User login
ANSWER
The correct answer is disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis (DSAP; choice “a”). This condition, caused by an inherited defect of the SART3 gene, is seen mostly on the sun-exposed skin of middle-aged women.
Stasis dermatitis (choice “b”) can cause a number of skin changes, but not the discrete annular lesions seen with DSAP.
Seborrheic keratoses (choice “c”) are common on the legs. However, they don’t display this same morphology.
Nummular eczema (choice “d”) presents with annular papulosquamous lesions (as opposed to the fixed lesions seen with DSAP), often on the legs and lower trunk, but without the thready circumferential scaly border.
Continue reading for Joe Monroe's discussion...
DISCUSSION
Leg skin is prey to an astonishing array of problems; many have to do with increased hydrostatic pressure (eg, venous stasis disease), with the almost complete lack of sebaceous glands (eg, nummular eczema), or with the simple fact of being “in harm’s way.” And there is no law that says a given patient can’t have more than one problem at a time, co-existing and serving to confuse the examiner. Such is the case with this patient.
Her concern about possible blood clots is misplaced but understandable. Deep vein thromboses would not present in multiples, would not be on the surface or scaly, and would almost certainly be painful.
The fixed nature of this patient’s scaly lesions is extremely significant—but only if you know about DSAP, which typically manifests in the third decade of life and slowly worsens. The lesions’ highly palpable and unique scaly border makes them hard to leave alone. This might not be a problem except for the warfarin, which makes otherwise minor trauma visible as purpuric macules. Chronic sun damage tends to accentuate them as well. The positive family history is nicely corroborative and quite common.
The brown macules on the patient’s legs are solar lentigines (sun-caused freckles), which many patients (and even younger providers) erroneously call “age spots.” When these individuals become “aged,” they’ll understand that there is no such thing as an age spot.
This patient could easily have had nummular eczema, but not for 30 years! Those lesions, treated or not, will come and go. But not DSAP, about which many questions remain: If they’re caused by sun exposure, why don’t we see them more often on the face and arms? And why don’t we see them on the sun-damaged skin of older men?
If needed, a biopsy could have been performed. It would have been confirmatory of the diagnosis and effectively would have ruled out the other items in the differential, including wart, squamous cell carcinoma, and actinic or seborrheic keratosis.
ANSWER
The correct answer is disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis (DSAP; choice “a”). This condition, caused by an inherited defect of the SART3 gene, is seen mostly on the sun-exposed skin of middle-aged women.
Stasis dermatitis (choice “b”) can cause a number of skin changes, but not the discrete annular lesions seen with DSAP.
Seborrheic keratoses (choice “c”) are common on the legs. However, they don’t display this same morphology.
Nummular eczema (choice “d”) presents with annular papulosquamous lesions (as opposed to the fixed lesions seen with DSAP), often on the legs and lower trunk, but without the thready circumferential scaly border.
Continue reading for Joe Monroe's discussion...
DISCUSSION
Leg skin is prey to an astonishing array of problems; many have to do with increased hydrostatic pressure (eg, venous stasis disease), with the almost complete lack of sebaceous glands (eg, nummular eczema), or with the simple fact of being “in harm’s way.” And there is no law that says a given patient can’t have more than one problem at a time, co-existing and serving to confuse the examiner. Such is the case with this patient.
Her concern about possible blood clots is misplaced but understandable. Deep vein thromboses would not present in multiples, would not be on the surface or scaly, and would almost certainly be painful.
The fixed nature of this patient’s scaly lesions is extremely significant—but only if you know about DSAP, which typically manifests in the third decade of life and slowly worsens. The lesions’ highly palpable and unique scaly border makes them hard to leave alone. This might not be a problem except for the warfarin, which makes otherwise minor trauma visible as purpuric macules. Chronic sun damage tends to accentuate them as well. The positive family history is nicely corroborative and quite common.
The brown macules on the patient’s legs are solar lentigines (sun-caused freckles), which many patients (and even younger providers) erroneously call “age spots.” When these individuals become “aged,” they’ll understand that there is no such thing as an age spot.
This patient could easily have had nummular eczema, but not for 30 years! Those lesions, treated or not, will come and go. But not DSAP, about which many questions remain: If they’re caused by sun exposure, why don’t we see them more often on the face and arms? And why don’t we see them on the sun-damaged skin of older men?
If needed, a biopsy could have been performed. It would have been confirmatory of the diagnosis and effectively would have ruled out the other items in the differential, including wart, squamous cell carcinoma, and actinic or seborrheic keratosis.
ANSWER
The correct answer is disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis (DSAP; choice “a”). This condition, caused by an inherited defect of the SART3 gene, is seen mostly on the sun-exposed skin of middle-aged women.
Stasis dermatitis (choice “b”) can cause a number of skin changes, but not the discrete annular lesions seen with DSAP.
Seborrheic keratoses (choice “c”) are common on the legs. However, they don’t display this same morphology.
Nummular eczema (choice “d”) presents with annular papulosquamous lesions (as opposed to the fixed lesions seen with DSAP), often on the legs and lower trunk, but without the thready circumferential scaly border.
Continue reading for Joe Monroe's discussion...
DISCUSSION
Leg skin is prey to an astonishing array of problems; many have to do with increased hydrostatic pressure (eg, venous stasis disease), with the almost complete lack of sebaceous glands (eg, nummular eczema), or with the simple fact of being “in harm’s way.” And there is no law that says a given patient can’t have more than one problem at a time, co-existing and serving to confuse the examiner. Such is the case with this patient.
Her concern about possible blood clots is misplaced but understandable. Deep vein thromboses would not present in multiples, would not be on the surface or scaly, and would almost certainly be painful.
The fixed nature of this patient’s scaly lesions is extremely significant—but only if you know about DSAP, which typically manifests in the third decade of life and slowly worsens. The lesions’ highly palpable and unique scaly border makes them hard to leave alone. This might not be a problem except for the warfarin, which makes otherwise minor trauma visible as purpuric macules. Chronic sun damage tends to accentuate them as well. The positive family history is nicely corroborative and quite common.
The brown macules on the patient’s legs are solar lentigines (sun-caused freckles), which many patients (and even younger providers) erroneously call “age spots.” When these individuals become “aged,” they’ll understand that there is no such thing as an age spot.
This patient could easily have had nummular eczema, but not for 30 years! Those lesions, treated or not, will come and go. But not DSAP, about which many questions remain: If they’re caused by sun exposure, why don’t we see them more often on the face and arms? And why don’t we see them on the sun-damaged skin of older men?
If needed, a biopsy could have been performed. It would have been confirmatory of the diagnosis and effectively would have ruled out the other items in the differential, including wart, squamous cell carcinoma, and actinic or seborrheic keratosis.
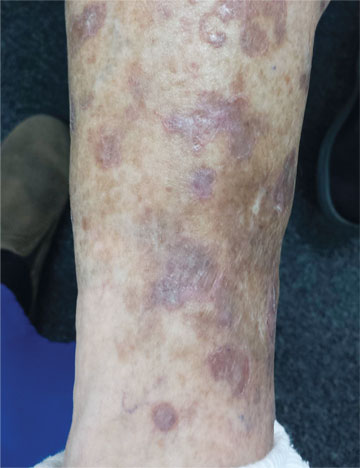
A 65-year-old woman is referred to dermatology with discoloration of her legs that started several weeks ago. Her family suggested it might be “blood clots,” although she has been taking warfarin since she was diagnosed with atrial fibrillation several months ago. Her dermatologic condition is basically asymptomatic, but the patient admits to scratching her legs, saying it’s “hard to leave them alone.” On further questioning, she reveals that she has had “rough places” on her legs for at least 20 years and volunteers that her sister had the same problem, which was diagnosed years ago as “fungal infection.” Both she and her sister spent a great deal of time in the sun as children, long before sunscreen was invented. The patient is otherwise fairly healthy. She takes medication for her lipids, as well as daily vitamins. Her atrial fibrillation is under control and requires no medications other than the warfarin. A great deal of focal discoloration is seen on both legs, circumferentially distributed from well below the knees to just above the ankles. Many of the lesions are brown macules, but more are purplish-red, annular, and scaly. On closer examination, these lesions—the ones the patient says she has had for decades—have a very fine, thready, scaly border that palpation reveals to be tough and adherent. They average about 2 cm in diameter. There are no such lesions noted elsewhere on the patient’s skin. There is, however, abundant evidence of excessive sun exposure, characterized by a multitude of solar lentigines, many fine wrinkles, and extremely thin arm skin.
