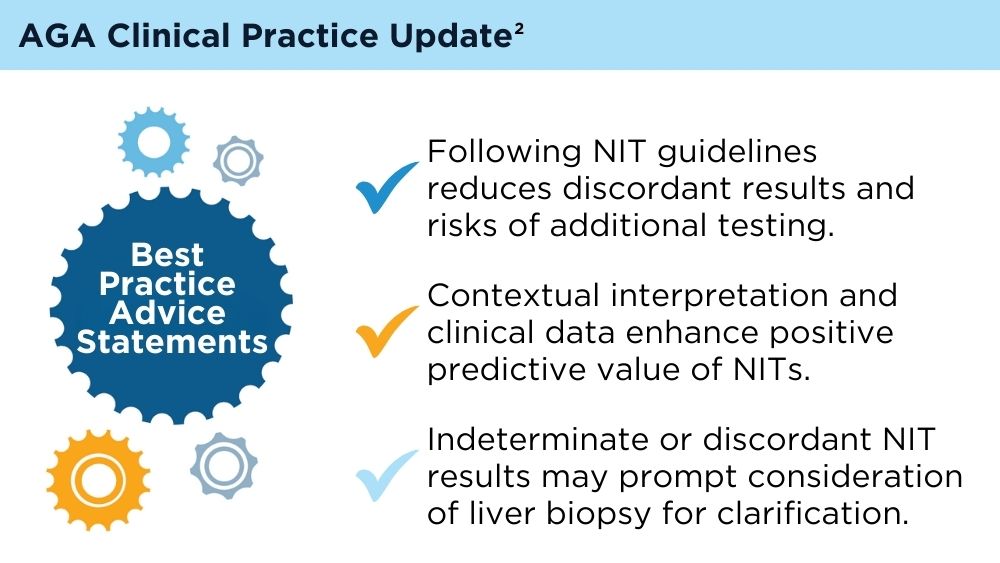
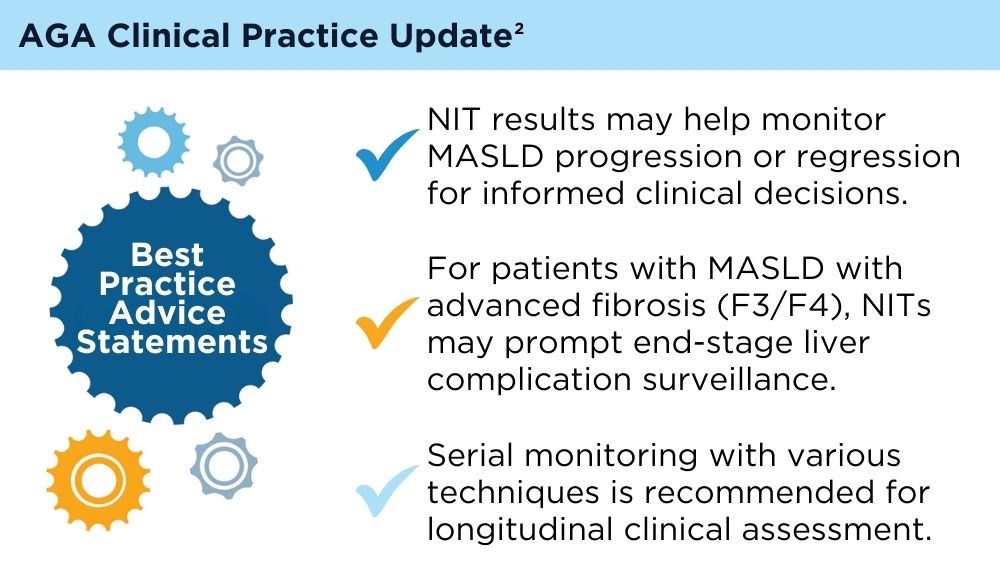
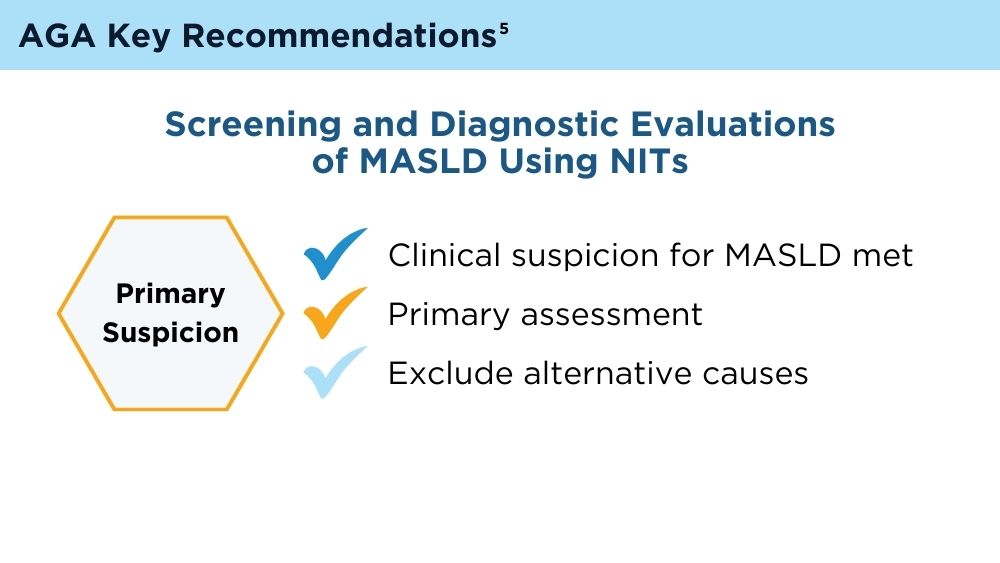
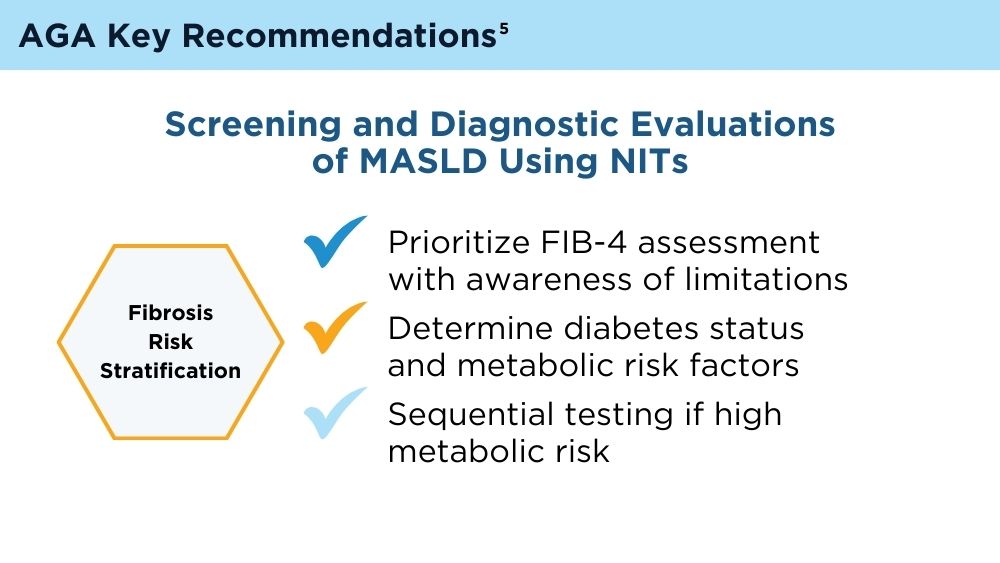
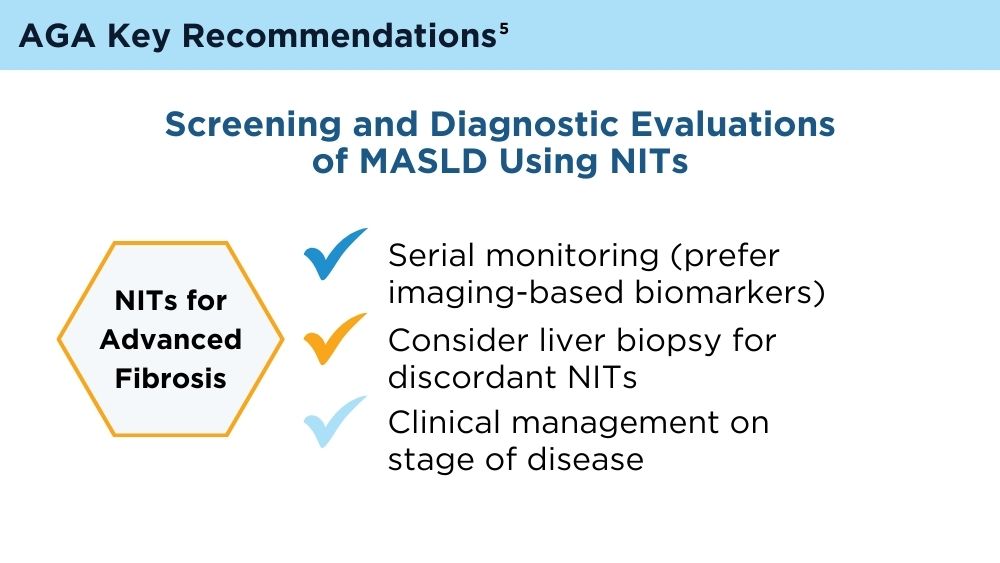
Clinicians' early identification and stratification of at-risk individuals may impact progression and regression, as only a minority of individuals with MASLD present with liver-related consequences.2 Although early identification and risk stratification may occur in gastroenterology and hepatology clinics, disease modifying interventions may occur outside of those settings. Continuously monitoring MASLD response to current treatments is also key. Histologic examination of the liver is the current established standard for assessing and monitoring this disease, grading necroinflammation, and staging hepatic fibrosis; however, the cost and invasiveness limit its routine and widespread use.2 Drug approvals independent of histology-based outcomes lay the groundwork for further standardization and validation of noninvasive tests (NITs) in the evaluation and management of MASLD. The latest AGA Clinical Practice Update (2023) can help healthcare professionals use NITs to identify patients who are at higher risk for MASLD progression for directed intervention.2 Ongoing research continues to refine the use of NITs in evaluating and managing MASLD; therefore, the landscape is likely to evolve and advance over time.
1
More Liver Disease News
- Short-Course Vasoconstrictors After EVL: Time for a New Standard of Care?
- MASH: Experts Offer Noninvasive Cutoffs for Prescribing Resmetirom
- Can We Repurpose Obesity Drugs to Reverse Liver Disease?
- Giving the Smallest GI Transplant Patients a New Lease On Life
- MASLD Healthcare Costs Climbing Fast in Canada
- AI-Assisted Pathology Poised to Transform Liver Disease Care
- Baveno VI Criteria Appear Cost-Effective for Detecting Varices in Cirrhosis
- Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease’s Changing Demographics
Liver Cirrhosis