User login
ANSWER
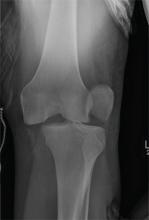
The radiograph shows that the distal femur is medially dislocated relative to the tibial plateau. In addition, the patella is laterally dislocated. No obvious fractures are evident.
Such injuries are typically associated with significant ligament injuries, especially of the medial collateral ligament (MCL), lateral collateral ligament (LCL), and anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). Orthopedics was consulted for reduction of the dislocation, as well as further workup (including MRI of the knee).
ANSWER
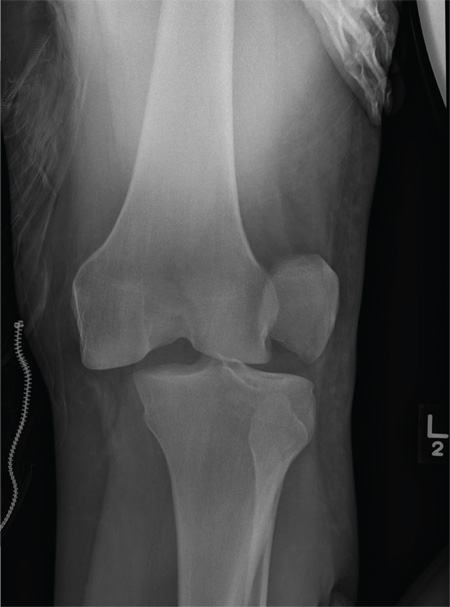
The radiograph shows that the distal femur is medially dislocated relative to the tibial plateau. In addition, the patella is laterally dislocated. No obvious fractures are evident.
Such injuries are typically associated with significant ligament injuries, especially of the medial collateral ligament (MCL), lateral collateral ligament (LCL), and anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). Orthopedics was consulted for reduction of the dislocation, as well as further workup (including MRI of the knee).
ANSWER
The radiograph shows that the distal femur is medially dislocated relative to the tibial plateau. In addition, the patella is laterally dislocated. No obvious fractures are evident.
Such injuries are typically associated with significant ligament injuries, especially of the medial collateral ligament (MCL), lateral collateral ligament (LCL), and anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). Orthopedics was consulted for reduction of the dislocation, as well as further workup (including MRI of the knee).
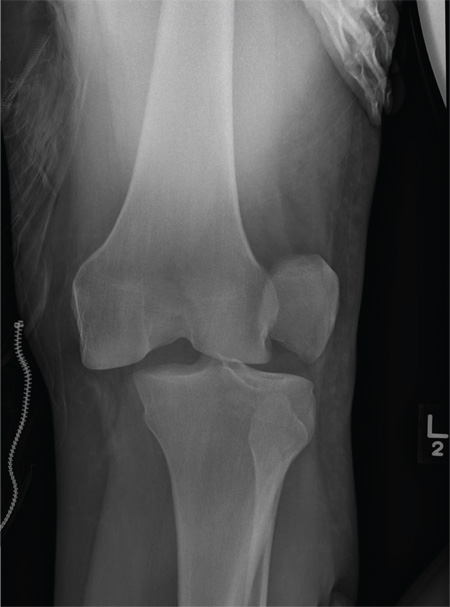
A 28-year-old man is brought to your facility by EMS for evaluation status post a motor vehicle accident. The patient was an unrestrained driver in a truck that went off the road into a ditch. The paramedics state that he was partially ejected, with his left leg caught in the window. There was brief loss of consciousness. Upon arrival, he is awake and alert, with a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15. His primary complaints are of back and left leg pain. His medical history is unremarkable, and vital signs are stable. Primary survey shows no obvious injury. Secondary survey reveals moderate swelling and decreased range of motion in the left knee. Good distal pulses are present. As part of your orders, you request a portable radiograph of the left knee. What is your impression?