User login
Infant mortality in the United Sates dropped very slightly from 2015 to 2016 and has not changed significantly since 2011, according to the National Center for Health Statistics.
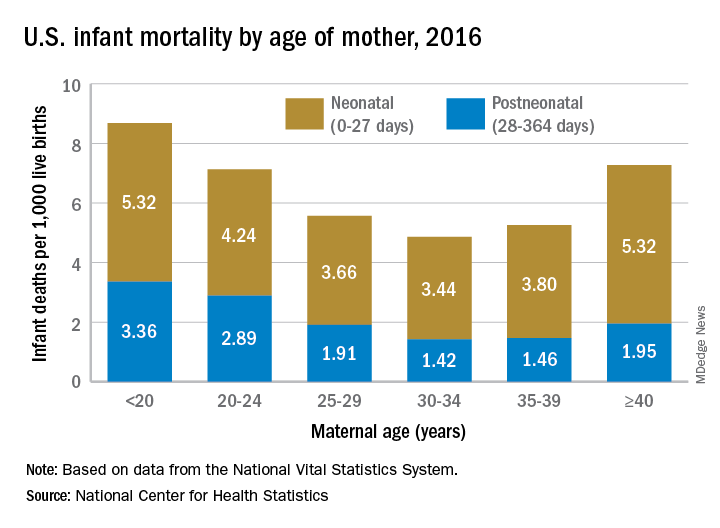
Overall infant mortality was 5.87 per 1,000 live births in 2016, which was not significantly less than the 2015 rate of 5.90 per 1,000 or the rate of 6.07 per 1,000 recorded in 2011, the NCHS said in a recent Data Brief. The rate for 2016 works out to 3.88 per 1,000 for the neonatal period (0-27 days) and 1.99 per 1,000 during the postneonatal period (28-364 days).
The rate was lowest for mothers aged 30-34 years (4.86 per 1,000) and highest for those under 20 years (8.69). All overall rates by maternal age were significantly different from each other, except for those of mothers aged 20-24 years (7.13) and those aged 40 years and over (7.27). Neonatal mortality was highest for the under-20 group and the 40-and-over group at 5.32 per 1,000, with the difference between them coming during the postneonatal period: 3.36 for those under 20 and 1.95 for the 40-and-overs, the NCHS investigators reported based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
The leading cause of death during the neonatal period in 2016 was low birth weight at 98 per 1,000 live births, with congenital malformations second at 86 per 1,000. The leading cause of death in the postneonatal period was congenital malformations at 36 per 1,000, followed by sudden infant death syndrome (35 per 1,000), unintentional injuries (27 per 1,000), diseases of the circulatory system (9 per 1,000), and homicide (6 per 1,000), they added.
Infant mortality in the United Sates dropped very slightly from 2015 to 2016 and has not changed significantly since 2011, according to the National Center for Health Statistics.

Overall infant mortality was 5.87 per 1,000 live births in 2016, which was not significantly less than the 2015 rate of 5.90 per 1,000 or the rate of 6.07 per 1,000 recorded in 2011, the NCHS said in a recent Data Brief. The rate for 2016 works out to 3.88 per 1,000 for the neonatal period (0-27 days) and 1.99 per 1,000 during the postneonatal period (28-364 days).
The rate was lowest for mothers aged 30-34 years (4.86 per 1,000) and highest for those under 20 years (8.69). All overall rates by maternal age were significantly different from each other, except for those of mothers aged 20-24 years (7.13) and those aged 40 years and over (7.27). Neonatal mortality was highest for the under-20 group and the 40-and-over group at 5.32 per 1,000, with the difference between them coming during the postneonatal period: 3.36 for those under 20 and 1.95 for the 40-and-overs, the NCHS investigators reported based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
The leading cause of death during the neonatal period in 2016 was low birth weight at 98 per 1,000 live births, with congenital malformations second at 86 per 1,000. The leading cause of death in the postneonatal period was congenital malformations at 36 per 1,000, followed by sudden infant death syndrome (35 per 1,000), unintentional injuries (27 per 1,000), diseases of the circulatory system (9 per 1,000), and homicide (6 per 1,000), they added.
Infant mortality in the United Sates dropped very slightly from 2015 to 2016 and has not changed significantly since 2011, according to the National Center for Health Statistics.

Overall infant mortality was 5.87 per 1,000 live births in 2016, which was not significantly less than the 2015 rate of 5.90 per 1,000 or the rate of 6.07 per 1,000 recorded in 2011, the NCHS said in a recent Data Brief. The rate for 2016 works out to 3.88 per 1,000 for the neonatal period (0-27 days) and 1.99 per 1,000 during the postneonatal period (28-364 days).
The rate was lowest for mothers aged 30-34 years (4.86 per 1,000) and highest for those under 20 years (8.69). All overall rates by maternal age were significantly different from each other, except for those of mothers aged 20-24 years (7.13) and those aged 40 years and over (7.27). Neonatal mortality was highest for the under-20 group and the 40-and-over group at 5.32 per 1,000, with the difference between them coming during the postneonatal period: 3.36 for those under 20 and 1.95 for the 40-and-overs, the NCHS investigators reported based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
The leading cause of death during the neonatal period in 2016 was low birth weight at 98 per 1,000 live births, with congenital malformations second at 86 per 1,000. The leading cause of death in the postneonatal period was congenital malformations at 36 per 1,000, followed by sudden infant death syndrome (35 per 1,000), unintentional injuries (27 per 1,000), diseases of the circulatory system (9 per 1,000), and homicide (6 per 1,000), they added.