User login
Providers typically rely on the “key components” (history, exam, medical decision-making) when documenting in the medical record, and they often misunderstand the use of time when selecting visit levels. Sometimes providers may report a lower service level than warranted because they didn’t feel that they spent the required amount of time with the patient; however, the duration of the visit is an ancillary factor and does not control the level of service to be billed unless more than 50% of the face-to-face time (for non-inpatient services) or more than 50% of the floor time (for inpatient services) is spent providing counseling or coordination of care (C/CC).1 In these instances, providers may choose to document only a brief history and exam, or none at all. They should update the medical decision-making based on the discussion.
Consider the hospitalization of an elderly patient who is newly diagnosed with diabetes. In addition to stabilizing the patient’s glucose levels and devising the appropriate care plan, the patient and/or caregivers also require extensive counseling regarding disease management, lifestyle modification, and medication regime. Coordination of care for outpatient programs and resources is also crucial. To make sure that this qualifies as a time-based service, ensure that the documentation contains the duration, the issues addressed, and the signature of the service provider.
Duration of Counseling and/or Coordination of Care
Time is not used for visit level selection if C/CC is minimal (<50%) or absent from the patient encounter. For inpatient services, total visit time is identified as provider face-to-face time (i.e., at the bedside) combined with time spent on the patient’s unit/floor performing services that are directly related to that patient, such as reviewing data, obtaining relevant patient information, and discussing the case with other involved healthcare providers.
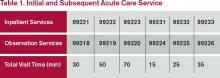
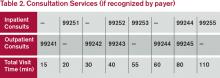
Time associated with activities performed in locations other than the patient’s unit/floor (e.g. reviewing current results or images from the physician’s office) is not allowable in calculating the total visit time. Time associated with teaching students/interns is also excluded, because this doesn’t reflect patient care activities. Once the provider documents all services rendered on a given calendar date, the provider selects the visit level that corresponds with the cumulative visit time documented in the chart (see Tables 1 and 2).
Issues Addressed
When counseling and/or coordination of care dominate more than 50% of the time a physician spends with a patient during an evaluation and management (E/M) service, then time may be considered as the controlling factor to qualify the E/M service for a particular level of care.2 The following must be documented in the patient’s medical record in order to report an E/M service based on time:
- The total length of time of the E/M visit;
- Evidence that more than half of the total length of time of the E/M visit was spent in counseling and coordinating of care; and
- The content of the counseling and coordination of care provided during the E/M visit.
History and exam, if performed or updated, should also be documented, along with the patient response or comprehension of information. An acceptable C/CC time entry may be noted as, “Total visit time = 35 minutes; > 50% spent counseling/coordinating care” or “20 of 35 minutes spent counseling/coordinating care.”
A payer may prefer one documentation style over another. It is always best to query payer policy and review local documentation standards to ensure compliance. Please remember that while this example constitutes the required elements for the notation of time, documentation must also include the details of counseling, care plan revisions, and any information that is pertinent to patient care and communication with other healthcare professionals.
Family Discussions
Family discussions are a typical event involved in taking care of patients and are appropriate to count as C/CC time. Special circumstances are considered when discussions must take place without the patient present. This type of counseling time is recognized but only counts towards C/CC time if the following criteria are met and documented:
- The patient is unable or clinically incompetent to participate in discussions;
- The time is spent on the unit/floor with the family members or surrogate decision makers obtaining a medical history, reviewing the patient’s condition or prognosis, or discussing treatment or limitation(s) of treatment; and
- The conversation bears directly on the management of the patient.3
Time cannot be counted if the discussion takes place in an area outside of the patient’s unit/floor (e.g. in the physician’s office) or if the time is spent counseling the family members through their grieving process.
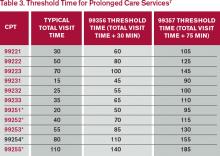
It is fairly common for the family discussion to take place later in the day, after the physician has completed morning rounds. If the earlier encounter involved C/CC, the physician would report the cumulative time spent for that service date. If the earlier encounter was a typical patient assessment incorporating the components of an evaluation (i.e., history update and physical) and management (i.e., care plan review/revision) service, the meeting time may qualify for prolonged care services.
Service Provider
Be sure to count only the physician’s time spent in C/CC. Counseling time by the nursing staff, the social worker, or the resident cannot contribute toward the physician’s total visit time. When more than one physician is involved in services throughout the day, the physicians should select a level of service representative of the combined visits and submit the appropriate code for that level under one physician’s name.4
Consider the following example: The hospitalist takes a brief history about overnight events and reviews some of the pertinent information with the patient. He/she then leaves the room to coordinate the patient’s ongoing care in anticipation that the patient will be discharged over the next few days (25 minutes). The resident is asked to continue the assessment and counsel the patient on the patient’s current disease process (20 minutes).
In the above scenario, the hospitalist is only able to report 99232, because the time spent by the resident is “nonbillable time.”
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center, Philadelphia. She is also on the faculty of SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12: Physicians/Nonphysician Practitioners, Section 30.6.1B. Available at: www.cms.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed December 11, 2014.
- Novitas Solutions, Inc. Frequently Asked Questions: Evaluation and Management Services (Part B). Available at: http://www.novitas-solutions.com/webcenter/faces/oracle/webcenter/page/scopedMD/sad78b265_6797_4ed0_a02f_81627913bc78/Page57.jspx?wc.contextURL=%2Fspaces%2FMedicareJH&wc.originURL=%2Fspaces%2FMedicareJH%2Fpage%2Fpagebyid&contentId=00005056&_afrLoop=1728453012371000#%40%3F_afrLoop%3D1728453012371000%26wc.originURL%3D%252Fspaces%252FMedicareJH%252Fpage%252Fpagebyid%26contentId%3D00005056%26wc.contextURL%3D%252Fspaces%252FMedicareJH%26_adf.ctrl-state%3D610bhasa4_134. Accessed on December 11, 2014.
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare National Coverage Determinations Manual: Chapter 1, Part 1: Coverage Determinations, Section 70.1. Available at: www.cms.gov/manuals/downloads/ncd103c1_Part1.pdf. Accessed December 11, 2014.
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12: Physicians/Nonphysician Practitioners, Section 30.6.5. Available at: www.cms.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed December 11, 2014.
- Abraham M, Ahlman JT, Boudreau AJ, Connelly J, Levreau-Davis L. Current Procedural Terminology 2014 Professional Edition. Chicago: American Medical Association Press; 2013:1-32.
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12: Physicians/Nonphysician Practitioners, Section 30.6.1C. Available at: www.cms.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed December 11, 2014.
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12: Physicians/Nonphysician Practitioners, Section 30.6.15.1G. Available at: www.cms.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf.
Providers typically rely on the “key components” (history, exam, medical decision-making) when documenting in the medical record, and they often misunderstand the use of time when selecting visit levels. Sometimes providers may report a lower service level than warranted because they didn’t feel that they spent the required amount of time with the patient; however, the duration of the visit is an ancillary factor and does not control the level of service to be billed unless more than 50% of the face-to-face time (for non-inpatient services) or more than 50% of the floor time (for inpatient services) is spent providing counseling or coordination of care (C/CC).1 In these instances, providers may choose to document only a brief history and exam, or none at all. They should update the medical decision-making based on the discussion.
Consider the hospitalization of an elderly patient who is newly diagnosed with diabetes. In addition to stabilizing the patient’s glucose levels and devising the appropriate care plan, the patient and/or caregivers also require extensive counseling regarding disease management, lifestyle modification, and medication regime. Coordination of care for outpatient programs and resources is also crucial. To make sure that this qualifies as a time-based service, ensure that the documentation contains the duration, the issues addressed, and the signature of the service provider.
Duration of Counseling and/or Coordination of Care
Time is not used for visit level selection if C/CC is minimal (<50%) or absent from the patient encounter. For inpatient services, total visit time is identified as provider face-to-face time (i.e., at the bedside) combined with time spent on the patient’s unit/floor performing services that are directly related to that patient, such as reviewing data, obtaining relevant patient information, and discussing the case with other involved healthcare providers.
Time associated with activities performed in locations other than the patient’s unit/floor (e.g. reviewing current results or images from the physician’s office) is not allowable in calculating the total visit time. Time associated with teaching students/interns is also excluded, because this doesn’t reflect patient care activities. Once the provider documents all services rendered on a given calendar date, the provider selects the visit level that corresponds with the cumulative visit time documented in the chart (see Tables 1 and 2).
Issues Addressed
When counseling and/or coordination of care dominate more than 50% of the time a physician spends with a patient during an evaluation and management (E/M) service, then time may be considered as the controlling factor to qualify the E/M service for a particular level of care.2 The following must be documented in the patient’s medical record in order to report an E/M service based on time:
- The total length of time of the E/M visit;
- Evidence that more than half of the total length of time of the E/M visit was spent in counseling and coordinating of care; and
- The content of the counseling and coordination of care provided during the E/M visit.
History and exam, if performed or updated, should also be documented, along with the patient response or comprehension of information. An acceptable C/CC time entry may be noted as, “Total visit time = 35 minutes; > 50% spent counseling/coordinating care” or “20 of 35 minutes spent counseling/coordinating care.”
A payer may prefer one documentation style over another. It is always best to query payer policy and review local documentation standards to ensure compliance. Please remember that while this example constitutes the required elements for the notation of time, documentation must also include the details of counseling, care plan revisions, and any information that is pertinent to patient care and communication with other healthcare professionals.
Family Discussions
Family discussions are a typical event involved in taking care of patients and are appropriate to count as C/CC time. Special circumstances are considered when discussions must take place without the patient present. This type of counseling time is recognized but only counts towards C/CC time if the following criteria are met and documented:
- The patient is unable or clinically incompetent to participate in discussions;
- The time is spent on the unit/floor with the family members or surrogate decision makers obtaining a medical history, reviewing the patient’s condition or prognosis, or discussing treatment or limitation(s) of treatment; and
- The conversation bears directly on the management of the patient.3
Time cannot be counted if the discussion takes place in an area outside of the patient’s unit/floor (e.g. in the physician’s office) or if the time is spent counseling the family members through their grieving process.
It is fairly common for the family discussion to take place later in the day, after the physician has completed morning rounds. If the earlier encounter involved C/CC, the physician would report the cumulative time spent for that service date. If the earlier encounter was a typical patient assessment incorporating the components of an evaluation (i.e., history update and physical) and management (i.e., care plan review/revision) service, the meeting time may qualify for prolonged care services.
Service Provider
Be sure to count only the physician’s time spent in C/CC. Counseling time by the nursing staff, the social worker, or the resident cannot contribute toward the physician’s total visit time. When more than one physician is involved in services throughout the day, the physicians should select a level of service representative of the combined visits and submit the appropriate code for that level under one physician’s name.4
Consider the following example: The hospitalist takes a brief history about overnight events and reviews some of the pertinent information with the patient. He/she then leaves the room to coordinate the patient’s ongoing care in anticipation that the patient will be discharged over the next few days (25 minutes). The resident is asked to continue the assessment and counsel the patient on the patient’s current disease process (20 minutes).
In the above scenario, the hospitalist is only able to report 99232, because the time spent by the resident is “nonbillable time.”
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center, Philadelphia. She is also on the faculty of SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12: Physicians/Nonphysician Practitioners, Section 30.6.1B. Available at: www.cms.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed December 11, 2014.
- Novitas Solutions, Inc. Frequently Asked Questions: Evaluation and Management Services (Part B). Available at: http://www.novitas-solutions.com/webcenter/faces/oracle/webcenter/page/scopedMD/sad78b265_6797_4ed0_a02f_81627913bc78/Page57.jspx?wc.contextURL=%2Fspaces%2FMedicareJH&wc.originURL=%2Fspaces%2FMedicareJH%2Fpage%2Fpagebyid&contentId=00005056&_afrLoop=1728453012371000#%40%3F_afrLoop%3D1728453012371000%26wc.originURL%3D%252Fspaces%252FMedicareJH%252Fpage%252Fpagebyid%26contentId%3D00005056%26wc.contextURL%3D%252Fspaces%252FMedicareJH%26_adf.ctrl-state%3D610bhasa4_134. Accessed on December 11, 2014.
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare National Coverage Determinations Manual: Chapter 1, Part 1: Coverage Determinations, Section 70.1. Available at: www.cms.gov/manuals/downloads/ncd103c1_Part1.pdf. Accessed December 11, 2014.
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12: Physicians/Nonphysician Practitioners, Section 30.6.5. Available at: www.cms.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed December 11, 2014.
- Abraham M, Ahlman JT, Boudreau AJ, Connelly J, Levreau-Davis L. Current Procedural Terminology 2014 Professional Edition. Chicago: American Medical Association Press; 2013:1-32.
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12: Physicians/Nonphysician Practitioners, Section 30.6.1C. Available at: www.cms.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed December 11, 2014.
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12: Physicians/Nonphysician Practitioners, Section 30.6.15.1G. Available at: www.cms.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf.
Providers typically rely on the “key components” (history, exam, medical decision-making) when documenting in the medical record, and they often misunderstand the use of time when selecting visit levels. Sometimes providers may report a lower service level than warranted because they didn’t feel that they spent the required amount of time with the patient; however, the duration of the visit is an ancillary factor and does not control the level of service to be billed unless more than 50% of the face-to-face time (for non-inpatient services) or more than 50% of the floor time (for inpatient services) is spent providing counseling or coordination of care (C/CC).1 In these instances, providers may choose to document only a brief history and exam, or none at all. They should update the medical decision-making based on the discussion.
Consider the hospitalization of an elderly patient who is newly diagnosed with diabetes. In addition to stabilizing the patient’s glucose levels and devising the appropriate care plan, the patient and/or caregivers also require extensive counseling regarding disease management, lifestyle modification, and medication regime. Coordination of care for outpatient programs and resources is also crucial. To make sure that this qualifies as a time-based service, ensure that the documentation contains the duration, the issues addressed, and the signature of the service provider.
Duration of Counseling and/or Coordination of Care
Time is not used for visit level selection if C/CC is minimal (<50%) or absent from the patient encounter. For inpatient services, total visit time is identified as provider face-to-face time (i.e., at the bedside) combined with time spent on the patient’s unit/floor performing services that are directly related to that patient, such as reviewing data, obtaining relevant patient information, and discussing the case with other involved healthcare providers.
Time associated with activities performed in locations other than the patient’s unit/floor (e.g. reviewing current results or images from the physician’s office) is not allowable in calculating the total visit time. Time associated with teaching students/interns is also excluded, because this doesn’t reflect patient care activities. Once the provider documents all services rendered on a given calendar date, the provider selects the visit level that corresponds with the cumulative visit time documented in the chart (see Tables 1 and 2).
Issues Addressed
When counseling and/or coordination of care dominate more than 50% of the time a physician spends with a patient during an evaluation and management (E/M) service, then time may be considered as the controlling factor to qualify the E/M service for a particular level of care.2 The following must be documented in the patient’s medical record in order to report an E/M service based on time:
- The total length of time of the E/M visit;
- Evidence that more than half of the total length of time of the E/M visit was spent in counseling and coordinating of care; and
- The content of the counseling and coordination of care provided during the E/M visit.
History and exam, if performed or updated, should also be documented, along with the patient response or comprehension of information. An acceptable C/CC time entry may be noted as, “Total visit time = 35 minutes; > 50% spent counseling/coordinating care” or “20 of 35 minutes spent counseling/coordinating care.”
A payer may prefer one documentation style over another. It is always best to query payer policy and review local documentation standards to ensure compliance. Please remember that while this example constitutes the required elements for the notation of time, documentation must also include the details of counseling, care plan revisions, and any information that is pertinent to patient care and communication with other healthcare professionals.
Family Discussions
Family discussions are a typical event involved in taking care of patients and are appropriate to count as C/CC time. Special circumstances are considered when discussions must take place without the patient present. This type of counseling time is recognized but only counts towards C/CC time if the following criteria are met and documented:
- The patient is unable or clinically incompetent to participate in discussions;
- The time is spent on the unit/floor with the family members or surrogate decision makers obtaining a medical history, reviewing the patient’s condition or prognosis, or discussing treatment or limitation(s) of treatment; and
- The conversation bears directly on the management of the patient.3
Time cannot be counted if the discussion takes place in an area outside of the patient’s unit/floor (e.g. in the physician’s office) or if the time is spent counseling the family members through their grieving process.
It is fairly common for the family discussion to take place later in the day, after the physician has completed morning rounds. If the earlier encounter involved C/CC, the physician would report the cumulative time spent for that service date. If the earlier encounter was a typical patient assessment incorporating the components of an evaluation (i.e., history update and physical) and management (i.e., care plan review/revision) service, the meeting time may qualify for prolonged care services.
Service Provider
Be sure to count only the physician’s time spent in C/CC. Counseling time by the nursing staff, the social worker, or the resident cannot contribute toward the physician’s total visit time. When more than one physician is involved in services throughout the day, the physicians should select a level of service representative of the combined visits and submit the appropriate code for that level under one physician’s name.4
Consider the following example: The hospitalist takes a brief history about overnight events and reviews some of the pertinent information with the patient. He/she then leaves the room to coordinate the patient’s ongoing care in anticipation that the patient will be discharged over the next few days (25 minutes). The resident is asked to continue the assessment and counsel the patient on the patient’s current disease process (20 minutes).
In the above scenario, the hospitalist is only able to report 99232, because the time spent by the resident is “nonbillable time.”
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center, Philadelphia. She is also on the faculty of SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12: Physicians/Nonphysician Practitioners, Section 30.6.1B. Available at: www.cms.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed December 11, 2014.
- Novitas Solutions, Inc. Frequently Asked Questions: Evaluation and Management Services (Part B). Available at: http://www.novitas-solutions.com/webcenter/faces/oracle/webcenter/page/scopedMD/sad78b265_6797_4ed0_a02f_81627913bc78/Page57.jspx?wc.contextURL=%2Fspaces%2FMedicareJH&wc.originURL=%2Fspaces%2FMedicareJH%2Fpage%2Fpagebyid&contentId=00005056&_afrLoop=1728453012371000#%40%3F_afrLoop%3D1728453012371000%26wc.originURL%3D%252Fspaces%252FMedicareJH%252Fpage%252Fpagebyid%26contentId%3D00005056%26wc.contextURL%3D%252Fspaces%252FMedicareJH%26_adf.ctrl-state%3D610bhasa4_134. Accessed on December 11, 2014.
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare National Coverage Determinations Manual: Chapter 1, Part 1: Coverage Determinations, Section 70.1. Available at: www.cms.gov/manuals/downloads/ncd103c1_Part1.pdf. Accessed December 11, 2014.
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12: Physicians/Nonphysician Practitioners, Section 30.6.5. Available at: www.cms.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed December 11, 2014.
- Abraham M, Ahlman JT, Boudreau AJ, Connelly J, Levreau-Davis L. Current Procedural Terminology 2014 Professional Edition. Chicago: American Medical Association Press; 2013:1-32.
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12: Physicians/Nonphysician Practitioners, Section 30.6.1C. Available at: www.cms.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed December 11, 2014.
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12: Physicians/Nonphysician Practitioners, Section 30.6.15.1G. Available at: www.cms.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf.