User login
On April 17, 2014, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) released a safety communication that discouraged the use of laparoscopic power morcellation during hysterectomy or myomectomy for the treatment of women with uterine fibroids. This recommendation was based mainly on the premise that fibroids may contain an underlying malignancy (in 1 in 350 women) that laparoscopic power morcellation could spread, thereby potentially worsening a cancer prognosis.1 Whether we liked it or not, minimally invasive gynecologic surgery as we knew it had changed forever on that fateful day.
During the last 2 years, the implications of that initial safety communication, along with its update in November of 2014,2 have been far reaching. From a health care industry perspective, the largest manufacturer of power morcellators, Johnson & Johnson, completely pulled its device out of the market within months of the initial FDA safety communication.3 Although several other companies remained in the market, health insurers such as Highmark and Aetna took the stance of not paying for the routine use of a power morcellator.4,5 Soon government officials became involved in the campaign against power morcellators and trial lawyers made this surgical device the latest “hot target.”6,7
The power morcellator’s absence impactFor clinicians, the narrative painted had moved the pendulum so far against power morcellation that it did not come as a surprise that practice patterns were significantly impacted. Harris and colleagues recently measured that impact by evaluating practice patterns and postoperative complications before and after the FDA safety communication on power morcellation. In their retrospective cohort study of patients within the Michigan Surgical Quality Collaborative, utilization of minimally invasive hysterectomy decreased and major surgical, nontransfusion complications and 30-day hospital readmission rates increased after release of the safety communication.8
Further support of this change in practice patterns was demonstrated in a recent survey conducted by the AAGL and American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Collaborative Ambulatory Research Network (ACOG CARN). In this survey study, Lum and colleagues were able to show that power morcellation use decreased among AAGL and ACOG CARN members after the FDA warnings, and rates of laparotomy increased.9
Critical to the discussion, yet apparently overlooked during the formulation of the initial FDA warning, was the potential clinical significance of the downstream impact of converting minimally invasive surgical cases to more invasive laparotomies. A decision-tree analysis published by Siedhoff and colleagues highlighted this point by predicting fewer overall deaths for laparoscopic hysterectomy with morcellation compared with abdominal hysterectomy.10 An ability to weigh the benefits and risks of procedure-related complications that are associated with laparotomy, including death, should have been part of the conversation from the beginning.
There is a silver lining emergingBased on this domino effect, it would seem that the damage done to minimally invasive gynecologic surgery over the past 2 years is irreparable. So is there any silver lining to the current state of affairs in tissue extraction? I would argue yes.
We have updated estimates for incidence of unsuspected leiomyosarcoma. First of all, discussions surrounding the FDA’s estimated 1 in 350 risk of encountering an unsuspected uterine sarcoma during the treatment of fibroids prompted a more critical evaluation of the scientific literature. In fact, Parker and colleagues, in a commentary published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, summarized very nicely the flawed methodology in the FDA’s determination of risk and in turn presented several updated calculations and studies that placed the prevalence somewhere in the range of 2 in 8,720 (0.023%) to 1 in 1,550 (0.064%).11
We are speaking with the FDA. Channels of communication with the FDA have since been developed and societies such as the AAGL were invited by the Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) at the FDA to serve in their Network of Experts. This Network of Experts is an FDA-vetted group of non−FDA affiliated scientists, clinicians, and engineers who provide the CDRH at the FDA with rapid access to scientific, engineering, and medical expertise when it is needed to supplement existing knowledge and expertise within the CDRH. By developing these lines of communication, the CDRH is able to broaden its exposure to scientific viewpoints without the influence of external, or non−FDA, policy advice or opinions.
We have been innovating our techniques. Clinicians also began to develop innovative techniques for tissue extraction that also included contained, in-bag power morcellation. Vargas and colleagues showed similar perioperative outcomes when comparing open power morcellation with contained power morcellation within an insufflated isolation bag. The mean operative time was prolonged by only 26 minutes with in-bag morcellation.12
Although the initial experience of surgeons involved various containment systems that were off label in their usage and not designed to be paired with a power morcellator, it allowed for the identification of potential limitations, such as the risk of leakage. Cohen and colleagues, in their published experience, demonstrated a 9.2% spillage in 76 patients who underwent contained power morcellation.13
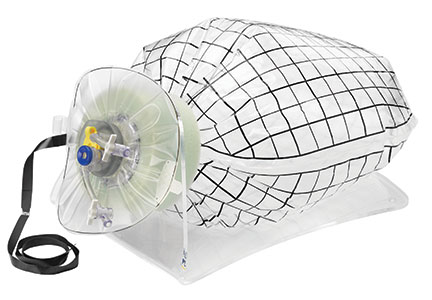
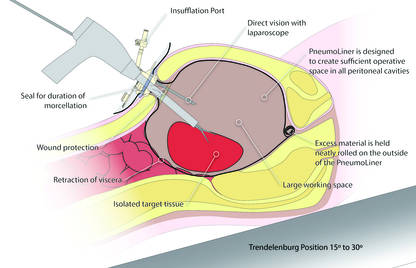
Could a new FDA approval turn the tide?In an interesting turn of events, the FDA, on April 7, 2016, nearly 2 years after their initial warning about power morcellation, gave de novo classification clearance to Advanced Surgical Concepts for its PneumoLiner device.14 This first-of-a-kind medical device was developed for the purpose of completely containing fluid, cells, and tissue fragments during laparoscopic power morcellation, isolating uterine tissue that is not suspected to contain cancer (FIGURES 1 and 2). It is important to note, however, that it has not been shown to reduce the risk of spreading cancer during this procedure. Although a surprise to some, the approval of such a product is in keeping with the FDA’s safety communication update in November 2014 that encouraged the development of containment systems designed specifically for gynecologic surgery.
| FIGURE 1 PneumoLiner tissue containment device | FIGURE 2 PneumoLiner device placement | |
 |  |
Currently, the PneumoLiner is not yet available for purchase until Olympus, who will be the exclusive distributor, finalizes its formal training program rollout for ensuring safe and effective use of the device by gynecologic surgeons. As part of the FDA approval process, a training protocol was validated in a laboratory setting by surgeons with varying levels of experience in order to demonstrate that adherence to this process showed no damage to any of the containment systems used during the study.
As I look forward to the opportunity to learn more about this new containment system and potentially incorporate it into my surgical armamentarium, several questions immediately come to mind.
- Will hospitals, many of which pulled morcellators off their shelves in the wake of the FDA safety communication, be willing to embrace such innovative new containment technology and make it available to their surgeons?
- Will the litigious landscape painted by trial lawyers prevent surgeons from offering this option to their patients?
- Can surgeons undo much of the misinformation being propagated by the media as it relates to tissue extraction and the risk of encountering a malignancy?
I hope the answer to all of these questions is yes.
I do believe the pendulum can change directionAs surgeons it is our duty to evaluate potentially innovative solutions to the surgical challenges we face in clinical practice while maintaining an evidence-based approach. Most importantly, all of this must be balanced by sound clinical judgment that no technology can replace. With these guiding principles in mind, I believe that the pendulum regarding tissue extraction can change direction.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Laparoscopic uterine power morcellation in hysterectomy and myomectomy: FDA safety communication. April 17, 2014. http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/Safety/AlertsandNotices/ucm393576.htm. Updated November 24, 2014. Accessed May 24, 2016.
- Updated laparoscopic uterine power morcellation in hysterectomy and myomectomy: FDA safety communication. November 24, 2014. http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/Safety/AlertsandNotices/ucm424443.htm. Updated April 7, 2014. Accessed May 24, 2016.
- Kamp J, Levitz J. Johnson & Johnson pulls hysterectomy device from hospitals. The Wall Street Journal. July 30, 2014. http://www.wsj.com/articles/johnson-johnson-to-call-for-voluntary-return-of-morcellators-1406754350. Accessed May 25, 2016.
- Levitz J. Health insurer to stop covering uterine procedure. The Wall Street Journal. August 2, 2014. http://www.wsj.com/articles/health-insurer-to-stop-covering-uterine-procedure-1406999176. Accessed May 25, 2016.
- Kamp J. Aetna to stop covering routine use of power morcellator. The Wall Street Journal. May 5, 2015. http://www.wsj.com/articles/aetna-to-stop-covering-routine-use-of-power-morcellator-1430838666. Accessed May 25, 2016.
- Kamp J. Senators want more companies to pull surgical device from market. The Wall Street Journal. August 19, 2014. http://www.wsj.com/articles/senators-want-more-companies-to-pull-surgical-device-from-market-1408405349. Accessed May 25, 2016.
- Silverman E. Power morcellators are the latest hot target among trial lawyers. The Wall Street Journal. December 2, 2014. http://blogs.wsj.com/pharmalot/2014/12/02/power-morcellators-are-the-latest-hot-target-among-trial-lawyers/. Accessed May 25, 2016.
- Harris JA, Swenson CW, Uppal S, et al. Practice patterns and postoperative complications before and after the US Food and Drug Administration safety communication on power morcellation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;214(1):98.e1−e13.
- Lum DA, Sokol ER, Berek JS, et al. Impact of the 2014 Food and Drug Administration warnings against power morcellation. J Minim Invasiv Gynecol. 2016;23(4):548−556.
- Siedhoff M, Wheeler SB, Rutstein SE, et al. Laparoscopic hysterectomy with morcellation vs abdominal hysterectomy for presumed fibroid tumors in premenopausal women: a decision analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;212(5):591.e1−e8.
- Parker WH, Kaunitz AM, Pritts EA, et al; Leiomyoma Morcellation Review Group. US Food and Drug Administration’s guidance regarding morcellation of leiomyomas: well-intentioned, but is it harmful for women? Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127(1):18−22.
- Vargas MV, Cohen SL, Fuchs-Weizman N, et al. Open power morcellation versus contained power morcellation within an insufflated isolation bag: comparison of perioperative outcomes. J Minim Invasiv Gynecol. 2015;22(3):433−438.
- Cohen SL, Morris SN, Brown DN, et al. Contained tissue extraction using power morcellation: prospective evaluation of leakage parameters. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;214(2):257.e1−e6.
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA allows marketing of first-of-kind tissue containment system for use with certain laparoscopic power morcellators in select patients. April 7, 2016. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm494650.htm. Updated April 7, 2016. Accessed May 24, 2016.
On April 17, 2014, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) released a safety communication that discouraged the use of laparoscopic power morcellation during hysterectomy or myomectomy for the treatment of women with uterine fibroids. This recommendation was based mainly on the premise that fibroids may contain an underlying malignancy (in 1 in 350 women) that laparoscopic power morcellation could spread, thereby potentially worsening a cancer prognosis.1 Whether we liked it or not, minimally invasive gynecologic surgery as we knew it had changed forever on that fateful day.
During the last 2 years, the implications of that initial safety communication, along with its update in November of 2014,2 have been far reaching. From a health care industry perspective, the largest manufacturer of power morcellators, Johnson & Johnson, completely pulled its device out of the market within months of the initial FDA safety communication.3 Although several other companies remained in the market, health insurers such as Highmark and Aetna took the stance of not paying for the routine use of a power morcellator.4,5 Soon government officials became involved in the campaign against power morcellators and trial lawyers made this surgical device the latest “hot target.”6,7
The power morcellator’s absence impactFor clinicians, the narrative painted had moved the pendulum so far against power morcellation that it did not come as a surprise that practice patterns were significantly impacted. Harris and colleagues recently measured that impact by evaluating practice patterns and postoperative complications before and after the FDA safety communication on power morcellation. In their retrospective cohort study of patients within the Michigan Surgical Quality Collaborative, utilization of minimally invasive hysterectomy decreased and major surgical, nontransfusion complications and 30-day hospital readmission rates increased after release of the safety communication.8
Further support of this change in practice patterns was demonstrated in a recent survey conducted by the AAGL and American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Collaborative Ambulatory Research Network (ACOG CARN). In this survey study, Lum and colleagues were able to show that power morcellation use decreased among AAGL and ACOG CARN members after the FDA warnings, and rates of laparotomy increased.9
Critical to the discussion, yet apparently overlooked during the formulation of the initial FDA warning, was the potential clinical significance of the downstream impact of converting minimally invasive surgical cases to more invasive laparotomies. A decision-tree analysis published by Siedhoff and colleagues highlighted this point by predicting fewer overall deaths for laparoscopic hysterectomy with morcellation compared with abdominal hysterectomy.10 An ability to weigh the benefits and risks of procedure-related complications that are associated with laparotomy, including death, should have been part of the conversation from the beginning.
There is a silver lining emergingBased on this domino effect, it would seem that the damage done to minimally invasive gynecologic surgery over the past 2 years is irreparable. So is there any silver lining to the current state of affairs in tissue extraction? I would argue yes.
We have updated estimates for incidence of unsuspected leiomyosarcoma. First of all, discussions surrounding the FDA’s estimated 1 in 350 risk of encountering an unsuspected uterine sarcoma during the treatment of fibroids prompted a more critical evaluation of the scientific literature. In fact, Parker and colleagues, in a commentary published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, summarized very nicely the flawed methodology in the FDA’s determination of risk and in turn presented several updated calculations and studies that placed the prevalence somewhere in the range of 2 in 8,720 (0.023%) to 1 in 1,550 (0.064%).11
We are speaking with the FDA. Channels of communication with the FDA have since been developed and societies such as the AAGL were invited by the Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) at the FDA to serve in their Network of Experts. This Network of Experts is an FDA-vetted group of non−FDA affiliated scientists, clinicians, and engineers who provide the CDRH at the FDA with rapid access to scientific, engineering, and medical expertise when it is needed to supplement existing knowledge and expertise within the CDRH. By developing these lines of communication, the CDRH is able to broaden its exposure to scientific viewpoints without the influence of external, or non−FDA, policy advice or opinions.
We have been innovating our techniques. Clinicians also began to develop innovative techniques for tissue extraction that also included contained, in-bag power morcellation. Vargas and colleagues showed similar perioperative outcomes when comparing open power morcellation with contained power morcellation within an insufflated isolation bag. The mean operative time was prolonged by only 26 minutes with in-bag morcellation.12
Although the initial experience of surgeons involved various containment systems that were off label in their usage and not designed to be paired with a power morcellator, it allowed for the identification of potential limitations, such as the risk of leakage. Cohen and colleagues, in their published experience, demonstrated a 9.2% spillage in 76 patients who underwent contained power morcellation.13
Could a new FDA approval turn the tide?In an interesting turn of events, the FDA, on April 7, 2016, nearly 2 years after their initial warning about power morcellation, gave de novo classification clearance to Advanced Surgical Concepts for its PneumoLiner device.14 This first-of-a-kind medical device was developed for the purpose of completely containing fluid, cells, and tissue fragments during laparoscopic power morcellation, isolating uterine tissue that is not suspected to contain cancer (FIGURES 1 and 2). It is important to note, however, that it has not been shown to reduce the risk of spreading cancer during this procedure. Although a surprise to some, the approval of such a product is in keeping with the FDA’s safety communication update in November 2014 that encouraged the development of containment systems designed specifically for gynecologic surgery.
| FIGURE 1 PneumoLiner tissue containment device | FIGURE 2 PneumoLiner device placement | |
 |  |
Currently, the PneumoLiner is not yet available for purchase until Olympus, who will be the exclusive distributor, finalizes its formal training program rollout for ensuring safe and effective use of the device by gynecologic surgeons. As part of the FDA approval process, a training protocol was validated in a laboratory setting by surgeons with varying levels of experience in order to demonstrate that adherence to this process showed no damage to any of the containment systems used during the study.
As I look forward to the opportunity to learn more about this new containment system and potentially incorporate it into my surgical armamentarium, several questions immediately come to mind.
- Will hospitals, many of which pulled morcellators off their shelves in the wake of the FDA safety communication, be willing to embrace such innovative new containment technology and make it available to their surgeons?
- Will the litigious landscape painted by trial lawyers prevent surgeons from offering this option to their patients?
- Can surgeons undo much of the misinformation being propagated by the media as it relates to tissue extraction and the risk of encountering a malignancy?
I hope the answer to all of these questions is yes.
I do believe the pendulum can change directionAs surgeons it is our duty to evaluate potentially innovative solutions to the surgical challenges we face in clinical practice while maintaining an evidence-based approach. Most importantly, all of this must be balanced by sound clinical judgment that no technology can replace. With these guiding principles in mind, I believe that the pendulum regarding tissue extraction can change direction.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
On April 17, 2014, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) released a safety communication that discouraged the use of laparoscopic power morcellation during hysterectomy or myomectomy for the treatment of women with uterine fibroids. This recommendation was based mainly on the premise that fibroids may contain an underlying malignancy (in 1 in 350 women) that laparoscopic power morcellation could spread, thereby potentially worsening a cancer prognosis.1 Whether we liked it or not, minimally invasive gynecologic surgery as we knew it had changed forever on that fateful day.
During the last 2 years, the implications of that initial safety communication, along with its update in November of 2014,2 have been far reaching. From a health care industry perspective, the largest manufacturer of power morcellators, Johnson & Johnson, completely pulled its device out of the market within months of the initial FDA safety communication.3 Although several other companies remained in the market, health insurers such as Highmark and Aetna took the stance of not paying for the routine use of a power morcellator.4,5 Soon government officials became involved in the campaign against power morcellators and trial lawyers made this surgical device the latest “hot target.”6,7
The power morcellator’s absence impactFor clinicians, the narrative painted had moved the pendulum so far against power morcellation that it did not come as a surprise that practice patterns were significantly impacted. Harris and colleagues recently measured that impact by evaluating practice patterns and postoperative complications before and after the FDA safety communication on power morcellation. In their retrospective cohort study of patients within the Michigan Surgical Quality Collaborative, utilization of minimally invasive hysterectomy decreased and major surgical, nontransfusion complications and 30-day hospital readmission rates increased after release of the safety communication.8
Further support of this change in practice patterns was demonstrated in a recent survey conducted by the AAGL and American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Collaborative Ambulatory Research Network (ACOG CARN). In this survey study, Lum and colleagues were able to show that power morcellation use decreased among AAGL and ACOG CARN members after the FDA warnings, and rates of laparotomy increased.9
Critical to the discussion, yet apparently overlooked during the formulation of the initial FDA warning, was the potential clinical significance of the downstream impact of converting minimally invasive surgical cases to more invasive laparotomies. A decision-tree analysis published by Siedhoff and colleagues highlighted this point by predicting fewer overall deaths for laparoscopic hysterectomy with morcellation compared with abdominal hysterectomy.10 An ability to weigh the benefits and risks of procedure-related complications that are associated with laparotomy, including death, should have been part of the conversation from the beginning.
There is a silver lining emergingBased on this domino effect, it would seem that the damage done to minimally invasive gynecologic surgery over the past 2 years is irreparable. So is there any silver lining to the current state of affairs in tissue extraction? I would argue yes.
We have updated estimates for incidence of unsuspected leiomyosarcoma. First of all, discussions surrounding the FDA’s estimated 1 in 350 risk of encountering an unsuspected uterine sarcoma during the treatment of fibroids prompted a more critical evaluation of the scientific literature. In fact, Parker and colleagues, in a commentary published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, summarized very nicely the flawed methodology in the FDA’s determination of risk and in turn presented several updated calculations and studies that placed the prevalence somewhere in the range of 2 in 8,720 (0.023%) to 1 in 1,550 (0.064%).11
We are speaking with the FDA. Channels of communication with the FDA have since been developed and societies such as the AAGL were invited by the Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) at the FDA to serve in their Network of Experts. This Network of Experts is an FDA-vetted group of non−FDA affiliated scientists, clinicians, and engineers who provide the CDRH at the FDA with rapid access to scientific, engineering, and medical expertise when it is needed to supplement existing knowledge and expertise within the CDRH. By developing these lines of communication, the CDRH is able to broaden its exposure to scientific viewpoints without the influence of external, or non−FDA, policy advice or opinions.
We have been innovating our techniques. Clinicians also began to develop innovative techniques for tissue extraction that also included contained, in-bag power morcellation. Vargas and colleagues showed similar perioperative outcomes when comparing open power morcellation with contained power morcellation within an insufflated isolation bag. The mean operative time was prolonged by only 26 minutes with in-bag morcellation.12
Although the initial experience of surgeons involved various containment systems that were off label in their usage and not designed to be paired with a power morcellator, it allowed for the identification of potential limitations, such as the risk of leakage. Cohen and colleagues, in their published experience, demonstrated a 9.2% spillage in 76 patients who underwent contained power morcellation.13
Could a new FDA approval turn the tide?In an interesting turn of events, the FDA, on April 7, 2016, nearly 2 years after their initial warning about power morcellation, gave de novo classification clearance to Advanced Surgical Concepts for its PneumoLiner device.14 This first-of-a-kind medical device was developed for the purpose of completely containing fluid, cells, and tissue fragments during laparoscopic power morcellation, isolating uterine tissue that is not suspected to contain cancer (FIGURES 1 and 2). It is important to note, however, that it has not been shown to reduce the risk of spreading cancer during this procedure. Although a surprise to some, the approval of such a product is in keeping with the FDA’s safety communication update in November 2014 that encouraged the development of containment systems designed specifically for gynecologic surgery.
| FIGURE 1 PneumoLiner tissue containment device | FIGURE 2 PneumoLiner device placement | |
 |  |
Currently, the PneumoLiner is not yet available for purchase until Olympus, who will be the exclusive distributor, finalizes its formal training program rollout for ensuring safe and effective use of the device by gynecologic surgeons. As part of the FDA approval process, a training protocol was validated in a laboratory setting by surgeons with varying levels of experience in order to demonstrate that adherence to this process showed no damage to any of the containment systems used during the study.
As I look forward to the opportunity to learn more about this new containment system and potentially incorporate it into my surgical armamentarium, several questions immediately come to mind.
- Will hospitals, many of which pulled morcellators off their shelves in the wake of the FDA safety communication, be willing to embrace such innovative new containment technology and make it available to their surgeons?
- Will the litigious landscape painted by trial lawyers prevent surgeons from offering this option to their patients?
- Can surgeons undo much of the misinformation being propagated by the media as it relates to tissue extraction and the risk of encountering a malignancy?
I hope the answer to all of these questions is yes.
I do believe the pendulum can change directionAs surgeons it is our duty to evaluate potentially innovative solutions to the surgical challenges we face in clinical practice while maintaining an evidence-based approach. Most importantly, all of this must be balanced by sound clinical judgment that no technology can replace. With these guiding principles in mind, I believe that the pendulum regarding tissue extraction can change direction.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Laparoscopic uterine power morcellation in hysterectomy and myomectomy: FDA safety communication. April 17, 2014. http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/Safety/AlertsandNotices/ucm393576.htm. Updated November 24, 2014. Accessed May 24, 2016.
- Updated laparoscopic uterine power morcellation in hysterectomy and myomectomy: FDA safety communication. November 24, 2014. http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/Safety/AlertsandNotices/ucm424443.htm. Updated April 7, 2014. Accessed May 24, 2016.
- Kamp J, Levitz J. Johnson & Johnson pulls hysterectomy device from hospitals. The Wall Street Journal. July 30, 2014. http://www.wsj.com/articles/johnson-johnson-to-call-for-voluntary-return-of-morcellators-1406754350. Accessed May 25, 2016.
- Levitz J. Health insurer to stop covering uterine procedure. The Wall Street Journal. August 2, 2014. http://www.wsj.com/articles/health-insurer-to-stop-covering-uterine-procedure-1406999176. Accessed May 25, 2016.
- Kamp J. Aetna to stop covering routine use of power morcellator. The Wall Street Journal. May 5, 2015. http://www.wsj.com/articles/aetna-to-stop-covering-routine-use-of-power-morcellator-1430838666. Accessed May 25, 2016.
- Kamp J. Senators want more companies to pull surgical device from market. The Wall Street Journal. August 19, 2014. http://www.wsj.com/articles/senators-want-more-companies-to-pull-surgical-device-from-market-1408405349. Accessed May 25, 2016.
- Silverman E. Power morcellators are the latest hot target among trial lawyers. The Wall Street Journal. December 2, 2014. http://blogs.wsj.com/pharmalot/2014/12/02/power-morcellators-are-the-latest-hot-target-among-trial-lawyers/. Accessed May 25, 2016.
- Harris JA, Swenson CW, Uppal S, et al. Practice patterns and postoperative complications before and after the US Food and Drug Administration safety communication on power morcellation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;214(1):98.e1−e13.
- Lum DA, Sokol ER, Berek JS, et al. Impact of the 2014 Food and Drug Administration warnings against power morcellation. J Minim Invasiv Gynecol. 2016;23(4):548−556.
- Siedhoff M, Wheeler SB, Rutstein SE, et al. Laparoscopic hysterectomy with morcellation vs abdominal hysterectomy for presumed fibroid tumors in premenopausal women: a decision analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;212(5):591.e1−e8.
- Parker WH, Kaunitz AM, Pritts EA, et al; Leiomyoma Morcellation Review Group. US Food and Drug Administration’s guidance regarding morcellation of leiomyomas: well-intentioned, but is it harmful for women? Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127(1):18−22.
- Vargas MV, Cohen SL, Fuchs-Weizman N, et al. Open power morcellation versus contained power morcellation within an insufflated isolation bag: comparison of perioperative outcomes. J Minim Invasiv Gynecol. 2015;22(3):433−438.
- Cohen SL, Morris SN, Brown DN, et al. Contained tissue extraction using power morcellation: prospective evaluation of leakage parameters. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;214(2):257.e1−e6.
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA allows marketing of first-of-kind tissue containment system for use with certain laparoscopic power morcellators in select patients. April 7, 2016. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm494650.htm. Updated April 7, 2016. Accessed May 24, 2016.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Laparoscopic uterine power morcellation in hysterectomy and myomectomy: FDA safety communication. April 17, 2014. http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/Safety/AlertsandNotices/ucm393576.htm. Updated November 24, 2014. Accessed May 24, 2016.
- Updated laparoscopic uterine power morcellation in hysterectomy and myomectomy: FDA safety communication. November 24, 2014. http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/Safety/AlertsandNotices/ucm424443.htm. Updated April 7, 2014. Accessed May 24, 2016.
- Kamp J, Levitz J. Johnson & Johnson pulls hysterectomy device from hospitals. The Wall Street Journal. July 30, 2014. http://www.wsj.com/articles/johnson-johnson-to-call-for-voluntary-return-of-morcellators-1406754350. Accessed May 25, 2016.
- Levitz J. Health insurer to stop covering uterine procedure. The Wall Street Journal. August 2, 2014. http://www.wsj.com/articles/health-insurer-to-stop-covering-uterine-procedure-1406999176. Accessed May 25, 2016.
- Kamp J. Aetna to stop covering routine use of power morcellator. The Wall Street Journal. May 5, 2015. http://www.wsj.com/articles/aetna-to-stop-covering-routine-use-of-power-morcellator-1430838666. Accessed May 25, 2016.
- Kamp J. Senators want more companies to pull surgical device from market. The Wall Street Journal. August 19, 2014. http://www.wsj.com/articles/senators-want-more-companies-to-pull-surgical-device-from-market-1408405349. Accessed May 25, 2016.
- Silverman E. Power morcellators are the latest hot target among trial lawyers. The Wall Street Journal. December 2, 2014. http://blogs.wsj.com/pharmalot/2014/12/02/power-morcellators-are-the-latest-hot-target-among-trial-lawyers/. Accessed May 25, 2016.
- Harris JA, Swenson CW, Uppal S, et al. Practice patterns and postoperative complications before and after the US Food and Drug Administration safety communication on power morcellation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;214(1):98.e1−e13.
- Lum DA, Sokol ER, Berek JS, et al. Impact of the 2014 Food and Drug Administration warnings against power morcellation. J Minim Invasiv Gynecol. 2016;23(4):548−556.
- Siedhoff M, Wheeler SB, Rutstein SE, et al. Laparoscopic hysterectomy with morcellation vs abdominal hysterectomy for presumed fibroid tumors in premenopausal women: a decision analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;212(5):591.e1−e8.
- Parker WH, Kaunitz AM, Pritts EA, et al; Leiomyoma Morcellation Review Group. US Food and Drug Administration’s guidance regarding morcellation of leiomyomas: well-intentioned, but is it harmful for women? Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127(1):18−22.
- Vargas MV, Cohen SL, Fuchs-Weizman N, et al. Open power morcellation versus contained power morcellation within an insufflated isolation bag: comparison of perioperative outcomes. J Minim Invasiv Gynecol. 2015;22(3):433−438.
- Cohen SL, Morris SN, Brown DN, et al. Contained tissue extraction using power morcellation: prospective evaluation of leakage parameters. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;214(2):257.e1−e6.
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA allows marketing of first-of-kind tissue containment system for use with certain laparoscopic power morcellators in select patients. April 7, 2016. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm494650.htm. Updated April 7, 2016. Accessed May 24, 2016.