User login
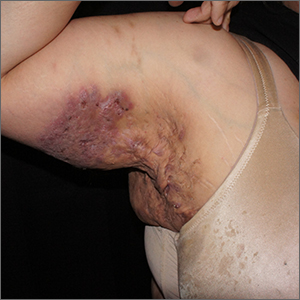
The persistent scars with recurrent abscesses and sinuses are indicative of advanced hidradenitis suppurativa. This painful and debilitating disease is characterized by the recurrent formation and inflammation of papules, cysts, sinuses, and scars in the axillae, inguinal folds, gluteal cleft, and inframammary folds. Pain, social isolation, depression, increased risk of substance abuse, and increased suicidality are all associated with hidradenitis suppurativa.
The disease may be graded based on severity, which can guide medical treatment options. The earliest stage appears similar to acne without significant sinus tract or scar formation and may be treated with topical therapies—including clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. When larger cysts associated with sinus tracts occur, systemic options with oral antibiotics (including doxycycline 100 mg bid for 3 months or combination clindamycin 300 mg and rifampin 300 mg, both bid for 3 months) are reasonable options. Intralesional triamcinolone in a concentration of 10 mg/mL injected directly into an inflamed cyst can provide acute relief. Severe disease is characterized by diffuse scars and sinus tracts. The TNF-alpha inhibitors adalimumab and infliximab are excellent options for severe disease that does not respond to antibiotics.
Surgical treatment may include either “deroofing” the sinuses or performing a wide excision of the whole area of involvement. Widely excised areas may be grafted, allowed to granulate, or closed if small enough. Although these options create significant wounds, patients experience good results; there is a 27% recurrence with deroofing and a 13% recurrence with wide excision.1
This patient underwent wide local excision of both axillae and the areas of involvement were allowed to granulate. Secondary intention healing occurred over 12 weeks.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
1. Orenstein LAV, Nguyen TV, Damiani G, et al. Medical and surgical management of hidradenitis suppurativa: a review of international treatment guidelines and implementation in general dermatology practice. Dermatology. 2020;236:393-412. doi: 10.1159/000507323

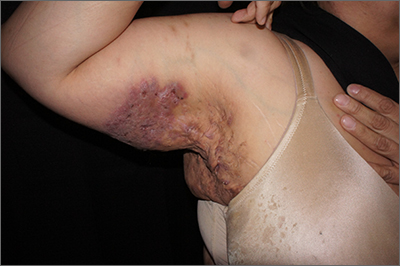
The persistent scars with recurrent abscesses and sinuses are indicative of advanced hidradenitis suppurativa. This painful and debilitating disease is characterized by the recurrent formation and inflammation of papules, cysts, sinuses, and scars in the axillae, inguinal folds, gluteal cleft, and inframammary folds. Pain, social isolation, depression, increased risk of substance abuse, and increased suicidality are all associated with hidradenitis suppurativa.
The disease may be graded based on severity, which can guide medical treatment options. The earliest stage appears similar to acne without significant sinus tract or scar formation and may be treated with topical therapies—including clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. When larger cysts associated with sinus tracts occur, systemic options with oral antibiotics (including doxycycline 100 mg bid for 3 months or combination clindamycin 300 mg and rifampin 300 mg, both bid for 3 months) are reasonable options. Intralesional triamcinolone in a concentration of 10 mg/mL injected directly into an inflamed cyst can provide acute relief. Severe disease is characterized by diffuse scars and sinus tracts. The TNF-alpha inhibitors adalimumab and infliximab are excellent options for severe disease that does not respond to antibiotics.
Surgical treatment may include either “deroofing” the sinuses or performing a wide excision of the whole area of involvement. Widely excised areas may be grafted, allowed to granulate, or closed if small enough. Although these options create significant wounds, patients experience good results; there is a 27% recurrence with deroofing and a 13% recurrence with wide excision.1
This patient underwent wide local excision of both axillae and the areas of involvement were allowed to granulate. Secondary intention healing occurred over 12 weeks.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.

The persistent scars with recurrent abscesses and sinuses are indicative of advanced hidradenitis suppurativa. This painful and debilitating disease is characterized by the recurrent formation and inflammation of papules, cysts, sinuses, and scars in the axillae, inguinal folds, gluteal cleft, and inframammary folds. Pain, social isolation, depression, increased risk of substance abuse, and increased suicidality are all associated with hidradenitis suppurativa.
The disease may be graded based on severity, which can guide medical treatment options. The earliest stage appears similar to acne without significant sinus tract or scar formation and may be treated with topical therapies—including clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. When larger cysts associated with sinus tracts occur, systemic options with oral antibiotics (including doxycycline 100 mg bid for 3 months or combination clindamycin 300 mg and rifampin 300 mg, both bid for 3 months) are reasonable options. Intralesional triamcinolone in a concentration of 10 mg/mL injected directly into an inflamed cyst can provide acute relief. Severe disease is characterized by diffuse scars and sinus tracts. The TNF-alpha inhibitors adalimumab and infliximab are excellent options for severe disease that does not respond to antibiotics.
Surgical treatment may include either “deroofing” the sinuses or performing a wide excision of the whole area of involvement. Widely excised areas may be grafted, allowed to granulate, or closed if small enough. Although these options create significant wounds, patients experience good results; there is a 27% recurrence with deroofing and a 13% recurrence with wide excision.1
This patient underwent wide local excision of both axillae and the areas of involvement were allowed to granulate. Secondary intention healing occurred over 12 weeks.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
1. Orenstein LAV, Nguyen TV, Damiani G, et al. Medical and surgical management of hidradenitis suppurativa: a review of international treatment guidelines and implementation in general dermatology practice. Dermatology. 2020;236:393-412. doi: 10.1159/000507323
1. Orenstein LAV, Nguyen TV, Damiani G, et al. Medical and surgical management of hidradenitis suppurativa: a review of international treatment guidelines and implementation in general dermatology practice. Dermatology. 2020;236:393-412. doi: 10.1159/000507323