User login
When you initiate antidepressant therapy for patients who have not been treated for depression previously, select either sertraline or escitalopram. A large meta-analysis found these medications to be superior to other “new-generation” antidepressants.1
Strength of recommendation
A: Meta-analysis of 117 high-quality studies.
Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373:746-758.
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
Mrs. D is a 45-year-old patient whom you’ve treated for type 2 diabetes for several years. On her latest visit, she reports a loss of energy and difficulty sleeping and wonders if they could be related to the diabetes. As you explore further and question Mrs. D about these symptoms, she becomes tearful—and tells you she has episodes of sadness and no longer enjoys things the way she used to. Although she has no past history of depression, when you suggest that her symptoms may be an indication of depression, she readily agrees.
You discuss treatment options, including antidepressants and therapy. Mrs. D decides to try medication. But with so many antidepressants on the market, how do you determine which to choose?
Major depression is the fourth leading cause of disease globally, according to the World Health Organization.2 Depression is common in the United States as well, and primary care physicians are often the ones who are diagnosing and treating it. In fact, the US Preventive Services Task Force recently expanded its recommendation that primary care providers screen adults for depression, to include adolescents ages 12 to 18 years.3 When depression is diagnosed, physicians must help patients decide on an initial treatment plan.
All antidepressants are not equal
Options for initial treatment of unipolar major depression include psychotherapy and the use of an antidepressant. For mild and moderate depression, psychotherapy alone is as effective as medication. Combined psychotherapy and antidepressants are more effective than either treatment alone for all degrees of depression.4
The ideal medication for depression would be a drug with a high level of effectiveness and a low side-effect profile; until now, however, there has been little evidence to support 1 antidepressant over another. Previous meta-analyses have concluded that there are no significant differences in either efficacy or acceptability among the various second-generation antidepressants on the market.5,6 Thus, physicians have historically made initial monotherapy treatment decisions based on side effects and cost.7,8 The meta-analysis we report on here tells a different story, providing strong evidence that some antidepressants are more effective and better tolerated than others.
STUDY SUMMARY: Meta-analysis reveals 2 “best” drugs
Cipriani et al1 conducted a systematic review and multiple-treatments meta-analysis of 117 prospective randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Taken together, the RCTs evaluated the comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 second-generation antidepressants: bupropion, citalopram, duloxetine, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, milnacipran, mirtazapine, paroxetine, reboxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine. The methodology of this meta-analysis differed from that of traditional meta-analyses by allowing the integration of data from both direct and indirect comparisons. (An indirect comparison is one in which drugs from different trials are assessed by combining the results of their effectiveness and comparing the combined finding with the effectiveness of a drug that all the trials have in common.) Previous studies, based only on direct comparisons, yielded inconsistent results.
The studies included in this meta-analysis were all RCTs in which 1 of these 12 antidepressants was tested against 1, or several, other second-generation antidepressants as monotherapy for the acute treatment phase of unipolar major depression. The authors excluded placebo-controlled trials in order to evaluate efficacy and acceptability of the study medications relative to other commonly used antidepressants. They defined acute treatment as 8 weeks of antidepressant therapy, with a range of 6 to 12 weeks. The primary outcomes studied were response to treatment and dropout rate.
Response to treatment (efficacy) was constructed as a Yes or No variable; a positive response was defined as a reduction of ≥50% in symptom score on either the Hamilton depression rating scale or the Montgomery-Asberg rating scale, or a rating of “improved” or “very much improved” on the clinical global impression at 8 weeks. Efficacy was calculated on an intention-to-treat basis; if data were missing for a participant, that person was classified as a nonresponder.
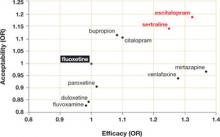
Dropout rate was used to represent acceptability, as the authors believed it to be a more clinically meaningful measure than either side effects or symptom scores. Comparative efficacy and acceptability were analyzed. Fluoxetine—the first of the second-generation antidepressants—was used as the reference medication. The ( FIGURE ) shows the outcomes for 9 of the antidepressants, compared with those of fluoxetine. The other 2 antidepressants, milnacipran and reboxetine, are omitted because they are not available in the United States.
The overall meta-analysis included 25,928 individuals, with 24,595 in the efficacy analysis and 24,693 in the acceptability analysis. Nearly two-thirds (64%) of the participants were women. The mean duration of follow-up was 8.1 weeks, and mean sample size per study was 110. Studies of women with postpartum depression were excluded.
Escitalopram and sertraline stand out. Overall, escitalopram, mirtazapine, sertraline, and venlafaxine were significantly more efficacious than fluoxetine or the other medications. Bupropion, citalopram, escitalopram, and sertraline were better tolerated than the other antidepressants. Escitalopram and sertraline were found to have the best combination of efficacy and acceptability.
Efficacy results. Fifty-nine percent of participants responded to sertraline, vs a 52% response rate for fluoxetine (number needed to treat [NNT]=14). Similarly, 52% of participants responded to escitalopram, compared with 47% of those taking fluoxetine (NNT=20).
Acceptability results. In terms of dropout rate, 28% of participants discontinued fluoxetine, vs 24% of patients taking sertraline. This means that 25 patients would need to be treated with sertraline, rather than fluoxetine, to avoid 1 discontinuation. In the comparison of fluoxetine vs escitalopram, 25% discontinued fluoxetine, compared with 24% who discontinued escitalopram.
The efficacy and acceptability of sertraline and escitalopram compared with other second-generation antidepressant medications show similar trends.
The generic advantage. The investigators recommend sertraline as the best choice for an initial antidepressant because it is available in generic form and is therefore lower in cost. They further recommend that sertraline, instead of fluoxetine or placebo, be the new standard against which other antidepressants are compared.
FIGURE
Sertraline and escitalopram come out on top
Using fluoxetine as the reference medication, the researchers analyzed various second-generation antidepressants. Sertraline and escitalopram had the best combination of efficacy and acceptability.
OR, odds ratio.
Source: Cipriani A et al. Lancet. 2009.1
WHAT’S NEW?: Antidepressant choice is evidence-based
We now have solid evidence for choosing sertraline or escitalopram as the first medication to use when treating a patient with newly diagnosed depression. This represents a practice change because antidepressants that are less effective and less acceptable have been chosen more frequently than either of these medications. That conclusion is based on our analysis of the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey database for outpatient and ambulatory clinic visits in 2005-2006 (the most recent data available). We conducted this analysis to determine which of the second-generation antidepressants were prescribed most for initial monotherapy of major depression.
Our finding: An estimated 4 million patients ages 18 years and older diagnosed with depression in the course of the study year received new prescriptions for a single antidepressant. Six medications accounted for 90% of the prescriptions, in the following order:
- fluoxetine (Prozac)
- duloxetine (Cymbalta)
- escitalopram (Lexapro)
- paroxetine (Paxil)
- venlafaxine (Effexor)
- sertraline (Zoloft).
Sertraline and escitalopram, the drugs shown to be most effective and acceptable in the Cipriani meta-analysis, accounted for 11.8% and 14.5% of the prescriptions, respectively.
CAVEATS: Meta-analysis looked only at acute treatment phase
The results of this study are limited to initial therapy as measured at 8 weeks. Little long-term outcome data are available; response to initial therapy may not be a predictor of full remission or long-term success. Current guidelines suggest maintenance of the initial successful therapy, often with increasing intervals between visits, to prevent relapse.9
This study does not add new insight into long-term response rates. Nor does it deal with choice of a replacement or second antidepressant for nonresponders or those who cannot tolerate the initial drug.
What’s more, the study covers drug treatment alone, which may not be the best initial treatment for depression. Psychotherapy, in the form of cognitive behavioral therapy or interpersonal therapy, when available, is equally effective, has fewer potential physiologic side effects, and may produce longer-lasting results.10,11
Little is known about study design
The authors of this study had access only to limited information about inclusion criteria and the composition of initial study populations or settings. There is a difference between a trial designed to evaluate the “efficacy” of an intervention (“the beneficial and harmful effects of an intervention under controlled circumstances”) and the “effectiveness” of an intervention (the “beneficial and harmful effects of the intervention under usual circumstances”).12 It is not clear which of the 117 studies were efficacy studies and which were effectiveness studies. This may limit the overall generalizability of the study results to a primary care population.
Studies included in this meta-analysis were selected exclusively from published literature. There is some evidence that there is a bias toward the publication of studies with positive results, which may have the effect of overstating the effectiveness of a given antidepressant.13 However, we have no reason to believe that this bias would favor any particular drug.
Most of the included studies were sponsored by drug companies. Notably, pharmaceutical companies have the option of continuing to conduct trials of medications until a study results in a positive finding for their medication, with no penalty for the suppression of equivocal or negative results (negative publication bias). Under current FDA guidelines, there is little transparency to the consumer as to how many trials have been undertaken and the direction of the results, published or unpublished.14
We doubt that either publication bias or the design and sponsorship of the studies included in this meta-analysis present significant threats to the validity of these findings over other sources upon which guidelines rely, given that these issues are common to much of the research on pharmacologic therapy. We also doubt that the compensation of the authors by pharmaceutical companies would bias the outcome of the study in this instance. One of the authors (TAF) received compensation from Pfizer, the maker of Zoloft, which is also available as generic sertraline. None of the authors received compensation from Forest Pharmaceuticals, the makers of Lexapro (escitalopram).
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION: No major barriers are anticipated
Both sertraline and escitalopram are covered by most health insurers. As noted above, sertraline is available in generic formulation, and is therefore much less expensive than escitalopram. In a check of online drug prices, we found a prescription for a 3-month supply of Lexapro (10 mg) to cost about $250; a 3-month supply of generic sertraline (100 mg) from the same sources would cost approximately $35 (www.pharmcychecker.com). Both Pfizer, the maker of Zoloft, and Forest Pharmaceuticals, the maker of Lexapro, have patient assistance programs to make these medications available to low-income, uninsured patients.
Acknowledgements
The PURLs Surveillance System is supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR02499 from the National Center for Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center for Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
The authors wish to acknowledge Sofia Medvedev, PhD, of the University HealthSystem Consortium in Oak Brook, Ill, for analysis of the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey data and the UHC Clinical Database.
1. Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373:746-758.
2. Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Global Burden of Disease. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1996.
3. Williams SB, O’Connor EA, Eder M, et al. Screening for child and adolescent depression in primary care settings: a systematic evidence review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Pediatrics. 2009;123:e716-e735.
4. Timonen M, Liukkonen T. Management of depression in adults. BMJ. 2008;336:435-439.
5. Gartlehner G, Hansen RA, Thieda P, et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Second-Generation Antidepressants in the Pharmacologic Treatment of Adult Depression. Comparative Effectiveness Review No. 7. (Prepared by RTI International-University of North Carolina Evidence Based Practice Center under Contract No. 290-02-0016.) Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; January 2007. Available at: www.effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/reports/final.cfm. Accessed May 18, 2009.
6. Hansen RA, Gartlehner G, Lohr KN, et al. Efficacy and safety of second-generation antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Ann Intern Med. 2005;143:415-426.
7. Adams SM, Miller KE, Zylstra RG. Pharmacologic management of adult depression. Am Fam Physician. 2008;77:785-792.
8. Qaseem A, Snow V, Denberg TD, et al. Using second-generation antidepressants to treat depressive disorders: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149:725-733.
9. DeRubeis RJ, Hollon SD, Amsterdam JD, et al. Cognitive therapy vs medications in the treatment of moderate to severe depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:409-416.
10. deMello MF, de Jesus MJ, Bacaltchuk J, et al. A systematic review of research findings on the efficacy of interpersonal therapy for depressive disorders. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2005;255:75-82.
11. APA Practice Guidelines. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder, second edition. Available at: http://www.psychiatryonline.com/content.aspx?aID=48727. Accessed June 16, 2009.
12. Sackett D. An introduction to performing therapeutic trials. In: Haynes RB, Sackett DL, et al, eds. Clinical Epidemiology: How to Do Clinical Practice Research. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006.
13. Turner EH, Matthews AM, Linardatos E, et al. Selective publication of antidepressant trials and its influence on apparent efficacy. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:252-260.
14. Mathew SJ, Charney DS. Publication bias and the efficacy of antidepressants. Am J Psychiatry. 2009;166:140-145.
PURLs methodology This study was selected and evaluated using FPIN’s Priority Updates from the Research Literature (PURL) Surveillance System methodology. The criteria and findings leading to the selection of this study as a PURL can be accessed at www.jfponline.com/purls.
When you initiate antidepressant therapy for patients who have not been treated for depression previously, select either sertraline or escitalopram. A large meta-analysis found these medications to be superior to other “new-generation” antidepressants.1
Strength of recommendation
A: Meta-analysis of 117 high-quality studies.
Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373:746-758.
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
Mrs. D is a 45-year-old patient whom you’ve treated for type 2 diabetes for several years. On her latest visit, she reports a loss of energy and difficulty sleeping and wonders if they could be related to the diabetes. As you explore further and question Mrs. D about these symptoms, she becomes tearful—and tells you she has episodes of sadness and no longer enjoys things the way she used to. Although she has no past history of depression, when you suggest that her symptoms may be an indication of depression, she readily agrees.
You discuss treatment options, including antidepressants and therapy. Mrs. D decides to try medication. But with so many antidepressants on the market, how do you determine which to choose?
Major depression is the fourth leading cause of disease globally, according to the World Health Organization.2 Depression is common in the United States as well, and primary care physicians are often the ones who are diagnosing and treating it. In fact, the US Preventive Services Task Force recently expanded its recommendation that primary care providers screen adults for depression, to include adolescents ages 12 to 18 years.3 When depression is diagnosed, physicians must help patients decide on an initial treatment plan.
All antidepressants are not equal
Options for initial treatment of unipolar major depression include psychotherapy and the use of an antidepressant. For mild and moderate depression, psychotherapy alone is as effective as medication. Combined psychotherapy and antidepressants are more effective than either treatment alone for all degrees of depression.4
The ideal medication for depression would be a drug with a high level of effectiveness and a low side-effect profile; until now, however, there has been little evidence to support 1 antidepressant over another. Previous meta-analyses have concluded that there are no significant differences in either efficacy or acceptability among the various second-generation antidepressants on the market.5,6 Thus, physicians have historically made initial monotherapy treatment decisions based on side effects and cost.7,8 The meta-analysis we report on here tells a different story, providing strong evidence that some antidepressants are more effective and better tolerated than others.
STUDY SUMMARY: Meta-analysis reveals 2 “best” drugs
Cipriani et al1 conducted a systematic review and multiple-treatments meta-analysis of 117 prospective randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Taken together, the RCTs evaluated the comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 second-generation antidepressants: bupropion, citalopram, duloxetine, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, milnacipran, mirtazapine, paroxetine, reboxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine. The methodology of this meta-analysis differed from that of traditional meta-analyses by allowing the integration of data from both direct and indirect comparisons. (An indirect comparison is one in which drugs from different trials are assessed by combining the results of their effectiveness and comparing the combined finding with the effectiveness of a drug that all the trials have in common.) Previous studies, based only on direct comparisons, yielded inconsistent results.
The studies included in this meta-analysis were all RCTs in which 1 of these 12 antidepressants was tested against 1, or several, other second-generation antidepressants as monotherapy for the acute treatment phase of unipolar major depression. The authors excluded placebo-controlled trials in order to evaluate efficacy and acceptability of the study medications relative to other commonly used antidepressants. They defined acute treatment as 8 weeks of antidepressant therapy, with a range of 6 to 12 weeks. The primary outcomes studied were response to treatment and dropout rate.
Response to treatment (efficacy) was constructed as a Yes or No variable; a positive response was defined as a reduction of ≥50% in symptom score on either the Hamilton depression rating scale or the Montgomery-Asberg rating scale, or a rating of “improved” or “very much improved” on the clinical global impression at 8 weeks. Efficacy was calculated on an intention-to-treat basis; if data were missing for a participant, that person was classified as a nonresponder.
Dropout rate was used to represent acceptability, as the authors believed it to be a more clinically meaningful measure than either side effects or symptom scores. Comparative efficacy and acceptability were analyzed. Fluoxetine—the first of the second-generation antidepressants—was used as the reference medication. The ( FIGURE ) shows the outcomes for 9 of the antidepressants, compared with those of fluoxetine. The other 2 antidepressants, milnacipran and reboxetine, are omitted because they are not available in the United States.
The overall meta-analysis included 25,928 individuals, with 24,595 in the efficacy analysis and 24,693 in the acceptability analysis. Nearly two-thirds (64%) of the participants were women. The mean duration of follow-up was 8.1 weeks, and mean sample size per study was 110. Studies of women with postpartum depression were excluded.
Escitalopram and sertraline stand out. Overall, escitalopram, mirtazapine, sertraline, and venlafaxine were significantly more efficacious than fluoxetine or the other medications. Bupropion, citalopram, escitalopram, and sertraline were better tolerated than the other antidepressants. Escitalopram and sertraline were found to have the best combination of efficacy and acceptability.
Efficacy results. Fifty-nine percent of participants responded to sertraline, vs a 52% response rate for fluoxetine (number needed to treat [NNT]=14). Similarly, 52% of participants responded to escitalopram, compared with 47% of those taking fluoxetine (NNT=20).
Acceptability results. In terms of dropout rate, 28% of participants discontinued fluoxetine, vs 24% of patients taking sertraline. This means that 25 patients would need to be treated with sertraline, rather than fluoxetine, to avoid 1 discontinuation. In the comparison of fluoxetine vs escitalopram, 25% discontinued fluoxetine, compared with 24% who discontinued escitalopram.
The efficacy and acceptability of sertraline and escitalopram compared with other second-generation antidepressant medications show similar trends.
The generic advantage. The investigators recommend sertraline as the best choice for an initial antidepressant because it is available in generic form and is therefore lower in cost. They further recommend that sertraline, instead of fluoxetine or placebo, be the new standard against which other antidepressants are compared.
FIGURE
Sertraline and escitalopram come out on top
Using fluoxetine as the reference medication, the researchers analyzed various second-generation antidepressants. Sertraline and escitalopram had the best combination of efficacy and acceptability.
OR, odds ratio.
Source: Cipriani A et al. Lancet. 2009.1
WHAT’S NEW?: Antidepressant choice is evidence-based
We now have solid evidence for choosing sertraline or escitalopram as the first medication to use when treating a patient with newly diagnosed depression. This represents a practice change because antidepressants that are less effective and less acceptable have been chosen more frequently than either of these medications. That conclusion is based on our analysis of the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey database for outpatient and ambulatory clinic visits in 2005-2006 (the most recent data available). We conducted this analysis to determine which of the second-generation antidepressants were prescribed most for initial monotherapy of major depression.
Our finding: An estimated 4 million patients ages 18 years and older diagnosed with depression in the course of the study year received new prescriptions for a single antidepressant. Six medications accounted for 90% of the prescriptions, in the following order:
- fluoxetine (Prozac)
- duloxetine (Cymbalta)
- escitalopram (Lexapro)
- paroxetine (Paxil)
- venlafaxine (Effexor)
- sertraline (Zoloft).
Sertraline and escitalopram, the drugs shown to be most effective and acceptable in the Cipriani meta-analysis, accounted for 11.8% and 14.5% of the prescriptions, respectively.
CAVEATS: Meta-analysis looked only at acute treatment phase
The results of this study are limited to initial therapy as measured at 8 weeks. Little long-term outcome data are available; response to initial therapy may not be a predictor of full remission or long-term success. Current guidelines suggest maintenance of the initial successful therapy, often with increasing intervals between visits, to prevent relapse.9
This study does not add new insight into long-term response rates. Nor does it deal with choice of a replacement or second antidepressant for nonresponders or those who cannot tolerate the initial drug.
What’s more, the study covers drug treatment alone, which may not be the best initial treatment for depression. Psychotherapy, in the form of cognitive behavioral therapy or interpersonal therapy, when available, is equally effective, has fewer potential physiologic side effects, and may produce longer-lasting results.10,11
Little is known about study design
The authors of this study had access only to limited information about inclusion criteria and the composition of initial study populations or settings. There is a difference between a trial designed to evaluate the “efficacy” of an intervention (“the beneficial and harmful effects of an intervention under controlled circumstances”) and the “effectiveness” of an intervention (the “beneficial and harmful effects of the intervention under usual circumstances”).12 It is not clear which of the 117 studies were efficacy studies and which were effectiveness studies. This may limit the overall generalizability of the study results to a primary care population.
Studies included in this meta-analysis were selected exclusively from published literature. There is some evidence that there is a bias toward the publication of studies with positive results, which may have the effect of overstating the effectiveness of a given antidepressant.13 However, we have no reason to believe that this bias would favor any particular drug.
Most of the included studies were sponsored by drug companies. Notably, pharmaceutical companies have the option of continuing to conduct trials of medications until a study results in a positive finding for their medication, with no penalty for the suppression of equivocal or negative results (negative publication bias). Under current FDA guidelines, there is little transparency to the consumer as to how many trials have been undertaken and the direction of the results, published or unpublished.14
We doubt that either publication bias or the design and sponsorship of the studies included in this meta-analysis present significant threats to the validity of these findings over other sources upon which guidelines rely, given that these issues are common to much of the research on pharmacologic therapy. We also doubt that the compensation of the authors by pharmaceutical companies would bias the outcome of the study in this instance. One of the authors (TAF) received compensation from Pfizer, the maker of Zoloft, which is also available as generic sertraline. None of the authors received compensation from Forest Pharmaceuticals, the makers of Lexapro (escitalopram).
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION: No major barriers are anticipated
Both sertraline and escitalopram are covered by most health insurers. As noted above, sertraline is available in generic formulation, and is therefore much less expensive than escitalopram. In a check of online drug prices, we found a prescription for a 3-month supply of Lexapro (10 mg) to cost about $250; a 3-month supply of generic sertraline (100 mg) from the same sources would cost approximately $35 (www.pharmcychecker.com). Both Pfizer, the maker of Zoloft, and Forest Pharmaceuticals, the maker of Lexapro, have patient assistance programs to make these medications available to low-income, uninsured patients.
Acknowledgements
The PURLs Surveillance System is supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR02499 from the National Center for Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center for Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
The authors wish to acknowledge Sofia Medvedev, PhD, of the University HealthSystem Consortium in Oak Brook, Ill, for analysis of the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey data and the UHC Clinical Database.
When you initiate antidepressant therapy for patients who have not been treated for depression previously, select either sertraline or escitalopram. A large meta-analysis found these medications to be superior to other “new-generation” antidepressants.1
Strength of recommendation
A: Meta-analysis of 117 high-quality studies.
Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373:746-758.
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
Mrs. D is a 45-year-old patient whom you’ve treated for type 2 diabetes for several years. On her latest visit, she reports a loss of energy and difficulty sleeping and wonders if they could be related to the diabetes. As you explore further and question Mrs. D about these symptoms, she becomes tearful—and tells you she has episodes of sadness and no longer enjoys things the way she used to. Although she has no past history of depression, when you suggest that her symptoms may be an indication of depression, she readily agrees.
You discuss treatment options, including antidepressants and therapy. Mrs. D decides to try medication. But with so many antidepressants on the market, how do you determine which to choose?
Major depression is the fourth leading cause of disease globally, according to the World Health Organization.2 Depression is common in the United States as well, and primary care physicians are often the ones who are diagnosing and treating it. In fact, the US Preventive Services Task Force recently expanded its recommendation that primary care providers screen adults for depression, to include adolescents ages 12 to 18 years.3 When depression is diagnosed, physicians must help patients decide on an initial treatment plan.
All antidepressants are not equal
Options for initial treatment of unipolar major depression include psychotherapy and the use of an antidepressant. For mild and moderate depression, psychotherapy alone is as effective as medication. Combined psychotherapy and antidepressants are more effective than either treatment alone for all degrees of depression.4
The ideal medication for depression would be a drug with a high level of effectiveness and a low side-effect profile; until now, however, there has been little evidence to support 1 antidepressant over another. Previous meta-analyses have concluded that there are no significant differences in either efficacy or acceptability among the various second-generation antidepressants on the market.5,6 Thus, physicians have historically made initial monotherapy treatment decisions based on side effects and cost.7,8 The meta-analysis we report on here tells a different story, providing strong evidence that some antidepressants are more effective and better tolerated than others.
STUDY SUMMARY: Meta-analysis reveals 2 “best” drugs
Cipriani et al1 conducted a systematic review and multiple-treatments meta-analysis of 117 prospective randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Taken together, the RCTs evaluated the comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 second-generation antidepressants: bupropion, citalopram, duloxetine, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, milnacipran, mirtazapine, paroxetine, reboxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine. The methodology of this meta-analysis differed from that of traditional meta-analyses by allowing the integration of data from both direct and indirect comparisons. (An indirect comparison is one in which drugs from different trials are assessed by combining the results of their effectiveness and comparing the combined finding with the effectiveness of a drug that all the trials have in common.) Previous studies, based only on direct comparisons, yielded inconsistent results.
The studies included in this meta-analysis were all RCTs in which 1 of these 12 antidepressants was tested against 1, or several, other second-generation antidepressants as monotherapy for the acute treatment phase of unipolar major depression. The authors excluded placebo-controlled trials in order to evaluate efficacy and acceptability of the study medications relative to other commonly used antidepressants. They defined acute treatment as 8 weeks of antidepressant therapy, with a range of 6 to 12 weeks. The primary outcomes studied were response to treatment and dropout rate.
Response to treatment (efficacy) was constructed as a Yes or No variable; a positive response was defined as a reduction of ≥50% in symptom score on either the Hamilton depression rating scale or the Montgomery-Asberg rating scale, or a rating of “improved” or “very much improved” on the clinical global impression at 8 weeks. Efficacy was calculated on an intention-to-treat basis; if data were missing for a participant, that person was classified as a nonresponder.
Dropout rate was used to represent acceptability, as the authors believed it to be a more clinically meaningful measure than either side effects or symptom scores. Comparative efficacy and acceptability were analyzed. Fluoxetine—the first of the second-generation antidepressants—was used as the reference medication. The ( FIGURE ) shows the outcomes for 9 of the antidepressants, compared with those of fluoxetine. The other 2 antidepressants, milnacipran and reboxetine, are omitted because they are not available in the United States.
The overall meta-analysis included 25,928 individuals, with 24,595 in the efficacy analysis and 24,693 in the acceptability analysis. Nearly two-thirds (64%) of the participants were women. The mean duration of follow-up was 8.1 weeks, and mean sample size per study was 110. Studies of women with postpartum depression were excluded.
Escitalopram and sertraline stand out. Overall, escitalopram, mirtazapine, sertraline, and venlafaxine were significantly more efficacious than fluoxetine or the other medications. Bupropion, citalopram, escitalopram, and sertraline were better tolerated than the other antidepressants. Escitalopram and sertraline were found to have the best combination of efficacy and acceptability.
Efficacy results. Fifty-nine percent of participants responded to sertraline, vs a 52% response rate for fluoxetine (number needed to treat [NNT]=14). Similarly, 52% of participants responded to escitalopram, compared with 47% of those taking fluoxetine (NNT=20).
Acceptability results. In terms of dropout rate, 28% of participants discontinued fluoxetine, vs 24% of patients taking sertraline. This means that 25 patients would need to be treated with sertraline, rather than fluoxetine, to avoid 1 discontinuation. In the comparison of fluoxetine vs escitalopram, 25% discontinued fluoxetine, compared with 24% who discontinued escitalopram.
The efficacy and acceptability of sertraline and escitalopram compared with other second-generation antidepressant medications show similar trends.
The generic advantage. The investigators recommend sertraline as the best choice for an initial antidepressant because it is available in generic form and is therefore lower in cost. They further recommend that sertraline, instead of fluoxetine or placebo, be the new standard against which other antidepressants are compared.
FIGURE
Sertraline and escitalopram come out on top
Using fluoxetine as the reference medication, the researchers analyzed various second-generation antidepressants. Sertraline and escitalopram had the best combination of efficacy and acceptability.
OR, odds ratio.
Source: Cipriani A et al. Lancet. 2009.1
WHAT’S NEW?: Antidepressant choice is evidence-based
We now have solid evidence for choosing sertraline or escitalopram as the first medication to use when treating a patient with newly diagnosed depression. This represents a practice change because antidepressants that are less effective and less acceptable have been chosen more frequently than either of these medications. That conclusion is based on our analysis of the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey database for outpatient and ambulatory clinic visits in 2005-2006 (the most recent data available). We conducted this analysis to determine which of the second-generation antidepressants were prescribed most for initial monotherapy of major depression.
Our finding: An estimated 4 million patients ages 18 years and older diagnosed with depression in the course of the study year received new prescriptions for a single antidepressant. Six medications accounted for 90% of the prescriptions, in the following order:
- fluoxetine (Prozac)
- duloxetine (Cymbalta)
- escitalopram (Lexapro)
- paroxetine (Paxil)
- venlafaxine (Effexor)
- sertraline (Zoloft).
Sertraline and escitalopram, the drugs shown to be most effective and acceptable in the Cipriani meta-analysis, accounted for 11.8% and 14.5% of the prescriptions, respectively.
CAVEATS: Meta-analysis looked only at acute treatment phase
The results of this study are limited to initial therapy as measured at 8 weeks. Little long-term outcome data are available; response to initial therapy may not be a predictor of full remission or long-term success. Current guidelines suggest maintenance of the initial successful therapy, often with increasing intervals between visits, to prevent relapse.9
This study does not add new insight into long-term response rates. Nor does it deal with choice of a replacement or second antidepressant for nonresponders or those who cannot tolerate the initial drug.
What’s more, the study covers drug treatment alone, which may not be the best initial treatment for depression. Psychotherapy, in the form of cognitive behavioral therapy or interpersonal therapy, when available, is equally effective, has fewer potential physiologic side effects, and may produce longer-lasting results.10,11
Little is known about study design
The authors of this study had access only to limited information about inclusion criteria and the composition of initial study populations or settings. There is a difference between a trial designed to evaluate the “efficacy” of an intervention (“the beneficial and harmful effects of an intervention under controlled circumstances”) and the “effectiveness” of an intervention (the “beneficial and harmful effects of the intervention under usual circumstances”).12 It is not clear which of the 117 studies were efficacy studies and which were effectiveness studies. This may limit the overall generalizability of the study results to a primary care population.
Studies included in this meta-analysis were selected exclusively from published literature. There is some evidence that there is a bias toward the publication of studies with positive results, which may have the effect of overstating the effectiveness of a given antidepressant.13 However, we have no reason to believe that this bias would favor any particular drug.
Most of the included studies were sponsored by drug companies. Notably, pharmaceutical companies have the option of continuing to conduct trials of medications until a study results in a positive finding for their medication, with no penalty for the suppression of equivocal or negative results (negative publication bias). Under current FDA guidelines, there is little transparency to the consumer as to how many trials have been undertaken and the direction of the results, published or unpublished.14
We doubt that either publication bias or the design and sponsorship of the studies included in this meta-analysis present significant threats to the validity of these findings over other sources upon which guidelines rely, given that these issues are common to much of the research on pharmacologic therapy. We also doubt that the compensation of the authors by pharmaceutical companies would bias the outcome of the study in this instance. One of the authors (TAF) received compensation from Pfizer, the maker of Zoloft, which is also available as generic sertraline. None of the authors received compensation from Forest Pharmaceuticals, the makers of Lexapro (escitalopram).
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION: No major barriers are anticipated
Both sertraline and escitalopram are covered by most health insurers. As noted above, sertraline is available in generic formulation, and is therefore much less expensive than escitalopram. In a check of online drug prices, we found a prescription for a 3-month supply of Lexapro (10 mg) to cost about $250; a 3-month supply of generic sertraline (100 mg) from the same sources would cost approximately $35 (www.pharmcychecker.com). Both Pfizer, the maker of Zoloft, and Forest Pharmaceuticals, the maker of Lexapro, have patient assistance programs to make these medications available to low-income, uninsured patients.
Acknowledgements
The PURLs Surveillance System is supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR02499 from the National Center for Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center for Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
The authors wish to acknowledge Sofia Medvedev, PhD, of the University HealthSystem Consortium in Oak Brook, Ill, for analysis of the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey data and the UHC Clinical Database.
1. Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373:746-758.
2. Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Global Burden of Disease. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1996.
3. Williams SB, O’Connor EA, Eder M, et al. Screening for child and adolescent depression in primary care settings: a systematic evidence review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Pediatrics. 2009;123:e716-e735.
4. Timonen M, Liukkonen T. Management of depression in adults. BMJ. 2008;336:435-439.
5. Gartlehner G, Hansen RA, Thieda P, et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Second-Generation Antidepressants in the Pharmacologic Treatment of Adult Depression. Comparative Effectiveness Review No. 7. (Prepared by RTI International-University of North Carolina Evidence Based Practice Center under Contract No. 290-02-0016.) Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; January 2007. Available at: www.effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/reports/final.cfm. Accessed May 18, 2009.
6. Hansen RA, Gartlehner G, Lohr KN, et al. Efficacy and safety of second-generation antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Ann Intern Med. 2005;143:415-426.
7. Adams SM, Miller KE, Zylstra RG. Pharmacologic management of adult depression. Am Fam Physician. 2008;77:785-792.
8. Qaseem A, Snow V, Denberg TD, et al. Using second-generation antidepressants to treat depressive disorders: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149:725-733.
9. DeRubeis RJ, Hollon SD, Amsterdam JD, et al. Cognitive therapy vs medications in the treatment of moderate to severe depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:409-416.
10. deMello MF, de Jesus MJ, Bacaltchuk J, et al. A systematic review of research findings on the efficacy of interpersonal therapy for depressive disorders. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2005;255:75-82.
11. APA Practice Guidelines. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder, second edition. Available at: http://www.psychiatryonline.com/content.aspx?aID=48727. Accessed June 16, 2009.
12. Sackett D. An introduction to performing therapeutic trials. In: Haynes RB, Sackett DL, et al, eds. Clinical Epidemiology: How to Do Clinical Practice Research. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006.
13. Turner EH, Matthews AM, Linardatos E, et al. Selective publication of antidepressant trials and its influence on apparent efficacy. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:252-260.
14. Mathew SJ, Charney DS. Publication bias and the efficacy of antidepressants. Am J Psychiatry. 2009;166:140-145.
PURLs methodology This study was selected and evaluated using FPIN’s Priority Updates from the Research Literature (PURL) Surveillance System methodology. The criteria and findings leading to the selection of this study as a PURL can be accessed at www.jfponline.com/purls.
1. Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373:746-758.
2. Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Global Burden of Disease. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1996.
3. Williams SB, O’Connor EA, Eder M, et al. Screening for child and adolescent depression in primary care settings: a systematic evidence review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Pediatrics. 2009;123:e716-e735.
4. Timonen M, Liukkonen T. Management of depression in adults. BMJ. 2008;336:435-439.
5. Gartlehner G, Hansen RA, Thieda P, et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Second-Generation Antidepressants in the Pharmacologic Treatment of Adult Depression. Comparative Effectiveness Review No. 7. (Prepared by RTI International-University of North Carolina Evidence Based Practice Center under Contract No. 290-02-0016.) Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; January 2007. Available at: www.effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/reports/final.cfm. Accessed May 18, 2009.
6. Hansen RA, Gartlehner G, Lohr KN, et al. Efficacy and safety of second-generation antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Ann Intern Med. 2005;143:415-426.
7. Adams SM, Miller KE, Zylstra RG. Pharmacologic management of adult depression. Am Fam Physician. 2008;77:785-792.
8. Qaseem A, Snow V, Denberg TD, et al. Using second-generation antidepressants to treat depressive disorders: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149:725-733.
9. DeRubeis RJ, Hollon SD, Amsterdam JD, et al. Cognitive therapy vs medications in the treatment of moderate to severe depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:409-416.
10. deMello MF, de Jesus MJ, Bacaltchuk J, et al. A systematic review of research findings on the efficacy of interpersonal therapy for depressive disorders. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2005;255:75-82.
11. APA Practice Guidelines. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder, second edition. Available at: http://www.psychiatryonline.com/content.aspx?aID=48727. Accessed June 16, 2009.
12. Sackett D. An introduction to performing therapeutic trials. In: Haynes RB, Sackett DL, et al, eds. Clinical Epidemiology: How to Do Clinical Practice Research. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006.
13. Turner EH, Matthews AM, Linardatos E, et al. Selective publication of antidepressant trials and its influence on apparent efficacy. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:252-260.
14. Mathew SJ, Charney DS. Publication bias and the efficacy of antidepressants. Am J Psychiatry. 2009;166:140-145.
PURLs methodology This study was selected and evaluated using FPIN’s Priority Updates from the Research Literature (PURL) Surveillance System methodology. The criteria and findings leading to the selection of this study as a PURL can be accessed at www.jfponline.com/purls.
Copyright © 2009 The Family Physicians Inquiries Network.
All rights reserved.