Lifestyle Modifications
Recommended lifestyle modifications include weight loss for patients with obesity, stress reduction, tobacco and alcohol cessation, elevating the head of the bed, staying upright during and after meals, avoidance of food intake < 3 hours before bedtime, and cessation of foods that potentially aggravate reflux symptoms such as coffee, chocolate, carbonated beverages, spicy foods, acidic foods, and foods with high fat content.6,8
Medications
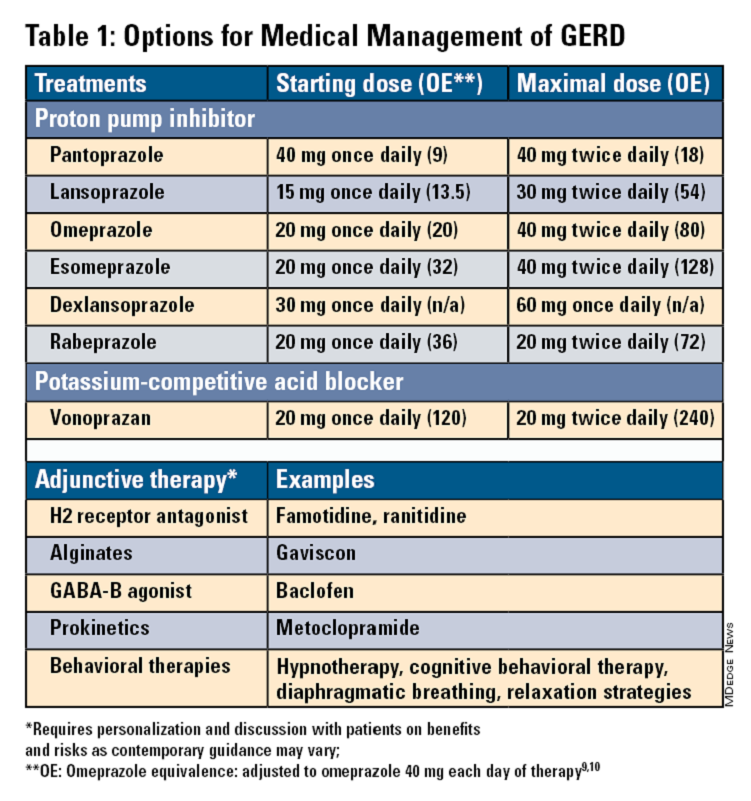
Pharmacologic therapy for GERD includes medications that primarily aim to neutralize or reduce gastric acid -- we summarize options in Table 1.3,8
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Most guidelines suggest a trial of 4-8 weeks of once-daily enteric-coated PPI before meals in patients with typical GERD symptoms and no alarm symptoms. Escalation to double-dose PPI may be considered in the case of persistent symptoms. The relative potencies of standard-dose pantoprazole, lansoprazole, esomeprazole, and rabeprazole are presented in Table 1.9 When a PPI switch is needed, rabeprazole may be considered as it is a PPI that does not rely on CYP2C19 for primary metabolism.9
Acid suppression should be weaned down to the lowest effective dose or converted to H2RAs or other antacids once symptoms are sufficiently controlled unless patients have EE, Barrett’s esophagus, or peptic stricture.3 Patients with severe GERD may require long-term PPI therapy or an invasive anti-reflux procedure.
Recent studies have shown that potassium-competitive acid blockers (PCAB) like vonoprazan may offer more effective gastric acid inhibition. While not included in the latest clinical practice update, vonoprazan is thought to be superior to lansoprazole for those with LA Grade C/D esophagitis for both symptom relief and healing at 2 weeks.10
Adjunctive Therapies
Alginates can function as a physical barrier to even neutral reflux and may be helpful for patients with postprandial or nighttime symptoms as well as those with hiatal hernia.3 H2RAs can also help mitigate nighttime symptoms.3 Baclofen is a gamma-aminobutyric acid–B agonist which inhibits transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation (TLESR) and may be effective for patients with belching.3 Prokinetics may be helpful for GERD with concomitant gastroparesis.3 Sucralfate is a mucosal protective agent, but there is a lack of data supporting its efficacy in GERD treatment. Consider referral to a behavioral therapist for supplemental therapies, hypnotherapy, cognitive-behavior therapy, diaphragmatic breathing, and relaxation strategies for functional heartburn or reflux-associated esophageal hypervigilance or reflux hypersensitivity.3
When to Refer to Higher Level of Care
For patients who do not wish to remain on longer-term pharmacologic therapy or would benefit from anatomic repair, clinicians should have a discussion of risks and benefits prior to consideration of referral for anti-reflux procedures.3,6,8 We advise this conversation should include review of patient health status, postsurgical side effects such as increased flatus, bloating and dysphagia as well as the potential need to still resume PPI post operation.8
Endoscopic Management
Patient Selection And Evaluation
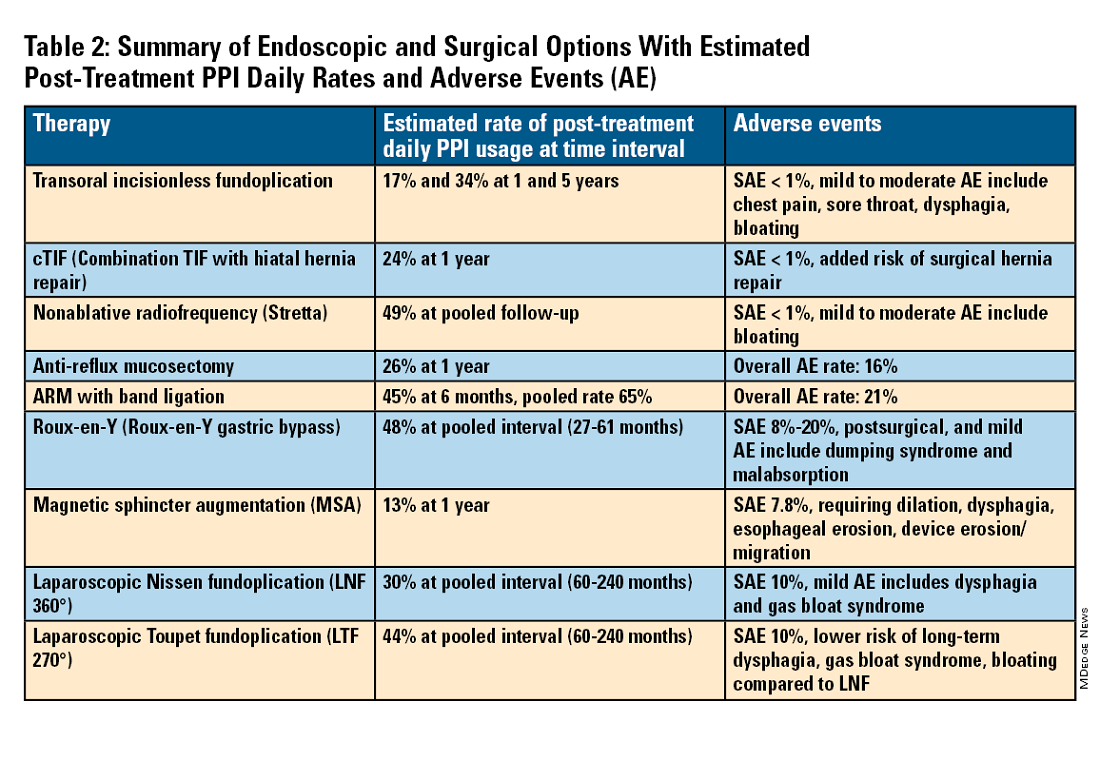
For the groups indicated for a higher level of care, we agree with AGA recommendations, multi-society guidelines, and expert review,3,7,11,12 and highlight potential options in Table 2. Step-up options should be based on patient characteristics and reviewed carefully with patients. Endoscopic therapies are less invasive than surgery and may be considered for those who do not require anatomic repair of hiatal hernia, do not want surgery, or are not suitable for surgery.
The pathophysiology of GERD is from a loss of the anti-reflux barrier of the esophageal gastric junction (EGJ) at the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) leading to unintended retrograde movement of gastric contents.6 Anatomically, the LES is composed of muscles of the distal esophagus and sling fibers of the proximal stomach, the “external valve” from the diaphragmatic crura, and the “internal valve” from the gastroesophageal flap valve (GEFV). GERD occurs from mechanical failure of the LES. First, there may be disproportional dilation of the diaphragmatic crura as categorized by Hill Grade of the GEFV as seen by a retroflexed view of EGJ after 30-45 seconds of insufflation.13 Second, there may be a migration of the LES away from the diaphragmatic crura as in the case of a hiatal hernia. Provocative maneuvers may reveal a sliding hernia by gentle retraction of the endoscope while under retroflexed view.13 Third, there may be more frequent TLESR associated with GERD.12
The aim of most interventions is to restore competency of the LES by reconstruction of the GEFV via suture or staple-based approximation of tissue.11,12 Intraluminal therapy may only target the GEFV at the internal valve. Therefore, most endoscopic interventions are limited to patients with intact diaphragmatic crura (ie, small to no hiatal hernia and GEFV Hill Grade 1 to 2). Contraindications for endoscopic therapy are moderate to severe reflux (ie, LA Grade C/ D), hiatus hernia 2 cm or larger, strictures, or long-segment Barrett’s esophagus.
Utility, Safety, and Outcomes of TIF
Historically, endoscopic therapy targeting endoscopic fundoplication started with EndoLuminal gastro-gastric fundoplication (ELF, 2005) which was a proof of concept of safe manipulation and suture for gastro-gastric plication to below the Z-line. Transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) 1.0 was suggested in 2007 for clinical application by proposing a longitudinal oriented esophago-gastric plication 1 cm above the Z-line.
In 2009, TIF2.0 was proposed as a rotational 270° wrap of the cardia and fundus to a full-thickness esophago-gastric fundoplication around 2-4 cm of the distal esophagus. Like a surgical fundoplication, this reinforces sling fibers, increases the Angle of His and improves the cardiac notch. TIF 2.0 is indicated for those with small (< 2 cm) or no hiatal hernia and a GEFV Hill Grade 1 or 2. The present iteration of TIF2.0 uses EsophyX-Z (EndoGastric Solutions; Redmond, Washington) which features dual fastener deployment and a simplified firing mechanism. Plication is secured via nonresorbable polypropylene T-fasteners with strength equivalence of 3-0 sutures.
Compared with the original, TIF2.0 represents a decrease of severe adverse events from 2%-2.5% to 0.4%-1%.11,14 Based on longitudinal TEMPO data, patient satisfaction ranges between 70% and 90% and rates of patients reverting to daily PPI use are 17% and 34% at 1 and 5 years. A 5% reintervention rate was noted to be comparable with surgical reoperation for fundoplication.15 One retrospective evaluation of patients with failed TIF followed by successful cTIF noted that in all failures there was a documented underestimation of a much larger crura defect at time of index procedure.16 Chest pain is common post procedure and patients and collaborating providers should be counseled on the expected course. In our practice, we admit patients for at least 1 postprocedure day and consider scheduling symptom control medications for those with significant pain.