User login
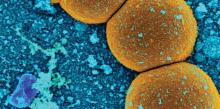
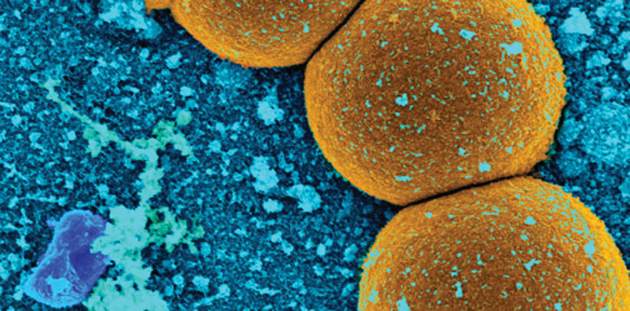
In Japan, sentinel disease surveillance systems may underestimate the actual number of patients with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection because they do not include information about patients who visit nonsentinel medical facilities, according to a study published in Epidemiology and Infection.
Dr. Shinichi Tanihara of the department of public health and preventive medicine in the School of Medicine at Fukuoka University and Dr. Satowa Suzuki of the department of bacteriology II at the National Institute of Infectious Diseases in Tokyo assessed and compared the incidences of MRSA patients based on health insurance claims data and data reported to the Japan Nosocomial Infections Surveillance system (Epidemiol Infect. 2016 April 8. doi: 10.1017/S0950268816000674).
The study results suggested that health insurance claims data for MRSA cases were more useful for determining the incidence of MRSA cases in Japan from 2011 to 2012. For example, of the 2,052 eligible hospitals with 200 or more beds in 2011, roughly one-quarter (495, 23.8%) participated in the Japan Nosocomial Infections Surveillance system. Data from this relatively low percentage of eligible facilities most likely underestimated the true number of MRSA patients in Japan, the authors said.
Based on their findings, the investigators noted three major advantages of using health insurance claims data for infection surveillance. Firstly, information from health insurance claims data is not affected by health care providers’ notifications to surveillance systems. Secondly, data on patients with MRSA can be collected at low cost because of Japan’s uniform and computerized health insurance system, and the data are easy to access. Lastly, health insurance claims data prevent the duplication of patient information, as insurers can determine if a patient was treated at multiple medical facilities for the same disease.
The only noted drawback involving the use of health insurance claims data for infection surveillance pertained to its timeliness, the researchers wrote. This issue arises because these data are submitted monthly rather than immediately, which may limit their use in surveillance systems.
According to Dr. Tanihara and Dr. Suzuki, strengths of the study include its evaluation of sentinel surveillance quality through the use of data that were not based on physician reports, as well as the calculation of MRSA incidence by use of a standardized definition in a specific population. Reported limitations included the assessment of anti-MRSA medicine use and patients’ age only, and the lack of information on the degree of drug resistance from health insurance claims data.
Funding was provided by the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare of Japan, and by the Research Programme on Emerging and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development. Neither author reported any conflicts of interest.
In Japan, sentinel disease surveillance systems may underestimate the actual number of patients with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection because they do not include information about patients who visit nonsentinel medical facilities, according to a study published in Epidemiology and Infection.
Dr. Shinichi Tanihara of the department of public health and preventive medicine in the School of Medicine at Fukuoka University and Dr. Satowa Suzuki of the department of bacteriology II at the National Institute of Infectious Diseases in Tokyo assessed and compared the incidences of MRSA patients based on health insurance claims data and data reported to the Japan Nosocomial Infections Surveillance system (Epidemiol Infect. 2016 April 8. doi: 10.1017/S0950268816000674).
The study results suggested that health insurance claims data for MRSA cases were more useful for determining the incidence of MRSA cases in Japan from 2011 to 2012. For example, of the 2,052 eligible hospitals with 200 or more beds in 2011, roughly one-quarter (495, 23.8%) participated in the Japan Nosocomial Infections Surveillance system. Data from this relatively low percentage of eligible facilities most likely underestimated the true number of MRSA patients in Japan, the authors said.
Based on their findings, the investigators noted three major advantages of using health insurance claims data for infection surveillance. Firstly, information from health insurance claims data is not affected by health care providers’ notifications to surveillance systems. Secondly, data on patients with MRSA can be collected at low cost because of Japan’s uniform and computerized health insurance system, and the data are easy to access. Lastly, health insurance claims data prevent the duplication of patient information, as insurers can determine if a patient was treated at multiple medical facilities for the same disease.
The only noted drawback involving the use of health insurance claims data for infection surveillance pertained to its timeliness, the researchers wrote. This issue arises because these data are submitted monthly rather than immediately, which may limit their use in surveillance systems.
According to Dr. Tanihara and Dr. Suzuki, strengths of the study include its evaluation of sentinel surveillance quality through the use of data that were not based on physician reports, as well as the calculation of MRSA incidence by use of a standardized definition in a specific population. Reported limitations included the assessment of anti-MRSA medicine use and patients’ age only, and the lack of information on the degree of drug resistance from health insurance claims data.
Funding was provided by the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare of Japan, and by the Research Programme on Emerging and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development. Neither author reported any conflicts of interest.
In Japan, sentinel disease surveillance systems may underestimate the actual number of patients with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection because they do not include information about patients who visit nonsentinel medical facilities, according to a study published in Epidemiology and Infection.
Dr. Shinichi Tanihara of the department of public health and preventive medicine in the School of Medicine at Fukuoka University and Dr. Satowa Suzuki of the department of bacteriology II at the National Institute of Infectious Diseases in Tokyo assessed and compared the incidences of MRSA patients based on health insurance claims data and data reported to the Japan Nosocomial Infections Surveillance system (Epidemiol Infect. 2016 April 8. doi: 10.1017/S0950268816000674).
The study results suggested that health insurance claims data for MRSA cases were more useful for determining the incidence of MRSA cases in Japan from 2011 to 2012. For example, of the 2,052 eligible hospitals with 200 or more beds in 2011, roughly one-quarter (495, 23.8%) participated in the Japan Nosocomial Infections Surveillance system. Data from this relatively low percentage of eligible facilities most likely underestimated the true number of MRSA patients in Japan, the authors said.
Based on their findings, the investigators noted three major advantages of using health insurance claims data for infection surveillance. Firstly, information from health insurance claims data is not affected by health care providers’ notifications to surveillance systems. Secondly, data on patients with MRSA can be collected at low cost because of Japan’s uniform and computerized health insurance system, and the data are easy to access. Lastly, health insurance claims data prevent the duplication of patient information, as insurers can determine if a patient was treated at multiple medical facilities for the same disease.
The only noted drawback involving the use of health insurance claims data for infection surveillance pertained to its timeliness, the researchers wrote. This issue arises because these data are submitted monthly rather than immediately, which may limit their use in surveillance systems.
According to Dr. Tanihara and Dr. Suzuki, strengths of the study include its evaluation of sentinel surveillance quality through the use of data that were not based on physician reports, as well as the calculation of MRSA incidence by use of a standardized definition in a specific population. Reported limitations included the assessment of anti-MRSA medicine use and patients’ age only, and the lack of information on the degree of drug resistance from health insurance claims data.
Funding was provided by the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare of Japan, and by the Research Programme on Emerging and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development. Neither author reported any conflicts of interest.
Key clinical point: Sentinel surveillance systems may substantially underestimate the number of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus cases in Japan.
Major finding: Direct notification to the Japan Nosocomial Infections Surveillance system regarding methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus patients was not affected by patients’ age, and information from health insurance claims was useful for evaluation of the sentinel infection surveillance system.
Data sources: The Japan Nosocomial Infections Surveillance system and the National Health Insurance Organization.
Disclosures: Funding was provided by the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare of Japan, and by the Research Programme on Emerging and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development. Neither author reported any conflicts of interest.