User login
MDedge latest news is breaking news from medical conferences, journals, guidelines, the FDA and CDC.
In a Parallel Universe, “I’d Be a Concert Pianist” Says Tennessee GI
She also relishes opportunities to think, to analyze, and solve problems for her patients.
One of her chief interests is inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It’s reassuring to focus on a field of work “where I know exactly what’s causing the issue, and I can select a therapeutic approach (medication and lifestyle changes) that help a patient achieve remission,” said Dr. Pointer, co-owner and managing partner of Digestive and Liver Health Specialists in Hendersonville, Tenn. She’s also the medical director and a principal investigator of Quality Medical Research in Nashville, and currently serves as chair of the AGA Trainee and Early Career Committee.
Starting her own practice has been just as challenging and rewarding as going through medical school. Medical training does not prepare you for starting your own practice, Dr. Pointer said, so she and her business partner have had to learn as they go. “But I think we’ve done very well. We’ve taken the ups and downs in stride.”
In an interview, Dr. Pointer spoke more about her work in IBD and the ways in which she’s given back to the community through music and mentoring.
Q: Why did you choose GI?
I knew from a very young age that I was going to be a physician. I had always been interested in science. When I got into medical school and became exposed to the different areas, I really liked the cognitive skills where you had to think through a problem or an issue. But I also liked the procedural things as well.
During my internal medicine residency training, I felt that I had a knack for it. As I was looking at different options, I decided on gastroenterology because it combined both cognitive thinking through issues, but also taking it to the next step and intervening through procedures.
Q: During fellowship, your focus was inflammatory bowel disease. What drew your interest to this condition?
There are a lot of different areas within gastroenterology that one can subspecialize in, as we see the full gamut of gastrointestinal and hepatic disorders. But treating some conditions, like functional disorders, means taking more of a ‘trial and error’ approach, and you may not always get the patient a hundred percent better. That’s not to say that we can’t improve a patient’s quality of life, but it’s not always a guarantee.
But inflammatory bowel disease is a little bit different. Because I can point to an exact spot in the intestines that’s causing the problem, it’s very fulfilling for me as a physician to take a patient who is having 10-12 bloody bowel movements a day, to normal form stools and no abdominal pain. They’re able to gain weight and go on about their lives and about their day. So that was why I picked inflammatory bowel disease as my subspecialty.
Q: Tell me about the gastroenterology elective you developed for family medicine residents and undergraduate students. What’s the status of the program now?
I’ve always been interested in teaching and giving back to the next generations. I feel like I had great mentor opportunities and people who helped me along the way. In my previous hospital position, I was able to work with the family medicine department and create an elective through which residents and even undergraduate students could come and shadow and work with me in the clinic and see me performing procedures.
That elective ended once I left that position, at least as far as I’m aware. But in the private practice that I co-own now, we have numerous shadowing opportunities. I was able to give a lecture at Middle Tennessee State University for some students. And through that lecture, many students have reached out to me to shadow. I have allowed them to come shadow and do clinic work as a medical assistant and watch me perform procedures. I have multiple students working with me weekly.
Q: Years ago, you founded the non-profit Enchanted Fingers Piano Lessons, which gave free piano lessons to underserved youth. What was that experience like?
Piano was one of my first loves. In some parallel universe, there’s a Dr. Pointer who is a classical, concert pianist. I started taking piano lessons when I was in early middle school, and I took to it very quickly. I was able to excel. I just loved it. I enjoyed practicing and I still play.
The impetus for starting Enchanted Fingers Piano lessons was because I wanted to give back again to the community. I came from an underserved community. Oftentimes children and young adults in those communities don’t get exposed to extracurricular activities and they don’t even know what they could potentially have a passion for. And I definitely had a passion for piano. I partnered with a church organization and they allowed me to use their church to host these piano lessons, and it was a phenomenal and rewarding experience. I would definitely like to start it up again one day in the future. It was an amazing experience.
It’s actually how I met my husband. He was one of the young adult students who signed up to take lessons. We both still enjoy playing the piano together.
Q: When you’re not being a GI, how do you spend your free weekend afternoons?
I’m a creative at heart. I really enjoy sewing and I’m working on a few sewing projects. I just got a serger. It is a machine that helps you finish a seam. It can also be used to sew entire garments. That has been fun, learning how to thread that machine. When I’m not doing that or just relaxing with my family, I do enjoy curling up with a good book. Stephen King is one of my favorite authors.
Lightning Round
Texting or talking?
Talking
Favorite junk food?
Chocolate chip cookies
Cat or dog person?
Cat
Favorite vacation?
Hawaii
How many cups of coffee do you drink per day?
I don’t drink coffee
Favorite ice cream?
Butter pecan
Favorite sport?
I don’t watch sports
Optimist or pessimist?
Optimist
She also relishes opportunities to think, to analyze, and solve problems for her patients.
One of her chief interests is inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It’s reassuring to focus on a field of work “where I know exactly what’s causing the issue, and I can select a therapeutic approach (medication and lifestyle changes) that help a patient achieve remission,” said Dr. Pointer, co-owner and managing partner of Digestive and Liver Health Specialists in Hendersonville, Tenn. She’s also the medical director and a principal investigator of Quality Medical Research in Nashville, and currently serves as chair of the AGA Trainee and Early Career Committee.
Starting her own practice has been just as challenging and rewarding as going through medical school. Medical training does not prepare you for starting your own practice, Dr. Pointer said, so she and her business partner have had to learn as they go. “But I think we’ve done very well. We’ve taken the ups and downs in stride.”
In an interview, Dr. Pointer spoke more about her work in IBD and the ways in which she’s given back to the community through music and mentoring.
Q: Why did you choose GI?
I knew from a very young age that I was going to be a physician. I had always been interested in science. When I got into medical school and became exposed to the different areas, I really liked the cognitive skills where you had to think through a problem or an issue. But I also liked the procedural things as well.
During my internal medicine residency training, I felt that I had a knack for it. As I was looking at different options, I decided on gastroenterology because it combined both cognitive thinking through issues, but also taking it to the next step and intervening through procedures.
Q: During fellowship, your focus was inflammatory bowel disease. What drew your interest to this condition?
There are a lot of different areas within gastroenterology that one can subspecialize in, as we see the full gamut of gastrointestinal and hepatic disorders. But treating some conditions, like functional disorders, means taking more of a ‘trial and error’ approach, and you may not always get the patient a hundred percent better. That’s not to say that we can’t improve a patient’s quality of life, but it’s not always a guarantee.
But inflammatory bowel disease is a little bit different. Because I can point to an exact spot in the intestines that’s causing the problem, it’s very fulfilling for me as a physician to take a patient who is having 10-12 bloody bowel movements a day, to normal form stools and no abdominal pain. They’re able to gain weight and go on about their lives and about their day. So that was why I picked inflammatory bowel disease as my subspecialty.
Q: Tell me about the gastroenterology elective you developed for family medicine residents and undergraduate students. What’s the status of the program now?
I’ve always been interested in teaching and giving back to the next generations. I feel like I had great mentor opportunities and people who helped me along the way. In my previous hospital position, I was able to work with the family medicine department and create an elective through which residents and even undergraduate students could come and shadow and work with me in the clinic and see me performing procedures.
That elective ended once I left that position, at least as far as I’m aware. But in the private practice that I co-own now, we have numerous shadowing opportunities. I was able to give a lecture at Middle Tennessee State University for some students. And through that lecture, many students have reached out to me to shadow. I have allowed them to come shadow and do clinic work as a medical assistant and watch me perform procedures. I have multiple students working with me weekly.
Q: Years ago, you founded the non-profit Enchanted Fingers Piano Lessons, which gave free piano lessons to underserved youth. What was that experience like?
Piano was one of my first loves. In some parallel universe, there’s a Dr. Pointer who is a classical, concert pianist. I started taking piano lessons when I was in early middle school, and I took to it very quickly. I was able to excel. I just loved it. I enjoyed practicing and I still play.
The impetus for starting Enchanted Fingers Piano lessons was because I wanted to give back again to the community. I came from an underserved community. Oftentimes children and young adults in those communities don’t get exposed to extracurricular activities and they don’t even know what they could potentially have a passion for. And I definitely had a passion for piano. I partnered with a church organization and they allowed me to use their church to host these piano lessons, and it was a phenomenal and rewarding experience. I would definitely like to start it up again one day in the future. It was an amazing experience.
It’s actually how I met my husband. He was one of the young adult students who signed up to take lessons. We both still enjoy playing the piano together.
Q: When you’re not being a GI, how do you spend your free weekend afternoons?
I’m a creative at heart. I really enjoy sewing and I’m working on a few sewing projects. I just got a serger. It is a machine that helps you finish a seam. It can also be used to sew entire garments. That has been fun, learning how to thread that machine. When I’m not doing that or just relaxing with my family, I do enjoy curling up with a good book. Stephen King is one of my favorite authors.
Lightning Round
Texting or talking?
Talking
Favorite junk food?
Chocolate chip cookies
Cat or dog person?
Cat
Favorite vacation?
Hawaii
How many cups of coffee do you drink per day?
I don’t drink coffee
Favorite ice cream?
Butter pecan
Favorite sport?
I don’t watch sports
Optimist or pessimist?
Optimist
She also relishes opportunities to think, to analyze, and solve problems for her patients.
One of her chief interests is inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It’s reassuring to focus on a field of work “where I know exactly what’s causing the issue, and I can select a therapeutic approach (medication and lifestyle changes) that help a patient achieve remission,” said Dr. Pointer, co-owner and managing partner of Digestive and Liver Health Specialists in Hendersonville, Tenn. She’s also the medical director and a principal investigator of Quality Medical Research in Nashville, and currently serves as chair of the AGA Trainee and Early Career Committee.
Starting her own practice has been just as challenging and rewarding as going through medical school. Medical training does not prepare you for starting your own practice, Dr. Pointer said, so she and her business partner have had to learn as they go. “But I think we’ve done very well. We’ve taken the ups and downs in stride.”
In an interview, Dr. Pointer spoke more about her work in IBD and the ways in which she’s given back to the community through music and mentoring.
Q: Why did you choose GI?
I knew from a very young age that I was going to be a physician. I had always been interested in science. When I got into medical school and became exposed to the different areas, I really liked the cognitive skills where you had to think through a problem or an issue. But I also liked the procedural things as well.
During my internal medicine residency training, I felt that I had a knack for it. As I was looking at different options, I decided on gastroenterology because it combined both cognitive thinking through issues, but also taking it to the next step and intervening through procedures.
Q: During fellowship, your focus was inflammatory bowel disease. What drew your interest to this condition?
There are a lot of different areas within gastroenterology that one can subspecialize in, as we see the full gamut of gastrointestinal and hepatic disorders. But treating some conditions, like functional disorders, means taking more of a ‘trial and error’ approach, and you may not always get the patient a hundred percent better. That’s not to say that we can’t improve a patient’s quality of life, but it’s not always a guarantee.
But inflammatory bowel disease is a little bit different. Because I can point to an exact spot in the intestines that’s causing the problem, it’s very fulfilling for me as a physician to take a patient who is having 10-12 bloody bowel movements a day, to normal form stools and no abdominal pain. They’re able to gain weight and go on about their lives and about their day. So that was why I picked inflammatory bowel disease as my subspecialty.
Q: Tell me about the gastroenterology elective you developed for family medicine residents and undergraduate students. What’s the status of the program now?
I’ve always been interested in teaching and giving back to the next generations. I feel like I had great mentor opportunities and people who helped me along the way. In my previous hospital position, I was able to work with the family medicine department and create an elective through which residents and even undergraduate students could come and shadow and work with me in the clinic and see me performing procedures.
That elective ended once I left that position, at least as far as I’m aware. But in the private practice that I co-own now, we have numerous shadowing opportunities. I was able to give a lecture at Middle Tennessee State University for some students. And through that lecture, many students have reached out to me to shadow. I have allowed them to come shadow and do clinic work as a medical assistant and watch me perform procedures. I have multiple students working with me weekly.
Q: Years ago, you founded the non-profit Enchanted Fingers Piano Lessons, which gave free piano lessons to underserved youth. What was that experience like?
Piano was one of my first loves. In some parallel universe, there’s a Dr. Pointer who is a classical, concert pianist. I started taking piano lessons when I was in early middle school, and I took to it very quickly. I was able to excel. I just loved it. I enjoyed practicing and I still play.
The impetus for starting Enchanted Fingers Piano lessons was because I wanted to give back again to the community. I came from an underserved community. Oftentimes children and young adults in those communities don’t get exposed to extracurricular activities and they don’t even know what they could potentially have a passion for. And I definitely had a passion for piano. I partnered with a church organization and they allowed me to use their church to host these piano lessons, and it was a phenomenal and rewarding experience. I would definitely like to start it up again one day in the future. It was an amazing experience.
It’s actually how I met my husband. He was one of the young adult students who signed up to take lessons. We both still enjoy playing the piano together.
Q: When you’re not being a GI, how do you spend your free weekend afternoons?
I’m a creative at heart. I really enjoy sewing and I’m working on a few sewing projects. I just got a serger. It is a machine that helps you finish a seam. It can also be used to sew entire garments. That has been fun, learning how to thread that machine. When I’m not doing that or just relaxing with my family, I do enjoy curling up with a good book. Stephen King is one of my favorite authors.
Lightning Round
Texting or talking?
Talking
Favorite junk food?
Chocolate chip cookies
Cat or dog person?
Cat
Favorite vacation?
Hawaii
How many cups of coffee do you drink per day?
I don’t drink coffee
Favorite ice cream?
Butter pecan
Favorite sport?
I don’t watch sports
Optimist or pessimist?
Optimist

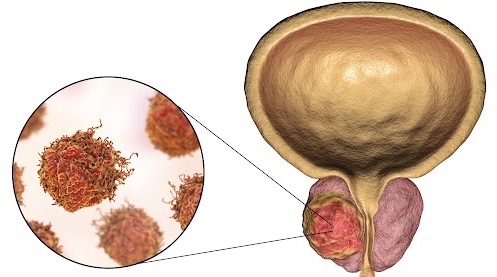
Transgender Women and Prostate Cancer: It’s Complicated
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) provides care for about 10,000 transgender women, and clinicians must understand their distinctive needs for prostate cancer screening, a urologist told cancer specialists during a presentation at the 2024 annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology in Atlanta.
Even if they’ve undergone gender reassignment surgery, “all transgender women still have a prostate, so therefore they remain at risk of prostate cancer and could still be considered for prostate cancer screening,” said Farnoosh Nik-Ahd, MD, a resident physician at the University of California San Francisco. However, “clinicians and patients may not be aware of prostate cancer risk, so that they may not think [of screening] transgender women.”
Nik-Ahd also noted another complication: The results of prostate screening tests may be misleading in this population.
Transgender women were born biologically male but now identify as female. These individuals may have undergone gender reassignment surgery to remove male genitalia, but the procedures do not remove the prostate. They also might be taking estrogen therapy. “Prostate cancer is a hormonally driven cancer, and the exact impact of gender-affirming hormones on prostate cancer risk and development is unknown,” Nik-Ahd said.
In a 2023 study in JAMA, Nik-Ahd and colleagues identified 155 cases of prostate cancer in transgender women within the VHA (about 14 cases per year) from 2000 to 2022. Of these patients, 116 had never used estrogen, while 17 had used it previously and 22 used it at diagnosis.
The median age of patients was 61 years, 88% identified as White, and the median prostate-specific antigen (PSA) was 6.8 ng/mL. “Given estimates of 10,000 transgender women in the US Department of Veterans Affairs, 33 cases per year would be expected. Instead, only about 14 per year were observed,” the researchers wrote. “Lower rates may stem from less PSA screening owing to barriers including lack of prostate cancer risk awareness or stigma, the suppressive effects of estrogen on prostate cancer development, or prostate cancers being missed in transgender women because of misinterpretation of ‘normal’ PSA levels among those receiving gender-affirming hormone therapies.”
In the presentation, Nik-Ahd said, “PSA density, which is a marker of prostate cancer aggressiveness, was highest in transgender women who were actively on estrogen.”
She noted, “the existing thyrotropin reference ranges, which is what we use to interpret PSA values, are all based on data from cisgender men.” The ranges would be expected to be far lower in transgender women who are taking estrogen, potentially throwing off screening tests, she said, and “ultimately missing clinically significant prostate cancer.”
In the larger picture, there are no specific guidelines about PSA screening in transgender women, she said.
A recent study published in JAMA by Nik-Ahd and colleagues examined PSA levels in 210 transgender women (mean age 60 years) treated within the VHA from 2000 to 2023. All were aged 40 to 80 years, had received estrogen for at least 6 months (mean duration 4.7 years), and didn’t have prostate cancer diagnoses.
“Median (IQR) PSA was 0.02 (0-0.2) ng/mL and the 95th percentile value was 0.6 ng/mL,” the report found. “PSAs were undetectable in 36% of patients (23% and 49% of PSAs in patients without and with orchiectomy, respectively).”
The researchers write that “the historic cut point of 4 ng/mL, often used as a threshold for further evaluation, is likely far too high a threshold for this population.”
Nik-Ahd noted, “clinicians should interpret PSA values in transgender women on estrogen with extreme caution. In this population, normal might actually not be normal, and a value that is considered normal might be very abnormal for somebody who is on estrogen. If you're unsure of whether a PSA value is appropriate for a transgender woman on estrogen, refer that patient to a urologist so they can undergo further evaluation.”
Farnoosh Nik-Ahd discloses consulting for Janssen.
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) provides care for about 10,000 transgender women, and clinicians must understand their distinctive needs for prostate cancer screening, a urologist told cancer specialists during a presentation at the 2024 annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology in Atlanta.
Even if they’ve undergone gender reassignment surgery, “all transgender women still have a prostate, so therefore they remain at risk of prostate cancer and could still be considered for prostate cancer screening,” said Farnoosh Nik-Ahd, MD, a resident physician at the University of California San Francisco. However, “clinicians and patients may not be aware of prostate cancer risk, so that they may not think [of screening] transgender women.”
Nik-Ahd also noted another complication: The results of prostate screening tests may be misleading in this population.
Transgender women were born biologically male but now identify as female. These individuals may have undergone gender reassignment surgery to remove male genitalia, but the procedures do not remove the prostate. They also might be taking estrogen therapy. “Prostate cancer is a hormonally driven cancer, and the exact impact of gender-affirming hormones on prostate cancer risk and development is unknown,” Nik-Ahd said.
In a 2023 study in JAMA, Nik-Ahd and colleagues identified 155 cases of prostate cancer in transgender women within the VHA (about 14 cases per year) from 2000 to 2022. Of these patients, 116 had never used estrogen, while 17 had used it previously and 22 used it at diagnosis.
The median age of patients was 61 years, 88% identified as White, and the median prostate-specific antigen (PSA) was 6.8 ng/mL. “Given estimates of 10,000 transgender women in the US Department of Veterans Affairs, 33 cases per year would be expected. Instead, only about 14 per year were observed,” the researchers wrote. “Lower rates may stem from less PSA screening owing to barriers including lack of prostate cancer risk awareness or stigma, the suppressive effects of estrogen on prostate cancer development, or prostate cancers being missed in transgender women because of misinterpretation of ‘normal’ PSA levels among those receiving gender-affirming hormone therapies.”
In the presentation, Nik-Ahd said, “PSA density, which is a marker of prostate cancer aggressiveness, was highest in transgender women who were actively on estrogen.”
She noted, “the existing thyrotropin reference ranges, which is what we use to interpret PSA values, are all based on data from cisgender men.” The ranges would be expected to be far lower in transgender women who are taking estrogen, potentially throwing off screening tests, she said, and “ultimately missing clinically significant prostate cancer.”
In the larger picture, there are no specific guidelines about PSA screening in transgender women, she said.
A recent study published in JAMA by Nik-Ahd and colleagues examined PSA levels in 210 transgender women (mean age 60 years) treated within the VHA from 2000 to 2023. All were aged 40 to 80 years, had received estrogen for at least 6 months (mean duration 4.7 years), and didn’t have prostate cancer diagnoses.
“Median (IQR) PSA was 0.02 (0-0.2) ng/mL and the 95th percentile value was 0.6 ng/mL,” the report found. “PSAs were undetectable in 36% of patients (23% and 49% of PSAs in patients without and with orchiectomy, respectively).”
The researchers write that “the historic cut point of 4 ng/mL, often used as a threshold for further evaluation, is likely far too high a threshold for this population.”
Nik-Ahd noted, “clinicians should interpret PSA values in transgender women on estrogen with extreme caution. In this population, normal might actually not be normal, and a value that is considered normal might be very abnormal for somebody who is on estrogen. If you're unsure of whether a PSA value is appropriate for a transgender woman on estrogen, refer that patient to a urologist so they can undergo further evaluation.”
Farnoosh Nik-Ahd discloses consulting for Janssen.
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) provides care for about 10,000 transgender women, and clinicians must understand their distinctive needs for prostate cancer screening, a urologist told cancer specialists during a presentation at the 2024 annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology in Atlanta.
Even if they’ve undergone gender reassignment surgery, “all transgender women still have a prostate, so therefore they remain at risk of prostate cancer and could still be considered for prostate cancer screening,” said Farnoosh Nik-Ahd, MD, a resident physician at the University of California San Francisco. However, “clinicians and patients may not be aware of prostate cancer risk, so that they may not think [of screening] transgender women.”
Nik-Ahd also noted another complication: The results of prostate screening tests may be misleading in this population.
Transgender women were born biologically male but now identify as female. These individuals may have undergone gender reassignment surgery to remove male genitalia, but the procedures do not remove the prostate. They also might be taking estrogen therapy. “Prostate cancer is a hormonally driven cancer, and the exact impact of gender-affirming hormones on prostate cancer risk and development is unknown,” Nik-Ahd said.
In a 2023 study in JAMA, Nik-Ahd and colleagues identified 155 cases of prostate cancer in transgender women within the VHA (about 14 cases per year) from 2000 to 2022. Of these patients, 116 had never used estrogen, while 17 had used it previously and 22 used it at diagnosis.
The median age of patients was 61 years, 88% identified as White, and the median prostate-specific antigen (PSA) was 6.8 ng/mL. “Given estimates of 10,000 transgender women in the US Department of Veterans Affairs, 33 cases per year would be expected. Instead, only about 14 per year were observed,” the researchers wrote. “Lower rates may stem from less PSA screening owing to barriers including lack of prostate cancer risk awareness or stigma, the suppressive effects of estrogen on prostate cancer development, or prostate cancers being missed in transgender women because of misinterpretation of ‘normal’ PSA levels among those receiving gender-affirming hormone therapies.”
In the presentation, Nik-Ahd said, “PSA density, which is a marker of prostate cancer aggressiveness, was highest in transgender women who were actively on estrogen.”
She noted, “the existing thyrotropin reference ranges, which is what we use to interpret PSA values, are all based on data from cisgender men.” The ranges would be expected to be far lower in transgender women who are taking estrogen, potentially throwing off screening tests, she said, and “ultimately missing clinically significant prostate cancer.”
In the larger picture, there are no specific guidelines about PSA screening in transgender women, she said.
A recent study published in JAMA by Nik-Ahd and colleagues examined PSA levels in 210 transgender women (mean age 60 years) treated within the VHA from 2000 to 2023. All were aged 40 to 80 years, had received estrogen for at least 6 months (mean duration 4.7 years), and didn’t have prostate cancer diagnoses.
“Median (IQR) PSA was 0.02 (0-0.2) ng/mL and the 95th percentile value was 0.6 ng/mL,” the report found. “PSAs were undetectable in 36% of patients (23% and 49% of PSAs in patients without and with orchiectomy, respectively).”
The researchers write that “the historic cut point of 4 ng/mL, often used as a threshold for further evaluation, is likely far too high a threshold for this population.”
Nik-Ahd noted, “clinicians should interpret PSA values in transgender women on estrogen with extreme caution. In this population, normal might actually not be normal, and a value that is considered normal might be very abnormal for somebody who is on estrogen. If you're unsure of whether a PSA value is appropriate for a transgender woman on estrogen, refer that patient to a urologist so they can undergo further evaluation.”
Farnoosh Nik-Ahd discloses consulting for Janssen.
Patient Navigators for Serious Illnesses Can Now Bill Under New Medicare Codes
In a move that acknowledges the gauntlet the US health system poses for people facing serious and fatal illnesses, Medicare will pay for a new class of workers to help patients manage treatments for conditions like cancer and heart failure.
The 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule includes new billing codes, including G0023, to pay for 60 minutes a month of care coordination by certified or trained auxiliary personnel working under the direction of a clinician.
A diagnosis of cancer or another serious illness takes a toll beyond the physical effects of the disease. Patients often scramble to make adjustments in family and work schedules to manage treatment, said Samyukta Mullangi, MD, MBA, medical director of oncology at Thyme Care, a Nashville, Tennessee–based firm that provides navigation and coordination services to oncology practices and insurers.
“It just really does create a bit of a pressure cooker for patients,” Dr. Mullangi told this news organization.
Medicare has for many years paid for medical professionals to help patients cope with the complexities of disease, such as chronic care management (CCM) provided by physicians, nurses, and physician assistants.
The new principal illness navigation (PIN) payments are intended to pay for work that to date typically has been done by people without medical degrees, including those involved in peer support networks and community health programs. The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services(CMS) expects these navigators will undergo training and work under the supervision of clinicians.
The new navigators may coordinate care transitions between medical settings, follow up with patients after emergency department (ED) visits, or communicate with skilled nursing facilities regarding the psychosocial needs and functional deficits of a patient, among other functions.
CMS expects the new navigators may:
- Conduct assessments to understand a patient’s life story, strengths, needs, goals, preferences, and desired outcomes, including understanding cultural and linguistic factors.
- Provide support to accomplish the clinician’s treatment plan.
- Coordinate the receipt of needed services from healthcare facilities, home- and community-based service providers, and caregivers.
Peers as Navigators
The new navigators can be former patients who have undergone similar treatments for serious diseases, CMS said. This approach sets the new program apart from other care management services Medicare already covers, program officials wrote in the 2024 physician fee schedule.
“For some conditions, patients are best able to engage with the healthcare system and access care if they have assistance from a single, dedicated individual who has ‘lived experience,’ ” according to the rule.
The agency has taken a broad initial approach in defining what kinds of illnesses a patient may have to qualify for services. Patients must have a serious condition that is expected to last at least 3 months, such as cancer, heart failure, or substance use disorder.
But those without a definitive diagnosis may also qualify to receive navigator services.
In the rule, CMS cited a case in which a CT scan identified a suspicious mass in a patient’s colon. A clinician might decide this person would benefit from navigation services due to the potential risks for an undiagnosed illness.
“Regardless of the definitive diagnosis of the mass, presence of a colonic mass for that patient may be a serious high-risk condition that could, for example, cause obstruction and lead the patient to present to the emergency department, as well as be potentially indicative of an underlying life-threatening illness such as colon cancer,” CMS wrote in the rule.
Navigators often start their work when cancer patients are screened and guide them through initial diagnosis, potential surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, said Sharon Gentry, MSN, RN, a former nurse navigator who is now the editor in chief of the Journal of the Academy of Oncology Nurse & Patient Navigators.
The navigators are meant to be a trusted and continual presence for patients, who otherwise might be left to start anew in finding help at each phase of care.
The navigators “see the whole picture. They see the whole journey the patient takes, from pre-diagnosis all the way through diagnosis care out through survival,” Ms. Gentry said.
Gaining a special Medicare payment for these kinds of services will elevate this work, she said.
Many newer drugs can target specific mechanisms and proteins of cancer. Often, oncology treatment involves testing to find out if mutations are allowing the cancer cells to evade a patient’s immune system.
Checking these biomarkers takes time, however. Patients sometimes become frustrated because they are anxious to begin treatment. Patients may receive inaccurate information from friends or family who went through treatment previously. Navigators can provide knowledge on the current state of care for a patient’s disease, helping them better manage anxieties.
“You have to explain to them that things have changed since the guy you drink coffee with was diagnosed with cancer, and there may be a drug that could target that,” Ms. Gentry said.
Potential Challenges
Initial uptake of the new PIN codes may be slow going, however, as clinicians and health systems may already use well-established codes. These include CCM and principal care management services, which may pay higher rates, Mullangi said.
“There might be sensitivity around not wanting to cannibalize existing programs with a new program,” Dr. Mullangi said.
In addition, many patients will have a copay for the services of principal illness navigators, Dr. Mullangi said.
While many patients have additional insurance that would cover the service, not all do. People with traditional Medicare coverage can sometimes pay 20% of the cost of some medical services.
“I think that may give patients pause, particularly if they’re already feeling the financial burden of a cancer treatment journey,” Dr. Mullangi said.
Pay rates for PIN services involve calculations of regional price differences, which are posted publicly by CMS, and potential added fees for services provided by hospital-affiliated organizations.
Consider payments for code G0023, covering 60 minutes of principal navigation services provided in a single month.
A set reimbursement for patients cared for in independent medical practices exists, with variation for local costs. Medicare’s non-facility price for G0023 would be $102.41 in some parts of Silicon Valley in California, including San Jose. In Arkansas, where costs are lower, reimbursement would be $73.14 for this same service.
Patients who get services covered by code G0023 in independent medical practices would have monthly copays of about $15-$20, depending on where they live.
The tab for patients tends to be higher for these same services if delivered through a medical practice owned by a hospital, as this would trigger the addition of facility fees to the payments made to cover the services. Facility fees are difficult for the public to ascertain before getting a treatment or service.
Dr. Mullangi and Ms. Gentry reported no relevant financial disclosures outside of their employers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a move that acknowledges the gauntlet the US health system poses for people facing serious and fatal illnesses, Medicare will pay for a new class of workers to help patients manage treatments for conditions like cancer and heart failure.
The 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule includes new billing codes, including G0023, to pay for 60 minutes a month of care coordination by certified or trained auxiliary personnel working under the direction of a clinician.
A diagnosis of cancer or another serious illness takes a toll beyond the physical effects of the disease. Patients often scramble to make adjustments in family and work schedules to manage treatment, said Samyukta Mullangi, MD, MBA, medical director of oncology at Thyme Care, a Nashville, Tennessee–based firm that provides navigation and coordination services to oncology practices and insurers.
“It just really does create a bit of a pressure cooker for patients,” Dr. Mullangi told this news organization.
Medicare has for many years paid for medical professionals to help patients cope with the complexities of disease, such as chronic care management (CCM) provided by physicians, nurses, and physician assistants.
The new principal illness navigation (PIN) payments are intended to pay for work that to date typically has been done by people without medical degrees, including those involved in peer support networks and community health programs. The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services(CMS) expects these navigators will undergo training and work under the supervision of clinicians.
The new navigators may coordinate care transitions between medical settings, follow up with patients after emergency department (ED) visits, or communicate with skilled nursing facilities regarding the psychosocial needs and functional deficits of a patient, among other functions.
CMS expects the new navigators may:
- Conduct assessments to understand a patient’s life story, strengths, needs, goals, preferences, and desired outcomes, including understanding cultural and linguistic factors.
- Provide support to accomplish the clinician’s treatment plan.
- Coordinate the receipt of needed services from healthcare facilities, home- and community-based service providers, and caregivers.
Peers as Navigators
The new navigators can be former patients who have undergone similar treatments for serious diseases, CMS said. This approach sets the new program apart from other care management services Medicare already covers, program officials wrote in the 2024 physician fee schedule.
“For some conditions, patients are best able to engage with the healthcare system and access care if they have assistance from a single, dedicated individual who has ‘lived experience,’ ” according to the rule.
The agency has taken a broad initial approach in defining what kinds of illnesses a patient may have to qualify for services. Patients must have a serious condition that is expected to last at least 3 months, such as cancer, heart failure, or substance use disorder.
But those without a definitive diagnosis may also qualify to receive navigator services.
In the rule, CMS cited a case in which a CT scan identified a suspicious mass in a patient’s colon. A clinician might decide this person would benefit from navigation services due to the potential risks for an undiagnosed illness.
“Regardless of the definitive diagnosis of the mass, presence of a colonic mass for that patient may be a serious high-risk condition that could, for example, cause obstruction and lead the patient to present to the emergency department, as well as be potentially indicative of an underlying life-threatening illness such as colon cancer,” CMS wrote in the rule.
Navigators often start their work when cancer patients are screened and guide them through initial diagnosis, potential surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, said Sharon Gentry, MSN, RN, a former nurse navigator who is now the editor in chief of the Journal of the Academy of Oncology Nurse & Patient Navigators.
The navigators are meant to be a trusted and continual presence for patients, who otherwise might be left to start anew in finding help at each phase of care.
The navigators “see the whole picture. They see the whole journey the patient takes, from pre-diagnosis all the way through diagnosis care out through survival,” Ms. Gentry said.
Gaining a special Medicare payment for these kinds of services will elevate this work, she said.
Many newer drugs can target specific mechanisms and proteins of cancer. Often, oncology treatment involves testing to find out if mutations are allowing the cancer cells to evade a patient’s immune system.
Checking these biomarkers takes time, however. Patients sometimes become frustrated because they are anxious to begin treatment. Patients may receive inaccurate information from friends or family who went through treatment previously. Navigators can provide knowledge on the current state of care for a patient’s disease, helping them better manage anxieties.
“You have to explain to them that things have changed since the guy you drink coffee with was diagnosed with cancer, and there may be a drug that could target that,” Ms. Gentry said.
Potential Challenges
Initial uptake of the new PIN codes may be slow going, however, as clinicians and health systems may already use well-established codes. These include CCM and principal care management services, which may pay higher rates, Mullangi said.
“There might be sensitivity around not wanting to cannibalize existing programs with a new program,” Dr. Mullangi said.
In addition, many patients will have a copay for the services of principal illness navigators, Dr. Mullangi said.
While many patients have additional insurance that would cover the service, not all do. People with traditional Medicare coverage can sometimes pay 20% of the cost of some medical services.
“I think that may give patients pause, particularly if they’re already feeling the financial burden of a cancer treatment journey,” Dr. Mullangi said.
Pay rates for PIN services involve calculations of regional price differences, which are posted publicly by CMS, and potential added fees for services provided by hospital-affiliated organizations.
Consider payments for code G0023, covering 60 minutes of principal navigation services provided in a single month.
A set reimbursement for patients cared for in independent medical practices exists, with variation for local costs. Medicare’s non-facility price for G0023 would be $102.41 in some parts of Silicon Valley in California, including San Jose. In Arkansas, where costs are lower, reimbursement would be $73.14 for this same service.
Patients who get services covered by code G0023 in independent medical practices would have monthly copays of about $15-$20, depending on where they live.
The tab for patients tends to be higher for these same services if delivered through a medical practice owned by a hospital, as this would trigger the addition of facility fees to the payments made to cover the services. Facility fees are difficult for the public to ascertain before getting a treatment or service.
Dr. Mullangi and Ms. Gentry reported no relevant financial disclosures outside of their employers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a move that acknowledges the gauntlet the US health system poses for people facing serious and fatal illnesses, Medicare will pay for a new class of workers to help patients manage treatments for conditions like cancer and heart failure.
The 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule includes new billing codes, including G0023, to pay for 60 minutes a month of care coordination by certified or trained auxiliary personnel working under the direction of a clinician.
A diagnosis of cancer or another serious illness takes a toll beyond the physical effects of the disease. Patients often scramble to make adjustments in family and work schedules to manage treatment, said Samyukta Mullangi, MD, MBA, medical director of oncology at Thyme Care, a Nashville, Tennessee–based firm that provides navigation and coordination services to oncology practices and insurers.
“It just really does create a bit of a pressure cooker for patients,” Dr. Mullangi told this news organization.
Medicare has for many years paid for medical professionals to help patients cope with the complexities of disease, such as chronic care management (CCM) provided by physicians, nurses, and physician assistants.
The new principal illness navigation (PIN) payments are intended to pay for work that to date typically has been done by people without medical degrees, including those involved in peer support networks and community health programs. The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services(CMS) expects these navigators will undergo training and work under the supervision of clinicians.
The new navigators may coordinate care transitions between medical settings, follow up with patients after emergency department (ED) visits, or communicate with skilled nursing facilities regarding the psychosocial needs and functional deficits of a patient, among other functions.
CMS expects the new navigators may:
- Conduct assessments to understand a patient’s life story, strengths, needs, goals, preferences, and desired outcomes, including understanding cultural and linguistic factors.
- Provide support to accomplish the clinician’s treatment plan.
- Coordinate the receipt of needed services from healthcare facilities, home- and community-based service providers, and caregivers.
Peers as Navigators
The new navigators can be former patients who have undergone similar treatments for serious diseases, CMS said. This approach sets the new program apart from other care management services Medicare already covers, program officials wrote in the 2024 physician fee schedule.
“For some conditions, patients are best able to engage with the healthcare system and access care if they have assistance from a single, dedicated individual who has ‘lived experience,’ ” according to the rule.
The agency has taken a broad initial approach in defining what kinds of illnesses a patient may have to qualify for services. Patients must have a serious condition that is expected to last at least 3 months, such as cancer, heart failure, or substance use disorder.
But those without a definitive diagnosis may also qualify to receive navigator services.
In the rule, CMS cited a case in which a CT scan identified a suspicious mass in a patient’s colon. A clinician might decide this person would benefit from navigation services due to the potential risks for an undiagnosed illness.
“Regardless of the definitive diagnosis of the mass, presence of a colonic mass for that patient may be a serious high-risk condition that could, for example, cause obstruction and lead the patient to present to the emergency department, as well as be potentially indicative of an underlying life-threatening illness such as colon cancer,” CMS wrote in the rule.
Navigators often start their work when cancer patients are screened and guide them through initial diagnosis, potential surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, said Sharon Gentry, MSN, RN, a former nurse navigator who is now the editor in chief of the Journal of the Academy of Oncology Nurse & Patient Navigators.
The navigators are meant to be a trusted and continual presence for patients, who otherwise might be left to start anew in finding help at each phase of care.
The navigators “see the whole picture. They see the whole journey the patient takes, from pre-diagnosis all the way through diagnosis care out through survival,” Ms. Gentry said.
Gaining a special Medicare payment for these kinds of services will elevate this work, she said.
Many newer drugs can target specific mechanisms and proteins of cancer. Often, oncology treatment involves testing to find out if mutations are allowing the cancer cells to evade a patient’s immune system.
Checking these biomarkers takes time, however. Patients sometimes become frustrated because they are anxious to begin treatment. Patients may receive inaccurate information from friends or family who went through treatment previously. Navigators can provide knowledge on the current state of care for a patient’s disease, helping them better manage anxieties.
“You have to explain to them that things have changed since the guy you drink coffee with was diagnosed with cancer, and there may be a drug that could target that,” Ms. Gentry said.
Potential Challenges
Initial uptake of the new PIN codes may be slow going, however, as clinicians and health systems may already use well-established codes. These include CCM and principal care management services, which may pay higher rates, Mullangi said.
“There might be sensitivity around not wanting to cannibalize existing programs with a new program,” Dr. Mullangi said.
In addition, many patients will have a copay for the services of principal illness navigators, Dr. Mullangi said.
While many patients have additional insurance that would cover the service, not all do. People with traditional Medicare coverage can sometimes pay 20% of the cost of some medical services.
“I think that may give patients pause, particularly if they’re already feeling the financial burden of a cancer treatment journey,” Dr. Mullangi said.
Pay rates for PIN services involve calculations of regional price differences, which are posted publicly by CMS, and potential added fees for services provided by hospital-affiliated organizations.
Consider payments for code G0023, covering 60 minutes of principal navigation services provided in a single month.
A set reimbursement for patients cared for in independent medical practices exists, with variation for local costs. Medicare’s non-facility price for G0023 would be $102.41 in some parts of Silicon Valley in California, including San Jose. In Arkansas, where costs are lower, reimbursement would be $73.14 for this same service.
Patients who get services covered by code G0023 in independent medical practices would have monthly copays of about $15-$20, depending on where they live.
The tab for patients tends to be higher for these same services if delivered through a medical practice owned by a hospital, as this would trigger the addition of facility fees to the payments made to cover the services. Facility fees are difficult for the public to ascertain before getting a treatment or service.
Dr. Mullangi and Ms. Gentry reported no relevant financial disclosures outside of their employers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.

No Benefit to High-Dose IV Vs Oral Steroids in Giant Cell Arteritis
TOPLINE:
In patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA), intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids alone does not improve visual acuity and increases the risk for diabetes within the first year. Survival rates do not differ with these two treatments.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a population-based retrospective study at three centers in Sweden to assess the clinical characteristics, treatment-related toxicity, and mortality in patients with GCA who were receiving high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone.
- A total of 419 patients with biopsy-confirmed GCA (mean age at diagnosis, 75 years; 69% women) diagnosed from 2004 to 2019 were included.
- Patients were treated with either intravenous methylprednisolone (n = 111) at a dose of 500-1000 mg per day for 3 consecutive days or oral glucocorticoids alone (n = 308).
- Ischemic visual complications considered to indicate visual involvement were confirmed by an ophthalmologist, and data on visual acuity were collected from ophthalmologic clinic records at initial consultations and follow-up at 3-18 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- Despite a tendency toward improvement, no significant difference in visual acuity was observed with intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids.
- Patients treated with intravenous methylprednisolone had a higher risk for newly diagnosed diabetes within a year of GCA diagnosis (odds ratio [OR], 2.59; P = .01).
- The risk for diabetes remained elevated even after adjustment for the cumulative oral glucocorticoid dose at 3 months (adjusted OR, 3.30; P = .01).
- Survival rates did not significantly differ between the treatment groups over a mean follow-up of 6.6 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this study on the use of intravenous methylprednisolone treatment in GCA, we found no evidence of a beneficial effect in improving visual acuity or enabling more rapid tapering of the oral glucocorticoid dose,” the authors wrote. “The use of IVMP [intravenous methylprednisolone] was associated with an increased risk of diabetes during the first year compared with oral GC [glucocorticoid], raising questions about the value of IVMP in GCA treatment.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Hampus Henningson, Department of Clinical Sciences, Rheumatology, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, was published online in Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of the study may have resulted in missing data and difficulty in accurately quantifying the cumulative glucocorticoid doses. The study did not validate the diagnoses of comorbidities but relied solely on diagnostic codes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Swedish Research Council, Swedish Rheumatism Association, Swedish Medical Society, Alfred Österlund’s Foundation, and King Gustaf V’s 80-year foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA), intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids alone does not improve visual acuity and increases the risk for diabetes within the first year. Survival rates do not differ with these two treatments.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a population-based retrospective study at three centers in Sweden to assess the clinical characteristics, treatment-related toxicity, and mortality in patients with GCA who were receiving high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone.
- A total of 419 patients with biopsy-confirmed GCA (mean age at diagnosis, 75 years; 69% women) diagnosed from 2004 to 2019 were included.
- Patients were treated with either intravenous methylprednisolone (n = 111) at a dose of 500-1000 mg per day for 3 consecutive days or oral glucocorticoids alone (n = 308).
- Ischemic visual complications considered to indicate visual involvement were confirmed by an ophthalmologist, and data on visual acuity were collected from ophthalmologic clinic records at initial consultations and follow-up at 3-18 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- Despite a tendency toward improvement, no significant difference in visual acuity was observed with intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids.
- Patients treated with intravenous methylprednisolone had a higher risk for newly diagnosed diabetes within a year of GCA diagnosis (odds ratio [OR], 2.59; P = .01).
- The risk for diabetes remained elevated even after adjustment for the cumulative oral glucocorticoid dose at 3 months (adjusted OR, 3.30; P = .01).
- Survival rates did not significantly differ between the treatment groups over a mean follow-up of 6.6 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this study on the use of intravenous methylprednisolone treatment in GCA, we found no evidence of a beneficial effect in improving visual acuity or enabling more rapid tapering of the oral glucocorticoid dose,” the authors wrote. “The use of IVMP [intravenous methylprednisolone] was associated with an increased risk of diabetes during the first year compared with oral GC [glucocorticoid], raising questions about the value of IVMP in GCA treatment.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Hampus Henningson, Department of Clinical Sciences, Rheumatology, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, was published online in Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of the study may have resulted in missing data and difficulty in accurately quantifying the cumulative glucocorticoid doses. The study did not validate the diagnoses of comorbidities but relied solely on diagnostic codes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Swedish Research Council, Swedish Rheumatism Association, Swedish Medical Society, Alfred Österlund’s Foundation, and King Gustaf V’s 80-year foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA), intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids alone does not improve visual acuity and increases the risk for diabetes within the first year. Survival rates do not differ with these two treatments.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a population-based retrospective study at three centers in Sweden to assess the clinical characteristics, treatment-related toxicity, and mortality in patients with GCA who were receiving high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone.
- A total of 419 patients with biopsy-confirmed GCA (mean age at diagnosis, 75 years; 69% women) diagnosed from 2004 to 2019 were included.
- Patients were treated with either intravenous methylprednisolone (n = 111) at a dose of 500-1000 mg per day for 3 consecutive days or oral glucocorticoids alone (n = 308).
- Ischemic visual complications considered to indicate visual involvement were confirmed by an ophthalmologist, and data on visual acuity were collected from ophthalmologic clinic records at initial consultations and follow-up at 3-18 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- Despite a tendency toward improvement, no significant difference in visual acuity was observed with intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids.
- Patients treated with intravenous methylprednisolone had a higher risk for newly diagnosed diabetes within a year of GCA diagnosis (odds ratio [OR], 2.59; P = .01).
- The risk for diabetes remained elevated even after adjustment for the cumulative oral glucocorticoid dose at 3 months (adjusted OR, 3.30; P = .01).
- Survival rates did not significantly differ between the treatment groups over a mean follow-up of 6.6 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this study on the use of intravenous methylprednisolone treatment in GCA, we found no evidence of a beneficial effect in improving visual acuity or enabling more rapid tapering of the oral glucocorticoid dose,” the authors wrote. “The use of IVMP [intravenous methylprednisolone] was associated with an increased risk of diabetes during the first year compared with oral GC [glucocorticoid], raising questions about the value of IVMP in GCA treatment.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Hampus Henningson, Department of Clinical Sciences, Rheumatology, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, was published online in Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of the study may have resulted in missing data and difficulty in accurately quantifying the cumulative glucocorticoid doses. The study did not validate the diagnoses of comorbidities but relied solely on diagnostic codes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Swedish Research Council, Swedish Rheumatism Association, Swedish Medical Society, Alfred Österlund’s Foundation, and King Gustaf V’s 80-year foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Digital Twin Model Predicts Sepsis Mortality
A “digital twin” model successfully predicted adverse outcomes in intensive care unit (ICU) patients treated for sepsis.
The digital twin could reduce the risk for some interventions, according to Amos Lal, MD, who presented the study at the CHEST Annual Meeting. That’s because the model can predict the outcome. “You don’t actually have to make an intervention to the patient, which might be risky. By doing that, you can actually prevent a lot of harm,” said Dr. Lal, assistant professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
The researchers used a one-dimensional convolutional neural network (CNN), similar to two-dimensional CNNs that are used to classify images, substituting the color channels used in imaging with 38 time-dependent variables. They applied it to predicting outcomes in the ICU, focusing on data generated within the first 24 hours of admission. The team made the model dynamic by adding time-sensitive data like vitals, laboratory values, and interventions every 15 minutes. That contrasts with existing models that are usually static, relying on values at admission or at 24 hours, for example. It also takes into account time-insensitive data like age, gender, and comorbidities. “Combining these two and coming up with the prediction model in real time can give you a more informed decision about how these patients are going to perform over a period of 2 weeks or 4 weeks of their stay within the ICU. And of course, as we get more and more data within the first 24 hours, the performance of the model improves as well,” said Dr. Lal.
The researchers tested the model by creating a virtual model of the patient and then performing an intervention on the patient and a simulated intervention on the virtual patient. “Then we advance the clock and the patient either improved or deteriorated, and we compared how the digital twin performed, whether the changes were concordant or discordant [between the virtual and real-world patients],” said Dr. Lal.
The model was designed to predict which patients with sepsis would be at greater risk for death or ICU stays longer than 14 days. It was created using data from 28,617 patients with critical care sepsis at a single hospital who were treated between 2011 and 2018, with 70% used as a training set, 20% as a test set, and 10% as a validation set. The researchers conducted an external validation using MIMIC-IV data on 30,903 patients from the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston. The model included 31 time-independent variables and 38 time-dependent variables that were collected every 15 minutes at the Mayo Clinic and every 60 minutes at Beth Israel Deaconess. Surgical patients represented 24% of the Mayo dataset and 58% of the MIMIC-IV dataset, but otherwise the two groups were demographically similar.
At 24 hours, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for predicting 14-day mortality was −0.82 in the Mayo validation cohort and −0.78 in the MIMIC validation cohort. The model improved in accuracy over time as more data were accumulated.
The session’s co-moderators, Sandeep Jain, MD, and Casey Cable, MD, praised the work. Dr. Cable, associate professor of pulmonary care medicine at VCU Health, Richmond, Virginia, noted that the model used both surgical patients and medical patients with sepsis, and the two groups can present quite differently. Another variable was the COVID pandemic, where some patients presented at the hospital when they were quite sick. “I’m curious how different starting points would play into it,” she said.
She called for institutions to develop such models on their own rather than relying on companies that might develop software solutions. “I think that this needs to be clinician-led, from the ground up,” said Dr. Cable.
Dr. Jain, an associate professor of pulmonary care medicine at Broward Health, suggested that such models might need to be individualized for each institution, but “my fear is it could become too expensive, so I think a group like CHEST could come together and [create] an open source system to have their researchers jumpstart the research on this,” he said.
Dr. Lal, Dr. Jain, and Dr. Cable reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A “digital twin” model successfully predicted adverse outcomes in intensive care unit (ICU) patients treated for sepsis.
The digital twin could reduce the risk for some interventions, according to Amos Lal, MD, who presented the study at the CHEST Annual Meeting. That’s because the model can predict the outcome. “You don’t actually have to make an intervention to the patient, which might be risky. By doing that, you can actually prevent a lot of harm,” said Dr. Lal, assistant professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
The researchers used a one-dimensional convolutional neural network (CNN), similar to two-dimensional CNNs that are used to classify images, substituting the color channels used in imaging with 38 time-dependent variables. They applied it to predicting outcomes in the ICU, focusing on data generated within the first 24 hours of admission. The team made the model dynamic by adding time-sensitive data like vitals, laboratory values, and interventions every 15 minutes. That contrasts with existing models that are usually static, relying on values at admission or at 24 hours, for example. It also takes into account time-insensitive data like age, gender, and comorbidities. “Combining these two and coming up with the prediction model in real time can give you a more informed decision about how these patients are going to perform over a period of 2 weeks or 4 weeks of their stay within the ICU. And of course, as we get more and more data within the first 24 hours, the performance of the model improves as well,” said Dr. Lal.
The researchers tested the model by creating a virtual model of the patient and then performing an intervention on the patient and a simulated intervention on the virtual patient. “Then we advance the clock and the patient either improved or deteriorated, and we compared how the digital twin performed, whether the changes were concordant or discordant [between the virtual and real-world patients],” said Dr. Lal.
The model was designed to predict which patients with sepsis would be at greater risk for death or ICU stays longer than 14 days. It was created using data from 28,617 patients with critical care sepsis at a single hospital who were treated between 2011 and 2018, with 70% used as a training set, 20% as a test set, and 10% as a validation set. The researchers conducted an external validation using MIMIC-IV data on 30,903 patients from the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston. The model included 31 time-independent variables and 38 time-dependent variables that were collected every 15 minutes at the Mayo Clinic and every 60 minutes at Beth Israel Deaconess. Surgical patients represented 24% of the Mayo dataset and 58% of the MIMIC-IV dataset, but otherwise the two groups were demographically similar.
At 24 hours, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for predicting 14-day mortality was −0.82 in the Mayo validation cohort and −0.78 in the MIMIC validation cohort. The model improved in accuracy over time as more data were accumulated.
The session’s co-moderators, Sandeep Jain, MD, and Casey Cable, MD, praised the work. Dr. Cable, associate professor of pulmonary care medicine at VCU Health, Richmond, Virginia, noted that the model used both surgical patients and medical patients with sepsis, and the two groups can present quite differently. Another variable was the COVID pandemic, where some patients presented at the hospital when they were quite sick. “I’m curious how different starting points would play into it,” she said.
She called for institutions to develop such models on their own rather than relying on companies that might develop software solutions. “I think that this needs to be clinician-led, from the ground up,” said Dr. Cable.
Dr. Jain, an associate professor of pulmonary care medicine at Broward Health, suggested that such models might need to be individualized for each institution, but “my fear is it could become too expensive, so I think a group like CHEST could come together and [create] an open source system to have their researchers jumpstart the research on this,” he said.
Dr. Lal, Dr. Jain, and Dr. Cable reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A “digital twin” model successfully predicted adverse outcomes in intensive care unit (ICU) patients treated for sepsis.
The digital twin could reduce the risk for some interventions, according to Amos Lal, MD, who presented the study at the CHEST Annual Meeting. That’s because the model can predict the outcome. “You don’t actually have to make an intervention to the patient, which might be risky. By doing that, you can actually prevent a lot of harm,” said Dr. Lal, assistant professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
The researchers used a one-dimensional convolutional neural network (CNN), similar to two-dimensional CNNs that are used to classify images, substituting the color channels used in imaging with 38 time-dependent variables. They applied it to predicting outcomes in the ICU, focusing on data generated within the first 24 hours of admission. The team made the model dynamic by adding time-sensitive data like vitals, laboratory values, and interventions every 15 minutes. That contrasts with existing models that are usually static, relying on values at admission or at 24 hours, for example. It also takes into account time-insensitive data like age, gender, and comorbidities. “Combining these two and coming up with the prediction model in real time can give you a more informed decision about how these patients are going to perform over a period of 2 weeks or 4 weeks of their stay within the ICU. And of course, as we get more and more data within the first 24 hours, the performance of the model improves as well,” said Dr. Lal.
The researchers tested the model by creating a virtual model of the patient and then performing an intervention on the patient and a simulated intervention on the virtual patient. “Then we advance the clock and the patient either improved or deteriorated, and we compared how the digital twin performed, whether the changes were concordant or discordant [between the virtual and real-world patients],” said Dr. Lal.
The model was designed to predict which patients with sepsis would be at greater risk for death or ICU stays longer than 14 days. It was created using data from 28,617 patients with critical care sepsis at a single hospital who were treated between 2011 and 2018, with 70% used as a training set, 20% as a test set, and 10% as a validation set. The researchers conducted an external validation using MIMIC-IV data on 30,903 patients from the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston. The model included 31 time-independent variables and 38 time-dependent variables that were collected every 15 minutes at the Mayo Clinic and every 60 minutes at Beth Israel Deaconess. Surgical patients represented 24% of the Mayo dataset and 58% of the MIMIC-IV dataset, but otherwise the two groups were demographically similar.
At 24 hours, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for predicting 14-day mortality was −0.82 in the Mayo validation cohort and −0.78 in the MIMIC validation cohort. The model improved in accuracy over time as more data were accumulated.
The session’s co-moderators, Sandeep Jain, MD, and Casey Cable, MD, praised the work. Dr. Cable, associate professor of pulmonary care medicine at VCU Health, Richmond, Virginia, noted that the model used both surgical patients and medical patients with sepsis, and the two groups can present quite differently. Another variable was the COVID pandemic, where some patients presented at the hospital when they were quite sick. “I’m curious how different starting points would play into it,” she said.
She called for institutions to develop such models on their own rather than relying on companies that might develop software solutions. “I think that this needs to be clinician-led, from the ground up,” said Dr. Cable.
Dr. Jain, an associate professor of pulmonary care medicine at Broward Health, suggested that such models might need to be individualized for each institution, but “my fear is it could become too expensive, so I think a group like CHEST could come together and [create] an open source system to have their researchers jumpstart the research on this,” he said.
Dr. Lal, Dr. Jain, and Dr. Cable reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CHEST 2024
Older Patients With COPD at Increased Risk for PE-Associated Death
BOSTON — Patients with COPD are at an increased risk for fatal pulmonary embolism (PE) and may require personalized, targeted thromboprophylaxis.
The data suggest that “maybe we should start thinking about if we are admitting a patient with COPD in that specific age group, higher thromboprophylaxis for PE,” said Marwa Oudah, MD, a pulmonary hypertension fellow at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. She presented her group’s findings in a rapid-fire oral abstract session at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
Known Risk Factor
COPD is a known risk factor for PE. To estimate how the obstructive lung disease may contribute to PE-related deaths among patients of varying ages, Oudah and colleagues drew data on deaths due to an underlying cause of PE from 1999 to 2020 from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s WONDER database.
They stratified the patients into two groups — those with or without COPD — whose data were included in the Multiple Causes of Death dataset, according to age groups ranging from 35 years to over 100 years. The investigators calculated proportional mortality ratios in the non-COPD group and applied these to the COPD-positive group among different age ranges to estimate the observed vs expected number of deaths.
A total of 10,434 persons who died from PE and had COPD listed among causes of death were identified. The sample was evenly divided by sex. The peak range of deaths was among those aged 75-84 years.
The authors saw an increase in PE-related mortality among patients with COPD aged 65-85 years (P < .001).
The ratios of observed-to-expected deaths among patients in this age range were “substantially greater than 1” said Oudah, with patients aged 75-79 years at highest risk for PE-related death, with an observed-to-expected ratio of 1.443.
In contrast, the rate of observed deaths among patients aged 85-89 years was similar to the expected rate, suggesting that the COPD-PE interaction may wane among older patients, she said.
Among patients aged 35-64 years, the risk for death from PE was not significantly higher for any of the 5-year age categories.
The investigators emphasized that “given the observed trend, individualized patient assessments are imperative to optimize preventable measures against PE in the aging COPD population.”
Confounding Comorbidities
In an interview, a pulmonary specialist who was not involved in the study commented that older persons with COPD tend to have multiple comorbidities that may contribute to the risk for PE.
“Older patients have so many comorbidities, and their risk for pulmonary embolism and thromboembolic disease is pretty high, so I’m not surprised that 75 to 79 years olds are having a higher mortality from PE, but it’s a little difficult to say whether that’s due to COPD,” said Krishna Sundar, MBBS, MD, FCCP, a pulmonary, sleep medicine, and critical care medicine specialist at St. John’s Medical Center in Jackson, Wyoming, who moderated the session.
The authors did not report a study funding source. Oudah and Sundar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — Patients with COPD are at an increased risk for fatal pulmonary embolism (PE) and may require personalized, targeted thromboprophylaxis.
The data suggest that “maybe we should start thinking about if we are admitting a patient with COPD in that specific age group, higher thromboprophylaxis for PE,” said Marwa Oudah, MD, a pulmonary hypertension fellow at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. She presented her group’s findings in a rapid-fire oral abstract session at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
Known Risk Factor
COPD is a known risk factor for PE. To estimate how the obstructive lung disease may contribute to PE-related deaths among patients of varying ages, Oudah and colleagues drew data on deaths due to an underlying cause of PE from 1999 to 2020 from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s WONDER database.
They stratified the patients into two groups — those with or without COPD — whose data were included in the Multiple Causes of Death dataset, according to age groups ranging from 35 years to over 100 years. The investigators calculated proportional mortality ratios in the non-COPD group and applied these to the COPD-positive group among different age ranges to estimate the observed vs expected number of deaths.
A total of 10,434 persons who died from PE and had COPD listed among causes of death were identified. The sample was evenly divided by sex. The peak range of deaths was among those aged 75-84 years.
The authors saw an increase in PE-related mortality among patients with COPD aged 65-85 years (P < .001).
The ratios of observed-to-expected deaths among patients in this age range were “substantially greater than 1” said Oudah, with patients aged 75-79 years at highest risk for PE-related death, with an observed-to-expected ratio of 1.443.
In contrast, the rate of observed deaths among patients aged 85-89 years was similar to the expected rate, suggesting that the COPD-PE interaction may wane among older patients, she said.
Among patients aged 35-64 years, the risk for death from PE was not significantly higher for any of the 5-year age categories.
The investigators emphasized that “given the observed trend, individualized patient assessments are imperative to optimize preventable measures against PE in the aging COPD population.”
Confounding Comorbidities
In an interview, a pulmonary specialist who was not involved in the study commented that older persons with COPD tend to have multiple comorbidities that may contribute to the risk for PE.
“Older patients have so many comorbidities, and their risk for pulmonary embolism and thromboembolic disease is pretty high, so I’m not surprised that 75 to 79 years olds are having a higher mortality from PE, but it’s a little difficult to say whether that’s due to COPD,” said Krishna Sundar, MBBS, MD, FCCP, a pulmonary, sleep medicine, and critical care medicine specialist at St. John’s Medical Center in Jackson, Wyoming, who moderated the session.
The authors did not report a study funding source. Oudah and Sundar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — Patients with COPD are at an increased risk for fatal pulmonary embolism (PE) and may require personalized, targeted thromboprophylaxis.
The data suggest that “maybe we should start thinking about if we are admitting a patient with COPD in that specific age group, higher thromboprophylaxis for PE,” said Marwa Oudah, MD, a pulmonary hypertension fellow at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. She presented her group’s findings in a rapid-fire oral abstract session at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
Known Risk Factor
COPD is a known risk factor for PE. To estimate how the obstructive lung disease may contribute to PE-related deaths among patients of varying ages, Oudah and colleagues drew data on deaths due to an underlying cause of PE from 1999 to 2020 from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s WONDER database.
They stratified the patients into two groups — those with or without COPD — whose data were included in the Multiple Causes of Death dataset, according to age groups ranging from 35 years to over 100 years. The investigators calculated proportional mortality ratios in the non-COPD group and applied these to the COPD-positive group among different age ranges to estimate the observed vs expected number of deaths.
A total of 10,434 persons who died from PE and had COPD listed among causes of death were identified. The sample was evenly divided by sex. The peak range of deaths was among those aged 75-84 years.
The authors saw an increase in PE-related mortality among patients with COPD aged 65-85 years (P < .001).
The ratios of observed-to-expected deaths among patients in this age range were “substantially greater than 1” said Oudah, with patients aged 75-79 years at highest risk for PE-related death, with an observed-to-expected ratio of 1.443.
In contrast, the rate of observed deaths among patients aged 85-89 years was similar to the expected rate, suggesting that the COPD-PE interaction may wane among older patients, she said.
Among patients aged 35-64 years, the risk for death from PE was not significantly higher for any of the 5-year age categories.
The investigators emphasized that “given the observed trend, individualized patient assessments are imperative to optimize preventable measures against PE in the aging COPD population.”
Confounding Comorbidities
In an interview, a pulmonary specialist who was not involved in the study commented that older persons with COPD tend to have multiple comorbidities that may contribute to the risk for PE.
“Older patients have so many comorbidities, and their risk for pulmonary embolism and thromboembolic disease is pretty high, so I’m not surprised that 75 to 79 years olds are having a higher mortality from PE, but it’s a little difficult to say whether that’s due to COPD,” said Krishna Sundar, MBBS, MD, FCCP, a pulmonary, sleep medicine, and critical care medicine specialist at St. John’s Medical Center in Jackson, Wyoming, who moderated the session.
The authors did not report a study funding source. Oudah and Sundar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CHEST 2024
AF Burden Increases Around Time of COPD Hospitalizations
BOSTON — Patients with COPD who have exacerbations requiring hospitalization should be monitored for cardiac arrhythmias, investigators said.
This recommendation is based on results of a study of medical records showing that among more than 20,000 hospitalizations for patients with COPD without concurrent heart failure (HF), 40% patients had at least 6 minutes of daily atrial fibrillation (AF) burden, and nearly half of these patients had at least an hour of daily AF burden; patients with COPD and concurrent HF had similar daily AF burdens, reported Trent Fischer, MD, MS, senior principal scientist at Medtronic in Minneapolis.
“We can conclude that AF burden increases in the weeks after a hospitalization for COPD if they don’t have a concurrent diagnosis of heart failure. Also, having concurrent heart failure increases the risk of atrial fibrillation and increases the atrial fibrillation burden around the time of COPD hospitalization,” he said in a rapid-fire oral abstract session at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
The findings indicated a need for increased vigilance for AF around the time of a serious COPD exacerbation and may explain at least some of the increased risks for stroke observed in patients who are hospitalized for COPD exacerbations, he said.
Retrospective Study
They drew data from 2007 through 2021 on patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators, cardiac resynchronization therapy devices, pacemakers, and implantable cardiac monitors, using the Optum de-identified electronic health record dataset linked with Medtronic’s CareLink database to conduct a retrospective analysis.
They looked at admissions for COPD linked to available device diagnostic parameters between 30 days prior to and 60 days after admission for COPD.
They identified a total of 20,056 COPD hospitalizations for patients with concurrent HF and 3877 for those without HF.
Among patients with HF, 43% had a daily AF burden of at least 6 minutes, and 22% had at least 1 hour of irregular rhythms. Among patients without HF, 40% had at least 6 minutes of irregular rhythms daily, and 18% had at least 1 hour.
Among patients with HF, the daily average AF burden increased from a baseline of 158 min/d 30 days before an admission to 170 min/d at admission, returning to baseline by 20 days after hospitalization.
For patients without HF, the AF burden increased from 107 min/d at baseline to 113 min/d during hospitalization and returned to baseline by 20 days after hospitalization.
Confounding Factor?
In the Q&A, session moderator Krishna Sundar, MBBS, MD, FCCP, a pulmonary, sleep medicine, and critical care medicine specialist at St. John’s Medical Center in Jackson, Wyoming, said that when patients with HF get admitted for COPD exacerbations, their HF typically worsens and asked Dr. Fischer how he could tell the difference.
“I know there’s a lot of interaction between heart failure and COPD. They’re well-know comorbidities, and the exacerbation of one can bring on worsening of the other. At least with this database, we can’t really tease out any sort of differences,” Dr. Fischer replied.
“I think that a diagnosis of COPD exacerbation is pretty well laid out, but it’s sometimes difficult to separate worsening of heart failure in these patients, and often these patients get treated for both problems. It’s clear that it’s the heart failure patients who are having more atrial fibrillation episodes, which is not surprising, but the question is how much is the COPD exacerbation contributing to the atrial fibrillation?” said Dr. Sundar.
The study was supported by Medtronic. Dr. Fischer is employed by the company. Dr. Sundar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — Patients with COPD who have exacerbations requiring hospitalization should be monitored for cardiac arrhythmias, investigators said.
This recommendation is based on results of a study of medical records showing that among more than 20,000 hospitalizations for patients with COPD without concurrent heart failure (HF), 40% patients had at least 6 minutes of daily atrial fibrillation (AF) burden, and nearly half of these patients had at least an hour of daily AF burden; patients with COPD and concurrent HF had similar daily AF burdens, reported Trent Fischer, MD, MS, senior principal scientist at Medtronic in Minneapolis.
“We can conclude that AF burden increases in the weeks after a hospitalization for COPD if they don’t have a concurrent diagnosis of heart failure. Also, having concurrent heart failure increases the risk of atrial fibrillation and increases the atrial fibrillation burden around the time of COPD hospitalization,” he said in a rapid-fire oral abstract session at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
The findings indicated a need for increased vigilance for AF around the time of a serious COPD exacerbation and may explain at least some of the increased risks for stroke observed in patients who are hospitalized for COPD exacerbations, he said.
Retrospective Study
They drew data from 2007 through 2021 on patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators, cardiac resynchronization therapy devices, pacemakers, and implantable cardiac monitors, using the Optum de-identified electronic health record dataset linked with Medtronic’s CareLink database to conduct a retrospective analysis.
They looked at admissions for COPD linked to available device diagnostic parameters between 30 days prior to and 60 days after admission for COPD.
They identified a total of 20,056 COPD hospitalizations for patients with concurrent HF and 3877 for those without HF.
Among patients with HF, 43% had a daily AF burden of at least 6 minutes, and 22% had at least 1 hour of irregular rhythms. Among patients without HF, 40% had at least 6 minutes of irregular rhythms daily, and 18% had at least 1 hour.
Among patients with HF, the daily average AF burden increased from a baseline of 158 min/d 30 days before an admission to 170 min/d at admission, returning to baseline by 20 days after hospitalization.
For patients without HF, the AF burden increased from 107 min/d at baseline to 113 min/d during hospitalization and returned to baseline by 20 days after hospitalization.
Confounding Factor?
In the Q&A, session moderator Krishna Sundar, MBBS, MD, FCCP, a pulmonary, sleep medicine, and critical care medicine specialist at St. John’s Medical Center in Jackson, Wyoming, said that when patients with HF get admitted for COPD exacerbations, their HF typically worsens and asked Dr. Fischer how he could tell the difference.
“I know there’s a lot of interaction between heart failure and COPD. They’re well-know comorbidities, and the exacerbation of one can bring on worsening of the other. At least with this database, we can’t really tease out any sort of differences,” Dr. Fischer replied.
“I think that a diagnosis of COPD exacerbation is pretty well laid out, but it’s sometimes difficult to separate worsening of heart failure in these patients, and often these patients get treated for both problems. It’s clear that it’s the heart failure patients who are having more atrial fibrillation episodes, which is not surprising, but the question is how much is the COPD exacerbation contributing to the atrial fibrillation?” said Dr. Sundar.
The study was supported by Medtronic. Dr. Fischer is employed by the company. Dr. Sundar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — Patients with COPD who have exacerbations requiring hospitalization should be monitored for cardiac arrhythmias, investigators said.
This recommendation is based on results of a study of medical records showing that among more than 20,000 hospitalizations for patients with COPD without concurrent heart failure (HF), 40% patients had at least 6 minutes of daily atrial fibrillation (AF) burden, and nearly half of these patients had at least an hour of daily AF burden; patients with COPD and concurrent HF had similar daily AF burdens, reported Trent Fischer, MD, MS, senior principal scientist at Medtronic in Minneapolis.
“We can conclude that AF burden increases in the weeks after a hospitalization for COPD if they don’t have a concurrent diagnosis of heart failure. Also, having concurrent heart failure increases the risk of atrial fibrillation and increases the atrial fibrillation burden around the time of COPD hospitalization,” he said in a rapid-fire oral abstract session at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
The findings indicated a need for increased vigilance for AF around the time of a serious COPD exacerbation and may explain at least some of the increased risks for stroke observed in patients who are hospitalized for COPD exacerbations, he said.
Retrospective Study
They drew data from 2007 through 2021 on patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators, cardiac resynchronization therapy devices, pacemakers, and implantable cardiac monitors, using the Optum de-identified electronic health record dataset linked with Medtronic’s CareLink database to conduct a retrospective analysis.
They looked at admissions for COPD linked to available device diagnostic parameters between 30 days prior to and 60 days after admission for COPD.
They identified a total of 20,056 COPD hospitalizations for patients with concurrent HF and 3877 for those without HF.
Among patients with HF, 43% had a daily AF burden of at least 6 minutes, and 22% had at least 1 hour of irregular rhythms. Among patients without HF, 40% had at least 6 minutes of irregular rhythms daily, and 18% had at least 1 hour.
Among patients with HF, the daily average AF burden increased from a baseline of 158 min/d 30 days before an admission to 170 min/d at admission, returning to baseline by 20 days after hospitalization.
For patients without HF, the AF burden increased from 107 min/d at baseline to 113 min/d during hospitalization and returned to baseline by 20 days after hospitalization.
Confounding Factor?
In the Q&A, session moderator Krishna Sundar, MBBS, MD, FCCP, a pulmonary, sleep medicine, and critical care medicine specialist at St. John’s Medical Center in Jackson, Wyoming, said that when patients with HF get admitted for COPD exacerbations, their HF typically worsens and asked Dr. Fischer how he could tell the difference.
“I know there’s a lot of interaction between heart failure and COPD. They’re well-know comorbidities, and the exacerbation of one can bring on worsening of the other. At least with this database, we can’t really tease out any sort of differences,” Dr. Fischer replied.
“I think that a diagnosis of COPD exacerbation is pretty well laid out, but it’s sometimes difficult to separate worsening of heart failure in these patients, and often these patients get treated for both problems. It’s clear that it’s the heart failure patients who are having more atrial fibrillation episodes, which is not surprising, but the question is how much is the COPD exacerbation contributing to the atrial fibrillation?” said Dr. Sundar.
The study was supported by Medtronic. Dr. Fischer is employed by the company. Dr. Sundar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CHEST 2024
Novel Intervention Slows Cognitive Decline in At-Risk Adults
new research suggests.
The cognitive remediation intervention included a series of progressively difficult computer-based and facilitator-monitored mental exercises designed to sharpen cognitive function.
Researchers found that using cognitive remediation with tDCS slowed decline in executive function and verbal memory more than other cognitive functions. The effect was stronger among people with rMDD versus those with MCI and in those at low genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease.
“We have developed a novel intervention, combining two interventions that if used separately have a weak effect but together have substantial and clinically meaningful effect of slowing the progression of cognitive decline,” said study author Benoit H. Mulsant, MD, chair of the Department of Psychiatry, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and senior scientist at the Center for Addiction and Mental Health, also in Toronto.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
High-Risk Group
Research shows that older adults with MDD or MCI are at high risk for cognitive decline and dementia. Evidence also suggests that depression in early or mid-life significantly increases the risk for dementia in late life, even if the depression has been in remission for decades.
A potential mechanism underlying this increased risk for dementia could be impaired cortical plasticity, or the ability of the brain to compensate for damage.
The PACt-MD trial included 375 older adults with rMDD, MCI, or both (mean age, 72 years; 62% women) at five academic hospitals in Toronto.
Participants received either cognitive remediation plus tDCS or sham intervention 5 days per week for 8 weeks (acute phase), followed by 5-day “boosters” every 6 months.
tDCS was administered by trained personnel and involved active stimulation for 30 minutes at the beginning of each cognitive remediation group session. The intervention targets the prefrontal cortex, a critical region for cognitive compensation in normal cognitive aging.
The sham group received a weakened version of cognitive remediation, with exercises that did not get progressively more difficult. For the sham stimulation, the current flowed at full intensity for only 54 seconds before and after 30-second ramp-up and ramp-down phases, to create a blinding effect, the authors noted.
A geriatric psychiatrist followed all participants throughout the study, conducting assessments at baseline, month 2, and yearly for 3-7 years (mean follow-up, 48.3 months).
Participants’ depressive symptoms were evaluated at baseline and at all follow-ups and underwent neuropsychological testing to assess six cognitive domains: processing speed, working memory, executive functioning, verbal memory, visual memory, and language.
To get a norm for the cognitive tests, researchers recruited a comparator group of 75 subjects similar in age, gender, and years of education, with no neuropsychiatric disorder or cognitive impairment. They completed the same assessments but not the intervention.
Study participants and assessors were blinded to treatment assignment.
Slower Cognitive Decline
Participants in the intervention group had a significantly slower decline in cognitive function, compared with those in the sham group (adjusted z score difference [active – sham] at month 60, 0.21; P = .006). This is equivalent to slowing cognitive decline by about 4 years, researchers reported. The intervention also showed a positive effect on executive function and verbal memory.
“If I can push dementia from 85 to 89 years and you die at 86, in practice, I have prevented you from ever developing dementia,” Mulsant said.
The efficacy of cognitive remediation plus tDCS in rMDD could be tied to enhanced neuroplasticity, said Mulsant.
The treatment worked well in people with a history of depression, regardless of MCI status, but was not as effective for people with just MCI, researchers noted. The intervention also did not work as well among people at genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease.
“We don’t believe we have discovered an intervention to prevent dementia in people who are at high risk for Alzheimer disease, but we have discovered an intervention that could prevent dementia in people who have an history of depression,” said Mulsant.
These results suggest the pathways to dementia among people with MCI and rMDD are different, he added.
Because previous research showed either treatment alone demonstrated little efficacy, researchers said the new results indicate that there may be a synergistic effect of combining the two.
The ideal amount of treatment and optimal age for initiation still need to be determined, said Mulsant. The study did not include a comparator group without rMDD or MCI, so the observed cognitive benefits might be specific to people with these high-risk conditions. Another study limitation is lack of diversity in terms of ethnicity, race, and education.
Promising, Important Findings
Commenting on the research, Badr Ratnakaran, MD, assistant professor and division director of geriatric psychiatry at Carilion Clinic–Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine, Roanoke, said the results are promising and important because there are so few treatment options for the increasing number of older patients with depression and dementia.
The side-effect profile of the combined treatment is better than that of many pharmacologic treatments, Ratnakaran noted. As more research like this comes out, Ratnakaran predicts that cognitive remediation and tCDS will become more readily available.
“This is telling us that the field of psychiatry, and also dementia, is progressing beyond your usual pharmacotherapy treatments,” said Ratnakaran, who also is chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Geriatric Psychiatry.
The study received support from the Canada Brain Research Fund of Brain Canada, Health Canada, the Chagnon Family, and the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health Discovery Fund. Mulsant reported holding and receiving support from the Labatt Family Chair in Biology of Depression in Late-Life Adults at the University of Toronto; being a member of the Center for Addiction and Mental Health Board of Trustees; research support from Brain Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Center for Addiction and Mental Health Foundation, Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, and National Institutes of Health; and nonfinancial support from Capital Solution Design and HappyNeuron. Ratnakaran reported no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
The cognitive remediation intervention included a series of progressively difficult computer-based and facilitator-monitored mental exercises designed to sharpen cognitive function.
Researchers found that using cognitive remediation with tDCS slowed decline in executive function and verbal memory more than other cognitive functions. The effect was stronger among people with rMDD versus those with MCI and in those at low genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease.
“We have developed a novel intervention, combining two interventions that if used separately have a weak effect but together have substantial and clinically meaningful effect of slowing the progression of cognitive decline,” said study author Benoit H. Mulsant, MD, chair of the Department of Psychiatry, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and senior scientist at the Center for Addiction and Mental Health, also in Toronto.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
High-Risk Group
Research shows that older adults with MDD or MCI are at high risk for cognitive decline and dementia. Evidence also suggests that depression in early or mid-life significantly increases the risk for dementia in late life, even if the depression has been in remission for decades.
A potential mechanism underlying this increased risk for dementia could be impaired cortical plasticity, or the ability of the brain to compensate for damage.
The PACt-MD trial included 375 older adults with rMDD, MCI, or both (mean age, 72 years; 62% women) at five academic hospitals in Toronto.
Participants received either cognitive remediation plus tDCS or sham intervention 5 days per week for 8 weeks (acute phase), followed by 5-day “boosters” every 6 months.
tDCS was administered by trained personnel and involved active stimulation for 30 minutes at the beginning of each cognitive remediation group session. The intervention targets the prefrontal cortex, a critical region for cognitive compensation in normal cognitive aging.
The sham group received a weakened version of cognitive remediation, with exercises that did not get progressively more difficult. For the sham stimulation, the current flowed at full intensity for only 54 seconds before and after 30-second ramp-up and ramp-down phases, to create a blinding effect, the authors noted.
A geriatric psychiatrist followed all participants throughout the study, conducting assessments at baseline, month 2, and yearly for 3-7 years (mean follow-up, 48.3 months).
Participants’ depressive symptoms were evaluated at baseline and at all follow-ups and underwent neuropsychological testing to assess six cognitive domains: processing speed, working memory, executive functioning, verbal memory, visual memory, and language.
To get a norm for the cognitive tests, researchers recruited a comparator group of 75 subjects similar in age, gender, and years of education, with no neuropsychiatric disorder or cognitive impairment. They completed the same assessments but not the intervention.
Study participants and assessors were blinded to treatment assignment.
Slower Cognitive Decline
Participants in the intervention group had a significantly slower decline in cognitive function, compared with those in the sham group (adjusted z score difference [active – sham] at month 60, 0.21; P = .006). This is equivalent to slowing cognitive decline by about 4 years, researchers reported. The intervention also showed a positive effect on executive function and verbal memory.
“If I can push dementia from 85 to 89 years and you die at 86, in practice, I have prevented you from ever developing dementia,” Mulsant said.
The efficacy of cognitive remediation plus tDCS in rMDD could be tied to enhanced neuroplasticity, said Mulsant.
The treatment worked well in people with a history of depression, regardless of MCI status, but was not as effective for people with just MCI, researchers noted. The intervention also did not work as well among people at genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease.
“We don’t believe we have discovered an intervention to prevent dementia in people who are at high risk for Alzheimer disease, but we have discovered an intervention that could prevent dementia in people who have an history of depression,” said Mulsant.
These results suggest the pathways to dementia among people with MCI and rMDD are different, he added.
Because previous research showed either treatment alone demonstrated little efficacy, researchers said the new results indicate that there may be a synergistic effect of combining the two.
The ideal amount of treatment and optimal age for initiation still need to be determined, said Mulsant. The study did not include a comparator group without rMDD or MCI, so the observed cognitive benefits might be specific to people with these high-risk conditions. Another study limitation is lack of diversity in terms of ethnicity, race, and education.
Promising, Important Findings
Commenting on the research, Badr Ratnakaran, MD, assistant professor and division director of geriatric psychiatry at Carilion Clinic–Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine, Roanoke, said the results are promising and important because there are so few treatment options for the increasing number of older patients with depression and dementia.
The side-effect profile of the combined treatment is better than that of many pharmacologic treatments, Ratnakaran noted. As more research like this comes out, Ratnakaran predicts that cognitive remediation and tCDS will become more readily available.
“This is telling us that the field of psychiatry, and also dementia, is progressing beyond your usual pharmacotherapy treatments,” said Ratnakaran, who also is chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Geriatric Psychiatry.
The study received support from the Canada Brain Research Fund of Brain Canada, Health Canada, the Chagnon Family, and the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health Discovery Fund. Mulsant reported holding and receiving support from the Labatt Family Chair in Biology of Depression in Late-Life Adults at the University of Toronto; being a member of the Center for Addiction and Mental Health Board of Trustees; research support from Brain Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Center for Addiction and Mental Health Foundation, Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, and National Institutes of Health; and nonfinancial support from Capital Solution Design and HappyNeuron. Ratnakaran reported no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
The cognitive remediation intervention included a series of progressively difficult computer-based and facilitator-monitored mental exercises designed to sharpen cognitive function.
Researchers found that using cognitive remediation with tDCS slowed decline in executive function and verbal memory more than other cognitive functions. The effect was stronger among people with rMDD versus those with MCI and in those at low genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease.
“We have developed a novel intervention, combining two interventions that if used separately have a weak effect but together have substantial and clinically meaningful effect of slowing the progression of cognitive decline,” said study author Benoit H. Mulsant, MD, chair of the Department of Psychiatry, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and senior scientist at the Center for Addiction and Mental Health, also in Toronto.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
High-Risk Group
Research shows that older adults with MDD or MCI are at high risk for cognitive decline and dementia. Evidence also suggests that depression in early or mid-life significantly increases the risk for dementia in late life, even if the depression has been in remission for decades.
A potential mechanism underlying this increased risk for dementia could be impaired cortical plasticity, or the ability of the brain to compensate for damage.
The PACt-MD trial included 375 older adults with rMDD, MCI, or both (mean age, 72 years; 62% women) at five academic hospitals in Toronto.
Participants received either cognitive remediation plus tDCS or sham intervention 5 days per week for 8 weeks (acute phase), followed by 5-day “boosters” every 6 months.
tDCS was administered by trained personnel and involved active stimulation for 30 minutes at the beginning of each cognitive remediation group session. The intervention targets the prefrontal cortex, a critical region for cognitive compensation in normal cognitive aging.
The sham group received a weakened version of cognitive remediation, with exercises that did not get progressively more difficult. For the sham stimulation, the current flowed at full intensity for only 54 seconds before and after 30-second ramp-up and ramp-down phases, to create a blinding effect, the authors noted.
A geriatric psychiatrist followed all participants throughout the study, conducting assessments at baseline, month 2, and yearly for 3-7 years (mean follow-up, 48.3 months).
Participants’ depressive symptoms were evaluated at baseline and at all follow-ups and underwent neuropsychological testing to assess six cognitive domains: processing speed, working memory, executive functioning, verbal memory, visual memory, and language.
To get a norm for the cognitive tests, researchers recruited a comparator group of 75 subjects similar in age, gender, and years of education, with no neuropsychiatric disorder or cognitive impairment. They completed the same assessments but not the intervention.
Study participants and assessors were blinded to treatment assignment.
Slower Cognitive Decline
Participants in the intervention group had a significantly slower decline in cognitive function, compared with those in the sham group (adjusted z score difference [active – sham] at month 60, 0.21; P = .006). This is equivalent to slowing cognitive decline by about 4 years, researchers reported. The intervention also showed a positive effect on executive function and verbal memory.
“If I can push dementia from 85 to 89 years and you die at 86, in practice, I have prevented you from ever developing dementia,” Mulsant said.
The efficacy of cognitive remediation plus tDCS in rMDD could be tied to enhanced neuroplasticity, said Mulsant.
The treatment worked well in people with a history of depression, regardless of MCI status, but was not as effective for people with just MCI, researchers noted. The intervention also did not work as well among people at genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease.
“We don’t believe we have discovered an intervention to prevent dementia in people who are at high risk for Alzheimer disease, but we have discovered an intervention that could prevent dementia in people who have an history of depression,” said Mulsant.
These results suggest the pathways to dementia among people with MCI and rMDD are different, he added.
Because previous research showed either treatment alone demonstrated little efficacy, researchers said the new results indicate that there may be a synergistic effect of combining the two.
The ideal amount of treatment and optimal age for initiation still need to be determined, said Mulsant. The study did not include a comparator group without rMDD or MCI, so the observed cognitive benefits might be specific to people with these high-risk conditions. Another study limitation is lack of diversity in terms of ethnicity, race, and education.
Promising, Important Findings
Commenting on the research, Badr Ratnakaran, MD, assistant professor and division director of geriatric psychiatry at Carilion Clinic–Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine, Roanoke, said the results are promising and important because there are so few treatment options for the increasing number of older patients with depression and dementia.
The side-effect profile of the combined treatment is better than that of many pharmacologic treatments, Ratnakaran noted. As more research like this comes out, Ratnakaran predicts that cognitive remediation and tCDS will become more readily available.
“This is telling us that the field of psychiatry, and also dementia, is progressing beyond your usual pharmacotherapy treatments,” said Ratnakaran, who also is chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Geriatric Psychiatry.
The study received support from the Canada Brain Research Fund of Brain Canada, Health Canada, the Chagnon Family, and the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health Discovery Fund. Mulsant reported holding and receiving support from the Labatt Family Chair in Biology of Depression in Late-Life Adults at the University of Toronto; being a member of the Center for Addiction and Mental Health Board of Trustees; research support from Brain Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Center for Addiction and Mental Health Foundation, Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, and National Institutes of Health; and nonfinancial support from Capital Solution Design and HappyNeuron. Ratnakaran reported no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA PSYCHIATRY
A Finger-Prick Test for Alzheimer’s Disease?
In a pilot study, researchers found a good correlation of p-tau217 levels from blood obtained via standard venous sampling and from a single finger prick.
“We see the potential that capillary p-tau217 from dried blood spots could overcome the limitations of standard venous collection of being invasive, dependent on centrifuges and ultra-low temperature freezers, and also requiring less volume than standard plasma analysis,” said lead investigator Hanna Huber, PhD, Department of Psychiatry and Neurochemistry, Institute of Neuroscience and Physiology, University of Gothenburg, Sweden.
The findings were presented at the 17th Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease (CTAD) conference.
Strong Link Between Venous and Capillary Samples
p-tau217 has emerged as the most effective blood test to identify Alzheimer’s disease. However, traditional venous blood sampling requires certain infrastructure and immediate processing. Increased and simplified access to this blood biomarker could be crucial for early diagnosis, proper patient management, and prompt initiation of disease-modifying treatments.
The DROP-AD project is investigating the diagnostic performance of finger-prick collection to accurately measure p-tau217. In the current study, the research team obtained paired venous blood and capillary blood samples from 206 adults (mean age, 71.8 years; 59% women), with or without cognitive impairment, from five European centers. A subset of participants provided a second finger-prick sample collected without any supervision.
The capillary blood samples were obtained via a single finger prick, and then single blood drops were applied to a dried plasma spot (DPS) card, which was then shipped to a lab (without temperature control or cooling) for p-tau217 measurement. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers were available for a subset of individuals.
Throughout the entire study population, there was a “very convincing correlation” between p-tau217 levels from capillary DPS and venous plasma, Huber told conference attendees.
Additionally, capillary DPS p-tau217 levels were able to discriminate amyloid-positive from amyloid-negative individuals, with levels of this biomarker increasing in a stepwise fashion, “from cognitively unimpaired individuals to individuals with mild cognitive impairment and, finally, to dementia patients,” Huber said.
Of note, capillary p-tau217 levels from DPS samples that were collected by research staff did not differ from unsupervised self-collected samples.
What about the stability of the samples? Capillary DPS p-tau-217 is “stable over 2 weeks at room temperature,” Huber said.
Ready for Prime Time?
Preliminary data from the DROP-AD project highlight the potential of using finger-prick blood collection to identify neurofilament light (NfL) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), two other Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers.
“We think that capillary p-tau217, but also other biomarkers, could be a widely accessible and cheap alternative for clinical practice and clinical trials in individuals with cognitive decline if the results are confirmed in longitudinal and home-sampling cohorts,” Huber concluded.
“Measuring biomarkers by a simple finger prick could facilitate regular and autonomous sampling at home, which would be particularly useful in remote and rural settings,” she noted.
The findings in this study confirm and extend earlier findings that the study team reported last year at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference (AAIC).
“The data shared at CTAD 2024, along with the related material previously presented at AAIC 2023, reporting on a ‘finger prick’ blood test approach is interesting and emerging work but not yet ready for clinical use,” said Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association vice president of scientific engagement.
“That said, the idea of a highly accessible and scalable tool that can aid in easier and more equitable diagnosis would be welcomed by researchers, clinicians, and individuals and families affected by Alzheimer’s disease and all other dementias,” Edelmayer said.
“This finger-prick blood testing technology for Alzheimer’s biomarkers still has to be validated more broadly, but it is very promising. Advancements in technology and practice demonstrate the simplicity, transportability, and diagnostic value of blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s,” she added.
The Alzheimer’s Association is currently conducting a systematic review of the evidence and preparing clinical practice guidelines on blood-based biomarker tests for specialized healthcare settings, with publications, clinical resources, and tools anticipated in 2025, Edelmayer noted.
The study had no commercial funding. Huber and Edelmayer report no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In a pilot study, researchers found a good correlation of p-tau217 levels from blood obtained via standard venous sampling and from a single finger prick.
“We see the potential that capillary p-tau217 from dried blood spots could overcome the limitations of standard venous collection of being invasive, dependent on centrifuges and ultra-low temperature freezers, and also requiring less volume than standard plasma analysis,” said lead investigator Hanna Huber, PhD, Department of Psychiatry and Neurochemistry, Institute of Neuroscience and Physiology, University of Gothenburg, Sweden.
The findings were presented at the 17th Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease (CTAD) conference.
Strong Link Between Venous and Capillary Samples
p-tau217 has emerged as the most effective blood test to identify Alzheimer’s disease. However, traditional venous blood sampling requires certain infrastructure and immediate processing. Increased and simplified access to this blood biomarker could be crucial for early diagnosis, proper patient management, and prompt initiation of disease-modifying treatments.
The DROP-AD project is investigating the diagnostic performance of finger-prick collection to accurately measure p-tau217. In the current study, the research team obtained paired venous blood and capillary blood samples from 206 adults (mean age, 71.8 years; 59% women), with or without cognitive impairment, from five European centers. A subset of participants provided a second finger-prick sample collected without any supervision.
The capillary blood samples were obtained via a single finger prick, and then single blood drops were applied to a dried plasma spot (DPS) card, which was then shipped to a lab (without temperature control or cooling) for p-tau217 measurement. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers were available for a subset of individuals.
Throughout the entire study population, there was a “very convincing correlation” between p-tau217 levels from capillary DPS and venous plasma, Huber told conference attendees.
Additionally, capillary DPS p-tau217 levels were able to discriminate amyloid-positive from amyloid-negative individuals, with levels of this biomarker increasing in a stepwise fashion, “from cognitively unimpaired individuals to individuals with mild cognitive impairment and, finally, to dementia patients,” Huber said.
Of note, capillary p-tau217 levels from DPS samples that were collected by research staff did not differ from unsupervised self-collected samples.
What about the stability of the samples? Capillary DPS p-tau-217 is “stable over 2 weeks at room temperature,” Huber said.
Ready for Prime Time?
Preliminary data from the DROP-AD project highlight the potential of using finger-prick blood collection to identify neurofilament light (NfL) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), two other Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers.
“We think that capillary p-tau217, but also other biomarkers, could be a widely accessible and cheap alternative for clinical practice and clinical trials in individuals with cognitive decline if the results are confirmed in longitudinal and home-sampling cohorts,” Huber concluded.
“Measuring biomarkers by a simple finger prick could facilitate regular and autonomous sampling at home, which would be particularly useful in remote and rural settings,” she noted.
The findings in this study confirm and extend earlier findings that the study team reported last year at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference (AAIC).
“The data shared at CTAD 2024, along with the related material previously presented at AAIC 2023, reporting on a ‘finger prick’ blood test approach is interesting and emerging work but not yet ready for clinical use,” said Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association vice president of scientific engagement.
“That said, the idea of a highly accessible and scalable tool that can aid in easier and more equitable diagnosis would be welcomed by researchers, clinicians, and individuals and families affected by Alzheimer’s disease and all other dementias,” Edelmayer said.
“This finger-prick blood testing technology for Alzheimer’s biomarkers still has to be validated more broadly, but it is very promising. Advancements in technology and practice demonstrate the simplicity, transportability, and diagnostic value of blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s,” she added.
The Alzheimer’s Association is currently conducting a systematic review of the evidence and preparing clinical practice guidelines on blood-based biomarker tests for specialized healthcare settings, with publications, clinical resources, and tools anticipated in 2025, Edelmayer noted.
The study had no commercial funding. Huber and Edelmayer report no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In a pilot study, researchers found a good correlation of p-tau217 levels from blood obtained via standard venous sampling and from a single finger prick.
“We see the potential that capillary p-tau217 from dried blood spots could overcome the limitations of standard venous collection of being invasive, dependent on centrifuges and ultra-low temperature freezers, and also requiring less volume than standard plasma analysis,” said lead investigator Hanna Huber, PhD, Department of Psychiatry and Neurochemistry, Institute of Neuroscience and Physiology, University of Gothenburg, Sweden.
The findings were presented at the 17th Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease (CTAD) conference.
Strong Link Between Venous and Capillary Samples
p-tau217 has emerged as the most effective blood test to identify Alzheimer’s disease. However, traditional venous blood sampling requires certain infrastructure and immediate processing. Increased and simplified access to this blood biomarker could be crucial for early diagnosis, proper patient management, and prompt initiation of disease-modifying treatments.
The DROP-AD project is investigating the diagnostic performance of finger-prick collection to accurately measure p-tau217. In the current study, the research team obtained paired venous blood and capillary blood samples from 206 adults (mean age, 71.8 years; 59% women), with or without cognitive impairment, from five European centers. A subset of participants provided a second finger-prick sample collected without any supervision.
The capillary blood samples were obtained via a single finger prick, and then single blood drops were applied to a dried plasma spot (DPS) card, which was then shipped to a lab (without temperature control or cooling) for p-tau217 measurement. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers were available for a subset of individuals.
Throughout the entire study population, there was a “very convincing correlation” between p-tau217 levels from capillary DPS and venous plasma, Huber told conference attendees.
Additionally, capillary DPS p-tau217 levels were able to discriminate amyloid-positive from amyloid-negative individuals, with levels of this biomarker increasing in a stepwise fashion, “from cognitively unimpaired individuals to individuals with mild cognitive impairment and, finally, to dementia patients,” Huber said.
Of note, capillary p-tau217 levels from DPS samples that were collected by research staff did not differ from unsupervised self-collected samples.
What about the stability of the samples? Capillary DPS p-tau-217 is “stable over 2 weeks at room temperature,” Huber said.
Ready for Prime Time?
Preliminary data from the DROP-AD project highlight the potential of using finger-prick blood collection to identify neurofilament light (NfL) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), two other Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers.
“We think that capillary p-tau217, but also other biomarkers, could be a widely accessible and cheap alternative for clinical practice and clinical trials in individuals with cognitive decline if the results are confirmed in longitudinal and home-sampling cohorts,” Huber concluded.
“Measuring biomarkers by a simple finger prick could facilitate regular and autonomous sampling at home, which would be particularly useful in remote and rural settings,” she noted.
The findings in this study confirm and extend earlier findings that the study team reported last year at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference (AAIC).
“The data shared at CTAD 2024, along with the related material previously presented at AAIC 2023, reporting on a ‘finger prick’ blood test approach is interesting and emerging work but not yet ready for clinical use,” said Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association vice president of scientific engagement.
“That said, the idea of a highly accessible and scalable tool that can aid in easier and more equitable diagnosis would be welcomed by researchers, clinicians, and individuals and families affected by Alzheimer’s disease and all other dementias,” Edelmayer said.
“This finger-prick blood testing technology for Alzheimer’s biomarkers still has to be validated more broadly, but it is very promising. Advancements in technology and practice demonstrate the simplicity, transportability, and diagnostic value of blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s,” she added.
The Alzheimer’s Association is currently conducting a systematic review of the evidence and preparing clinical practice guidelines on blood-based biomarker tests for specialized healthcare settings, with publications, clinical resources, and tools anticipated in 2025, Edelmayer noted.
The study had no commercial funding. Huber and Edelmayer report no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CTAD 2024
Minor Progress in Gender Pay Equity, But a Big Gap Persists
Despite some recent progress in compensation equity, women in medicine continue to be paid significantly lower salaries than men.
According to the Female Compensation Report 2024 by Medscape, male doctors of any kind earned an average salary of about $400,000, whereas female doctors earned approximately $309,000 — a 29% gap.
The report analyzed survey data from 7000 practicing physicians who were recruited over a 4-month period starting in October 2023. The respondents comprised roughly 60% women representing over 29 specialties.
In the 2022 report, the pay gap between the genders was 32%. But some women in the field argued substantial headway is still needed.
“You can try and pick apart the data, but I’d say we’re not really making progress,” said Susan T. Hingle, MD, an internist in Illinois and president of the American Medical Women’s Association. “A decline by a couple of percentage points is not significantly addressing this pay gap that over a lifetime is huge, can be millions of dollars.”
The gender gap was narrower among female primary care physicians (PCPs) vs medical specialists. Female PCPs earned around $253,000 per year, whereas male PCPs earned about $295,000 per year. Hingle suggested that female PCPs may enjoy more pay equity because health systems have a harder time filling these positions.
On the other hand, the gap for specialists rose from 27% in 2022 to 31% in 2023. Differences in how aggressively women and men negotiate compensation packages may play a role, said Hingle.
“Taking negotiation out of the equation would be progress to me,” said Hingle.
Pay disparity did not appear to be the result of time spent on the job — female doctors reported an average of 49 work hours per week, whereas their male counterparts reported 50 work hours per week.
Meanwhile, the pay gap progressively worsened over time. Among doctors aged 28-34 years, men earned an average of $53,000 more than women. By ages 46-49, men earned an average of $157,000 more than women.
“I had to take my employer to court to get equal compensation, sad as it is to say,” said a hospitalist in North Carolina.
Nearly 60% of women surveyed felt they were not being paid fairly for their efforts, up from less than half reported in Medscape’s 2021 report. Hingle said that this figure may not only reflect sentiments about the compensation gap, but also less support on the job, including fewer physician assistants (PAs), nurses, and administrative staff.
“At my job, I do the work of multiple people,” said a survey respondent. “Junior resident, senior resident, social worker, nurse practitioner, PA — as well as try to be a teacher, researcher, [and] an excellent doctor and have the time to make patients feel as if they are not in a rush.”
Roughly 30% of women physicians said they would not choose to go into medicine again if given the chance compared with 26% of male physicians.
“Gender inequities in our profession have a direct impact,” said Shikha Jain, MD, an oncologist in Chicago and founder of the Women in Medicine nonprofit. “I think women in general don’t feel valued in the care they’re providing.”
Jain cited bullying, harassment, and fewer opportunities for leadership and recognition as factors beyond pay that affect female physicians’ feelings of being valued.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite some recent progress in compensation equity, women in medicine continue to be paid significantly lower salaries than men.
According to the Female Compensation Report 2024 by Medscape, male doctors of any kind earned an average salary of about $400,000, whereas female doctors earned approximately $309,000 — a 29% gap.
The report analyzed survey data from 7000 practicing physicians who were recruited over a 4-month period starting in October 2023. The respondents comprised roughly 60% women representing over 29 specialties.
In the 2022 report, the pay gap between the genders was 32%. But some women in the field argued substantial headway is still needed.
“You can try and pick apart the data, but I’d say we’re not really making progress,” said Susan T. Hingle, MD, an internist in Illinois and president of the American Medical Women’s Association. “A decline by a couple of percentage points is not significantly addressing this pay gap that over a lifetime is huge, can be millions of dollars.”
The gender gap was narrower among female primary care physicians (PCPs) vs medical specialists. Female PCPs earned around $253,000 per year, whereas male PCPs earned about $295,000 per year. Hingle suggested that female PCPs may enjoy more pay equity because health systems have a harder time filling these positions.
On the other hand, the gap for specialists rose from 27% in 2022 to 31% in 2023. Differences in how aggressively women and men negotiate compensation packages may play a role, said Hingle.
“Taking negotiation out of the equation would be progress to me,” said Hingle.
Pay disparity did not appear to be the result of time spent on the job — female doctors reported an average of 49 work hours per week, whereas their male counterparts reported 50 work hours per week.
Meanwhile, the pay gap progressively worsened over time. Among doctors aged 28-34 years, men earned an average of $53,000 more than women. By ages 46-49, men earned an average of $157,000 more than women.
“I had to take my employer to court to get equal compensation, sad as it is to say,” said a hospitalist in North Carolina.
Nearly 60% of women surveyed felt they were not being paid fairly for their efforts, up from less than half reported in Medscape’s 2021 report. Hingle said that this figure may not only reflect sentiments about the compensation gap, but also less support on the job, including fewer physician assistants (PAs), nurses, and administrative staff.
“At my job, I do the work of multiple people,” said a survey respondent. “Junior resident, senior resident, social worker, nurse practitioner, PA — as well as try to be a teacher, researcher, [and] an excellent doctor and have the time to make patients feel as if they are not in a rush.”
Roughly 30% of women physicians said they would not choose to go into medicine again if given the chance compared with 26% of male physicians.
“Gender inequities in our profession have a direct impact,” said Shikha Jain, MD, an oncologist in Chicago and founder of the Women in Medicine nonprofit. “I think women in general don’t feel valued in the care they’re providing.”
Jain cited bullying, harassment, and fewer opportunities for leadership and recognition as factors beyond pay that affect female physicians’ feelings of being valued.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite some recent progress in compensation equity, women in medicine continue to be paid significantly lower salaries than men.
According to the Female Compensation Report 2024 by Medscape, male doctors of any kind earned an average salary of about $400,000, whereas female doctors earned approximately $309,000 — a 29% gap.
The report analyzed survey data from 7000 practicing physicians who were recruited over a 4-month period starting in October 2023. The respondents comprised roughly 60% women representing over 29 specialties.
In the 2022 report, the pay gap between the genders was 32%. But some women in the field argued substantial headway is still needed.
“You can try and pick apart the data, but I’d say we’re not really making progress,” said Susan T. Hingle, MD, an internist in Illinois and president of the American Medical Women’s Association. “A decline by a couple of percentage points is not significantly addressing this pay gap that over a lifetime is huge, can be millions of dollars.”
The gender gap was narrower among female primary care physicians (PCPs) vs medical specialists. Female PCPs earned around $253,000 per year, whereas male PCPs earned about $295,000 per year. Hingle suggested that female PCPs may enjoy more pay equity because health systems have a harder time filling these positions.
On the other hand, the gap for specialists rose from 27% in 2022 to 31% in 2023. Differences in how aggressively women and men negotiate compensation packages may play a role, said Hingle.
“Taking negotiation out of the equation would be progress to me,” said Hingle.
Pay disparity did not appear to be the result of time spent on the job — female doctors reported an average of 49 work hours per week, whereas their male counterparts reported 50 work hours per week.
Meanwhile, the pay gap progressively worsened over time. Among doctors aged 28-34 years, men earned an average of $53,000 more than women. By ages 46-49, men earned an average of $157,000 more than women.
“I had to take my employer to court to get equal compensation, sad as it is to say,” said a hospitalist in North Carolina.
Nearly 60% of women surveyed felt they were not being paid fairly for their efforts, up from less than half reported in Medscape’s 2021 report. Hingle said that this figure may not only reflect sentiments about the compensation gap, but also less support on the job, including fewer physician assistants (PAs), nurses, and administrative staff.
“At my job, I do the work of multiple people,” said a survey respondent. “Junior resident, senior resident, social worker, nurse practitioner, PA — as well as try to be a teacher, researcher, [and] an excellent doctor and have the time to make patients feel as if they are not in a rush.”
Roughly 30% of women physicians said they would not choose to go into medicine again if given the chance compared with 26% of male physicians.
“Gender inequities in our profession have a direct impact,” said Shikha Jain, MD, an oncologist in Chicago and founder of the Women in Medicine nonprofit. “I think women in general don’t feel valued in the care they’re providing.”
Jain cited bullying, harassment, and fewer opportunities for leadership and recognition as factors beyond pay that affect female physicians’ feelings of being valued.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.




