User login
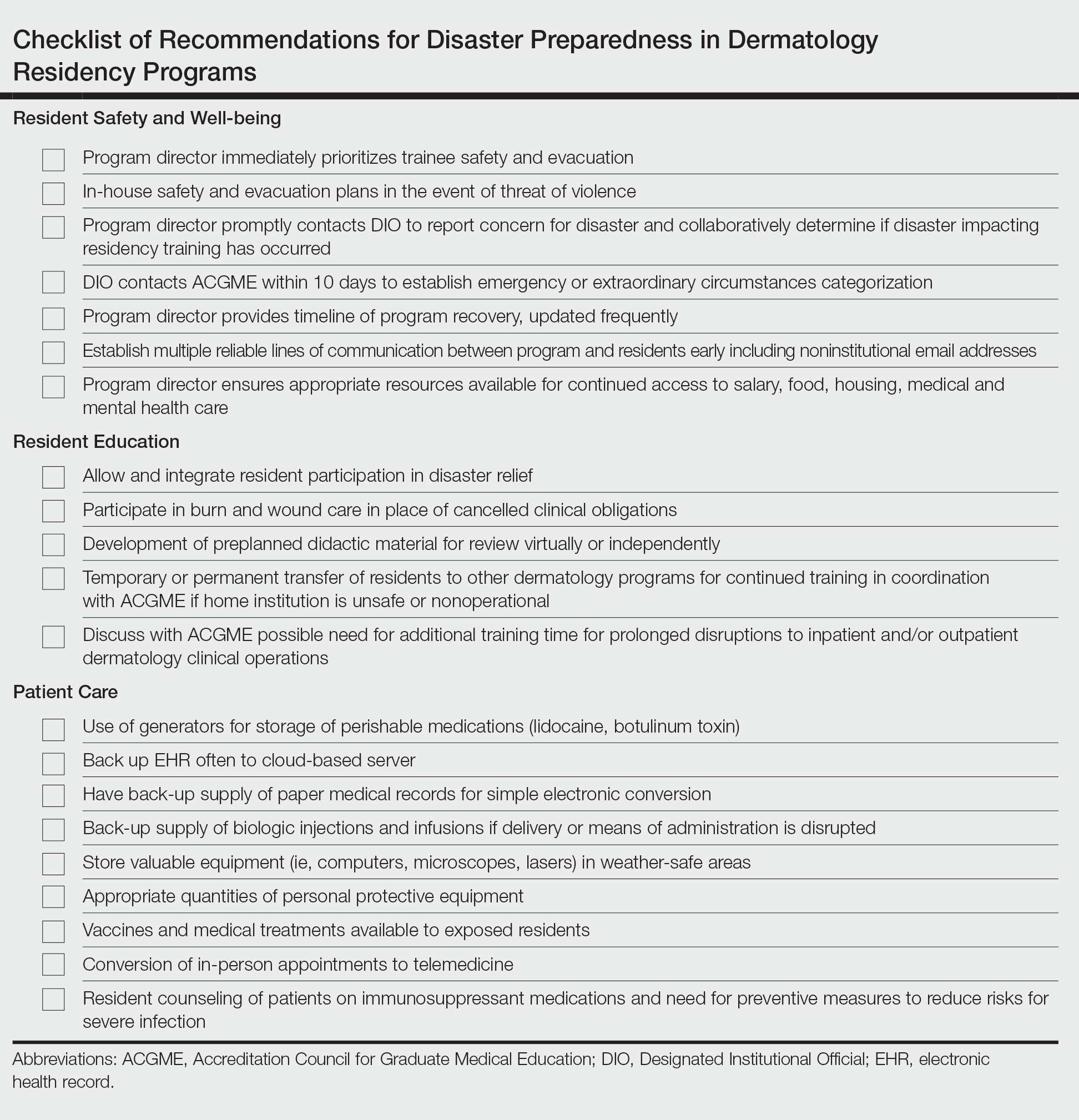
In an age of changing climate and emerging global pandemics, the ability of residency programs to prepare for and adapt to potential disasters may be paramount in preserving the training of physicians. The current literature regarding residency program disaster preparedness, which focuses predominantly on hurricanes and COVID-19,1-8 is lacking in recommendations specific to dermatology residency programs. Likewise, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) guidelines9 do not address dermatology-specific concerns in disaster preparedness or response. Herein, we propose recommendations to mitigate the impact of various types of disasters on dermatology residency programs and their trainees with regard to resident safety and wellness, resident education, and patient care (Table).
Resident Safety and Wellness
Role of the Program Director—The role of the program director is critical, serving as a figure of structure and reassurance.4,7,10 Once concern of disaster arises, the program director should contact the Designated Institutional Official (DIO) to express concerns about possible disruptions to resident training. The DIO should then contact the ACGME within 10 days to report the disaster and submit a request for emergency (eg, pandemic) or extraordinary circumstances (eg, natural disaster) categorization.4,9 Program directors should promptly prepare plans for program reconfiguration and resident transfers in alignment with ACGME requirements to maintain evaluation and completion of core competencies of training during disasters.9 Program directors should prioritize the safety of trainees during the immediate threat with clear guidelines on sheltering, evacuations, or quarantines; a timeline of program recovery based on communication with residents, faculty, and administration should then be established.10,11
Communication—Establishing a strong line of communication between program directors and residents is paramount. Collection of emergency noninstitutional contact information, establishment of a centralized website for information dissemination, use of noninstitutional email and proxy servers outside of the location of impact, social media updates, on-site use of 2-way radios, and program-wide conference calls when possible should be strongly considered as part of the disaster response.2-4,12,13
Resident Accommodations and Mental Health—If training is disrupted, residents should be reassured of continued access to salary, housing, food, or other resources as necessary.3,4,11 There should be clear contingency plans if residents need to leave the program for extended periods of time due to injury, illness, or personal circumstances. Although relevant in all types of disasters, resident mental health and response to trauma also must be addressed. Access to counseling, morale-building opportunities (eg, resident social events), and screening for depression or posttraumatic stress disorder may help promote well-being among residents following traumatic events.14
Resident Education
Participation in Disaster Relief—Residents may seek to aid in the disaster response, which may prove challenging in the setting of programs with high patient volume.4 In coordination with the ACGME and graduate medical education governing bodies, program directors should consider how residents may fulfill dermatology training requirements in conjunction with disaster relief efforts, such as working in an inpatient setting or providing wound care.10
Continued Didactic Education—The use of online learning and conference calls for continuing the dermatology curriculum is an efficient means to maintaining resident education when meeting in person poses risks to residents.15 Projections of microscopy images, clinical photographs, or other instructional materials allow for continued instruction on resident examination, histopathology, and diagnostic skills.
Continued Clinical Training—If the home institution cannot support the operation of dermatology clinics, residents should be guaranteed continued training at other institutions. Agreements with other dermatology programs, community hospitals, or private dermatology practices should be established in advance, with consideration given to the number of residents a program can support, funding transfers, and credentialing requirements.2,4,5
Prolonged Disruptions—Nonessential departments of medical institutions may cease to function during war or mass casualty disasters, and it may be unsafe to send dermatology residents to other institutions or clinical areas. If the threat is prolonged, programs may need to consider allowing current residents a longer duration of training despite potential overlap with incoming dermatology residents.7
Patient Care
Disruptions to Clinic Operations—Regarding threats of violence, dangerous exposures, or natural disasters, there should be clear guidelines on sheltering in the clinical setting or stabilizing patients during a procedure.11 Equipment used by residents such as laptops, microscopes, and treatment devices (eg, lasers) should be stored in weather-safe locations that would not be notably impacted by moisture or structural damage to the clinic building. If electricity or internet access are compromised, paper medical records should be available to residents to continue clinical operations. Electronic health records used by residents should regularly be backed up on remote servers or cloud storage to allow continued access to patient health information if on-site servers are not functional.12 If disruptions are prolonged, residency program administration should coordinate with the institution to ensure there is adequate supply and storage of medications (eg, lidocaine, botulinum toxin) as well as a continued means of delivering biologic medications to patients and an ability to obtain laboratory or dermatopathology services.
In-Person Appointments vs Telemedicine—There are benefits to both residency training and patient care when physicians are able to perform in-person examinations, biopsies, and in-office treatments.16 Programs should ensure an adequate supply of personal protective equipment to continue in-office appointments, vaccinations, and medical care if a resident or other members of the team are exposed to an infectious disease.7 If in-person appointments are limited or impossible, telemedicine capabilities may still allow residents to meet program requirements.7,10,15 However, reduced patient volume due to decreased elective visits or procedures may complicate the fulfillment of clinical requirements, which may need to be adjusted in the wake of a disaster.7
Use of Immunosuppressive Therapies—Residency programs should address the risks of prescribing immunosuppressive therapies (eg, biologics) during an infectious threat with their residents and encourage trainees to counsel patients on the importance of preventative measures to reduce risks for severe infection.17
Final Thoughts
- Davis W. Hurricane Katrina: the challenge to graduate medical education. Ochsner J. 2006;6:39.
- Cefalu CA, Schwartz RS. Salvaging a geriatric medicine academic program in disaster mode—the LSU training program post-Katrina.J Natl Med Assoc. 2007;99:590-596.
- Ayyala R. Lessons from Katrina: a program director’s perspective. Ophthalmology. 2007;114:1425-1426.
- Wiese JG. Leadership in graduate medical education: eleven steps instrumental in recovering residency programs after a disaster. Am J Med Sci. 2008;336:168-173.
- Griffies WS. Post-Katrina stabilization of the LSU/Ochsner Psychiatry Residency Program: caveats for disaster preparedness. Acad Psychiatry. 2009;33:418-422.
- Kearns DG, Chat VS, Uppal S, et al. Applying to dermatology residency during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1214-1215.
- Matthews JB, Blair PG, Ellison EC, et al. Checklist framework for surgical education disaster plans. J Am Coll Surg. 2021;233:557-563.
- Litchman GH, Marson JW, Rigel DS. The continuing impact of COVID-19 on dermatology practice: office workflow, economics, and future implications. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:576-579.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Sponsoring institution emergency categorization. Accessed October 20, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/covid-19/sponsoring-institution-emergency-categorization/
- Li YM, Galimberti F, Abrouk M, et al. US dermatology resident responses about the COVID-19 pandemic: results from a nationwide survey. South Med J. 2020;113:462-465.
- Newman B, Gallion C. Hurricane Harvey: firsthand perspectives for disaster preparedness in graduate medical education. Acad Med. 2019;94:1267-1269.
- Pero CD, Pou AM, Arriaga MA, et al. Post-Katrina: study in crisis-related program adaptability. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008;138:394-397.
- Hattaway R, Singh N, Rais-Bahrami S, et al. Adaptations of dermatology residency programs to changes in medical education amid the COVID-19 pandemic: virtual opportunities and social media. SKIN. 2021;5:94-100.
- Hillier K, Paskaradevan J, Wilkes JK, et al. Disaster plans: resident involvement and well-being during Hurricane Harvey. J Grad Med Educ. 2019;11:129-131.
- Samimi S, Choi J, Rosman IS, et al. Impact of COVID-19 on dermatology residency. Dermatol Clin. 2021;39:609-618.
- Bastola M, Locatis C, Fontelo P. Diagnostic reliability of in-person versus remote dermatology: a meta-analysis. Telemed J E Health. 2021;27:247-250.
- Bashyam AM, Feldman SR. Should patients stop their biologic treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic? J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;31:317-318.
In an age of changing climate and emerging global pandemics, the ability of residency programs to prepare for and adapt to potential disasters may be paramount in preserving the training of physicians. The current literature regarding residency program disaster preparedness, which focuses predominantly on hurricanes and COVID-19,1-8 is lacking in recommendations specific to dermatology residency programs. Likewise, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) guidelines9 do not address dermatology-specific concerns in disaster preparedness or response. Herein, we propose recommendations to mitigate the impact of various types of disasters on dermatology residency programs and their trainees with regard to resident safety and wellness, resident education, and patient care (Table).

Resident Safety and Wellness
Role of the Program Director—The role of the program director is critical, serving as a figure of structure and reassurance.4,7,10 Once concern of disaster arises, the program director should contact the Designated Institutional Official (DIO) to express concerns about possible disruptions to resident training. The DIO should then contact the ACGME within 10 days to report the disaster and submit a request for emergency (eg, pandemic) or extraordinary circumstances (eg, natural disaster) categorization.4,9 Program directors should promptly prepare plans for program reconfiguration and resident transfers in alignment with ACGME requirements to maintain evaluation and completion of core competencies of training during disasters.9 Program directors should prioritize the safety of trainees during the immediate threat with clear guidelines on sheltering, evacuations, or quarantines; a timeline of program recovery based on communication with residents, faculty, and administration should then be established.10,11
Communication—Establishing a strong line of communication between program directors and residents is paramount. Collection of emergency noninstitutional contact information, establishment of a centralized website for information dissemination, use of noninstitutional email and proxy servers outside of the location of impact, social media updates, on-site use of 2-way radios, and program-wide conference calls when possible should be strongly considered as part of the disaster response.2-4,12,13
Resident Accommodations and Mental Health—If training is disrupted, residents should be reassured of continued access to salary, housing, food, or other resources as necessary.3,4,11 There should be clear contingency plans if residents need to leave the program for extended periods of time due to injury, illness, or personal circumstances. Although relevant in all types of disasters, resident mental health and response to trauma also must be addressed. Access to counseling, morale-building opportunities (eg, resident social events), and screening for depression or posttraumatic stress disorder may help promote well-being among residents following traumatic events.14
Resident Education
Participation in Disaster Relief—Residents may seek to aid in the disaster response, which may prove challenging in the setting of programs with high patient volume.4 In coordination with the ACGME and graduate medical education governing bodies, program directors should consider how residents may fulfill dermatology training requirements in conjunction with disaster relief efforts, such as working in an inpatient setting or providing wound care.10
Continued Didactic Education—The use of online learning and conference calls for continuing the dermatology curriculum is an efficient means to maintaining resident education when meeting in person poses risks to residents.15 Projections of microscopy images, clinical photographs, or other instructional materials allow for continued instruction on resident examination, histopathology, and diagnostic skills.
Continued Clinical Training—If the home institution cannot support the operation of dermatology clinics, residents should be guaranteed continued training at other institutions. Agreements with other dermatology programs, community hospitals, or private dermatology practices should be established in advance, with consideration given to the number of residents a program can support, funding transfers, and credentialing requirements.2,4,5
Prolonged Disruptions—Nonessential departments of medical institutions may cease to function during war or mass casualty disasters, and it may be unsafe to send dermatology residents to other institutions or clinical areas. If the threat is prolonged, programs may need to consider allowing current residents a longer duration of training despite potential overlap with incoming dermatology residents.7
Patient Care
Disruptions to Clinic Operations—Regarding threats of violence, dangerous exposures, or natural disasters, there should be clear guidelines on sheltering in the clinical setting or stabilizing patients during a procedure.11 Equipment used by residents such as laptops, microscopes, and treatment devices (eg, lasers) should be stored in weather-safe locations that would not be notably impacted by moisture or structural damage to the clinic building. If electricity or internet access are compromised, paper medical records should be available to residents to continue clinical operations. Electronic health records used by residents should regularly be backed up on remote servers or cloud storage to allow continued access to patient health information if on-site servers are not functional.12 If disruptions are prolonged, residency program administration should coordinate with the institution to ensure there is adequate supply and storage of medications (eg, lidocaine, botulinum toxin) as well as a continued means of delivering biologic medications to patients and an ability to obtain laboratory or dermatopathology services.
In-Person Appointments vs Telemedicine—There are benefits to both residency training and patient care when physicians are able to perform in-person examinations, biopsies, and in-office treatments.16 Programs should ensure an adequate supply of personal protective equipment to continue in-office appointments, vaccinations, and medical care if a resident or other members of the team are exposed to an infectious disease.7 If in-person appointments are limited or impossible, telemedicine capabilities may still allow residents to meet program requirements.7,10,15 However, reduced patient volume due to decreased elective visits or procedures may complicate the fulfillment of clinical requirements, which may need to be adjusted in the wake of a disaster.7
Use of Immunosuppressive Therapies—Residency programs should address the risks of prescribing immunosuppressive therapies (eg, biologics) during an infectious threat with their residents and encourage trainees to counsel patients on the importance of preventative measures to reduce risks for severe infection.17
Final Thoughts
In an age of changing climate and emerging global pandemics, the ability of residency programs to prepare for and adapt to potential disasters may be paramount in preserving the training of physicians. The current literature regarding residency program disaster preparedness, which focuses predominantly on hurricanes and COVID-19,1-8 is lacking in recommendations specific to dermatology residency programs. Likewise, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) guidelines9 do not address dermatology-specific concerns in disaster preparedness or response. Herein, we propose recommendations to mitigate the impact of various types of disasters on dermatology residency programs and their trainees with regard to resident safety and wellness, resident education, and patient care (Table).

Resident Safety and Wellness
Role of the Program Director—The role of the program director is critical, serving as a figure of structure and reassurance.4,7,10 Once concern of disaster arises, the program director should contact the Designated Institutional Official (DIO) to express concerns about possible disruptions to resident training. The DIO should then contact the ACGME within 10 days to report the disaster and submit a request for emergency (eg, pandemic) or extraordinary circumstances (eg, natural disaster) categorization.4,9 Program directors should promptly prepare plans for program reconfiguration and resident transfers in alignment with ACGME requirements to maintain evaluation and completion of core competencies of training during disasters.9 Program directors should prioritize the safety of trainees during the immediate threat with clear guidelines on sheltering, evacuations, or quarantines; a timeline of program recovery based on communication with residents, faculty, and administration should then be established.10,11
Communication—Establishing a strong line of communication between program directors and residents is paramount. Collection of emergency noninstitutional contact information, establishment of a centralized website for information dissemination, use of noninstitutional email and proxy servers outside of the location of impact, social media updates, on-site use of 2-way radios, and program-wide conference calls when possible should be strongly considered as part of the disaster response.2-4,12,13
Resident Accommodations and Mental Health—If training is disrupted, residents should be reassured of continued access to salary, housing, food, or other resources as necessary.3,4,11 There should be clear contingency plans if residents need to leave the program for extended periods of time due to injury, illness, or personal circumstances. Although relevant in all types of disasters, resident mental health and response to trauma also must be addressed. Access to counseling, morale-building opportunities (eg, resident social events), and screening for depression or posttraumatic stress disorder may help promote well-being among residents following traumatic events.14
Resident Education
Participation in Disaster Relief—Residents may seek to aid in the disaster response, which may prove challenging in the setting of programs with high patient volume.4 In coordination with the ACGME and graduate medical education governing bodies, program directors should consider how residents may fulfill dermatology training requirements in conjunction with disaster relief efforts, such as working in an inpatient setting or providing wound care.10
Continued Didactic Education—The use of online learning and conference calls for continuing the dermatology curriculum is an efficient means to maintaining resident education when meeting in person poses risks to residents.15 Projections of microscopy images, clinical photographs, or other instructional materials allow for continued instruction on resident examination, histopathology, and diagnostic skills.
Continued Clinical Training—If the home institution cannot support the operation of dermatology clinics, residents should be guaranteed continued training at other institutions. Agreements with other dermatology programs, community hospitals, or private dermatology practices should be established in advance, with consideration given to the number of residents a program can support, funding transfers, and credentialing requirements.2,4,5
Prolonged Disruptions—Nonessential departments of medical institutions may cease to function during war or mass casualty disasters, and it may be unsafe to send dermatology residents to other institutions or clinical areas. If the threat is prolonged, programs may need to consider allowing current residents a longer duration of training despite potential overlap with incoming dermatology residents.7
Patient Care
Disruptions to Clinic Operations—Regarding threats of violence, dangerous exposures, or natural disasters, there should be clear guidelines on sheltering in the clinical setting or stabilizing patients during a procedure.11 Equipment used by residents such as laptops, microscopes, and treatment devices (eg, lasers) should be stored in weather-safe locations that would not be notably impacted by moisture or structural damage to the clinic building. If electricity or internet access are compromised, paper medical records should be available to residents to continue clinical operations. Electronic health records used by residents should regularly be backed up on remote servers or cloud storage to allow continued access to patient health information if on-site servers are not functional.12 If disruptions are prolonged, residency program administration should coordinate with the institution to ensure there is adequate supply and storage of medications (eg, lidocaine, botulinum toxin) as well as a continued means of delivering biologic medications to patients and an ability to obtain laboratory or dermatopathology services.
In-Person Appointments vs Telemedicine—There are benefits to both residency training and patient care when physicians are able to perform in-person examinations, biopsies, and in-office treatments.16 Programs should ensure an adequate supply of personal protective equipment to continue in-office appointments, vaccinations, and medical care if a resident or other members of the team are exposed to an infectious disease.7 If in-person appointments are limited or impossible, telemedicine capabilities may still allow residents to meet program requirements.7,10,15 However, reduced patient volume due to decreased elective visits or procedures may complicate the fulfillment of clinical requirements, which may need to be adjusted in the wake of a disaster.7
Use of Immunosuppressive Therapies—Residency programs should address the risks of prescribing immunosuppressive therapies (eg, biologics) during an infectious threat with their residents and encourage trainees to counsel patients on the importance of preventative measures to reduce risks for severe infection.17
Final Thoughts
- Davis W. Hurricane Katrina: the challenge to graduate medical education. Ochsner J. 2006;6:39.
- Cefalu CA, Schwartz RS. Salvaging a geriatric medicine academic program in disaster mode—the LSU training program post-Katrina.J Natl Med Assoc. 2007;99:590-596.
- Ayyala R. Lessons from Katrina: a program director’s perspective. Ophthalmology. 2007;114:1425-1426.
- Wiese JG. Leadership in graduate medical education: eleven steps instrumental in recovering residency programs after a disaster. Am J Med Sci. 2008;336:168-173.
- Griffies WS. Post-Katrina stabilization of the LSU/Ochsner Psychiatry Residency Program: caveats for disaster preparedness. Acad Psychiatry. 2009;33:418-422.
- Kearns DG, Chat VS, Uppal S, et al. Applying to dermatology residency during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1214-1215.
- Matthews JB, Blair PG, Ellison EC, et al. Checklist framework for surgical education disaster plans. J Am Coll Surg. 2021;233:557-563.
- Litchman GH, Marson JW, Rigel DS. The continuing impact of COVID-19 on dermatology practice: office workflow, economics, and future implications. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:576-579.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Sponsoring institution emergency categorization. Accessed October 20, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/covid-19/sponsoring-institution-emergency-categorization/
- Li YM, Galimberti F, Abrouk M, et al. US dermatology resident responses about the COVID-19 pandemic: results from a nationwide survey. South Med J. 2020;113:462-465.
- Newman B, Gallion C. Hurricane Harvey: firsthand perspectives for disaster preparedness in graduate medical education. Acad Med. 2019;94:1267-1269.
- Pero CD, Pou AM, Arriaga MA, et al. Post-Katrina: study in crisis-related program adaptability. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008;138:394-397.
- Hattaway R, Singh N, Rais-Bahrami S, et al. Adaptations of dermatology residency programs to changes in medical education amid the COVID-19 pandemic: virtual opportunities and social media. SKIN. 2021;5:94-100.
- Hillier K, Paskaradevan J, Wilkes JK, et al. Disaster plans: resident involvement and well-being during Hurricane Harvey. J Grad Med Educ. 2019;11:129-131.
- Samimi S, Choi J, Rosman IS, et al. Impact of COVID-19 on dermatology residency. Dermatol Clin. 2021;39:609-618.
- Bastola M, Locatis C, Fontelo P. Diagnostic reliability of in-person versus remote dermatology: a meta-analysis. Telemed J E Health. 2021;27:247-250.
- Bashyam AM, Feldman SR. Should patients stop their biologic treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic? J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;31:317-318.
- Davis W. Hurricane Katrina: the challenge to graduate medical education. Ochsner J. 2006;6:39.
- Cefalu CA, Schwartz RS. Salvaging a geriatric medicine academic program in disaster mode—the LSU training program post-Katrina.J Natl Med Assoc. 2007;99:590-596.
- Ayyala R. Lessons from Katrina: a program director’s perspective. Ophthalmology. 2007;114:1425-1426.
- Wiese JG. Leadership in graduate medical education: eleven steps instrumental in recovering residency programs after a disaster. Am J Med Sci. 2008;336:168-173.
- Griffies WS. Post-Katrina stabilization of the LSU/Ochsner Psychiatry Residency Program: caveats for disaster preparedness. Acad Psychiatry. 2009;33:418-422.
- Kearns DG, Chat VS, Uppal S, et al. Applying to dermatology residency during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1214-1215.
- Matthews JB, Blair PG, Ellison EC, et al. Checklist framework for surgical education disaster plans. J Am Coll Surg. 2021;233:557-563.
- Litchman GH, Marson JW, Rigel DS. The continuing impact of COVID-19 on dermatology practice: office workflow, economics, and future implications. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:576-579.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Sponsoring institution emergency categorization. Accessed October 20, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/covid-19/sponsoring-institution-emergency-categorization/
- Li YM, Galimberti F, Abrouk M, et al. US dermatology resident responses about the COVID-19 pandemic: results from a nationwide survey. South Med J. 2020;113:462-465.
- Newman B, Gallion C. Hurricane Harvey: firsthand perspectives for disaster preparedness in graduate medical education. Acad Med. 2019;94:1267-1269.
- Pero CD, Pou AM, Arriaga MA, et al. Post-Katrina: study in crisis-related program adaptability. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008;138:394-397.
- Hattaway R, Singh N, Rais-Bahrami S, et al. Adaptations of dermatology residency programs to changes in medical education amid the COVID-19 pandemic: virtual opportunities and social media. SKIN. 2021;5:94-100.
- Hillier K, Paskaradevan J, Wilkes JK, et al. Disaster plans: resident involvement and well-being during Hurricane Harvey. J Grad Med Educ. 2019;11:129-131.
- Samimi S, Choi J, Rosman IS, et al. Impact of COVID-19 on dermatology residency. Dermatol Clin. 2021;39:609-618.
- Bastola M, Locatis C, Fontelo P. Diagnostic reliability of in-person versus remote dermatology: a meta-analysis. Telemed J E Health. 2021;27:247-250.
- Bashyam AM, Feldman SR. Should patients stop their biologic treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic? J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;31:317-318.
Practice Points
- Dermatology residency programs should prioritize the development of disaster preparedness plans prior to the onset of disasters.
- Comprehensive disaster preparedness addresses many possible disruptions to dermatology resident training and clinic operations, including natural and manmade disasters and threats of widespread infectious disease.
- Safety being paramount, dermatology residency programs may be tasked with maintaining resident wellness, continuing resident education—potentially in unconventional ways—and adapting clinical operations to continue patient care.