Renal impairment in severe falciparum malaria independently predicts a poor outcome in both adults and children.1 Prompt recognition of malaria-associated renal failure and immediate management with renal replacement therapy reduces mortality and can support the recovery of renal function.2-4 In addition, adjunctive treatment with acetaminophen has demonstrated improvement in the level of creatinine and reduced progression of kidney injury in a randomized, controlled trial of patients with severe falciparum malaria, particularly in patients with notable intravascular hemolysis.5 In this open-label, randomized controlled trial, 62 patients were randomly assigned to receive acetaminophen (n = 31) or no acetaminophen (n = 31).5 Antimalarial treatment was with IV artesunate, followed by artemether/lumefantrine. Median (IQR) reduction in creatinine after 72 hours was 23% (37, 18) in patients assigned to acetaminophen vs 14% (29, 0) in patients assigned to no acetaminophen (P = .04).5 Acetaminophen showed renoprotection without evidence of safety concerns in patients with severe falciparum malaria, especially those with prominent intravascular hemolysis.
Another study showed consistent findings in other malarial infections with prominent hemolysis, namely, Plasmodium knowlesi malaria. In the PACKNOW open-label, randomized controlled trial, 396 patients aged 12 to 96 years with knowlesi malaria of any severity were randomized to acetaminophen (500 mg or 1000 mg every 6 hours for 72 hours) vs no acetaminophen.6 All patients received artesunate and/or oral artemether-lumefantrine for malaria.6 No difference was seen overall in patients with acute kidney injury (AKI); however, in those with AKI and hemolysis, creatinine fell by a mean (SD) 34.5% (20.7) in the acetaminophen arm vs 25.9% (15.8) in the control arm (P = .04).6 Mixed-effects modeling demonstrated a benefit of acetaminophen at 72 hours (P = .04) and 1 week (P = .002) in patients with severe malaria and with AKI and hemolysis (P = .03 and P = .002, respectively).6
Earlier models suggest that the redox cycling of hemoproteins between ferric and ferryl states generates the radical species responsible for severe oxidative damage to the kidneys and subsequent renal impairment.7 Reduction of heme-ferryl radicals with therapeutic plasma concentrations of acetaminophen can inhibit this oxidative process.7 Rhabdomyolysis models treated with acetaminophen have shown reduced oxidative damage to the kidneys and improved renal functioning, supporting acetaminophen as a potential therapeutic option for disease processes involving hemoprotein-mediated oxidative injury.7 In this case report, we discuss the use of acetaminophen as a renoprotective treatment in a patient with renal impairment associated with severe falciparum malaria.
Case Presentation
A 50-year-old man with comorbidities, including hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and chronic kidney disease stage 2, with a baseline creatinine level of 1.4 mg/dL presented with severe falciparum malaria with renal impairment. About 7 months prior, the patient received treatment for his first known case of Plasmodium falciparum (P falciparum) infection. He again contracted P falciparum for a second time after traveling to a malaria-endemic country without taking prophylactic medication before travel.
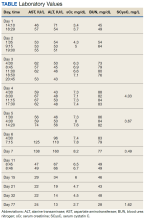
The patient reported fevers, chills, night sweats, and progressive fatigue. His vital signs recorded a fever of 38.9 ºC with tachycardia and relative hypotension. A thin blood smear revealed P falciparum with approximately 8.5% parasitemia. Laboratory tests confirmed hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia reflected by consistently decreased hemoglobin, hematocrit, haptoglobin, and platelets with elevated lactate dehydrogenase and hyperbilirubinemia. Initial renal function testing included an elevated creatinine level of 3.4 mg/dL and an elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level of 45 mg/dL.
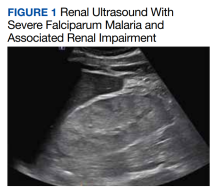
Creatinine and BUN levels peaked at 8.2 mg/dL and 88 mg/dL, respectively. Cystatin C levels ranged from 4.03 to 3.49 mg/dL before the patient left (against medical advice). Renal ultrasound demonstrated significantly increased renal length, echogenicity, abnormal cortical-medullary differentiation, and cortical thickening typically indicative of significant inflammation associated with acute tubular necrosis (Figure 1). Hepatic function testing included mild elevations in aminotransferases. The patient did not meet the criteria for rhabdomyolysis with a creatine kinase level of 25 U/L.