User login
, a 1-year, phase 3 clinical trial has shown. The trial was an add-on study involving a subset of subjects from the STEADY-PD III trial of isradipine in early Parkinson’s disease.
Although the trial was conducted before SARS-CoV-2 arrived on the scene, the findings have particular relevance for being able to conduct a variety of clinical trials in the face of COVID-19 and the need to limit in-person interactions.
The 40 participants used tablets to complete three remote, video-based assessments during 1 year, with each remote visit planned to be completed within 4 weeks of an in-person visit. It was easy to enroll patients, and they completed about 95% of planned visits, said neurologist Christopher Tarolli, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.).
He presented the study findings at the Movement Disorder Society’s 23rd International Congress of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders (Virtual) 2020.
“The visits were clearly feasible, and we were able to do them [84%] within that 4-week time frame around the in-person visit,” he said. “The visits were also reasonably reliable, particularly so for what we call the nonmotor outcomes and the patient-reported outcomes.”
In-person versus remote assessment
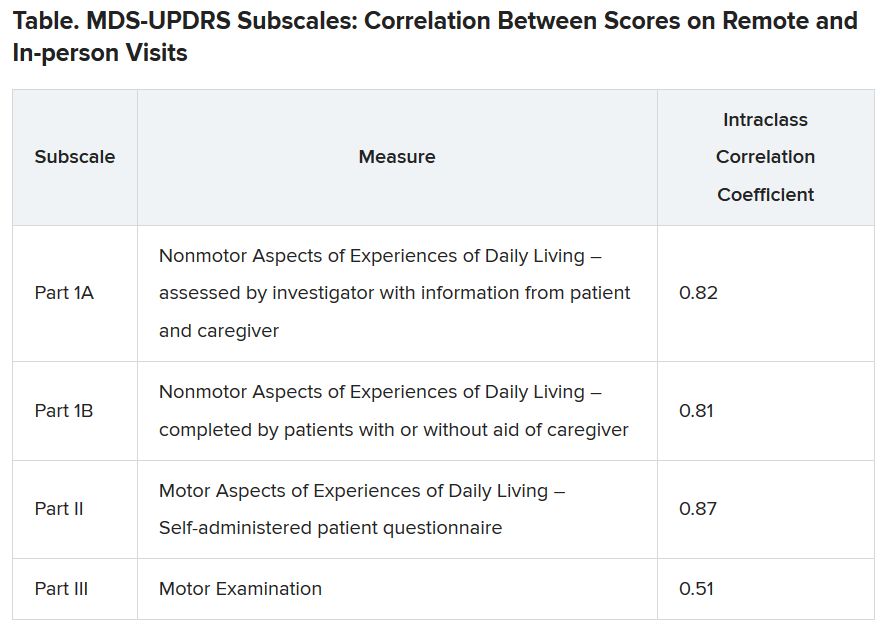
For the remote visits, participants completed primarily the same battery of tests as the in-person visits. Responses on the Movement Disorder Society-Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS) subscales demonstrated “that there was excellent correlation between patient-reported and nonmotor outcome measures and moderate correlation between in-person and remote-performed motor assessments,” Dr. Tarolli said.
He explained that the study used modified motor assessments (MDS-UPDRS Part III) that excluded testing of rigidity and postural instability, which require hands-on testing by a trained examiner and thus are impossible to do remotely.
Additionally, the somewhat lower correlation on this subscale was probably the result of different investigators conducting in-person versus remote assessments, with a subset of in-person investigators who tended to rate participants more severely driving down the correlation. “I think if these methods were applied in future trials, the in-person and remote investigators would optimally be the same person,” Dr. Tarolli suggested.
Room for error?
Indu Subramanian, MD, of the department of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, and director of the Parkinson’s Disease Research, Education, and Clinical Center at the West Los Angeles Veterans Affairs Hospital, commented that “the reliability of UPDRS [part] III is where I would want to have, for sure, a little bit more of a deep dive. … possibly the same patient be rated by the same person.”
She also noted that doing remote and in-person assessments within 4 weeks of each other leaves a lot of room for variability. “You could see the same patient in the morning and then do UPDRS in the afternoon, and it can be totally different depending on when you meet the person,” she said.
Only so much testing can be done remotely. Nonetheless, she questioned whether it is really a valid UPDRS if rigidity and postural stability measures are eliminated. “[Is] this now a new modified UPDRS that we’re going to use that is as good as the old UPDRS moving forward, a home version of UPDRS or whatever we’re going to call it?”
Dr. Subramanian mentioned that patients have told her that UPDRS part III does not really measure what is most important to them, such as making pastries for their grandchildren rather than rapidly tapping their fingers.
“That speaks a little bit to the fact that we should have more patient-centered outcomes and things that patients can report. … things that are not going to require necessarily an in-person exam as maybe measures that really can be used moving forward in studies,” she suggested.
Patient satisfaction with remote visits
Greater than 90% of the patients were satisfied or very satisfied overall with the remote visits, including the convenience, comfort, and connection (using the devices and Internet connection), with “patients describing enjoying being able to do these visits from the comfort of their own home, not having to travel,” Dr. Tarolli said. Not having to drive in an ‘off’ state “was actually something that some participants identified as a safety benefit from this as well.”
There was also a time benefit to the patients and investigators. The average length of the remote visits was 54.3 minutes each versus 74 minutes of interaction for in-person visits, mainly a result of more efficient hand-offs between the neurologist and the study coordinator during the remote visits, plus being able to pause the remote visit to give a medication dose time to take effect.
For the patient, there was a large amount of time saved when travel time was considered – a total of 190.2 minutes on average for travel and testing for the in-person visits.
About three-quarters (76%) of the study patients said that remote visits would increase their likelihood of participating in future trials. However, that result may be skewed by the fact that these were already people willing to participate in a remote trial, so the generalizability of the result may be affected. Nonetheless, Dr. Tarolli said he thinks that, as technology gets better and older people become more comfortable with it, remote visits within Parkinson’s research studies may become more common.
One caveat he mentioned is that, with remote visits, the neurologist misses a chance to observe a patient’s whole body and construct a global impression of how he or she is moving. On the other hand, remote video gives the investigator the chance to see the living environment of the patient and suggest changes for safety, such as to reduce the risk of falling for a person with unsteadiness of gait living in a crowded house.
“It really allows us to make a more holistic assessment of how our patient is functioning outside the clinic, which I think we’ve traditionally had really no way of doing,” Dr. Tarolli said.
His final suggestion for anyone contemplating conducting studies with remote visits is to develop a team that is comfortable troubleshooting the technological aspects of those visits.
UCLA’s Dr. Subramanian lauded the University of Rochester team for their efforts in moving remote visits forward. “They’re at the cutting edge of these sorts of things,” she said. “So I’m assuming that they’ll come out with more things [for visits] to become better that are going to move this forward, which is exciting.”
Dr. Tarolli has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Subramanian has given talks for Acorda Pharmaceuticals and Acadia Pharmaceuticals in the past. The study had only university, government, foundation, and other nonprofit support.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, a 1-year, phase 3 clinical trial has shown. The trial was an add-on study involving a subset of subjects from the STEADY-PD III trial of isradipine in early Parkinson’s disease.
Although the trial was conducted before SARS-CoV-2 arrived on the scene, the findings have particular relevance for being able to conduct a variety of clinical trials in the face of COVID-19 and the need to limit in-person interactions.
The 40 participants used tablets to complete three remote, video-based assessments during 1 year, with each remote visit planned to be completed within 4 weeks of an in-person visit. It was easy to enroll patients, and they completed about 95% of planned visits, said neurologist Christopher Tarolli, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.).
He presented the study findings at the Movement Disorder Society’s 23rd International Congress of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders (Virtual) 2020.
“The visits were clearly feasible, and we were able to do them [84%] within that 4-week time frame around the in-person visit,” he said. “The visits were also reasonably reliable, particularly so for what we call the nonmotor outcomes and the patient-reported outcomes.”
In-person versus remote assessment
For the remote visits, participants completed primarily the same battery of tests as the in-person visits. Responses on the Movement Disorder Society-Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS) subscales demonstrated “that there was excellent correlation between patient-reported and nonmotor outcome measures and moderate correlation between in-person and remote-performed motor assessments,” Dr. Tarolli said.
He explained that the study used modified motor assessments (MDS-UPDRS Part III) that excluded testing of rigidity and postural instability, which require hands-on testing by a trained examiner and thus are impossible to do remotely.
Additionally, the somewhat lower correlation on this subscale was probably the result of different investigators conducting in-person versus remote assessments, with a subset of in-person investigators who tended to rate participants more severely driving down the correlation. “I think if these methods were applied in future trials, the in-person and remote investigators would optimally be the same person,” Dr. Tarolli suggested.
Room for error?
Indu Subramanian, MD, of the department of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, and director of the Parkinson’s Disease Research, Education, and Clinical Center at the West Los Angeles Veterans Affairs Hospital, commented that “the reliability of UPDRS [part] III is where I would want to have, for sure, a little bit more of a deep dive. … possibly the same patient be rated by the same person.”
She also noted that doing remote and in-person assessments within 4 weeks of each other leaves a lot of room for variability. “You could see the same patient in the morning and then do UPDRS in the afternoon, and it can be totally different depending on when you meet the person,” she said.
Only so much testing can be done remotely. Nonetheless, she questioned whether it is really a valid UPDRS if rigidity and postural stability measures are eliminated. “[Is] this now a new modified UPDRS that we’re going to use that is as good as the old UPDRS moving forward, a home version of UPDRS or whatever we’re going to call it?”
Dr. Subramanian mentioned that patients have told her that UPDRS part III does not really measure what is most important to them, such as making pastries for their grandchildren rather than rapidly tapping their fingers.
“That speaks a little bit to the fact that we should have more patient-centered outcomes and things that patients can report. … things that are not going to require necessarily an in-person exam as maybe measures that really can be used moving forward in studies,” she suggested.
Patient satisfaction with remote visits
Greater than 90% of the patients were satisfied or very satisfied overall with the remote visits, including the convenience, comfort, and connection (using the devices and Internet connection), with “patients describing enjoying being able to do these visits from the comfort of their own home, not having to travel,” Dr. Tarolli said. Not having to drive in an ‘off’ state “was actually something that some participants identified as a safety benefit from this as well.”
There was also a time benefit to the patients and investigators. The average length of the remote visits was 54.3 minutes each versus 74 minutes of interaction for in-person visits, mainly a result of more efficient hand-offs between the neurologist and the study coordinator during the remote visits, plus being able to pause the remote visit to give a medication dose time to take effect.
For the patient, there was a large amount of time saved when travel time was considered – a total of 190.2 minutes on average for travel and testing for the in-person visits.
About three-quarters (76%) of the study patients said that remote visits would increase their likelihood of participating in future trials. However, that result may be skewed by the fact that these were already people willing to participate in a remote trial, so the generalizability of the result may be affected. Nonetheless, Dr. Tarolli said he thinks that, as technology gets better and older people become more comfortable with it, remote visits within Parkinson’s research studies may become more common.
One caveat he mentioned is that, with remote visits, the neurologist misses a chance to observe a patient’s whole body and construct a global impression of how he or she is moving. On the other hand, remote video gives the investigator the chance to see the living environment of the patient and suggest changes for safety, such as to reduce the risk of falling for a person with unsteadiness of gait living in a crowded house.
“It really allows us to make a more holistic assessment of how our patient is functioning outside the clinic, which I think we’ve traditionally had really no way of doing,” Dr. Tarolli said.
His final suggestion for anyone contemplating conducting studies with remote visits is to develop a team that is comfortable troubleshooting the technological aspects of those visits.
UCLA’s Dr. Subramanian lauded the University of Rochester team for their efforts in moving remote visits forward. “They’re at the cutting edge of these sorts of things,” she said. “So I’m assuming that they’ll come out with more things [for visits] to become better that are going to move this forward, which is exciting.”
Dr. Tarolli has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Subramanian has given talks for Acorda Pharmaceuticals and Acadia Pharmaceuticals in the past. The study had only university, government, foundation, and other nonprofit support.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, a 1-year, phase 3 clinical trial has shown. The trial was an add-on study involving a subset of subjects from the STEADY-PD III trial of isradipine in early Parkinson’s disease.
Although the trial was conducted before SARS-CoV-2 arrived on the scene, the findings have particular relevance for being able to conduct a variety of clinical trials in the face of COVID-19 and the need to limit in-person interactions.
The 40 participants used tablets to complete three remote, video-based assessments during 1 year, with each remote visit planned to be completed within 4 weeks of an in-person visit. It was easy to enroll patients, and they completed about 95% of planned visits, said neurologist Christopher Tarolli, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.).
He presented the study findings at the Movement Disorder Society’s 23rd International Congress of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders (Virtual) 2020.
“The visits were clearly feasible, and we were able to do them [84%] within that 4-week time frame around the in-person visit,” he said. “The visits were also reasonably reliable, particularly so for what we call the nonmotor outcomes and the patient-reported outcomes.”
In-person versus remote assessment
For the remote visits, participants completed primarily the same battery of tests as the in-person visits. Responses on the Movement Disorder Society-Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS) subscales demonstrated “that there was excellent correlation between patient-reported and nonmotor outcome measures and moderate correlation between in-person and remote-performed motor assessments,” Dr. Tarolli said.
He explained that the study used modified motor assessments (MDS-UPDRS Part III) that excluded testing of rigidity and postural instability, which require hands-on testing by a trained examiner and thus are impossible to do remotely.
Additionally, the somewhat lower correlation on this subscale was probably the result of different investigators conducting in-person versus remote assessments, with a subset of in-person investigators who tended to rate participants more severely driving down the correlation. “I think if these methods were applied in future trials, the in-person and remote investigators would optimally be the same person,” Dr. Tarolli suggested.
Room for error?
Indu Subramanian, MD, of the department of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, and director of the Parkinson’s Disease Research, Education, and Clinical Center at the West Los Angeles Veterans Affairs Hospital, commented that “the reliability of UPDRS [part] III is where I would want to have, for sure, a little bit more of a deep dive. … possibly the same patient be rated by the same person.”
She also noted that doing remote and in-person assessments within 4 weeks of each other leaves a lot of room for variability. “You could see the same patient in the morning and then do UPDRS in the afternoon, and it can be totally different depending on when you meet the person,” she said.
Only so much testing can be done remotely. Nonetheless, she questioned whether it is really a valid UPDRS if rigidity and postural stability measures are eliminated. “[Is] this now a new modified UPDRS that we’re going to use that is as good as the old UPDRS moving forward, a home version of UPDRS or whatever we’re going to call it?”
Dr. Subramanian mentioned that patients have told her that UPDRS part III does not really measure what is most important to them, such as making pastries for their grandchildren rather than rapidly tapping their fingers.
“That speaks a little bit to the fact that we should have more patient-centered outcomes and things that patients can report. … things that are not going to require necessarily an in-person exam as maybe measures that really can be used moving forward in studies,” she suggested.
Patient satisfaction with remote visits
Greater than 90% of the patients were satisfied or very satisfied overall with the remote visits, including the convenience, comfort, and connection (using the devices and Internet connection), with “patients describing enjoying being able to do these visits from the comfort of their own home, not having to travel,” Dr. Tarolli said. Not having to drive in an ‘off’ state “was actually something that some participants identified as a safety benefit from this as well.”
There was also a time benefit to the patients and investigators. The average length of the remote visits was 54.3 minutes each versus 74 minutes of interaction for in-person visits, mainly a result of more efficient hand-offs between the neurologist and the study coordinator during the remote visits, plus being able to pause the remote visit to give a medication dose time to take effect.
For the patient, there was a large amount of time saved when travel time was considered – a total of 190.2 minutes on average for travel and testing for the in-person visits.
About three-quarters (76%) of the study patients said that remote visits would increase their likelihood of participating in future trials. However, that result may be skewed by the fact that these were already people willing to participate in a remote trial, so the generalizability of the result may be affected. Nonetheless, Dr. Tarolli said he thinks that, as technology gets better and older people become more comfortable with it, remote visits within Parkinson’s research studies may become more common.
One caveat he mentioned is that, with remote visits, the neurologist misses a chance to observe a patient’s whole body and construct a global impression of how he or she is moving. On the other hand, remote video gives the investigator the chance to see the living environment of the patient and suggest changes for safety, such as to reduce the risk of falling for a person with unsteadiness of gait living in a crowded house.
“It really allows us to make a more holistic assessment of how our patient is functioning outside the clinic, which I think we’ve traditionally had really no way of doing,” Dr. Tarolli said.
His final suggestion for anyone contemplating conducting studies with remote visits is to develop a team that is comfortable troubleshooting the technological aspects of those visits.
UCLA’s Dr. Subramanian lauded the University of Rochester team for their efforts in moving remote visits forward. “They’re at the cutting edge of these sorts of things,” she said. “So I’m assuming that they’ll come out with more things [for visits] to become better that are going to move this forward, which is exciting.”
Dr. Tarolli has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Subramanian has given talks for Acorda Pharmaceuticals and Acadia Pharmaceuticals in the past. The study had only university, government, foundation, and other nonprofit support.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.