User login
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
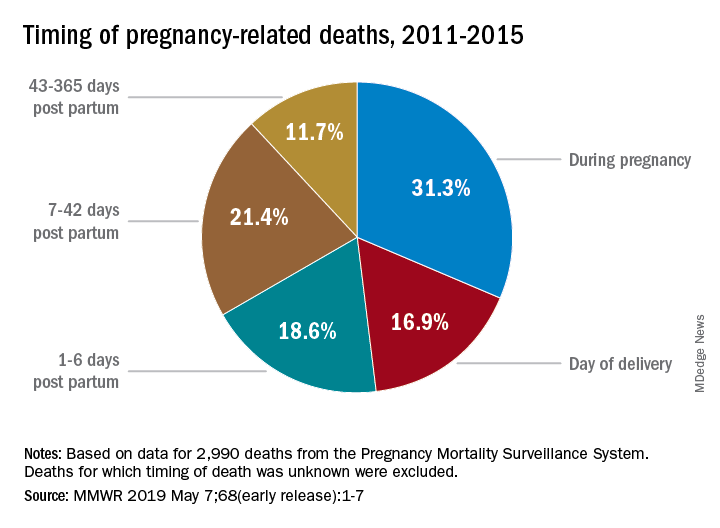
Deaths from pregnancy-related complications can occur “up to a year after delivery,” the CDC emphasized in a report released May 7. Indeed, 31% of pregnancy-related deaths happen during pregnancy, 36% happen at delivery or in the week after, and 33% happen 1 week to 1 year post partum. Yet detailed data from 13 state maternal mortality review committees (MMRCs) showed that 60% of such deaths are preventable.
There were 17 pregnancy-related deaths per 100,000 live births during 2011-2015, based on another data source: 3,410 pregnancy-related deaths (an average of 682 deaths per year) in the CDC’s Pregnancy Mortality Surveillance System. That pregnancy-related mortality ratio varied by race/ethnicity, Emily E. Peterson, MD, and the other CDC investigators reported in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report: Hispanic (11 deaths per 100,000), white (13), Asian/Pacific Islander (14), American Indian/Alaska Native (33), and black (43).
One aspect of the disparity was addressed by Wanda Barfield, MD, MPH, director of the CDC’s division of reproductive health and assistant surgeon general in the U.S. Public Health Service. “Recent studies have shown that racial and ethnic minority women deliver at different and lower-quality hospitals than white women and that these hospitals disproportionately care for black women at delivery,” she said at a CDC telebriefing.
Analysis of the timing of 2,990 deaths from the Pregnancy Mortality Surveillance System showed that almost a third (31.3%) occurred during pregnancy and 16.9% occurred on the day of delivery. Dr. Peterson and her CDC associates noted that more than half of pregnancy-related deaths, however, took place later: 1-6 days post partum (18.6%), 7-42 days (21.4%), and 43-365 days (11.7%).
The data on preventability were collected by the state MMRCs and included 232 deaths that occurred during 2013-2017. The MMRCs considered deaths preventable if they could be “averted by one or more reasonable changes to patient, community, provider, health facility, and/or system factors.”
“Our new analysis underscores the need for access to quality services, risk awareness, and early diagnosis, but it also highlights opportunities for preventing future pregnancy-related deaths,” Dr. Barfield said. “By identifying and promptly responding to warning signs not just during pregnancy, but even up to a year after delivery, we can save lives.”
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Deaths from pregnancy-related complications can occur “up to a year after delivery,” the CDC emphasized in a report released May 7. Indeed, 31% of pregnancy-related deaths happen during pregnancy, 36% happen at delivery or in the week after, and 33% happen 1 week to 1 year post partum. Yet detailed data from 13 state maternal mortality review committees (MMRCs) showed that 60% of such deaths are preventable.
There were 17 pregnancy-related deaths per 100,000 live births during 2011-2015, based on another data source: 3,410 pregnancy-related deaths (an average of 682 deaths per year) in the CDC’s Pregnancy Mortality Surveillance System. That pregnancy-related mortality ratio varied by race/ethnicity, Emily E. Peterson, MD, and the other CDC investigators reported in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report: Hispanic (11 deaths per 100,000), white (13), Asian/Pacific Islander (14), American Indian/Alaska Native (33), and black (43).
One aspect of the disparity was addressed by Wanda Barfield, MD, MPH, director of the CDC’s division of reproductive health and assistant surgeon general in the U.S. Public Health Service. “Recent studies have shown that racial and ethnic minority women deliver at different and lower-quality hospitals than white women and that these hospitals disproportionately care for black women at delivery,” she said at a CDC telebriefing.
Analysis of the timing of 2,990 deaths from the Pregnancy Mortality Surveillance System showed that almost a third (31.3%) occurred during pregnancy and 16.9% occurred on the day of delivery. Dr. Peterson and her CDC associates noted that more than half of pregnancy-related deaths, however, took place later: 1-6 days post partum (18.6%), 7-42 days (21.4%), and 43-365 days (11.7%).
The data on preventability were collected by the state MMRCs and included 232 deaths that occurred during 2013-2017. The MMRCs considered deaths preventable if they could be “averted by one or more reasonable changes to patient, community, provider, health facility, and/or system factors.”
“Our new analysis underscores the need for access to quality services, risk awareness, and early diagnosis, but it also highlights opportunities for preventing future pregnancy-related deaths,” Dr. Barfield said. “By identifying and promptly responding to warning signs not just during pregnancy, but even up to a year after delivery, we can save lives.”
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Deaths from pregnancy-related complications can occur “up to a year after delivery,” the CDC emphasized in a report released May 7. Indeed, 31% of pregnancy-related deaths happen during pregnancy, 36% happen at delivery or in the week after, and 33% happen 1 week to 1 year post partum. Yet detailed data from 13 state maternal mortality review committees (MMRCs) showed that 60% of such deaths are preventable.
There were 17 pregnancy-related deaths per 100,000 live births during 2011-2015, based on another data source: 3,410 pregnancy-related deaths (an average of 682 deaths per year) in the CDC’s Pregnancy Mortality Surveillance System. That pregnancy-related mortality ratio varied by race/ethnicity, Emily E. Peterson, MD, and the other CDC investigators reported in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report: Hispanic (11 deaths per 100,000), white (13), Asian/Pacific Islander (14), American Indian/Alaska Native (33), and black (43).
One aspect of the disparity was addressed by Wanda Barfield, MD, MPH, director of the CDC’s division of reproductive health and assistant surgeon general in the U.S. Public Health Service. “Recent studies have shown that racial and ethnic minority women deliver at different and lower-quality hospitals than white women and that these hospitals disproportionately care for black women at delivery,” she said at a CDC telebriefing.
Analysis of the timing of 2,990 deaths from the Pregnancy Mortality Surveillance System showed that almost a third (31.3%) occurred during pregnancy and 16.9% occurred on the day of delivery. Dr. Peterson and her CDC associates noted that more than half of pregnancy-related deaths, however, took place later: 1-6 days post partum (18.6%), 7-42 days (21.4%), and 43-365 days (11.7%).
The data on preventability were collected by the state MMRCs and included 232 deaths that occurred during 2013-2017. The MMRCs considered deaths preventable if they could be “averted by one or more reasonable changes to patient, community, provider, health facility, and/or system factors.”
“Our new analysis underscores the need for access to quality services, risk awareness, and early diagnosis, but it also highlights opportunities for preventing future pregnancy-related deaths,” Dr. Barfield said. “By identifying and promptly responding to warning signs not just during pregnancy, but even up to a year after delivery, we can save lives.”