User login
Pharmacotherapy for psychiatric disorders is a mixed blessing. The advent of psychotropic medications since the 1950s (antipsychotics, antidepressants, anxiolytics, mood stabilizers) has revolutionized the treatment of serious psychiatric brain disorders, allowing certain patients to be discharged to the community after a lifetime of institutionalization.
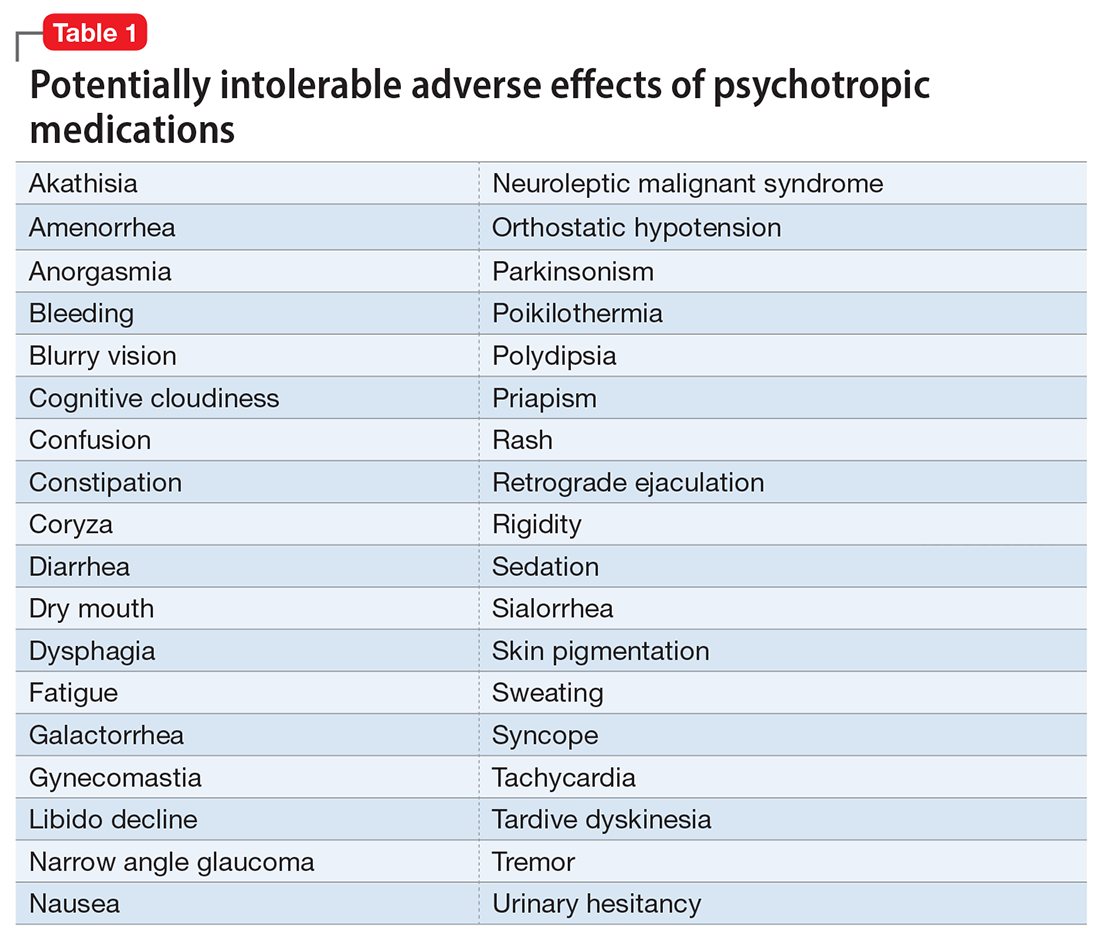
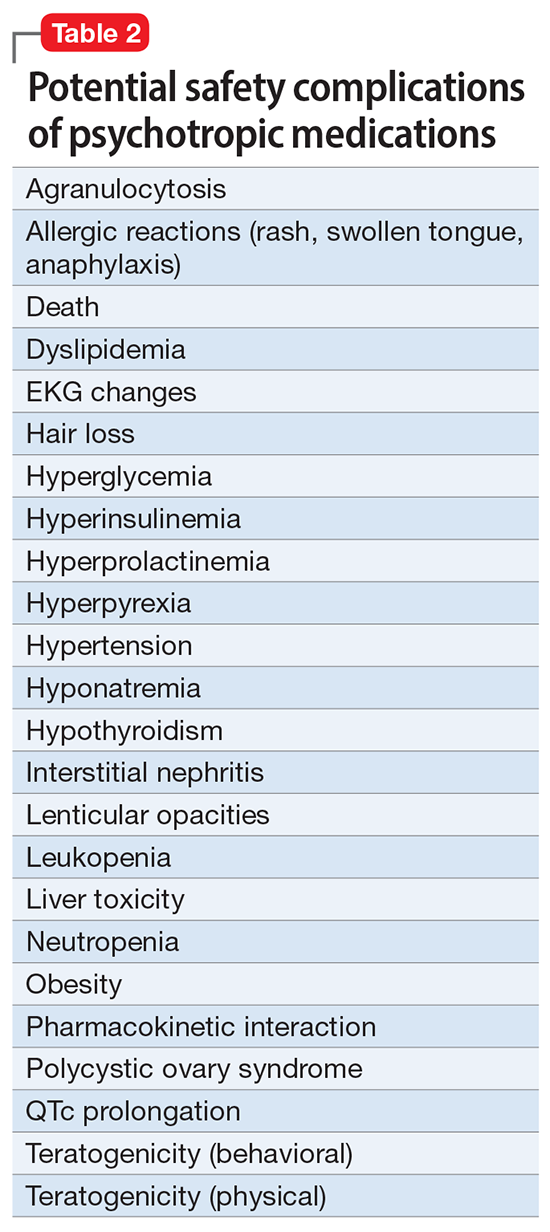
However, like all medications, psychotropic agents are often associated with various potentially intolerable symptoms (Table 1) or safety complications (Table 2) because they interact with every organ in the body besides their intended target, the brain, and its neurochemical circuitry.
Imagine if we could treat our psychiatric patients while bypassing the body and achieve response, remission, and ultimately recovery without any systemic adverse effects. Adherence would dramatically improve, our patients’ quality of life would be enhanced, and the overall effectiveness (defined as the complex package of efficacy, safety, and tolerability) would be superior to current pharmacotherapies. This is important because most psychiatric medications must be taken daily for years, even a lifetime, to avoid a relapse of the illness. Psychiatrists frequently must manage adverse effects or switch the patient to a different medication if a tolerability or safety issue emerges, which is very common in psychiatric practice. A significant part of psychopharmacologic management includes ordering various laboratory tests to monitor adverse reactions in major organs, especially the liver, kidney, and heart. Additionally, psychiatric physicians must be constantly cognizant of medications prescribed by other clinicians for comorbid medical conditions to successfully navigate the turbulent seas of pharmacokinetic interactions.
I am sure you have noticed that whenever you watch a direct-to-consumer commercial for any medication, 90% of the advertisement is a background voice listing the various tolerability and safety complications of the medication as required by the FDA. Interestingly, these ads frequently contain colorful scenery and joyful clips, which I suspect are cleverly designed to distract the audience from focusing on the list of adverse effects.
Benefits of nonpharmacologic treatments
No wonder I am a fan of psychotherapy, a well-established psychiatric treatment modality that completely avoids body tissues. It directly targets the brain without needlessly interacting with any other organ. Psychotherapy’s many benefits (improving insight, enhancing adherence, improving self-esteem, reducing risky behaviors, guiding stress management and coping skills, modifying unhealthy beliefs, and ultimately relieving symptoms such as anxiety and depression) are achieved without any somatic adverse effects! Psychotherapy has also been shown to induce neuroplasticity and reduce inflammatory biomarkers.1 Unlike FDA-approved medications, psychotherapy does not include a “package insert,” 10 to 20 pages (in small print) that mostly focus on warnings, precautions, and sundry physical adverse effects. Even the dosing of psychotherapy is left entirely up to the treating clinician!
Although I have had many gratifying results with pharmacotherapy in my practice, especially in combination with psychotherapy,2 I also have observed excellent outcomes with nonpharmacologic approaches, especially neuromodulation therapies. The best antidepressant I have ever used since my residency training days is electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). My experience is consistent with a large meta-analysis3showing a huge effect size (Cohen d = .91) in contrast to the usual effect size of .3 to .5 for standard antidepressants (except IV ketamine). A recent study showed ECT is even better than the vaunted rapid-acting ketamine,4 which is further evidence of its remarkable efficacy in depression. Neuroimaging studies report that ECT rapidly increases the volume of the hippocampus,5,6 which shrinks in size in patients with unipolar or bipolar depression.
Neuromodulation may very well be the future of psychiatric therapeutics. It targets the brain and avoids the body, thus achieving efficacy with minimal systemic tolerability (ie, patient complaints) (Table 1) or safety (abnormal laboratory test results) issues (Table 2). This sounds ideal, and it is arguably an optimal approach to repairing the brain and healing the mind.
Continue to: ECT is the oldest...
ECT is the oldest neuromodulation technique (developed almost 100 years ago and significantly refined since then). Newer FDA-approved neuromodulation therapies include repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), which was approved for depression in 2013, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in 2018, smoking cessation in 2020, and anxious depression in 2021.7 Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is used for drug-resistant epilepsy and was later approved for treatment-resistant depression,8,9 but some studies report it can be helpful for fear and anxiety in autism spectrum disorder10 and primary insomnia.11
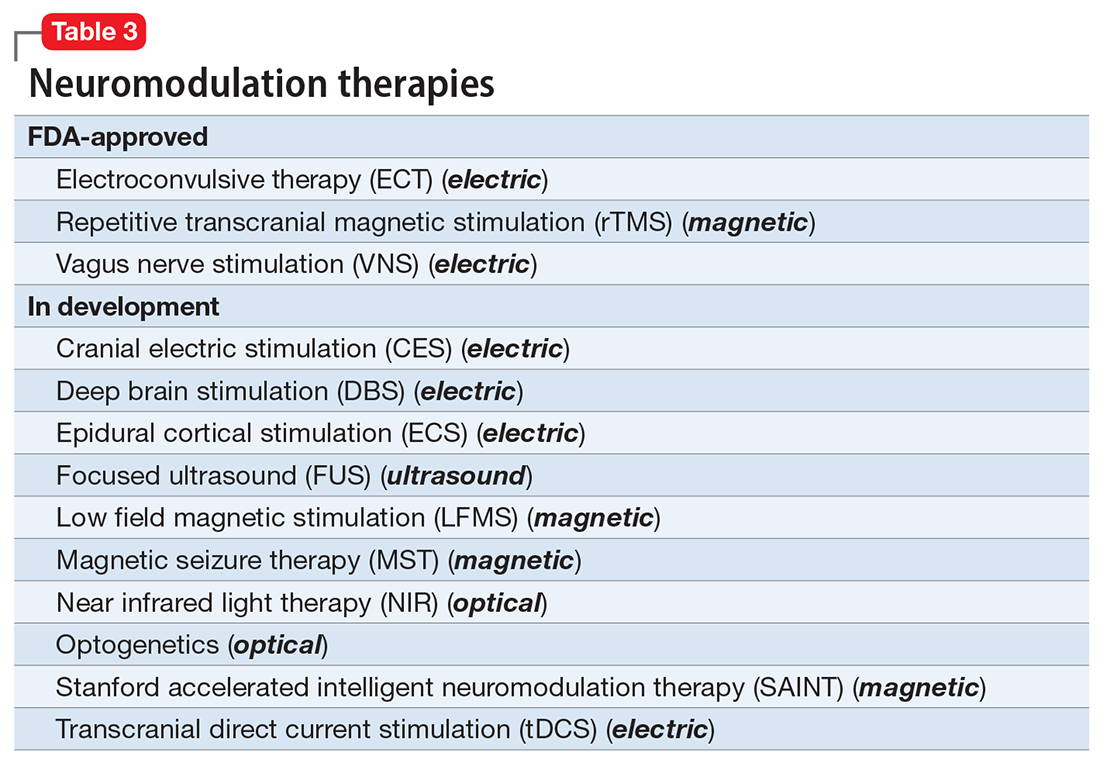
There are many other neuromodulation therapies in development12 that have not yet been FDA approved (Table 3). The most prominent of these is deep brain stimulation (DBS), which is approved for Parkinson disease and has been reported in many studies to improve treatment-resistant depression13,14 and OCD.15 Another promising neuromodulation therapy is transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), which has promising results in schizophrenia16 similar to ECT’s effects in treatment-resistant schizophrenia.17
A particularly exciting neuromodulation approach published by Stanford University researchers is Stanford accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy (SAINT),18 which uses intermittent theta-burst stimulation (iTBS) daily for 5 days, targeted at the subgenual anterior cingulate gyrus (Brodman area 25). Remarkably, efficacy was rapid, with a very high remission rate (absence of symptoms) in approximately 90% of patients with severe depression.18
The future is bright for neuromodulation therapies, and for a good reason. Why send a chemical agent to every cell and organ in the body when the brain can be targeted directly? As psychiatric neuroscience advances to a point where we can localize the abnormal neurologic circuit in a specific brain region for each psychiatric disorder, it will be possible to treat almost all psychiatric disorders without burdening patients with the intolerable symptoms or safety adverse effects of medications. Psychiatrists should modulate their perspective about the future of psychiatric treatments. And finally, I propose that psychotherapy should be reclassified as a “verbal neuromodulation” technique.
1. Nasrallah HA. Repositioning psychotherapy as a neurobiological intervention. Current Psychiatry. 2013;12(12):18-19.
2. Nasrallah HA. Bipolar disorder: clinical questions beg for answers. Current Psychiatry. 2006;5(12):11-12.
3. UK ECT Review Group. Efficacy and safety of electroconvulsive therapy in depressive disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2003;361(9360):799-808.
4. Rhee TG, Shim SR, Forester BP, et al. Efficacy and safety of ketamine vs electroconvulsive therapy among patients with major depressive episode: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2022:e223352. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2022.3352
5. Nuninga JO, Mandl RCW, Boks MP, et al. Volume increase in the dentate gyrus after electroconvulsive therapy in depressed patients as measured with 7T. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(7):1559-1568.
6. Joshi SH, Espinoza RT, Pirnia T, et al. Structural plasticity of the hippocampus and amygdala induced by electroconvulsive therapy in major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2016;79(4):282-292.
7. Rhee TG, Olfson M, Nierenberg AA, et al. 20-year trends in the pharmacologic treatment of bipolar disorder by psychiatrists in outpatient care settings. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(8):706-715.
8. Hilz MJ. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation - a brief introduction and overview. Auton Neurosci. 2022;243:103038. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2022.103038
9. Pigato G, Rosson S, Bresolin N, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation in treatment-resistant depression: a case series of long-term follow-up. J ECT. 2022. doi:10.1097/YCT.0000000000000869
10. Shivaswamy T, Souza RR, Engineer CT, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation as a treatment for fear and anxiety in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. J Psychiatr Brain Sci. 2022;7(4):e220007. doi:10.20900/jpbs.20220007
11. Wu Y, Song L, Wang X, et al. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation could improve the effective rate on the quality of sleep in the treatment of primary insomnia: a randomized control trial. Brain Sci. 2022;12(10):1296. doi:10.3390/brainsci12101296
12. Rosa MA, Lisanby SH. Somatic treatments for mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37(1):102-116.
13. Mayberg HS, Lozano AM, Voon V, et al. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron. 2005;45(5):651-660.
14. Choi KS, Mayberg H. Connectomic DBS in major depression. In: Horn A, ed. Connectomic Deep Brain Stimulation. Academic Press; 2022:433-447.
15. Cruz S, Gutiérrez-Rojas L, González-Domenech P, et al. Deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder: results from meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2022;317:114869. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2022.114869
16. Lisoni J, Baldacci G, Nibbio G, et al. Effects of bilateral, bipolar-nonbalanced, frontal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) on negative symptoms and neurocognition in a sample of patients living with schizophrenia: results of a randomized double-blind sham-controlled trial. J Psychiatr Res. 2022;155:430-442.
17. Sinclair DJ, Zhao S, Qi F, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy for treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;3(3):CD011847. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011847.pub2
18. Cole EJ, Stimpson KH, Bentzley BS, et al. Stanford accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy for treatment-resistant depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(8):716-726.
Pharmacotherapy for psychiatric disorders is a mixed blessing. The advent of psychotropic medications since the 1950s (antipsychotics, antidepressants, anxiolytics, mood stabilizers) has revolutionized the treatment of serious psychiatric brain disorders, allowing certain patients to be discharged to the community after a lifetime of institutionalization.

However, like all medications, psychotropic agents are often associated with various potentially intolerable symptoms (Table 1) or safety complications (Table 2) because they interact with every organ in the body besides their intended target, the brain, and its neurochemical circuitry.

Imagine if we could treat our psychiatric patients while bypassing the body and achieve response, remission, and ultimately recovery without any systemic adverse effects. Adherence would dramatically improve, our patients’ quality of life would be enhanced, and the overall effectiveness (defined as the complex package of efficacy, safety, and tolerability) would be superior to current pharmacotherapies. This is important because most psychiatric medications must be taken daily for years, even a lifetime, to avoid a relapse of the illness. Psychiatrists frequently must manage adverse effects or switch the patient to a different medication if a tolerability or safety issue emerges, which is very common in psychiatric practice. A significant part of psychopharmacologic management includes ordering various laboratory tests to monitor adverse reactions in major organs, especially the liver, kidney, and heart. Additionally, psychiatric physicians must be constantly cognizant of medications prescribed by other clinicians for comorbid medical conditions to successfully navigate the turbulent seas of pharmacokinetic interactions.
I am sure you have noticed that whenever you watch a direct-to-consumer commercial for any medication, 90% of the advertisement is a background voice listing the various tolerability and safety complications of the medication as required by the FDA. Interestingly, these ads frequently contain colorful scenery and joyful clips, which I suspect are cleverly designed to distract the audience from focusing on the list of adverse effects.
Benefits of nonpharmacologic treatments
No wonder I am a fan of psychotherapy, a well-established psychiatric treatment modality that completely avoids body tissues. It directly targets the brain without needlessly interacting with any other organ. Psychotherapy’s many benefits (improving insight, enhancing adherence, improving self-esteem, reducing risky behaviors, guiding stress management and coping skills, modifying unhealthy beliefs, and ultimately relieving symptoms such as anxiety and depression) are achieved without any somatic adverse effects! Psychotherapy has also been shown to induce neuroplasticity and reduce inflammatory biomarkers.1 Unlike FDA-approved medications, psychotherapy does not include a “package insert,” 10 to 20 pages (in small print) that mostly focus on warnings, precautions, and sundry physical adverse effects. Even the dosing of psychotherapy is left entirely up to the treating clinician!
Although I have had many gratifying results with pharmacotherapy in my practice, especially in combination with psychotherapy,2 I also have observed excellent outcomes with nonpharmacologic approaches, especially neuromodulation therapies. The best antidepressant I have ever used since my residency training days is electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). My experience is consistent with a large meta-analysis3showing a huge effect size (Cohen d = .91) in contrast to the usual effect size of .3 to .5 for standard antidepressants (except IV ketamine). A recent study showed ECT is even better than the vaunted rapid-acting ketamine,4 which is further evidence of its remarkable efficacy in depression. Neuroimaging studies report that ECT rapidly increases the volume of the hippocampus,5,6 which shrinks in size in patients with unipolar or bipolar depression.
Neuromodulation may very well be the future of psychiatric therapeutics. It targets the brain and avoids the body, thus achieving efficacy with minimal systemic tolerability (ie, patient complaints) (Table 1) or safety (abnormal laboratory test results) issues (Table 2). This sounds ideal, and it is arguably an optimal approach to repairing the brain and healing the mind.
Continue to: ECT is the oldest...
ECT is the oldest neuromodulation technique (developed almost 100 years ago and significantly refined since then). Newer FDA-approved neuromodulation therapies include repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), which was approved for depression in 2013, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in 2018, smoking cessation in 2020, and anxious depression in 2021.7 Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is used for drug-resistant epilepsy and was later approved for treatment-resistant depression,8,9 but some studies report it can be helpful for fear and anxiety in autism spectrum disorder10 and primary insomnia.11
There are many other neuromodulation therapies in development12 that have not yet been FDA approved (Table 3). The most prominent of these is deep brain stimulation (DBS), which is approved for Parkinson disease and has been reported in many studies to improve treatment-resistant depression13,14 and OCD.15 Another promising neuromodulation therapy is transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), which has promising results in schizophrenia16 similar to ECT’s effects in treatment-resistant schizophrenia.17

A particularly exciting neuromodulation approach published by Stanford University researchers is Stanford accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy (SAINT),18 which uses intermittent theta-burst stimulation (iTBS) daily for 5 days, targeted at the subgenual anterior cingulate gyrus (Brodman area 25). Remarkably, efficacy was rapid, with a very high remission rate (absence of symptoms) in approximately 90% of patients with severe depression.18
The future is bright for neuromodulation therapies, and for a good reason. Why send a chemical agent to every cell and organ in the body when the brain can be targeted directly? As psychiatric neuroscience advances to a point where we can localize the abnormal neurologic circuit in a specific brain region for each psychiatric disorder, it will be possible to treat almost all psychiatric disorders without burdening patients with the intolerable symptoms or safety adverse effects of medications. Psychiatrists should modulate their perspective about the future of psychiatric treatments. And finally, I propose that psychotherapy should be reclassified as a “verbal neuromodulation” technique.
Pharmacotherapy for psychiatric disorders is a mixed blessing. The advent of psychotropic medications since the 1950s (antipsychotics, antidepressants, anxiolytics, mood stabilizers) has revolutionized the treatment of serious psychiatric brain disorders, allowing certain patients to be discharged to the community after a lifetime of institutionalization.

However, like all medications, psychotropic agents are often associated with various potentially intolerable symptoms (Table 1) or safety complications (Table 2) because they interact with every organ in the body besides their intended target, the brain, and its neurochemical circuitry.

Imagine if we could treat our psychiatric patients while bypassing the body and achieve response, remission, and ultimately recovery without any systemic adverse effects. Adherence would dramatically improve, our patients’ quality of life would be enhanced, and the overall effectiveness (defined as the complex package of efficacy, safety, and tolerability) would be superior to current pharmacotherapies. This is important because most psychiatric medications must be taken daily for years, even a lifetime, to avoid a relapse of the illness. Psychiatrists frequently must manage adverse effects or switch the patient to a different medication if a tolerability or safety issue emerges, which is very common in psychiatric practice. A significant part of psychopharmacologic management includes ordering various laboratory tests to monitor adverse reactions in major organs, especially the liver, kidney, and heart. Additionally, psychiatric physicians must be constantly cognizant of medications prescribed by other clinicians for comorbid medical conditions to successfully navigate the turbulent seas of pharmacokinetic interactions.
I am sure you have noticed that whenever you watch a direct-to-consumer commercial for any medication, 90% of the advertisement is a background voice listing the various tolerability and safety complications of the medication as required by the FDA. Interestingly, these ads frequently contain colorful scenery and joyful clips, which I suspect are cleverly designed to distract the audience from focusing on the list of adverse effects.
Benefits of nonpharmacologic treatments
No wonder I am a fan of psychotherapy, a well-established psychiatric treatment modality that completely avoids body tissues. It directly targets the brain without needlessly interacting with any other organ. Psychotherapy’s many benefits (improving insight, enhancing adherence, improving self-esteem, reducing risky behaviors, guiding stress management and coping skills, modifying unhealthy beliefs, and ultimately relieving symptoms such as anxiety and depression) are achieved without any somatic adverse effects! Psychotherapy has also been shown to induce neuroplasticity and reduce inflammatory biomarkers.1 Unlike FDA-approved medications, psychotherapy does not include a “package insert,” 10 to 20 pages (in small print) that mostly focus on warnings, precautions, and sundry physical adverse effects. Even the dosing of psychotherapy is left entirely up to the treating clinician!
Although I have had many gratifying results with pharmacotherapy in my practice, especially in combination with psychotherapy,2 I also have observed excellent outcomes with nonpharmacologic approaches, especially neuromodulation therapies. The best antidepressant I have ever used since my residency training days is electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). My experience is consistent with a large meta-analysis3showing a huge effect size (Cohen d = .91) in contrast to the usual effect size of .3 to .5 for standard antidepressants (except IV ketamine). A recent study showed ECT is even better than the vaunted rapid-acting ketamine,4 which is further evidence of its remarkable efficacy in depression. Neuroimaging studies report that ECT rapidly increases the volume of the hippocampus,5,6 which shrinks in size in patients with unipolar or bipolar depression.
Neuromodulation may very well be the future of psychiatric therapeutics. It targets the brain and avoids the body, thus achieving efficacy with minimal systemic tolerability (ie, patient complaints) (Table 1) or safety (abnormal laboratory test results) issues (Table 2). This sounds ideal, and it is arguably an optimal approach to repairing the brain and healing the mind.
Continue to: ECT is the oldest...
ECT is the oldest neuromodulation technique (developed almost 100 years ago and significantly refined since then). Newer FDA-approved neuromodulation therapies include repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), which was approved for depression in 2013, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in 2018, smoking cessation in 2020, and anxious depression in 2021.7 Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is used for drug-resistant epilepsy and was later approved for treatment-resistant depression,8,9 but some studies report it can be helpful for fear and anxiety in autism spectrum disorder10 and primary insomnia.11
There are many other neuromodulation therapies in development12 that have not yet been FDA approved (Table 3). The most prominent of these is deep brain stimulation (DBS), which is approved for Parkinson disease and has been reported in many studies to improve treatment-resistant depression13,14 and OCD.15 Another promising neuromodulation therapy is transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), which has promising results in schizophrenia16 similar to ECT’s effects in treatment-resistant schizophrenia.17

A particularly exciting neuromodulation approach published by Stanford University researchers is Stanford accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy (SAINT),18 which uses intermittent theta-burst stimulation (iTBS) daily for 5 days, targeted at the subgenual anterior cingulate gyrus (Brodman area 25). Remarkably, efficacy was rapid, with a very high remission rate (absence of symptoms) in approximately 90% of patients with severe depression.18
The future is bright for neuromodulation therapies, and for a good reason. Why send a chemical agent to every cell and organ in the body when the brain can be targeted directly? As psychiatric neuroscience advances to a point where we can localize the abnormal neurologic circuit in a specific brain region for each psychiatric disorder, it will be possible to treat almost all psychiatric disorders without burdening patients with the intolerable symptoms or safety adverse effects of medications. Psychiatrists should modulate their perspective about the future of psychiatric treatments. And finally, I propose that psychotherapy should be reclassified as a “verbal neuromodulation” technique.
1. Nasrallah HA. Repositioning psychotherapy as a neurobiological intervention. Current Psychiatry. 2013;12(12):18-19.
2. Nasrallah HA. Bipolar disorder: clinical questions beg for answers. Current Psychiatry. 2006;5(12):11-12.
3. UK ECT Review Group. Efficacy and safety of electroconvulsive therapy in depressive disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2003;361(9360):799-808.
4. Rhee TG, Shim SR, Forester BP, et al. Efficacy and safety of ketamine vs electroconvulsive therapy among patients with major depressive episode: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2022:e223352. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2022.3352
5. Nuninga JO, Mandl RCW, Boks MP, et al. Volume increase in the dentate gyrus after electroconvulsive therapy in depressed patients as measured with 7T. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(7):1559-1568.
6. Joshi SH, Espinoza RT, Pirnia T, et al. Structural plasticity of the hippocampus and amygdala induced by electroconvulsive therapy in major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2016;79(4):282-292.
7. Rhee TG, Olfson M, Nierenberg AA, et al. 20-year trends in the pharmacologic treatment of bipolar disorder by psychiatrists in outpatient care settings. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(8):706-715.
8. Hilz MJ. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation - a brief introduction and overview. Auton Neurosci. 2022;243:103038. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2022.103038
9. Pigato G, Rosson S, Bresolin N, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation in treatment-resistant depression: a case series of long-term follow-up. J ECT. 2022. doi:10.1097/YCT.0000000000000869
10. Shivaswamy T, Souza RR, Engineer CT, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation as a treatment for fear and anxiety in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. J Psychiatr Brain Sci. 2022;7(4):e220007. doi:10.20900/jpbs.20220007
11. Wu Y, Song L, Wang X, et al. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation could improve the effective rate on the quality of sleep in the treatment of primary insomnia: a randomized control trial. Brain Sci. 2022;12(10):1296. doi:10.3390/brainsci12101296
12. Rosa MA, Lisanby SH. Somatic treatments for mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37(1):102-116.
13. Mayberg HS, Lozano AM, Voon V, et al. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron. 2005;45(5):651-660.
14. Choi KS, Mayberg H. Connectomic DBS in major depression. In: Horn A, ed. Connectomic Deep Brain Stimulation. Academic Press; 2022:433-447.
15. Cruz S, Gutiérrez-Rojas L, González-Domenech P, et al. Deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder: results from meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2022;317:114869. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2022.114869
16. Lisoni J, Baldacci G, Nibbio G, et al. Effects of bilateral, bipolar-nonbalanced, frontal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) on negative symptoms and neurocognition in a sample of patients living with schizophrenia: results of a randomized double-blind sham-controlled trial. J Psychiatr Res. 2022;155:430-442.
17. Sinclair DJ, Zhao S, Qi F, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy for treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;3(3):CD011847. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011847.pub2
18. Cole EJ, Stimpson KH, Bentzley BS, et al. Stanford accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy for treatment-resistant depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(8):716-726.
1. Nasrallah HA. Repositioning psychotherapy as a neurobiological intervention. Current Psychiatry. 2013;12(12):18-19.
2. Nasrallah HA. Bipolar disorder: clinical questions beg for answers. Current Psychiatry. 2006;5(12):11-12.
3. UK ECT Review Group. Efficacy and safety of electroconvulsive therapy in depressive disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2003;361(9360):799-808.
4. Rhee TG, Shim SR, Forester BP, et al. Efficacy and safety of ketamine vs electroconvulsive therapy among patients with major depressive episode: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2022:e223352. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2022.3352
5. Nuninga JO, Mandl RCW, Boks MP, et al. Volume increase in the dentate gyrus after electroconvulsive therapy in depressed patients as measured with 7T. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(7):1559-1568.
6. Joshi SH, Espinoza RT, Pirnia T, et al. Structural plasticity of the hippocampus and amygdala induced by electroconvulsive therapy in major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2016;79(4):282-292.
7. Rhee TG, Olfson M, Nierenberg AA, et al. 20-year trends in the pharmacologic treatment of bipolar disorder by psychiatrists in outpatient care settings. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(8):706-715.
8. Hilz MJ. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation - a brief introduction and overview. Auton Neurosci. 2022;243:103038. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2022.103038
9. Pigato G, Rosson S, Bresolin N, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation in treatment-resistant depression: a case series of long-term follow-up. J ECT. 2022. doi:10.1097/YCT.0000000000000869
10. Shivaswamy T, Souza RR, Engineer CT, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation as a treatment for fear and anxiety in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. J Psychiatr Brain Sci. 2022;7(4):e220007. doi:10.20900/jpbs.20220007
11. Wu Y, Song L, Wang X, et al. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation could improve the effective rate on the quality of sleep in the treatment of primary insomnia: a randomized control trial. Brain Sci. 2022;12(10):1296. doi:10.3390/brainsci12101296
12. Rosa MA, Lisanby SH. Somatic treatments for mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37(1):102-116.
13. Mayberg HS, Lozano AM, Voon V, et al. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron. 2005;45(5):651-660.
14. Choi KS, Mayberg H. Connectomic DBS in major depression. In: Horn A, ed. Connectomic Deep Brain Stimulation. Academic Press; 2022:433-447.
15. Cruz S, Gutiérrez-Rojas L, González-Domenech P, et al. Deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder: results from meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2022;317:114869. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2022.114869
16. Lisoni J, Baldacci G, Nibbio G, et al. Effects of bilateral, bipolar-nonbalanced, frontal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) on negative symptoms and neurocognition in a sample of patients living with schizophrenia: results of a randomized double-blind sham-controlled trial. J Psychiatr Res. 2022;155:430-442.
17. Sinclair DJ, Zhao S, Qi F, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy for treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;3(3):CD011847. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011847.pub2
18. Cole EJ, Stimpson KH, Bentzley BS, et al. Stanford accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy for treatment-resistant depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(8):716-726.
