User login
Delirious mania is a syndrome characterized by the acute onset of severe hyperactivity, psychosis, catatonia, and intermittent confusion. While there have been growing reports of this phenomenon over the last 2 decades, it remains poorly recognized and understood.1,2 There is no widely accepted nosology for delirious mania and the condition is absent from DSM-5, which magnifies the difficulties in making a timely diagnosis and initiating appropriate treatment. Delayed diagnosis and treatment may result in a detrimental outcome.2,3 Delirious mania has also been labeled as lethal catatonia, specific febrile delirium, hyperactive or exhaustive mania, and Bell’s mania.2,4,5 The characterization and diagnosis of this condition have a long and inconsistent history (Box1,6-11).
Box
Delirious mania was originally recognized in 1849 by Luther Bell in McLean Hospital after he observed 40 cases that were uniquely distinct from 1,700 other cases from 1836 to 1849.6 He described these patients as being suddenly confused, demonstrating unprovoked combativeness, remarkable decreased need for sleep, excessive motor restlessness, extreme fearfulness, and certain physiological signs, including rapid pulse and sweating. Bell was limited to the psychiatric treatment of his time, which largely was confined to physical restraints. Approximately three-fourths of these patients died.6
Following Bell’s report, this syndrome remained unexplored and rarely described. Some researchers postulated that the development of confusion was a natural progression of late-phase mania in close to 20% of patients.7 However, this did not account for the rapid onset of symptoms as well as certain unexplained movement abnormalities. In 1980, Bond8 presented 3 cases that were similar in nature to Bell’s depiction: acute onset with extraordinary irritability, withdrawal, delirium, and mania.
For the next 2 decades, delirious mania was seldom reported in the literature. The term was often reserved to illustrate when a patient had nothing more than mania with features of delirium.9
By 1996, catatonia became better recognized in its wide array of symptomology and diagnostic scales.10,11 In 1999, in addition to the sudden onset of excitement, paranoia, grandiosity, and disorientation, Fink1 reported catatonic signs including negativism, stereotypy, posturing, grimacing, and echo phenomena in patients with delirious mania. He identified its sensitive response to electroconvulsive therapy.
Delirious mania continues to be met with incertitude in clinical practice, and numerous inconsistencies have been reported in the literature. For example, some cases that have been reported as delirious mania had more evidence of primary delirium due to another medical condition or primary mania.12,13 Other cases have demonstrated swift improvement of symptoms after monotherapy with antipsychotics without a trial of benzodiazepines or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT); the exclusion of a sudden onset questions the validity of the diagnosis and promotes the use of less efficacious treatments.14,15 Other reports have confirmed that the diagnosis is missed when certain symptoms are more predominant, such as a thought disorder (acute schizophrenia), grandiosity and delusional ideation (bipolar disorder [BD]), and less commonly assessed catatonic signs (ambitendency, automatic obedience). These symptoms are mistakenly attributed to the respective disease.1,16 This especially holds true when delirious mania is initially diagnosed as a primary psychosis, which leads to the administration of antipsychotics.17 Other cases have reported that delirious mania was resistant to treatment, but ECT was never pursued.18
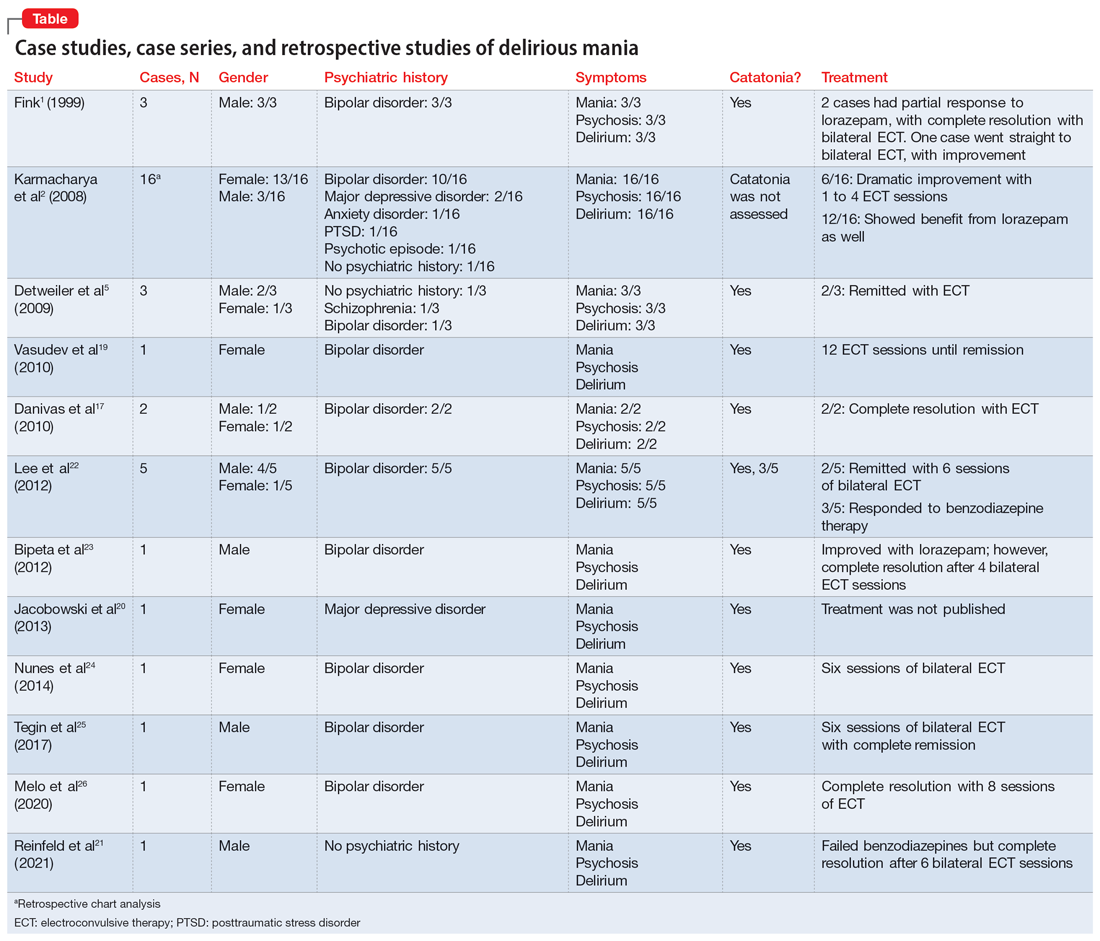
In this review, we provide a more comprehensive perspective of the clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management of delirious mania. We searched PubMed and Google Scholar using the keywords “delirious mania,” “delirious mania AND catatonia,” or “manic delirium.” Most articles we found were case reports, case series, or retrospective chart reviews. There were no systematic reviews, meta analyses, or randomized control trials (RCTs). The 12 articles included in this review consist of 7 individual case reports, 4 case series, and 1 retrospective chart review that describe a total of 36 cases (Table1,2,5,17,19-26).
Clinical presentation: What to look for
Patients with delirious mania typically develop symptoms extremely rapidly. In virtually all published literature, symptoms were reported to emerge within hours to days and consisted of severe forms of mania, psychosis, and delirium; 100% of the cases in our review had these symptoms. Commonly reported symptoms were:
- intense excitement
- emotional lability
- grandiose delusions
- profound insomnia
- pressured and rapid speech
- auditory and visual hallucinations
- hypersexuality
- thought disorganization.
Exquisite paranoia can also result in violent aggression (and may require the use of physical restraints). Patients may confine themselves to very small spaces (such as a closet) in response to the intense paranoia. Impairments in various neurocognitive domains—including inability to focus; disorientation; language and visuospatial disturbances; difficulty with shifting and sustaining attention; and short-term memory impairments—have been reported. Patients often cannot recall the events during the episode.1,2,5,27,28
Catatonia has been closely associated with delirious mania.29 Features of excited catatonia—such as excessive motor activity, negativism, grimacing, posturing, echolalia, echopraxia, stereotypy, automatic obedience, verbigeration, combativeness, impulsivity, and rigidity—typically accompany delirious mania.1,5,10,19,27
In addition to these symptoms, patients may engage in specific behaviors. They may exhibit inappropriate toileting such as smearing feces on walls or in bags, fecal or urinary incontinence, disrobing or running naked in public places, or pouring liquid on the floor or on one’s head.1,2
Continue to: Of the 36 cases...
Of the 36 cases reported in the literature we reviewed, 20 (55%) were female. Most patients had an underlining psychiatric condition, including BD (72%), major depressive disorder (8%), and schizophrenia (2%). Three patients had no psychiatric history.
Physical examination
On initial presentation, a patient with delirious mania may be dehydrated, with dry mucous membranes, pale conjunctiva, tongue dryness, and poor skin turgor.28,30 Due to excessive motor activity, diaphoresis with tachycardia, fluctuating blood pressure, and fever may be present.31
Certain basic cognitive tasks should be assessed to determine the patient’s orientation to place, date, and time. Assess if the patient can recall recent events, names of objects, or perform serial 7s; clock drawing capabilities also should be ascertained.1,2,5 A Mini-Mental State Examination is useful.32
The Bush-Francis Catatonia Rating Scale should be used to elicit features of catatonia, such as waxy flexibility, negativism, gegenhalten, mitgehen, catalepsy, ambitendency, automatic obedience, and grasp reflex.10
Laboratory findings are nonspecific
Although no specific laboratory findings are associated with delirious mania, bloodwork and imaging are routinely investigated, especially if delirium characteristics are most striking. A complete blood count, chemistries, hepatic panel, thyroid functioning, blood and/or urine cultures, creatinine phosphokinase (CPK), and urinalysis can be ordered. Head imaging such as MRI and CT to rule out intracranial pathology are typically performed.19 However, the diagnosis of delirious mania is based on the presence of the phenotypic features, by verification of catatonia, and by the responsiveness to the treatment delivered.29
Continue to: Pathogenisis: Several hypotheses
Pathogenesis: Several hypotheses
The pathogenesis of delirious mania is not well understood. There are several postulations but no salient theory. Most patients with delirious mania have an underlying systemic medical or psychiatric condition.
Mood disorders. Patients with BD or schizoaffective disorder are especially susceptible to delirious mania. The percentage of manic patients who present with delirious mania varies by study. One study suggested approximately 19% have features of the phenomenon,33 while others estimated 15% to 25%.34 Elias et al35 calculated that 15% of patients with mania succumb to manic exhaustion; from this it can be reasonably concluded that these were cases of misdiagnosed delirious mania.
Delirium hypothesis. Patients with delirious mania typically have features of delirium, including fluctuation of consciousness, disorientation, and/or poor sleep-wake cycle.36 During rapid eye movement (REM) and non-REM sleep, memory circuits are fortified. When there is a substantial loss of REM and non-REM sleep, these circuits become faulty, even after 1 night. Pathological brain waves on EEG reflect the inability to reinforce the memory circuits. Patients with these waves may develop hallucinations, bizarre delusions, and altered sensorium. ECT reduces the pathological slow wave morphologies, thus restoring the synaptic maintenance and correcting the incompetent circuitry. This can explain the robust and rapid response of ECT in a patient with delirious mania.37,38
Neurotransmitter hypothesis. It has been shown that in patients with delirious mania there is dysregulation of dopamine transport, which leads to dopamine overflow in the synapse. In contrast to a drug effect (ie, cocaine or methamphetamine) that acts by inhibiting dopamine reuptake, dopamine overflow in delirious mania is caused by the loss of dopamine transporter regulation. This results in a dysfunctional dopaminergic state that precipitates an acute state of delirium and agitation.39,40
Serotonin plays a role in mood disorders, including mania and depression.41,42 More specifically, serotonin has been implicated in impulsivity and aggression as shown by reduced levels of CSF 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) and depletion of 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP).43
Continue to: Alterations in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transmission...
Alterations in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transmission are known to occur in delirium and catatonia. In delirium, GABA signaling is increased, which disrupts the circadian rhythm and melatonin release, thus impairing the sleep-wake cycle.44 Deficiencies in acetylcholine and melatonin are seen as well as excess of other neurotransmitters, including norepinephrine and glutamate.45 Conversely, in catatonia, functional imaging studies found decreased GABA-A binding in orbitofrontal, prefrontal, parietal, and motor cortical regions.46 A study analyzing 10 catatonic patients found decreased density of GABA-A receptors in the left sensorimotor cortex compared to psychiatric and healthy controls.47
Other neurotransmitters, such as glutamate, at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDAR) have been hypothesized to be hyperactive, causing downstream dysregulation of GABA functioning.48 However, the exact connection between delirious mania and all these receptors and neurotransmitters remains unknown.
Encephalitis hypothesis. The relationship between delirious mania and autoimmune encephalitis suggests delirious mania has etiologies other than a primary psychiatric illness. In a 2020 retrospective study49 that analyzed 79 patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis, 25.3% met criteria for delirious mania, and 95% of these patients had catatonic features. Dalmau et al50 found that in many cases, patients tend to respond to ECT; in a cases series of 3 patients, 2 responded to benzodiazepines.
COVID-19 hypothesis. The SARS-CoV-2 virion has been associated with many neuropsychiatric complications, including mood, psychotic, and neurocognitive disorders.51,52 There also have been cases of COVID-19–induced catatonia.53-55 One case of delirious mania in a patient with COVID-19 has been reported.21 The general mechanism has been proposed to be related to the stimulation of the proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6, which the virus produces in large quantities.56 These cytokines have been linked to psychosis and other psychiatric disorders.57 The patient with COVID-19–induced delirious mania had elevated inflammatory markers, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, ferritin, and D-dimer, which supports a proinflammatory state. This patient had a complete resolution of symptoms with ECT.21
Management: Benzodiazepines and ECT
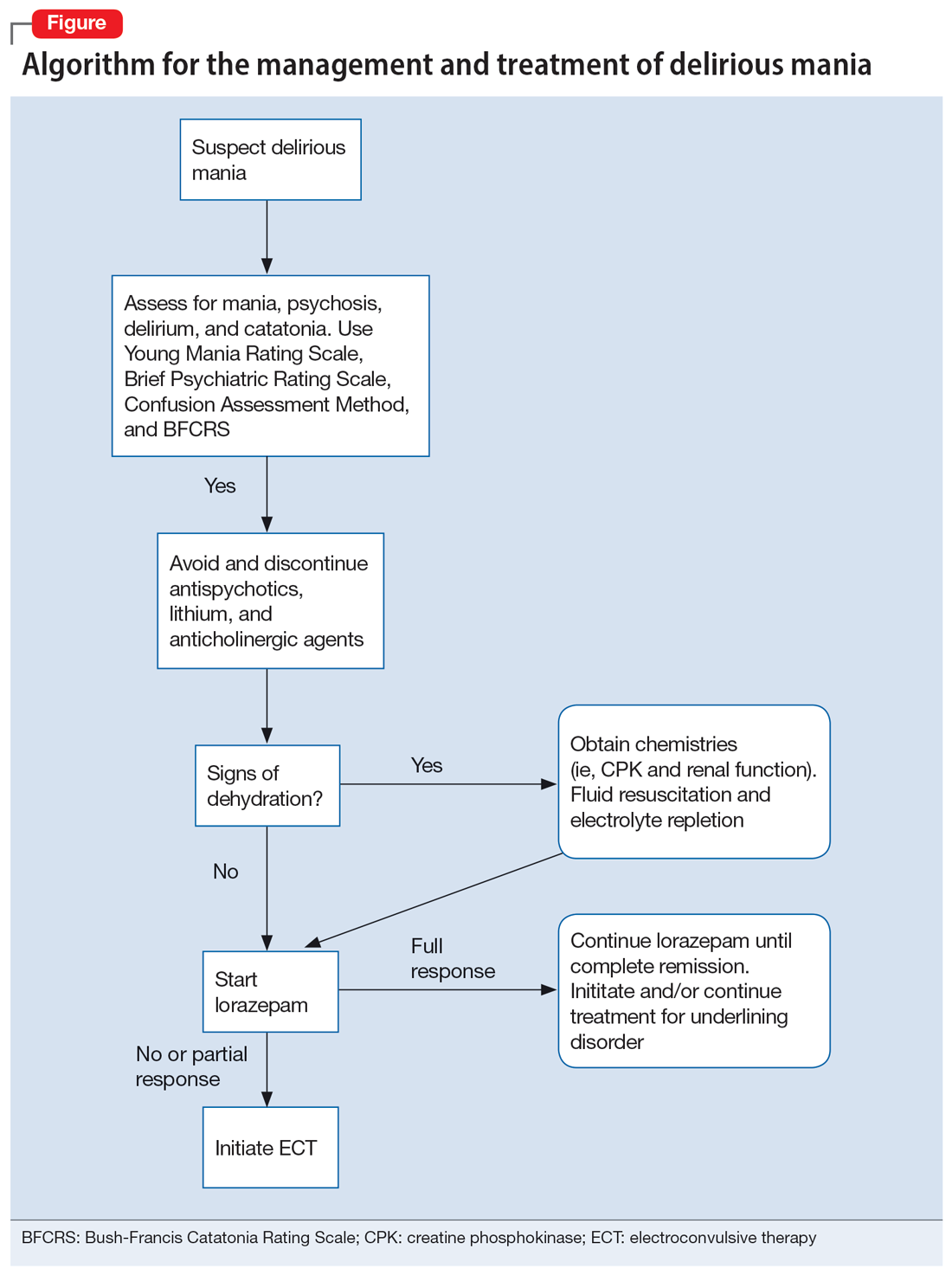
A step-by-step algorithm for managing delirious mania is outlined in the Figure. Regardless of the underlining etiology, management of delirious mania consists of benzodiazepines (lorazepam and diazepam); prompt use of ECT, particularly for patients who do not improve with large doses of lorazepam; or (if applicable) continued treatment of the underlining medical condition, which does not preclude the use of benzodiazepines or ECT. Recent reports27,58 have described details for using ECT for delirious mania, highlighting the use of high-energy dosing, bilateral electrode placement, and frequent sessions.
Continue to: Knowing which medications...
Knowing which medications to avoid is as important as knowing which agents to administer. Be vigilant in avoiding high-potency antipsychotics, as these medications can worsen extrapyramidal symptoms and may precipitate seizures or neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS).28 Anticholinergic agents should also be avoided because they worsen confusion. Although lithium is effective in BD, in delirious mania, high doses of lithium and haloperidol may cause severe encephalopathic syndromes, with symptoms that can include lethargy, tremors, cerebellar dysfunction, and worsened confusion; it may also cause widespread and irreversible brain damage.59
Due to long periods of hyperactivity, withdrawal, and diaphoresis, patients with delirious mania may be severely dehydrated with metabolic derangements, including elevated CPK due to rhabdomyolysis from prolonged exertion, IM antipsychotics, or rigidity. To prevent acute renal failure, this must be immediately addressed with rapid fluid resuscitation and electrolyte repletion.61
Benzodiazepines. The rapid use of lorazepam should be initiated when delirious mania is suspected. Doses of 6 to 20 mg have been reported to be effective if tolerated.5,20 Typically, high-dose lorazepam will not have the sedative effect that would normally occur in a patient who does not have delirious mania.2 Lorazepam should be titrated until full resolution of symptoms. Doses up to 30 mg have been reported as effective and tolerable.62 In our literature review, 50% of patients (18/36) responded or partially responded to lorazepam. However, only 3 case reports documented a complete remission with lorazepam, and many patients needed ECT for remission of symptoms.
ECT is generally reserved for patients who are not helped by benzodiazepine therapy, which is estimated to be up to 20%.5 ECT is highly effective in delirious mania, with remission rates ranging from 80% to 100%.1 ECT is also effective in acute nondelirious mania (comparable to depression); however, it is only used in a small minority of cases (0.2% to 12%).35 In our review, 58% of cases (21/36) reported using ECT, and in all cases it resulted in complete remission.
A dramatic improvement can be seen even after a single ECT session, though most patients show improvement after 4 sessions or 3 to 7 days.1,2,5 In our review, most patients received 4 to 12 sessions until achieving complete remission.
Continue to: No RCTs have evaluated...
No RCTs have evaluated ECT electrode placement in patients with delirious mania. However, several RCTs have investigated electrode placement in patients with acute nondelirious mania. Hiremani et al63 found that bitemporal placement had a more rapid response rate than bifrontal placement, but there was no overall difference in response rate. Barekatain et al64 found no difference between these 2 bilateral approaches. Many of the delirious mania cases report using a bilateral placement (including 42% of the ECT cases in our review) due to the emergent need for rapid relief of symptoms, which is especially necessary if the patient is experiencing hemodynamic instability, excessive violence, risk for self-harm, worsening delirium, or resistance to lorazepam.
Prognosis: Often fatal if left untreated
Patients with delirious mania are at high risk to progress to a more severe form of NMS or malignant catatonia. Therefore, high-potency antipsychotics should be avoided; mortality can be elevated from 60% without antipsychotics to 78% with antipsychotics.4 Some researchers estimate 75% to 78% of cases of delirious mania can be fatal if left untreated.3,6
Bottom Line
Delirious mania is routinely mistaken for more conventional manic or psychotic disorders. Clinicians need to be able to rapidly recognize the symptoms of this syndrome, which include mania, psychosis, delirium, and possible catatonia, so they can avoid administering toxic agents and instead initiate effective treatments such as benzodiazepines and electroconvulsive therapy.
Related Resources
- Arsan C, Baker C, Wong J, et al. Delirious mania: an approach to diagnosis and treatment. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2021;23(1):20f02744. doi:10.4088/PCC.20f02744
- Lamba G, Kennedy EA, Vu CP. Case report: ECT for delirious mania. Clinical Psychiatry News. December 14, 2021. https://www.mdedge.com/psychiatry/article/249909/bipolar-disorder/case-report-ect-delirious-mania
Drug Brand Names
Diazepam • Valium
Haloperidol • Haldol
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Lorazepam • Ativan
1. Fink M. Delirious mania. Bipolar Disord. 1999;1(1):54-60.
2. Karmacharya R, England ML, Ongür D. Delirious mania: clinical features and treatment response. J Affect Disord. 2008;109(3):312-316.
3. Friedman RS, Mufson MJ, Eisenberg TD, et al. Medically and psychiatrically ill: the challenge of delirious mania. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2003;11(2):91-98.
4. Mann SC, Caroff SN, Bleier HR, et al. Lethal catatonia. Am J Psychiatry. 1986;143(11):1374-1381.
5. Detweiler MB, Mehra A, Rowell T, et al. Delirious mania and malignant catatonia: a report of 3 cases and review. Psychiatr Q. 2009;80(1):23-40.
6. Bell L. On a form of disease resembling some advanced stages of mania and fever. American Journal of Insanity. 1849;6(2):97-127.
7. Carlson GA, Goodwin FK. The stages of mania. A longitudinal analysis of the manic episode. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1973;28(2):221-228.
8. Bond TC. Recognition of acute delirious mania. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1980;37(5):553-554.
9. Hutchinson G, David A. Manic pseudo-delirium - two case reports. Behav Neurol. 1997;10(1):21-23.
10. Bush G, Fink M, Petrides G, et al. Catatonia. I. Rating scale and standardized examination. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1996;93(2):129-136.
11. Bush G, Fink M, Petrides G, et al. Catatonia. II. Treatment with lorazepam and electroconvulsive therapy. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1996;93(2):137-143.
12. Cordeiro CR, Saraiva R, Côrte-Real B, et al. When the bell rings: clinical features of Bell’s mania. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2020;22(2):19l02511. doi:10.4088/PCC.19l02511
13. Yeo LX, Kuo TC, Hu KC, et al. Lurasidone-induced delirious mania. Am J Ther. 2019;26(6):e786-e787.
14. Jung WY, Lee BD. Quetiapine treatment for delirious mania in a military soldier. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;12(2):PCC.09l00830. doi:10.4088/PCC.09l00830yel
15. Wahid N, Chin G, Turner AH, et al. Clinical response of clozapine as a treatment for delirious mania. Ment Illn. 2017;9(2):7182. doi:10.4081/mi.2017.7182
16. Taylor MA, Fink M. Catatonia in psychiatric classification: a home of its own. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(7):1233-1241.
17. Danivas V, Behere RV, Varambally S, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy in the treatment of delirious mania: a report of 2 patients. J ECT. 2010;26(4):278-279.
18. O’Callaghan N, McDonald C, Hallahan B. Delirious mania intractable to treatment. Ir J Psychol Med. 2016;33(2):129-132.
19. Vasudev K, Grunze H. What works for delirious catatonic mania? BMJ Case Rep. 2010;2010:bcr0220102713. doi:10.1136/bcr.02.2010.2713
20. Jacobowski NL, Heckers S, Bobo WV. Delirious mania: detection, diagnosis, and clinical management in the acute setting. J Psychiatr Pract. 2013;19(1):15-28.
21. Reinfeld S, Yacoub A. A case of delirious mania induced by COVID-19 treated with electroconvulsive therapy. J ECT. 2021;37(4):e38-e39.
22. Lee BS, Huang SS, Hsu WY, et al. Clinical features of delirious mania: a series of five cases and a brief literature review. BMC Psychiatry. 2012;12:65. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-12-65
23. Bipeta R, Khan MA. Delirious mania: can we get away with this concept? A case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2012;2012:720354. doi:10.1155/2012/720354
24. Nunes AL, Cheniaux E. Delirium and mania with catatonic features in a Brazilian patient: response to ECT. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2014;26(1):E1-E3.
25. Tegin C, Kalayil G, Lippmann S. Electroconvulsive therapy and delirious catatonic mania. J ECT. 2017;33(4):e33-e34.
26. Melo AL, Serra M. Delirious mania and catatonia. Bipolar Disord. 2020;22(6):647-649.
27. Fink M. Expanding the catatonia tent: recognizing electroconvulsive therapy responsive syndromes. J ECT. 2021;37(2):77-79.
28. Fink M. Electroconvulsive Therapy: A Guide for Professionals and Their Patients. Oxford University Press; 2009.
29. Fink M, Taylor MA. The many varieties of catatonia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2001;251 Suppl 1:I8-I13.
30. Vivanti A, Harvey K, Ash S, et al. Clinical assessment of dehydration in older people admitted to hospital: what are the strongest indicators? Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2008;47(3):340-355.
31. Ware MR, Feller DB, Hall KL. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome: diagnosis and management. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2018;20(1):17r02185. doi:10.4088/PCC.17r0218
32. Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12(3):189-198.
33. Taylor MA, Abrams R. The phenomenology of mania. A new look at some old patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1973;29(4):520-522.
34. Klerman GL. The spectrum of mania. Compr Psychiatry. 1981;22(1):11-20.
35. Elias A, Thomas N, Sackeim HA. Electroconvulsive therapy in mania: a review of 80 years of clinical experience. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(3):229-239.
36. Thom RP, Levy-Carrick NC, Bui M, et al. Delirium. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176(10):785-793.
37. Charlton BG, Kavanau JL. Delirium and psychotic symptoms--an integrative model. Med Hypotheses. 2002;58(1):24-27.
38. Kramp P, Bolwig TG. Electroconvulsive therapy in acute delirious states. Compr Psychiatry. 1981;22(4):368-371.
39. Mash DC. Excited delirium and sudden death: a syndromal disorder at the extreme end of the neuropsychiatric continuum. Front Physiol. 2016;7:435.
40. Strawn JR, Keck PE Jr, Caroff SN. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(6):870-876.
41. Charney DS. Monoamine dysfunction and the pathophysiology and treatment of depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998;59 Suppl 14:11-14.
42. Shiah IS, Yatham LN. Serotonin in mania and in the mechanism of action of mood stabilizers: a review of clinical studies. Bipolar Disord. 2000;2(2):77-92.
43. Dalley JW, Roiser JP. Dopamine, serotonin and impulsivity. Neuroscience. 2012;215:42-58.
44. Maldonado JR. Pathoetiological model of delirium: a comprehensive understanding of the neurobiology of delirium and an evidence-based approach to prevention and treatment. Crit Care Clin. 2008;24(4):789-856, ix.
45. Maldonado JR. Neuropathogenesis of delirium: review of current etiologic theories and common pathways. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2013;21(12):1190-1222.
46. Rasmussen SA, Mazurek MF, Rosebush PI. Catatonia: our current understanding of its diagnosis, treatment and pathophysiology. World J Psychiatry. 2016;6(4):391-398.
47. Northoff G, Steinke R, Czcervenka C, et al. Decreased density of GABA-A receptors in the left sensorimotor cortex in akinetic catatonia: investigation of in vivo benzodiazepine receptor binding. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999;67(4):445-450.
48. Daniels J. Catatonia: clinical aspects and neurobiological correlates. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2009;21(4):371-380.
49. Restrepo-Martínez M, Chacón-González J, Bayliss L, et al. Delirious mania as a neuropsychiatric presentation in patients with anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis. Psychosomatics. 2020;61(1):64-69.
50. Dalmau J, Armangué T, Planagumà J, et al. An update on anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis for neurologists and psychiatrists: mechanisms and models. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(11):1045-1057.
51. Steardo L Jr, Steardo L, Verkhratsky A. Psychiatric face of COVID-19. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10(1):261.
52. Iqbal Y, Al Abdulla MA, Albrahim S, et al. Psychiatric presentation of patients with acute SARS-CoV-2 infection: a retrospective review of 50 consecutive patients seen by a consultation-liaison psychiatry team. BJPsych Open. 2020;6(5):e109.
53. Gouse BM, Spears WE, Nieves Archibald A, et al. Catatonia in a hospitalized patient with COVID-19 and proposed immune-mediated mechanism. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;89:529-530.
54. Caan MP, Lim CT, Howard M. A case of catatonia in a man with COVID-19. Psychosomatics. 2020;61(5):556-560.
55. Zain SM, Muthukanagaraj P, Rahman N. Excited catatonia - a delayed neuropsychiatric complication of COVID-19 infection. Cureus. 2021;13(3):e13891.
56. Chowdhury MA, Hossain N, Kashem MA, et al. Immune response in COVID-19: a review. J Infect Public Health. 2020;13(11):1619-1629.
57. Radhakrishnan R, Kaser M, Guloksuz S. The link between the immune system, environment, and psychosis. Schizophr Bull. 2017;43(4):693-697.
58. Fink M, Kellner CH, McCall WV. Optimizing ECT technique in treating catatonia. J ECT. 2016;32(3):149-150.
59. Cohen WJ, Cohen NH. Lithium carbonate, haloperidol, and irreversible brain damage. JAMA. 1974;230(9):1283-1287.
60. Davis MJ, de Nesnera A, Folks DG. Confused and nearly naked after going on spending sprees. Current Psychiatry. 2014;13(7):56-62.
61. Stanley M, Chippa V, Aeddula NR, et al. Rhabdomyolysis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
62. Fink M, Taylor MA. The catatonia syndrome: forgotten but not gone. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(11):1173-1177.
63. Hiremani RM, Thirthalli J, Tharayil BS, et al. Double-blind randomized controlled study comparing short-term efficacy of bifrontal and bitemporal electroconvulsive therapy in acute mania. Bipolar Disord. 2008;10(6):701-707.
64. Barekatain M, Jahangard L, Haghighi M, et al. Bifrontal versus bitemporal electroconvulsive therapy in severe manic patients. J ECT. 2008;24(3):199-202.
Delirious mania is a syndrome characterized by the acute onset of severe hyperactivity, psychosis, catatonia, and intermittent confusion. While there have been growing reports of this phenomenon over the last 2 decades, it remains poorly recognized and understood.1,2 There is no widely accepted nosology for delirious mania and the condition is absent from DSM-5, which magnifies the difficulties in making a timely diagnosis and initiating appropriate treatment. Delayed diagnosis and treatment may result in a detrimental outcome.2,3 Delirious mania has also been labeled as lethal catatonia, specific febrile delirium, hyperactive or exhaustive mania, and Bell’s mania.2,4,5 The characterization and diagnosis of this condition have a long and inconsistent history (Box1,6-11).
Box
Delirious mania was originally recognized in 1849 by Luther Bell in McLean Hospital after he observed 40 cases that were uniquely distinct from 1,700 other cases from 1836 to 1849.6 He described these patients as being suddenly confused, demonstrating unprovoked combativeness, remarkable decreased need for sleep, excessive motor restlessness, extreme fearfulness, and certain physiological signs, including rapid pulse and sweating. Bell was limited to the psychiatric treatment of his time, which largely was confined to physical restraints. Approximately three-fourths of these patients died.6
Following Bell’s report, this syndrome remained unexplored and rarely described. Some researchers postulated that the development of confusion was a natural progression of late-phase mania in close to 20% of patients.7 However, this did not account for the rapid onset of symptoms as well as certain unexplained movement abnormalities. In 1980, Bond8 presented 3 cases that were similar in nature to Bell’s depiction: acute onset with extraordinary irritability, withdrawal, delirium, and mania.
For the next 2 decades, delirious mania was seldom reported in the literature. The term was often reserved to illustrate when a patient had nothing more than mania with features of delirium.9
By 1996, catatonia became better recognized in its wide array of symptomology and diagnostic scales.10,11 In 1999, in addition to the sudden onset of excitement, paranoia, grandiosity, and disorientation, Fink1 reported catatonic signs including negativism, stereotypy, posturing, grimacing, and echo phenomena in patients with delirious mania. He identified its sensitive response to electroconvulsive therapy.
Delirious mania continues to be met with incertitude in clinical practice, and numerous inconsistencies have been reported in the literature. For example, some cases that have been reported as delirious mania had more evidence of primary delirium due to another medical condition or primary mania.12,13 Other cases have demonstrated swift improvement of symptoms after monotherapy with antipsychotics without a trial of benzodiazepines or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT); the exclusion of a sudden onset questions the validity of the diagnosis and promotes the use of less efficacious treatments.14,15 Other reports have confirmed that the diagnosis is missed when certain symptoms are more predominant, such as a thought disorder (acute schizophrenia), grandiosity and delusional ideation (bipolar disorder [BD]), and less commonly assessed catatonic signs (ambitendency, automatic obedience). These symptoms are mistakenly attributed to the respective disease.1,16 This especially holds true when delirious mania is initially diagnosed as a primary psychosis, which leads to the administration of antipsychotics.17 Other cases have reported that delirious mania was resistant to treatment, but ECT was never pursued.18
In this review, we provide a more comprehensive perspective of the clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management of delirious mania. We searched PubMed and Google Scholar using the keywords “delirious mania,” “delirious mania AND catatonia,” or “manic delirium.” Most articles we found were case reports, case series, or retrospective chart reviews. There were no systematic reviews, meta analyses, or randomized control trials (RCTs). The 12 articles included in this review consist of 7 individual case reports, 4 case series, and 1 retrospective chart review that describe a total of 36 cases (Table1,2,5,17,19-26).

Clinical presentation: What to look for
Patients with delirious mania typically develop symptoms extremely rapidly. In virtually all published literature, symptoms were reported to emerge within hours to days and consisted of severe forms of mania, psychosis, and delirium; 100% of the cases in our review had these symptoms. Commonly reported symptoms were:
- intense excitement
- emotional lability
- grandiose delusions
- profound insomnia
- pressured and rapid speech
- auditory and visual hallucinations
- hypersexuality
- thought disorganization.
Exquisite paranoia can also result in violent aggression (and may require the use of physical restraints). Patients may confine themselves to very small spaces (such as a closet) in response to the intense paranoia. Impairments in various neurocognitive domains—including inability to focus; disorientation; language and visuospatial disturbances; difficulty with shifting and sustaining attention; and short-term memory impairments—have been reported. Patients often cannot recall the events during the episode.1,2,5,27,28
Catatonia has been closely associated with delirious mania.29 Features of excited catatonia—such as excessive motor activity, negativism, grimacing, posturing, echolalia, echopraxia, stereotypy, automatic obedience, verbigeration, combativeness, impulsivity, and rigidity—typically accompany delirious mania.1,5,10,19,27
In addition to these symptoms, patients may engage in specific behaviors. They may exhibit inappropriate toileting such as smearing feces on walls or in bags, fecal or urinary incontinence, disrobing or running naked in public places, or pouring liquid on the floor or on one’s head.1,2
Continue to: Of the 36 cases...
Of the 36 cases reported in the literature we reviewed, 20 (55%) were female. Most patients had an underlining psychiatric condition, including BD (72%), major depressive disorder (8%), and schizophrenia (2%). Three patients had no psychiatric history.
Physical examination
On initial presentation, a patient with delirious mania may be dehydrated, with dry mucous membranes, pale conjunctiva, tongue dryness, and poor skin turgor.28,30 Due to excessive motor activity, diaphoresis with tachycardia, fluctuating blood pressure, and fever may be present.31
Certain basic cognitive tasks should be assessed to determine the patient’s orientation to place, date, and time. Assess if the patient can recall recent events, names of objects, or perform serial 7s; clock drawing capabilities also should be ascertained.1,2,5 A Mini-Mental State Examination is useful.32
The Bush-Francis Catatonia Rating Scale should be used to elicit features of catatonia, such as waxy flexibility, negativism, gegenhalten, mitgehen, catalepsy, ambitendency, automatic obedience, and grasp reflex.10
Laboratory findings are nonspecific
Although no specific laboratory findings are associated with delirious mania, bloodwork and imaging are routinely investigated, especially if delirium characteristics are most striking. A complete blood count, chemistries, hepatic panel, thyroid functioning, blood and/or urine cultures, creatinine phosphokinase (CPK), and urinalysis can be ordered. Head imaging such as MRI and CT to rule out intracranial pathology are typically performed.19 However, the diagnosis of delirious mania is based on the presence of the phenotypic features, by verification of catatonia, and by the responsiveness to the treatment delivered.29
Continue to: Pathogenisis: Several hypotheses
Pathogenesis: Several hypotheses
The pathogenesis of delirious mania is not well understood. There are several postulations but no salient theory. Most patients with delirious mania have an underlying systemic medical or psychiatric condition.
Mood disorders. Patients with BD or schizoaffective disorder are especially susceptible to delirious mania. The percentage of manic patients who present with delirious mania varies by study. One study suggested approximately 19% have features of the phenomenon,33 while others estimated 15% to 25%.34 Elias et al35 calculated that 15% of patients with mania succumb to manic exhaustion; from this it can be reasonably concluded that these were cases of misdiagnosed delirious mania.
Delirium hypothesis. Patients with delirious mania typically have features of delirium, including fluctuation of consciousness, disorientation, and/or poor sleep-wake cycle.36 During rapid eye movement (REM) and non-REM sleep, memory circuits are fortified. When there is a substantial loss of REM and non-REM sleep, these circuits become faulty, even after 1 night. Pathological brain waves on EEG reflect the inability to reinforce the memory circuits. Patients with these waves may develop hallucinations, bizarre delusions, and altered sensorium. ECT reduces the pathological slow wave morphologies, thus restoring the synaptic maintenance and correcting the incompetent circuitry. This can explain the robust and rapid response of ECT in a patient with delirious mania.37,38
Neurotransmitter hypothesis. It has been shown that in patients with delirious mania there is dysregulation of dopamine transport, which leads to dopamine overflow in the synapse. In contrast to a drug effect (ie, cocaine or methamphetamine) that acts by inhibiting dopamine reuptake, dopamine overflow in delirious mania is caused by the loss of dopamine transporter regulation. This results in a dysfunctional dopaminergic state that precipitates an acute state of delirium and agitation.39,40
Serotonin plays a role in mood disorders, including mania and depression.41,42 More specifically, serotonin has been implicated in impulsivity and aggression as shown by reduced levels of CSF 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) and depletion of 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP).43
Continue to: Alterations in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transmission...
Alterations in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transmission are known to occur in delirium and catatonia. In delirium, GABA signaling is increased, which disrupts the circadian rhythm and melatonin release, thus impairing the sleep-wake cycle.44 Deficiencies in acetylcholine and melatonin are seen as well as excess of other neurotransmitters, including norepinephrine and glutamate.45 Conversely, in catatonia, functional imaging studies found decreased GABA-A binding in orbitofrontal, prefrontal, parietal, and motor cortical regions.46 A study analyzing 10 catatonic patients found decreased density of GABA-A receptors in the left sensorimotor cortex compared to psychiatric and healthy controls.47
Other neurotransmitters, such as glutamate, at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDAR) have been hypothesized to be hyperactive, causing downstream dysregulation of GABA functioning.48 However, the exact connection between delirious mania and all these receptors and neurotransmitters remains unknown.
Encephalitis hypothesis. The relationship between delirious mania and autoimmune encephalitis suggests delirious mania has etiologies other than a primary psychiatric illness. In a 2020 retrospective study49 that analyzed 79 patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis, 25.3% met criteria for delirious mania, and 95% of these patients had catatonic features. Dalmau et al50 found that in many cases, patients tend to respond to ECT; in a cases series of 3 patients, 2 responded to benzodiazepines.
COVID-19 hypothesis. The SARS-CoV-2 virion has been associated with many neuropsychiatric complications, including mood, psychotic, and neurocognitive disorders.51,52 There also have been cases of COVID-19–induced catatonia.53-55 One case of delirious mania in a patient with COVID-19 has been reported.21 The general mechanism has been proposed to be related to the stimulation of the proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6, which the virus produces in large quantities.56 These cytokines have been linked to psychosis and other psychiatric disorders.57 The patient with COVID-19–induced delirious mania had elevated inflammatory markers, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, ferritin, and D-dimer, which supports a proinflammatory state. This patient had a complete resolution of symptoms with ECT.21
Management: Benzodiazepines and ECT
A step-by-step algorithm for managing delirious mania is outlined in the Figure. Regardless of the underlining etiology, management of delirious mania consists of benzodiazepines (lorazepam and diazepam); prompt use of ECT, particularly for patients who do not improve with large doses of lorazepam; or (if applicable) continued treatment of the underlining medical condition, which does not preclude the use of benzodiazepines or ECT. Recent reports27,58 have described details for using ECT for delirious mania, highlighting the use of high-energy dosing, bilateral electrode placement, and frequent sessions.

Continue to: Knowing which medications...
Knowing which medications to avoid is as important as knowing which agents to administer. Be vigilant in avoiding high-potency antipsychotics, as these medications can worsen extrapyramidal symptoms and may precipitate seizures or neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS).28 Anticholinergic agents should also be avoided because they worsen confusion. Although lithium is effective in BD, in delirious mania, high doses of lithium and haloperidol may cause severe encephalopathic syndromes, with symptoms that can include lethargy, tremors, cerebellar dysfunction, and worsened confusion; it may also cause widespread and irreversible brain damage.59
Due to long periods of hyperactivity, withdrawal, and diaphoresis, patients with delirious mania may be severely dehydrated with metabolic derangements, including elevated CPK due to rhabdomyolysis from prolonged exertion, IM antipsychotics, or rigidity. To prevent acute renal failure, this must be immediately addressed with rapid fluid resuscitation and electrolyte repletion.61
Benzodiazepines. The rapid use of lorazepam should be initiated when delirious mania is suspected. Doses of 6 to 20 mg have been reported to be effective if tolerated.5,20 Typically, high-dose lorazepam will not have the sedative effect that would normally occur in a patient who does not have delirious mania.2 Lorazepam should be titrated until full resolution of symptoms. Doses up to 30 mg have been reported as effective and tolerable.62 In our literature review, 50% of patients (18/36) responded or partially responded to lorazepam. However, only 3 case reports documented a complete remission with lorazepam, and many patients needed ECT for remission of symptoms.
ECT is generally reserved for patients who are not helped by benzodiazepine therapy, which is estimated to be up to 20%.5 ECT is highly effective in delirious mania, with remission rates ranging from 80% to 100%.1 ECT is also effective in acute nondelirious mania (comparable to depression); however, it is only used in a small minority of cases (0.2% to 12%).35 In our review, 58% of cases (21/36) reported using ECT, and in all cases it resulted in complete remission.
A dramatic improvement can be seen even after a single ECT session, though most patients show improvement after 4 sessions or 3 to 7 days.1,2,5 In our review, most patients received 4 to 12 sessions until achieving complete remission.
Continue to: No RCTs have evaluated...
No RCTs have evaluated ECT electrode placement in patients with delirious mania. However, several RCTs have investigated electrode placement in patients with acute nondelirious mania. Hiremani et al63 found that bitemporal placement had a more rapid response rate than bifrontal placement, but there was no overall difference in response rate. Barekatain et al64 found no difference between these 2 bilateral approaches. Many of the delirious mania cases report using a bilateral placement (including 42% of the ECT cases in our review) due to the emergent need for rapid relief of symptoms, which is especially necessary if the patient is experiencing hemodynamic instability, excessive violence, risk for self-harm, worsening delirium, or resistance to lorazepam.
Prognosis: Often fatal if left untreated
Patients with delirious mania are at high risk to progress to a more severe form of NMS or malignant catatonia. Therefore, high-potency antipsychotics should be avoided; mortality can be elevated from 60% without antipsychotics to 78% with antipsychotics.4 Some researchers estimate 75% to 78% of cases of delirious mania can be fatal if left untreated.3,6
Bottom Line
Delirious mania is routinely mistaken for more conventional manic or psychotic disorders. Clinicians need to be able to rapidly recognize the symptoms of this syndrome, which include mania, psychosis, delirium, and possible catatonia, so they can avoid administering toxic agents and instead initiate effective treatments such as benzodiazepines and electroconvulsive therapy.
Related Resources
- Arsan C, Baker C, Wong J, et al. Delirious mania: an approach to diagnosis and treatment. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2021;23(1):20f02744. doi:10.4088/PCC.20f02744
- Lamba G, Kennedy EA, Vu CP. Case report: ECT for delirious mania. Clinical Psychiatry News. December 14, 2021. https://www.mdedge.com/psychiatry/article/249909/bipolar-disorder/case-report-ect-delirious-mania
Drug Brand Names
Diazepam • Valium
Haloperidol • Haldol
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Lorazepam • Ativan
Delirious mania is a syndrome characterized by the acute onset of severe hyperactivity, psychosis, catatonia, and intermittent confusion. While there have been growing reports of this phenomenon over the last 2 decades, it remains poorly recognized and understood.1,2 There is no widely accepted nosology for delirious mania and the condition is absent from DSM-5, which magnifies the difficulties in making a timely diagnosis and initiating appropriate treatment. Delayed diagnosis and treatment may result in a detrimental outcome.2,3 Delirious mania has also been labeled as lethal catatonia, specific febrile delirium, hyperactive or exhaustive mania, and Bell’s mania.2,4,5 The characterization and diagnosis of this condition have a long and inconsistent history (Box1,6-11).
Box
Delirious mania was originally recognized in 1849 by Luther Bell in McLean Hospital after he observed 40 cases that were uniquely distinct from 1,700 other cases from 1836 to 1849.6 He described these patients as being suddenly confused, demonstrating unprovoked combativeness, remarkable decreased need for sleep, excessive motor restlessness, extreme fearfulness, and certain physiological signs, including rapid pulse and sweating. Bell was limited to the psychiatric treatment of his time, which largely was confined to physical restraints. Approximately three-fourths of these patients died.6
Following Bell’s report, this syndrome remained unexplored and rarely described. Some researchers postulated that the development of confusion was a natural progression of late-phase mania in close to 20% of patients.7 However, this did not account for the rapid onset of symptoms as well as certain unexplained movement abnormalities. In 1980, Bond8 presented 3 cases that were similar in nature to Bell’s depiction: acute onset with extraordinary irritability, withdrawal, delirium, and mania.
For the next 2 decades, delirious mania was seldom reported in the literature. The term was often reserved to illustrate when a patient had nothing more than mania with features of delirium.9
By 1996, catatonia became better recognized in its wide array of symptomology and diagnostic scales.10,11 In 1999, in addition to the sudden onset of excitement, paranoia, grandiosity, and disorientation, Fink1 reported catatonic signs including negativism, stereotypy, posturing, grimacing, and echo phenomena in patients with delirious mania. He identified its sensitive response to electroconvulsive therapy.
Delirious mania continues to be met with incertitude in clinical practice, and numerous inconsistencies have been reported in the literature. For example, some cases that have been reported as delirious mania had more evidence of primary delirium due to another medical condition or primary mania.12,13 Other cases have demonstrated swift improvement of symptoms after monotherapy with antipsychotics without a trial of benzodiazepines or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT); the exclusion of a sudden onset questions the validity of the diagnosis and promotes the use of less efficacious treatments.14,15 Other reports have confirmed that the diagnosis is missed when certain symptoms are more predominant, such as a thought disorder (acute schizophrenia), grandiosity and delusional ideation (bipolar disorder [BD]), and less commonly assessed catatonic signs (ambitendency, automatic obedience). These symptoms are mistakenly attributed to the respective disease.1,16 This especially holds true when delirious mania is initially diagnosed as a primary psychosis, which leads to the administration of antipsychotics.17 Other cases have reported that delirious mania was resistant to treatment, but ECT was never pursued.18
In this review, we provide a more comprehensive perspective of the clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management of delirious mania. We searched PubMed and Google Scholar using the keywords “delirious mania,” “delirious mania AND catatonia,” or “manic delirium.” Most articles we found were case reports, case series, or retrospective chart reviews. There were no systematic reviews, meta analyses, or randomized control trials (RCTs). The 12 articles included in this review consist of 7 individual case reports, 4 case series, and 1 retrospective chart review that describe a total of 36 cases (Table1,2,5,17,19-26).

Clinical presentation: What to look for
Patients with delirious mania typically develop symptoms extremely rapidly. In virtually all published literature, symptoms were reported to emerge within hours to days and consisted of severe forms of mania, psychosis, and delirium; 100% of the cases in our review had these symptoms. Commonly reported symptoms were:
- intense excitement
- emotional lability
- grandiose delusions
- profound insomnia
- pressured and rapid speech
- auditory and visual hallucinations
- hypersexuality
- thought disorganization.
Exquisite paranoia can also result in violent aggression (and may require the use of physical restraints). Patients may confine themselves to very small spaces (such as a closet) in response to the intense paranoia. Impairments in various neurocognitive domains—including inability to focus; disorientation; language and visuospatial disturbances; difficulty with shifting and sustaining attention; and short-term memory impairments—have been reported. Patients often cannot recall the events during the episode.1,2,5,27,28
Catatonia has been closely associated with delirious mania.29 Features of excited catatonia—such as excessive motor activity, negativism, grimacing, posturing, echolalia, echopraxia, stereotypy, automatic obedience, verbigeration, combativeness, impulsivity, and rigidity—typically accompany delirious mania.1,5,10,19,27
In addition to these symptoms, patients may engage in specific behaviors. They may exhibit inappropriate toileting such as smearing feces on walls or in bags, fecal or urinary incontinence, disrobing or running naked in public places, or pouring liquid on the floor or on one’s head.1,2
Continue to: Of the 36 cases...
Of the 36 cases reported in the literature we reviewed, 20 (55%) were female. Most patients had an underlining psychiatric condition, including BD (72%), major depressive disorder (8%), and schizophrenia (2%). Three patients had no psychiatric history.
Physical examination
On initial presentation, a patient with delirious mania may be dehydrated, with dry mucous membranes, pale conjunctiva, tongue dryness, and poor skin turgor.28,30 Due to excessive motor activity, diaphoresis with tachycardia, fluctuating blood pressure, and fever may be present.31
Certain basic cognitive tasks should be assessed to determine the patient’s orientation to place, date, and time. Assess if the patient can recall recent events, names of objects, or perform serial 7s; clock drawing capabilities also should be ascertained.1,2,5 A Mini-Mental State Examination is useful.32
The Bush-Francis Catatonia Rating Scale should be used to elicit features of catatonia, such as waxy flexibility, negativism, gegenhalten, mitgehen, catalepsy, ambitendency, automatic obedience, and grasp reflex.10
Laboratory findings are nonspecific
Although no specific laboratory findings are associated with delirious mania, bloodwork and imaging are routinely investigated, especially if delirium characteristics are most striking. A complete blood count, chemistries, hepatic panel, thyroid functioning, blood and/or urine cultures, creatinine phosphokinase (CPK), and urinalysis can be ordered. Head imaging such as MRI and CT to rule out intracranial pathology are typically performed.19 However, the diagnosis of delirious mania is based on the presence of the phenotypic features, by verification of catatonia, and by the responsiveness to the treatment delivered.29
Continue to: Pathogenisis: Several hypotheses
Pathogenesis: Several hypotheses
The pathogenesis of delirious mania is not well understood. There are several postulations but no salient theory. Most patients with delirious mania have an underlying systemic medical or psychiatric condition.
Mood disorders. Patients with BD or schizoaffective disorder are especially susceptible to delirious mania. The percentage of manic patients who present with delirious mania varies by study. One study suggested approximately 19% have features of the phenomenon,33 while others estimated 15% to 25%.34 Elias et al35 calculated that 15% of patients with mania succumb to manic exhaustion; from this it can be reasonably concluded that these were cases of misdiagnosed delirious mania.
Delirium hypothesis. Patients with delirious mania typically have features of delirium, including fluctuation of consciousness, disorientation, and/or poor sleep-wake cycle.36 During rapid eye movement (REM) and non-REM sleep, memory circuits are fortified. When there is a substantial loss of REM and non-REM sleep, these circuits become faulty, even after 1 night. Pathological brain waves on EEG reflect the inability to reinforce the memory circuits. Patients with these waves may develop hallucinations, bizarre delusions, and altered sensorium. ECT reduces the pathological slow wave morphologies, thus restoring the synaptic maintenance and correcting the incompetent circuitry. This can explain the robust and rapid response of ECT in a patient with delirious mania.37,38
Neurotransmitter hypothesis. It has been shown that in patients with delirious mania there is dysregulation of dopamine transport, which leads to dopamine overflow in the synapse. In contrast to a drug effect (ie, cocaine or methamphetamine) that acts by inhibiting dopamine reuptake, dopamine overflow in delirious mania is caused by the loss of dopamine transporter regulation. This results in a dysfunctional dopaminergic state that precipitates an acute state of delirium and agitation.39,40
Serotonin plays a role in mood disorders, including mania and depression.41,42 More specifically, serotonin has been implicated in impulsivity and aggression as shown by reduced levels of CSF 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) and depletion of 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP).43
Continue to: Alterations in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transmission...
Alterations in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transmission are known to occur in delirium and catatonia. In delirium, GABA signaling is increased, which disrupts the circadian rhythm and melatonin release, thus impairing the sleep-wake cycle.44 Deficiencies in acetylcholine and melatonin are seen as well as excess of other neurotransmitters, including norepinephrine and glutamate.45 Conversely, in catatonia, functional imaging studies found decreased GABA-A binding in orbitofrontal, prefrontal, parietal, and motor cortical regions.46 A study analyzing 10 catatonic patients found decreased density of GABA-A receptors in the left sensorimotor cortex compared to psychiatric and healthy controls.47
Other neurotransmitters, such as glutamate, at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDAR) have been hypothesized to be hyperactive, causing downstream dysregulation of GABA functioning.48 However, the exact connection between delirious mania and all these receptors and neurotransmitters remains unknown.
Encephalitis hypothesis. The relationship between delirious mania and autoimmune encephalitis suggests delirious mania has etiologies other than a primary psychiatric illness. In a 2020 retrospective study49 that analyzed 79 patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis, 25.3% met criteria for delirious mania, and 95% of these patients had catatonic features. Dalmau et al50 found that in many cases, patients tend to respond to ECT; in a cases series of 3 patients, 2 responded to benzodiazepines.
COVID-19 hypothesis. The SARS-CoV-2 virion has been associated with many neuropsychiatric complications, including mood, psychotic, and neurocognitive disorders.51,52 There also have been cases of COVID-19–induced catatonia.53-55 One case of delirious mania in a patient with COVID-19 has been reported.21 The general mechanism has been proposed to be related to the stimulation of the proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6, which the virus produces in large quantities.56 These cytokines have been linked to psychosis and other psychiatric disorders.57 The patient with COVID-19–induced delirious mania had elevated inflammatory markers, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, ferritin, and D-dimer, which supports a proinflammatory state. This patient had a complete resolution of symptoms with ECT.21
Management: Benzodiazepines and ECT
A step-by-step algorithm for managing delirious mania is outlined in the Figure. Regardless of the underlining etiology, management of delirious mania consists of benzodiazepines (lorazepam and diazepam); prompt use of ECT, particularly for patients who do not improve with large doses of lorazepam; or (if applicable) continued treatment of the underlining medical condition, which does not preclude the use of benzodiazepines or ECT. Recent reports27,58 have described details for using ECT for delirious mania, highlighting the use of high-energy dosing, bilateral electrode placement, and frequent sessions.

Continue to: Knowing which medications...
Knowing which medications to avoid is as important as knowing which agents to administer. Be vigilant in avoiding high-potency antipsychotics, as these medications can worsen extrapyramidal symptoms and may precipitate seizures or neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS).28 Anticholinergic agents should also be avoided because they worsen confusion. Although lithium is effective in BD, in delirious mania, high doses of lithium and haloperidol may cause severe encephalopathic syndromes, with symptoms that can include lethargy, tremors, cerebellar dysfunction, and worsened confusion; it may also cause widespread and irreversible brain damage.59
Due to long periods of hyperactivity, withdrawal, and diaphoresis, patients with delirious mania may be severely dehydrated with metabolic derangements, including elevated CPK due to rhabdomyolysis from prolonged exertion, IM antipsychotics, or rigidity. To prevent acute renal failure, this must be immediately addressed with rapid fluid resuscitation and electrolyte repletion.61
Benzodiazepines. The rapid use of lorazepam should be initiated when delirious mania is suspected. Doses of 6 to 20 mg have been reported to be effective if tolerated.5,20 Typically, high-dose lorazepam will not have the sedative effect that would normally occur in a patient who does not have delirious mania.2 Lorazepam should be titrated until full resolution of symptoms. Doses up to 30 mg have been reported as effective and tolerable.62 In our literature review, 50% of patients (18/36) responded or partially responded to lorazepam. However, only 3 case reports documented a complete remission with lorazepam, and many patients needed ECT for remission of symptoms.
ECT is generally reserved for patients who are not helped by benzodiazepine therapy, which is estimated to be up to 20%.5 ECT is highly effective in delirious mania, with remission rates ranging from 80% to 100%.1 ECT is also effective in acute nondelirious mania (comparable to depression); however, it is only used in a small minority of cases (0.2% to 12%).35 In our review, 58% of cases (21/36) reported using ECT, and in all cases it resulted in complete remission.
A dramatic improvement can be seen even after a single ECT session, though most patients show improvement after 4 sessions or 3 to 7 days.1,2,5 In our review, most patients received 4 to 12 sessions until achieving complete remission.
Continue to: No RCTs have evaluated...
No RCTs have evaluated ECT electrode placement in patients with delirious mania. However, several RCTs have investigated electrode placement in patients with acute nondelirious mania. Hiremani et al63 found that bitemporal placement had a more rapid response rate than bifrontal placement, but there was no overall difference in response rate. Barekatain et al64 found no difference between these 2 bilateral approaches. Many of the delirious mania cases report using a bilateral placement (including 42% of the ECT cases in our review) due to the emergent need for rapid relief of symptoms, which is especially necessary if the patient is experiencing hemodynamic instability, excessive violence, risk for self-harm, worsening delirium, or resistance to lorazepam.
Prognosis: Often fatal if left untreated
Patients with delirious mania are at high risk to progress to a more severe form of NMS or malignant catatonia. Therefore, high-potency antipsychotics should be avoided; mortality can be elevated from 60% without antipsychotics to 78% with antipsychotics.4 Some researchers estimate 75% to 78% of cases of delirious mania can be fatal if left untreated.3,6
Bottom Line
Delirious mania is routinely mistaken for more conventional manic or psychotic disorders. Clinicians need to be able to rapidly recognize the symptoms of this syndrome, which include mania, psychosis, delirium, and possible catatonia, so they can avoid administering toxic agents and instead initiate effective treatments such as benzodiazepines and electroconvulsive therapy.
Related Resources
- Arsan C, Baker C, Wong J, et al. Delirious mania: an approach to diagnosis and treatment. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2021;23(1):20f02744. doi:10.4088/PCC.20f02744
- Lamba G, Kennedy EA, Vu CP. Case report: ECT for delirious mania. Clinical Psychiatry News. December 14, 2021. https://www.mdedge.com/psychiatry/article/249909/bipolar-disorder/case-report-ect-delirious-mania
Drug Brand Names
Diazepam • Valium
Haloperidol • Haldol
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Lorazepam • Ativan
1. Fink M. Delirious mania. Bipolar Disord. 1999;1(1):54-60.
2. Karmacharya R, England ML, Ongür D. Delirious mania: clinical features and treatment response. J Affect Disord. 2008;109(3):312-316.
3. Friedman RS, Mufson MJ, Eisenberg TD, et al. Medically and psychiatrically ill: the challenge of delirious mania. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2003;11(2):91-98.
4. Mann SC, Caroff SN, Bleier HR, et al. Lethal catatonia. Am J Psychiatry. 1986;143(11):1374-1381.
5. Detweiler MB, Mehra A, Rowell T, et al. Delirious mania and malignant catatonia: a report of 3 cases and review. Psychiatr Q. 2009;80(1):23-40.
6. Bell L. On a form of disease resembling some advanced stages of mania and fever. American Journal of Insanity. 1849;6(2):97-127.
7. Carlson GA, Goodwin FK. The stages of mania. A longitudinal analysis of the manic episode. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1973;28(2):221-228.
8. Bond TC. Recognition of acute delirious mania. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1980;37(5):553-554.
9. Hutchinson G, David A. Manic pseudo-delirium - two case reports. Behav Neurol. 1997;10(1):21-23.
10. Bush G, Fink M, Petrides G, et al. Catatonia. I. Rating scale and standardized examination. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1996;93(2):129-136.
11. Bush G, Fink M, Petrides G, et al. Catatonia. II. Treatment with lorazepam and electroconvulsive therapy. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1996;93(2):137-143.
12. Cordeiro CR, Saraiva R, Côrte-Real B, et al. When the bell rings: clinical features of Bell’s mania. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2020;22(2):19l02511. doi:10.4088/PCC.19l02511
13. Yeo LX, Kuo TC, Hu KC, et al. Lurasidone-induced delirious mania. Am J Ther. 2019;26(6):e786-e787.
14. Jung WY, Lee BD. Quetiapine treatment for delirious mania in a military soldier. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;12(2):PCC.09l00830. doi:10.4088/PCC.09l00830yel
15. Wahid N, Chin G, Turner AH, et al. Clinical response of clozapine as a treatment for delirious mania. Ment Illn. 2017;9(2):7182. doi:10.4081/mi.2017.7182
16. Taylor MA, Fink M. Catatonia in psychiatric classification: a home of its own. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(7):1233-1241.
17. Danivas V, Behere RV, Varambally S, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy in the treatment of delirious mania: a report of 2 patients. J ECT. 2010;26(4):278-279.
18. O’Callaghan N, McDonald C, Hallahan B. Delirious mania intractable to treatment. Ir J Psychol Med. 2016;33(2):129-132.
19. Vasudev K, Grunze H. What works for delirious catatonic mania? BMJ Case Rep. 2010;2010:bcr0220102713. doi:10.1136/bcr.02.2010.2713
20. Jacobowski NL, Heckers S, Bobo WV. Delirious mania: detection, diagnosis, and clinical management in the acute setting. J Psychiatr Pract. 2013;19(1):15-28.
21. Reinfeld S, Yacoub A. A case of delirious mania induced by COVID-19 treated with electroconvulsive therapy. J ECT. 2021;37(4):e38-e39.
22. Lee BS, Huang SS, Hsu WY, et al. Clinical features of delirious mania: a series of five cases and a brief literature review. BMC Psychiatry. 2012;12:65. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-12-65
23. Bipeta R, Khan MA. Delirious mania: can we get away with this concept? A case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2012;2012:720354. doi:10.1155/2012/720354
24. Nunes AL, Cheniaux E. Delirium and mania with catatonic features in a Brazilian patient: response to ECT. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2014;26(1):E1-E3.
25. Tegin C, Kalayil G, Lippmann S. Electroconvulsive therapy and delirious catatonic mania. J ECT. 2017;33(4):e33-e34.
26. Melo AL, Serra M. Delirious mania and catatonia. Bipolar Disord. 2020;22(6):647-649.
27. Fink M. Expanding the catatonia tent: recognizing electroconvulsive therapy responsive syndromes. J ECT. 2021;37(2):77-79.
28. Fink M. Electroconvulsive Therapy: A Guide for Professionals and Their Patients. Oxford University Press; 2009.
29. Fink M, Taylor MA. The many varieties of catatonia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2001;251 Suppl 1:I8-I13.
30. Vivanti A, Harvey K, Ash S, et al. Clinical assessment of dehydration in older people admitted to hospital: what are the strongest indicators? Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2008;47(3):340-355.
31. Ware MR, Feller DB, Hall KL. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome: diagnosis and management. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2018;20(1):17r02185. doi:10.4088/PCC.17r0218
32. Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12(3):189-198.
33. Taylor MA, Abrams R. The phenomenology of mania. A new look at some old patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1973;29(4):520-522.
34. Klerman GL. The spectrum of mania. Compr Psychiatry. 1981;22(1):11-20.
35. Elias A, Thomas N, Sackeim HA. Electroconvulsive therapy in mania: a review of 80 years of clinical experience. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(3):229-239.
36. Thom RP, Levy-Carrick NC, Bui M, et al. Delirium. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176(10):785-793.
37. Charlton BG, Kavanau JL. Delirium and psychotic symptoms--an integrative model. Med Hypotheses. 2002;58(1):24-27.
38. Kramp P, Bolwig TG. Electroconvulsive therapy in acute delirious states. Compr Psychiatry. 1981;22(4):368-371.
39. Mash DC. Excited delirium and sudden death: a syndromal disorder at the extreme end of the neuropsychiatric continuum. Front Physiol. 2016;7:435.
40. Strawn JR, Keck PE Jr, Caroff SN. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(6):870-876.
41. Charney DS. Monoamine dysfunction and the pathophysiology and treatment of depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998;59 Suppl 14:11-14.
42. Shiah IS, Yatham LN. Serotonin in mania and in the mechanism of action of mood stabilizers: a review of clinical studies. Bipolar Disord. 2000;2(2):77-92.
43. Dalley JW, Roiser JP. Dopamine, serotonin and impulsivity. Neuroscience. 2012;215:42-58.
44. Maldonado JR. Pathoetiological model of delirium: a comprehensive understanding of the neurobiology of delirium and an evidence-based approach to prevention and treatment. Crit Care Clin. 2008;24(4):789-856, ix.
45. Maldonado JR. Neuropathogenesis of delirium: review of current etiologic theories and common pathways. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2013;21(12):1190-1222.
46. Rasmussen SA, Mazurek MF, Rosebush PI. Catatonia: our current understanding of its diagnosis, treatment and pathophysiology. World J Psychiatry. 2016;6(4):391-398.
47. Northoff G, Steinke R, Czcervenka C, et al. Decreased density of GABA-A receptors in the left sensorimotor cortex in akinetic catatonia: investigation of in vivo benzodiazepine receptor binding. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999;67(4):445-450.
48. Daniels J. Catatonia: clinical aspects and neurobiological correlates. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2009;21(4):371-380.
49. Restrepo-Martínez M, Chacón-González J, Bayliss L, et al. Delirious mania as a neuropsychiatric presentation in patients with anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis. Psychosomatics. 2020;61(1):64-69.
50. Dalmau J, Armangué T, Planagumà J, et al. An update on anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis for neurologists and psychiatrists: mechanisms and models. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(11):1045-1057.
51. Steardo L Jr, Steardo L, Verkhratsky A. Psychiatric face of COVID-19. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10(1):261.
52. Iqbal Y, Al Abdulla MA, Albrahim S, et al. Psychiatric presentation of patients with acute SARS-CoV-2 infection: a retrospective review of 50 consecutive patients seen by a consultation-liaison psychiatry team. BJPsych Open. 2020;6(5):e109.
53. Gouse BM, Spears WE, Nieves Archibald A, et al. Catatonia in a hospitalized patient with COVID-19 and proposed immune-mediated mechanism. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;89:529-530.
54. Caan MP, Lim CT, Howard M. A case of catatonia in a man with COVID-19. Psychosomatics. 2020;61(5):556-560.
55. Zain SM, Muthukanagaraj P, Rahman N. Excited catatonia - a delayed neuropsychiatric complication of COVID-19 infection. Cureus. 2021;13(3):e13891.
56. Chowdhury MA, Hossain N, Kashem MA, et al. Immune response in COVID-19: a review. J Infect Public Health. 2020;13(11):1619-1629.
57. Radhakrishnan R, Kaser M, Guloksuz S. The link between the immune system, environment, and psychosis. Schizophr Bull. 2017;43(4):693-697.
58. Fink M, Kellner CH, McCall WV. Optimizing ECT technique in treating catatonia. J ECT. 2016;32(3):149-150.
59. Cohen WJ, Cohen NH. Lithium carbonate, haloperidol, and irreversible brain damage. JAMA. 1974;230(9):1283-1287.
60. Davis MJ, de Nesnera A, Folks DG. Confused and nearly naked after going on spending sprees. Current Psychiatry. 2014;13(7):56-62.
61. Stanley M, Chippa V, Aeddula NR, et al. Rhabdomyolysis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
62. Fink M, Taylor MA. The catatonia syndrome: forgotten but not gone. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(11):1173-1177.
63. Hiremani RM, Thirthalli J, Tharayil BS, et al. Double-blind randomized controlled study comparing short-term efficacy of bifrontal and bitemporal electroconvulsive therapy in acute mania. Bipolar Disord. 2008;10(6):701-707.
64. Barekatain M, Jahangard L, Haghighi M, et al. Bifrontal versus bitemporal electroconvulsive therapy in severe manic patients. J ECT. 2008;24(3):199-202.
1. Fink M. Delirious mania. Bipolar Disord. 1999;1(1):54-60.
2. Karmacharya R, England ML, Ongür D. Delirious mania: clinical features and treatment response. J Affect Disord. 2008;109(3):312-316.
3. Friedman RS, Mufson MJ, Eisenberg TD, et al. Medically and psychiatrically ill: the challenge of delirious mania. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2003;11(2):91-98.
4. Mann SC, Caroff SN, Bleier HR, et al. Lethal catatonia. Am J Psychiatry. 1986;143(11):1374-1381.
5. Detweiler MB, Mehra A, Rowell T, et al. Delirious mania and malignant catatonia: a report of 3 cases and review. Psychiatr Q. 2009;80(1):23-40.
6. Bell L. On a form of disease resembling some advanced stages of mania and fever. American Journal of Insanity. 1849;6(2):97-127.
7. Carlson GA, Goodwin FK. The stages of mania. A longitudinal analysis of the manic episode. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1973;28(2):221-228.
8. Bond TC. Recognition of acute delirious mania. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1980;37(5):553-554.
9. Hutchinson G, David A. Manic pseudo-delirium - two case reports. Behav Neurol. 1997;10(1):21-23.
10. Bush G, Fink M, Petrides G, et al. Catatonia. I. Rating scale and standardized examination. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1996;93(2):129-136.
11. Bush G, Fink M, Petrides G, et al. Catatonia. II. Treatment with lorazepam and electroconvulsive therapy. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1996;93(2):137-143.
12. Cordeiro CR, Saraiva R, Côrte-Real B, et al. When the bell rings: clinical features of Bell’s mania. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2020;22(2):19l02511. doi:10.4088/PCC.19l02511
13. Yeo LX, Kuo TC, Hu KC, et al. Lurasidone-induced delirious mania. Am J Ther. 2019;26(6):e786-e787.
14. Jung WY, Lee BD. Quetiapine treatment for delirious mania in a military soldier. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;12(2):PCC.09l00830. doi:10.4088/PCC.09l00830yel
15. Wahid N, Chin G, Turner AH, et al. Clinical response of clozapine as a treatment for delirious mania. Ment Illn. 2017;9(2):7182. doi:10.4081/mi.2017.7182
16. Taylor MA, Fink M. Catatonia in psychiatric classification: a home of its own. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(7):1233-1241.
17. Danivas V, Behere RV, Varambally S, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy in the treatment of delirious mania: a report of 2 patients. J ECT. 2010;26(4):278-279.
18. O’Callaghan N, McDonald C, Hallahan B. Delirious mania intractable to treatment. Ir J Psychol Med. 2016;33(2):129-132.
19. Vasudev K, Grunze H. What works for delirious catatonic mania? BMJ Case Rep. 2010;2010:bcr0220102713. doi:10.1136/bcr.02.2010.2713
20. Jacobowski NL, Heckers S, Bobo WV. Delirious mania: detection, diagnosis, and clinical management in the acute setting. J Psychiatr Pract. 2013;19(1):15-28.
21. Reinfeld S, Yacoub A. A case of delirious mania induced by COVID-19 treated with electroconvulsive therapy. J ECT. 2021;37(4):e38-e39.
22. Lee BS, Huang SS, Hsu WY, et al. Clinical features of delirious mania: a series of five cases and a brief literature review. BMC Psychiatry. 2012;12:65. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-12-65
23. Bipeta R, Khan MA. Delirious mania: can we get away with this concept? A case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2012;2012:720354. doi:10.1155/2012/720354
24. Nunes AL, Cheniaux E. Delirium and mania with catatonic features in a Brazilian patient: response to ECT. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2014;26(1):E1-E3.
25. Tegin C, Kalayil G, Lippmann S. Electroconvulsive therapy and delirious catatonic mania. J ECT. 2017;33(4):e33-e34.
26. Melo AL, Serra M. Delirious mania and catatonia. Bipolar Disord. 2020;22(6):647-649.
27. Fink M. Expanding the catatonia tent: recognizing electroconvulsive therapy responsive syndromes. J ECT. 2021;37(2):77-79.
28. Fink M. Electroconvulsive Therapy: A Guide for Professionals and Their Patients. Oxford University Press; 2009.
29. Fink M, Taylor MA. The many varieties of catatonia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2001;251 Suppl 1:I8-I13.
30. Vivanti A, Harvey K, Ash S, et al. Clinical assessment of dehydration in older people admitted to hospital: what are the strongest indicators? Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2008;47(3):340-355.
31. Ware MR, Feller DB, Hall KL. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome: diagnosis and management. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2018;20(1):17r02185. doi:10.4088/PCC.17r0218
32. Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12(3):189-198.
33. Taylor MA, Abrams R. The phenomenology of mania. A new look at some old patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1973;29(4):520-522.
34. Klerman GL. The spectrum of mania. Compr Psychiatry. 1981;22(1):11-20.
35. Elias A, Thomas N, Sackeim HA. Electroconvulsive therapy in mania: a review of 80 years of clinical experience. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(3):229-239.
36. Thom RP, Levy-Carrick NC, Bui M, et al. Delirium. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176(10):785-793.
37. Charlton BG, Kavanau JL. Delirium and psychotic symptoms--an integrative model. Med Hypotheses. 2002;58(1):24-27.
38. Kramp P, Bolwig TG. Electroconvulsive therapy in acute delirious states. Compr Psychiatry. 1981;22(4):368-371.
39. Mash DC. Excited delirium and sudden death: a syndromal disorder at the extreme end of the neuropsychiatric continuum. Front Physiol. 2016;7:435.
40. Strawn JR, Keck PE Jr, Caroff SN. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(6):870-876.
41. Charney DS. Monoamine dysfunction and the pathophysiology and treatment of depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998;59 Suppl 14:11-14.
42. Shiah IS, Yatham LN. Serotonin in mania and in the mechanism of action of mood stabilizers: a review of clinical studies. Bipolar Disord. 2000;2(2):77-92.
43. Dalley JW, Roiser JP. Dopamine, serotonin and impulsivity. Neuroscience. 2012;215:42-58.
44. Maldonado JR. Pathoetiological model of delirium: a comprehensive understanding of the neurobiology of delirium and an evidence-based approach to prevention and treatment. Crit Care Clin. 2008;24(4):789-856, ix.
45. Maldonado JR. Neuropathogenesis of delirium: review of current etiologic theories and common pathways. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2013;21(12):1190-1222.
46. Rasmussen SA, Mazurek MF, Rosebush PI. Catatonia: our current understanding of its diagnosis, treatment and pathophysiology. World J Psychiatry. 2016;6(4):391-398.
47. Northoff G, Steinke R, Czcervenka C, et al. Decreased density of GABA-A receptors in the left sensorimotor cortex in akinetic catatonia: investigation of in vivo benzodiazepine receptor binding. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999;67(4):445-450.
48. Daniels J. Catatonia: clinical aspects and neurobiological correlates. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2009;21(4):371-380.
49. Restrepo-Martínez M, Chacón-González J, Bayliss L, et al. Delirious mania as a neuropsychiatric presentation in patients with anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis. Psychosomatics. 2020;61(1):64-69.
50. Dalmau J, Armangué T, Planagumà J, et al. An update on anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis for neurologists and psychiatrists: mechanisms and models. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(11):1045-1057.
51. Steardo L Jr, Steardo L, Verkhratsky A. Psychiatric face of COVID-19. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10(1):261.
52. Iqbal Y, Al Abdulla MA, Albrahim S, et al. Psychiatric presentation of patients with acute SARS-CoV-2 infection: a retrospective review of 50 consecutive patients seen by a consultation-liaison psychiatry team. BJPsych Open. 2020;6(5):e109.
53. Gouse BM, Spears WE, Nieves Archibald A, et al. Catatonia in a hospitalized patient with COVID-19 and proposed immune-mediated mechanism. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;89:529-530.
54. Caan MP, Lim CT, Howard M. A case of catatonia in a man with COVID-19. Psychosomatics. 2020;61(5):556-560.
55. Zain SM, Muthukanagaraj P, Rahman N. Excited catatonia - a delayed neuropsychiatric complication of COVID-19 infection. Cureus. 2021;13(3):e13891.
56. Chowdhury MA, Hossain N, Kashem MA, et al. Immune response in COVID-19: a review. J Infect Public Health. 2020;13(11):1619-1629.
57. Radhakrishnan R, Kaser M, Guloksuz S. The link between the immune system, environment, and psychosis. Schizophr Bull. 2017;43(4):693-697.
58. Fink M, Kellner CH, McCall WV. Optimizing ECT technique in treating catatonia. J ECT. 2016;32(3):149-150.
59. Cohen WJ, Cohen NH. Lithium carbonate, haloperidol, and irreversible brain damage. JAMA. 1974;230(9):1283-1287.
60. Davis MJ, de Nesnera A, Folks DG. Confused and nearly naked after going on spending sprees. Current Psychiatry. 2014;13(7):56-62.
61. Stanley M, Chippa V, Aeddula NR, et al. Rhabdomyolysis. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
62. Fink M, Taylor MA. The catatonia syndrome: forgotten but not gone. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(11):1173-1177.
63. Hiremani RM, Thirthalli J, Tharayil BS, et al. Double-blind randomized controlled study comparing short-term efficacy of bifrontal and bitemporal electroconvulsive therapy in acute mania. Bipolar Disord. 2008;10(6):701-707.
64. Barekatain M, Jahangard L, Haghighi M, et al. Bifrontal versus bitemporal electroconvulsive therapy in severe manic patients. J ECT. 2008;24(3):199-202.
