User login
Does XR injectable naltrexone prevent relapse as effectively as daily sublingual buprenorphine-naloxone?
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
Two recent multicenter, open-label RCTs, 1 in the United States and 1 in Norway, compared monthly XR-NTX with daily BUP-NX.1,2 Both studies evaluated effectiveness (defined by either the number of people who relapsed or self-reported opioid use), cravings, and safety (defined as the absence of serious adverse events such as medically complex withdrawal or fatal overdose).
The participant populations were similar in both mean age and mean age of onset of opioid use. Duration of opioid use was reported differently (total duration or years of heavy heroin or other opioid use) and couldn’t be compared directly.
Naltrexone and buprenorphine-naloxone are similarly effective
The US study enrolled 570 opioid-dependent participants in a 24-week comparative effectiveness trial.1 The 8 study sites were community treatment programs, and the participants were recruited during voluntary inpatient detoxification admissions. Some participants were randomized while on methadone or buprenorphine tapers and some after complete detoxification.
The intention-to-treat analysis included 283 patients in the XR-NTX group and 287 in the BUP-NX group. At 24 weeks, the number of participants who’d had a relapse event (self-reported use or positive urine drug test for nonstudy opioids or refusal to provide a urine sample) was 185 (65%) for XR-NTX compared with 163 (57%) for BUP-NX (odds ratio [OR] = 1.44, 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02 to 2.01; P = .036).
The 12-week Norwegian noninferiority trial enrolled 159 participants.2 In contrast to the US study, all participants were required to complete inpatient detoxification before randomization and induction onto the study medication.
Patients on BUP-NX reported 3.6 more days of heroin use within the previous 28 days than patients in the XR-NTX group (95% CI, 1.2 to 6; P = .003). For other illicit opioids, self-reported use was 2.4 days greater in the BUP-NX group (95% CI, −0.1 to 4.9; P = .06). Retention with XR-NTX was noninferior to BUP-NX (mean days in therapy [standard deviation], 69.3 [25.9] and 63.7 [29.9]; P = .33).
Randomizing after complete detox reduces induction failures
Naltrexone, a full opioid antagonist, precipitates withdrawal when a full or partial opioid agonist is engaging the opioid receptor. For this reason, an opioid-free interval of 7 to 10 days is generally recommended before initiating naltrexone, raising the risk for relapse during the induction process.
Continue to: The Norwegian trial...
The Norwegian trial randomized participants after detoxification. The US trial, in which some participants were randomized before completing detoxification, reported 79 (28%) induction failures for XR-NTX and 17 (6%) for BUP-NX.1 As a result, a per protocol analysis was completed with the 204 patients on XR-NTX and 270 patients on BUP-NX who were successfully inducted onto a study medication. The 24-week relapse rate was 52% (106) for XR-NTX and 56% (150) for BUP-NX (OR = 0.87; 95% CI, 0.60 to 1.25; P = .44).
Cravings, adverse events, and cost considerations
Patients reported cravings using a visual analog scale. At 12 weeks in both studies, the XR-NTX groups reported fewer cravings than the BUP-NX groups, although by the end of the 24-week US trial, no statistically significant difference in cravings was found between the 2 groups.1,2
The Norwegian trial found a difference between the XR-NTX and the BUP-NX groups in the percentage of nonserious adverse events such as nausea or chills (60.6% in the XR-NTX group vs 30.6% in the BUP-NX group; P < .001), and the US trial found a difference in total number of overdoses (64% of the total overdoses were in the XR-NTX group). Neither trial, however, reported a statistically significant difference in serious adverse events or fatal overdoses between the 2 groups.1,2
The price for naltrexone is $1665.06 per monthly injection.3 The price for buprenorphine-naloxone varies depending on dose and formulation, with a general range of $527 to $600 per month at 16 mg/d.4
Editor’s takeaway
Two higher-quality RCTs show similar but imperfect effectiveness for both XR-NTX and daily sublingual BUP-NX. Injectable naltrexone’s higher cost may influence medication choice.
1. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391:309-318.
2. Tanum L, Solli KK, Latif ZE, et al. Effectiveness of injectable extended-release naltrexone vs daily buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid dependence: a randomized clinical noninferiority trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74:1197-1205.
3. Naltrexone: drug information. Lexi-Comp, Inc (Lexi-Drugs). Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. Riverwoods, IL. http://online.lexi.com. Accessed November 20, 2020.
4. Buprenorphine and naloxone: drug information. Lexi-Comp, Inc (Lexi-Drugs). Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. Riverwoods, IL. http://online.lexi.com. Accessed November 20, 2020.
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
Two recent multicenter, open-label RCTs, 1 in the United States and 1 in Norway, compared monthly XR-NTX with daily BUP-NX.1,2 Both studies evaluated effectiveness (defined by either the number of people who relapsed or self-reported opioid use), cravings, and safety (defined as the absence of serious adverse events such as medically complex withdrawal or fatal overdose).
The participant populations were similar in both mean age and mean age of onset of opioid use. Duration of opioid use was reported differently (total duration or years of heavy heroin or other opioid use) and couldn’t be compared directly.
Naltrexone and buprenorphine-naloxone are similarly effective
The US study enrolled 570 opioid-dependent participants in a 24-week comparative effectiveness trial.1 The 8 study sites were community treatment programs, and the participants were recruited during voluntary inpatient detoxification admissions. Some participants were randomized while on methadone or buprenorphine tapers and some after complete detoxification.
The intention-to-treat analysis included 283 patients in the XR-NTX group and 287 in the BUP-NX group. At 24 weeks, the number of participants who’d had a relapse event (self-reported use or positive urine drug test for nonstudy opioids or refusal to provide a urine sample) was 185 (65%) for XR-NTX compared with 163 (57%) for BUP-NX (odds ratio [OR] = 1.44, 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02 to 2.01; P = .036).
The 12-week Norwegian noninferiority trial enrolled 159 participants.2 In contrast to the US study, all participants were required to complete inpatient detoxification before randomization and induction onto the study medication.
Patients on BUP-NX reported 3.6 more days of heroin use within the previous 28 days than patients in the XR-NTX group (95% CI, 1.2 to 6; P = .003). For other illicit opioids, self-reported use was 2.4 days greater in the BUP-NX group (95% CI, −0.1 to 4.9; P = .06). Retention with XR-NTX was noninferior to BUP-NX (mean days in therapy [standard deviation], 69.3 [25.9] and 63.7 [29.9]; P = .33).
Randomizing after complete detox reduces induction failures
Naltrexone, a full opioid antagonist, precipitates withdrawal when a full or partial opioid agonist is engaging the opioid receptor. For this reason, an opioid-free interval of 7 to 10 days is generally recommended before initiating naltrexone, raising the risk for relapse during the induction process.
Continue to: The Norwegian trial...
The Norwegian trial randomized participants after detoxification. The US trial, in which some participants were randomized before completing detoxification, reported 79 (28%) induction failures for XR-NTX and 17 (6%) for BUP-NX.1 As a result, a per protocol analysis was completed with the 204 patients on XR-NTX and 270 patients on BUP-NX who were successfully inducted onto a study medication. The 24-week relapse rate was 52% (106) for XR-NTX and 56% (150) for BUP-NX (OR = 0.87; 95% CI, 0.60 to 1.25; P = .44).
Cravings, adverse events, and cost considerations
Patients reported cravings using a visual analog scale. At 12 weeks in both studies, the XR-NTX groups reported fewer cravings than the BUP-NX groups, although by the end of the 24-week US trial, no statistically significant difference in cravings was found between the 2 groups.1,2
The Norwegian trial found a difference between the XR-NTX and the BUP-NX groups in the percentage of nonserious adverse events such as nausea or chills (60.6% in the XR-NTX group vs 30.6% in the BUP-NX group; P < .001), and the US trial found a difference in total number of overdoses (64% of the total overdoses were in the XR-NTX group). Neither trial, however, reported a statistically significant difference in serious adverse events or fatal overdoses between the 2 groups.1,2
The price for naltrexone is $1665.06 per monthly injection.3 The price for buprenorphine-naloxone varies depending on dose and formulation, with a general range of $527 to $600 per month at 16 mg/d.4
Editor’s takeaway
Two higher-quality RCTs show similar but imperfect effectiveness for both XR-NTX and daily sublingual BUP-NX. Injectable naltrexone’s higher cost may influence medication choice.
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
Two recent multicenter, open-label RCTs, 1 in the United States and 1 in Norway, compared monthly XR-NTX with daily BUP-NX.1,2 Both studies evaluated effectiveness (defined by either the number of people who relapsed or self-reported opioid use), cravings, and safety (defined as the absence of serious adverse events such as medically complex withdrawal or fatal overdose).
The participant populations were similar in both mean age and mean age of onset of opioid use. Duration of opioid use was reported differently (total duration or years of heavy heroin or other opioid use) and couldn’t be compared directly.
Naltrexone and buprenorphine-naloxone are similarly effective
The US study enrolled 570 opioid-dependent participants in a 24-week comparative effectiveness trial.1 The 8 study sites were community treatment programs, and the participants were recruited during voluntary inpatient detoxification admissions. Some participants were randomized while on methadone or buprenorphine tapers and some after complete detoxification.
The intention-to-treat analysis included 283 patients in the XR-NTX group and 287 in the BUP-NX group. At 24 weeks, the number of participants who’d had a relapse event (self-reported use or positive urine drug test for nonstudy opioids or refusal to provide a urine sample) was 185 (65%) for XR-NTX compared with 163 (57%) for BUP-NX (odds ratio [OR] = 1.44, 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02 to 2.01; P = .036).
The 12-week Norwegian noninferiority trial enrolled 159 participants.2 In contrast to the US study, all participants were required to complete inpatient detoxification before randomization and induction onto the study medication.
Patients on BUP-NX reported 3.6 more days of heroin use within the previous 28 days than patients in the XR-NTX group (95% CI, 1.2 to 6; P = .003). For other illicit opioids, self-reported use was 2.4 days greater in the BUP-NX group (95% CI, −0.1 to 4.9; P = .06). Retention with XR-NTX was noninferior to BUP-NX (mean days in therapy [standard deviation], 69.3 [25.9] and 63.7 [29.9]; P = .33).
Randomizing after complete detox reduces induction failures
Naltrexone, a full opioid antagonist, precipitates withdrawal when a full or partial opioid agonist is engaging the opioid receptor. For this reason, an opioid-free interval of 7 to 10 days is generally recommended before initiating naltrexone, raising the risk for relapse during the induction process.
Continue to: The Norwegian trial...
The Norwegian trial randomized participants after detoxification. The US trial, in which some participants were randomized before completing detoxification, reported 79 (28%) induction failures for XR-NTX and 17 (6%) for BUP-NX.1 As a result, a per protocol analysis was completed with the 204 patients on XR-NTX and 270 patients on BUP-NX who were successfully inducted onto a study medication. The 24-week relapse rate was 52% (106) for XR-NTX and 56% (150) for BUP-NX (OR = 0.87; 95% CI, 0.60 to 1.25; P = .44).
Cravings, adverse events, and cost considerations
Patients reported cravings using a visual analog scale. At 12 weeks in both studies, the XR-NTX groups reported fewer cravings than the BUP-NX groups, although by the end of the 24-week US trial, no statistically significant difference in cravings was found between the 2 groups.1,2
The Norwegian trial found a difference between the XR-NTX and the BUP-NX groups in the percentage of nonserious adverse events such as nausea or chills (60.6% in the XR-NTX group vs 30.6% in the BUP-NX group; P < .001), and the US trial found a difference in total number of overdoses (64% of the total overdoses were in the XR-NTX group). Neither trial, however, reported a statistically significant difference in serious adverse events or fatal overdoses between the 2 groups.1,2
The price for naltrexone is $1665.06 per monthly injection.3 The price for buprenorphine-naloxone varies depending on dose and formulation, with a general range of $527 to $600 per month at 16 mg/d.4
Editor’s takeaway
Two higher-quality RCTs show similar but imperfect effectiveness for both XR-NTX and daily sublingual BUP-NX. Injectable naltrexone’s higher cost may influence medication choice.
1. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391:309-318.
2. Tanum L, Solli KK, Latif ZE, et al. Effectiveness of injectable extended-release naltrexone vs daily buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid dependence: a randomized clinical noninferiority trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74:1197-1205.
3. Naltrexone: drug information. Lexi-Comp, Inc (Lexi-Drugs). Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. Riverwoods, IL. http://online.lexi.com. Accessed November 20, 2020.
4. Buprenorphine and naloxone: drug information. Lexi-Comp, Inc (Lexi-Drugs). Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. Riverwoods, IL. http://online.lexi.com. Accessed November 20, 2020.
1. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391:309-318.
2. Tanum L, Solli KK, Latif ZE, et al. Effectiveness of injectable extended-release naltrexone vs daily buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid dependence: a randomized clinical noninferiority trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74:1197-1205.
3. Naltrexone: drug information. Lexi-Comp, Inc (Lexi-Drugs). Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. Riverwoods, IL. http://online.lexi.com. Accessed November 20, 2020.
4. Buprenorphine and naloxone: drug information. Lexi-Comp, Inc (Lexi-Drugs). Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. Riverwoods, IL. http://online.lexi.com. Accessed November 20, 2020.
EVIDENCE-BASED ANSWER:
Yes. Monthly extended-release injectable naltrexone (XR-NTX) treats opioid use disorder as effectively as daily sublingual buprenorphine-naloxone (BUP-NX) without causing any increase in serious adverse events or fatal overdoses. (strength of recommendation: A, 2 good-quality RCTs).
Which oral nonopioid agents are most effective for OA pain?
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
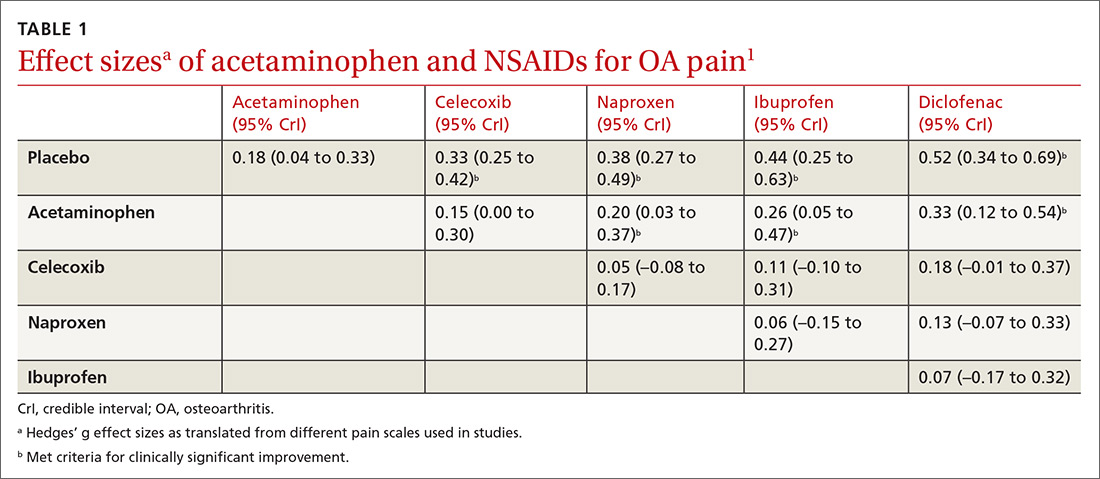
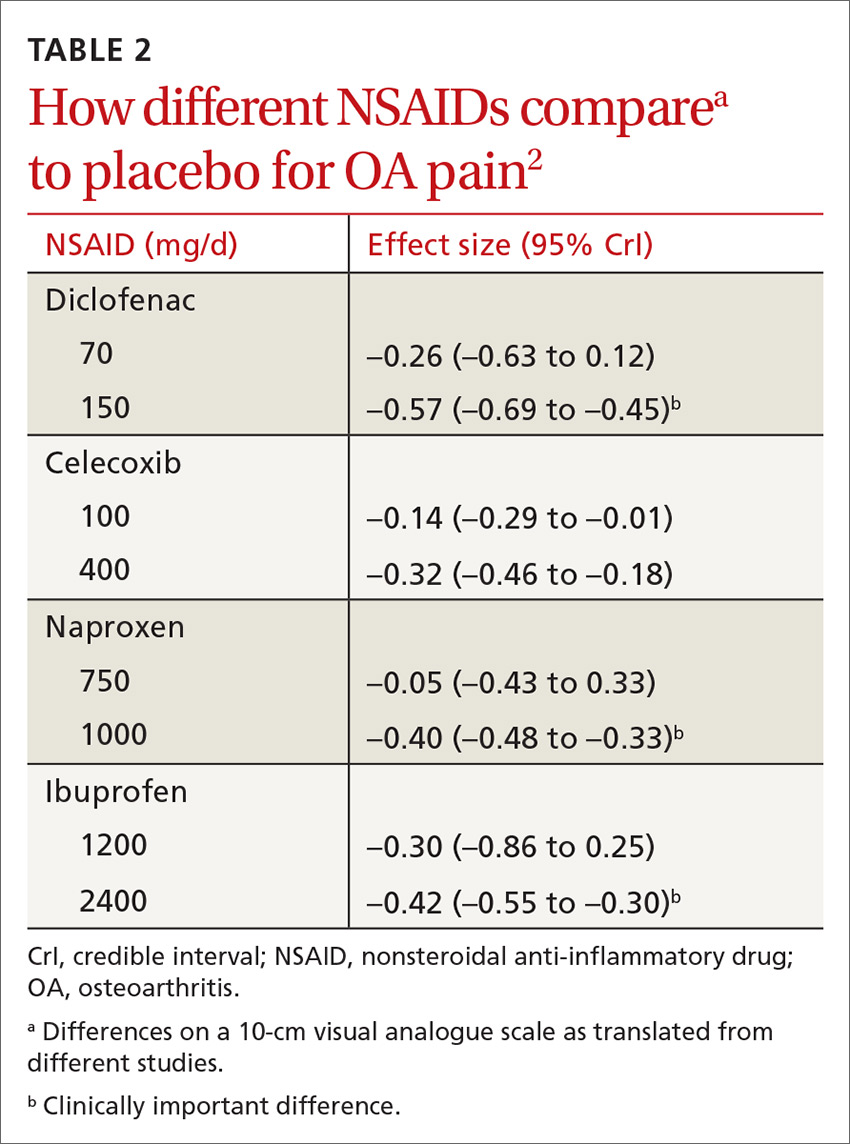
All NSAIDs at maximum clinical doses reduced large joint OA pain more effectively than placebo and acetaminophen based on data from a network meta-analysis of 129 RCTs with 32,129 patients (TABLE 1).1 When various doses of NSAIDs are ranked for efficacy based on their effect size compared to placebo, diclofenac 150 mg/d had the greatest treatment effect, followed by ibuprofen 2400 mg/d.2 Lower doses of NSAIDs—including diclofenac 70 mg/d, naproxen 750 mg/d, and ibuprofen 1200 mg/d—were not statistically superior to placebo (TABLE 2).2
Selective vs nonselective. There was no statistical difference in pain relief between the selective COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib and the nonselective NSAIDs naproxen, diclofenac, and ibuprofen (TABLE 1).1
Meloxicam. A systematic review of 16 RCTs and 22,886 patients found that meloxicam reduced pain more effectively than placebo (10-point visual analogue scale [VAS] score pain difference of –6.8; 95% CI, –9.3 to –4.2) but was marginally less effective than other NSAIDs (VAS score pain difference of 1.7; 95% CI, 0.8 to 2.7).3
Acetaminophen. Data from 6 RCTs involving 2083 adults with knee OA indicate acetaminophen did not achieve clinical significance compared to placebo (TABLE 1).1 Another meta-analysis of 5 RCTs involving 1741 patients with hip or knee OA also demonstrated that acetaminophen failed to achieve a clinically significant effect on pain, defined as a reduction of 9 mm on a 0 to 100 mm VAS (–3.7; 95% CI, –5.5 to –1.9).4 Another network meta-analysis of 6 RCTs including 58,556 patients with knee or hip OA, with the primary outcome of pain (using a hierarchy of pain scores, with global pain score taking precedence) also found no clinically significant difference between acetaminophen at the highest dose (4000 mg/d) and placebo (–0.17; 95% credible interval [CrI], –0.27 to –0.6).2
RECOMMENDATIONS
In a systematic review of mixed evidence-based and expert opinion recommendations and guidelines on the management of OA, 10 of the 11 guidelines that included pharmacologic management recommended acetaminophen as a first-line agent, followed by topical NSAIDs, and then oral NSAIDs. The exception is the most recent American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons guideline, which continues to recommend NSAIDs but is now unable to recommend for or against acetaminophen.5
1. Bannuru RR, Schmid CH, Kent DM, et al. Comparative effectiveness of pharmacologic interventions for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162:46-54.
2. da Costa BR, Reichenbach S, Keller N, et al. Effectiveness of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of pain in knee and hip osteoarthritis: a network meta-analysis. Lancet. 2017;390:e23-e33.
3. Chen YF, Jobanputra P, Barton P, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (etodolac, meloxicam, celecoxib, rofecoxib, etoricoxib, valdecoxib and lumiracoxib) for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 2008;12:1-278, iii.
4. Machado GC, Maher CG, Ferreira PH, et al. Efficacy and safety of paracetamol for spinal pain and osteoarthritis: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo controlled trials. BMJ. 2015;350:h1225.
5. Nelson AE, Allen KD, Golightly YM, et al. A systematic review of recommendations and guidelines for the management of osteoarthritis: The Chronic Osteoarthritis Management Initiative of the U.S. Bone and Joint Initiative. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;43:701-712.
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
All NSAIDs at maximum clinical doses reduced large joint OA pain more effectively than placebo and acetaminophen based on data from a network meta-analysis of 129 RCTs with 32,129 patients (TABLE 1).1 When various doses of NSAIDs are ranked for efficacy based on their effect size compared to placebo, diclofenac 150 mg/d had the greatest treatment effect, followed by ibuprofen 2400 mg/d.2 Lower doses of NSAIDs—including diclofenac 70 mg/d, naproxen 750 mg/d, and ibuprofen 1200 mg/d—were not statistically superior to placebo (TABLE 2).2
Selective vs nonselective. There was no statistical difference in pain relief between the selective COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib and the nonselective NSAIDs naproxen, diclofenac, and ibuprofen (TABLE 1).1
Meloxicam. A systematic review of 16 RCTs and 22,886 patients found that meloxicam reduced pain more effectively than placebo (10-point visual analogue scale [VAS] score pain difference of –6.8; 95% CI, –9.3 to –4.2) but was marginally less effective than other NSAIDs (VAS score pain difference of 1.7; 95% CI, 0.8 to 2.7).3
Acetaminophen. Data from 6 RCTs involving 2083 adults with knee OA indicate acetaminophen did not achieve clinical significance compared to placebo (TABLE 1).1 Another meta-analysis of 5 RCTs involving 1741 patients with hip or knee OA also demonstrated that acetaminophen failed to achieve a clinically significant effect on pain, defined as a reduction of 9 mm on a 0 to 100 mm VAS (–3.7; 95% CI, –5.5 to –1.9).4 Another network meta-analysis of 6 RCTs including 58,556 patients with knee or hip OA, with the primary outcome of pain (using a hierarchy of pain scores, with global pain score taking precedence) also found no clinically significant difference between acetaminophen at the highest dose (4000 mg/d) and placebo (–0.17; 95% credible interval [CrI], –0.27 to –0.6).2
RECOMMENDATIONS
In a systematic review of mixed evidence-based and expert opinion recommendations and guidelines on the management of OA, 10 of the 11 guidelines that included pharmacologic management recommended acetaminophen as a first-line agent, followed by topical NSAIDs, and then oral NSAIDs. The exception is the most recent American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons guideline, which continues to recommend NSAIDs but is now unable to recommend for or against acetaminophen.5
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
All NSAIDs at maximum clinical doses reduced large joint OA pain more effectively than placebo and acetaminophen based on data from a network meta-analysis of 129 RCTs with 32,129 patients (TABLE 1).1 When various doses of NSAIDs are ranked for efficacy based on their effect size compared to placebo, diclofenac 150 mg/d had the greatest treatment effect, followed by ibuprofen 2400 mg/d.2 Lower doses of NSAIDs—including diclofenac 70 mg/d, naproxen 750 mg/d, and ibuprofen 1200 mg/d—were not statistically superior to placebo (TABLE 2).2
Selective vs nonselective. There was no statistical difference in pain relief between the selective COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib and the nonselective NSAIDs naproxen, diclofenac, and ibuprofen (TABLE 1).1
Meloxicam. A systematic review of 16 RCTs and 22,886 patients found that meloxicam reduced pain more effectively than placebo (10-point visual analogue scale [VAS] score pain difference of –6.8; 95% CI, –9.3 to –4.2) but was marginally less effective than other NSAIDs (VAS score pain difference of 1.7; 95% CI, 0.8 to 2.7).3
Acetaminophen. Data from 6 RCTs involving 2083 adults with knee OA indicate acetaminophen did not achieve clinical significance compared to placebo (TABLE 1).1 Another meta-analysis of 5 RCTs involving 1741 patients with hip or knee OA also demonstrated that acetaminophen failed to achieve a clinically significant effect on pain, defined as a reduction of 9 mm on a 0 to 100 mm VAS (–3.7; 95% CI, –5.5 to –1.9).4 Another network meta-analysis of 6 RCTs including 58,556 patients with knee or hip OA, with the primary outcome of pain (using a hierarchy of pain scores, with global pain score taking precedence) also found no clinically significant difference between acetaminophen at the highest dose (4000 mg/d) and placebo (–0.17; 95% credible interval [CrI], –0.27 to –0.6).2
RECOMMENDATIONS
In a systematic review of mixed evidence-based and expert opinion recommendations and guidelines on the management of OA, 10 of the 11 guidelines that included pharmacologic management recommended acetaminophen as a first-line agent, followed by topical NSAIDs, and then oral NSAIDs. The exception is the most recent American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons guideline, which continues to recommend NSAIDs but is now unable to recommend for or against acetaminophen.5
1. Bannuru RR, Schmid CH, Kent DM, et al. Comparative effectiveness of pharmacologic interventions for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162:46-54.
2. da Costa BR, Reichenbach S, Keller N, et al. Effectiveness of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of pain in knee and hip osteoarthritis: a network meta-analysis. Lancet. 2017;390:e23-e33.
3. Chen YF, Jobanputra P, Barton P, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (etodolac, meloxicam, celecoxib, rofecoxib, etoricoxib, valdecoxib and lumiracoxib) for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 2008;12:1-278, iii.
4. Machado GC, Maher CG, Ferreira PH, et al. Efficacy and safety of paracetamol for spinal pain and osteoarthritis: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo controlled trials. BMJ. 2015;350:h1225.
5. Nelson AE, Allen KD, Golightly YM, et al. A systematic review of recommendations and guidelines for the management of osteoarthritis: The Chronic Osteoarthritis Management Initiative of the U.S. Bone and Joint Initiative. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;43:701-712.
1. Bannuru RR, Schmid CH, Kent DM, et al. Comparative effectiveness of pharmacologic interventions for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162:46-54.
2. da Costa BR, Reichenbach S, Keller N, et al. Effectiveness of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of pain in knee and hip osteoarthritis: a network meta-analysis. Lancet. 2017;390:e23-e33.
3. Chen YF, Jobanputra P, Barton P, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (etodolac, meloxicam, celecoxib, rofecoxib, etoricoxib, valdecoxib and lumiracoxib) for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 2008;12:1-278, iii.
4. Machado GC, Maher CG, Ferreira PH, et al. Efficacy and safety of paracetamol for spinal pain and osteoarthritis: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo controlled trials. BMJ. 2015;350:h1225.
5. Nelson AE, Allen KD, Golightly YM, et al. A systematic review of recommendations and guidelines for the management of osteoarthritis: The Chronic Osteoarthritis Management Initiative of the U.S. Bone and Joint Initiative. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;43:701-712.
EVIDENCE-BASED ANSWER:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), when used at the maximum clinically effective dose, reduce osteoarthritis (OA) pain in large joints more effectively than either placebo or acetaminophen (strength of recommendation [SOR]: A, network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [RCTs]).
When ranked for efficacy, diclofenac 150 mg/d was the most effective (SOR: A, network meta-analysis of RCTs). The selective COX-2 inhibitors, such as celecoxib, are not more effective at reducing pain than the nonselective NSAIDs (SOR: A, meta-analysis of RCTs). Meloxicam is superior to placebo but marginally inferior to other NSAIDs (SOR: A, systematic review of RCTs).
Acetaminophen is no more effective than placebo (SOR: A, meta-analysis of RCTs).