Results
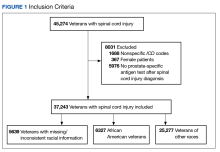
A total of 45,274 veterans were initially identified of which 367 females were excluded (Figure 1).
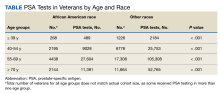
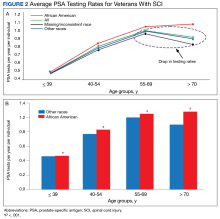
Moreover, 1688 male veterans were excluded for ICD codes that were less relevant, yielding 43,219 male veterans with relevant ICD codes. From this group, an additional 5976 were excluded because no PSA test was found after the SCI date. The racial makeup of the remaining 37,243 male veterans included 6327 African American patients, 25,277 of other races, and 5639 with missing/inconsistent race data. The included sample received care in ≥ 1 of 129 VAMCs. The final cohort yielded 261,125 PSA tests. The Table shows PSA tests categorized by age group and race.The PSA testing rate rose for veterans in the age groups ≤ 39, 40 to 54, and 55 to 69 years (Figure 2A).
The PSA testing rate dropped for the oldest age group (≥ 70 years), for the entire population, and the other race and missing/inconsistent race groups; however, PSA testing rates continued to rise in the African American group aged ≥ 70 years. For the entire population, average PSA testing rates in tests per year for the age groups were 0.46 (aged ≤ 39 years), 0.78 (aged 40-54 years), 1.0 (aged 55-69 years), and 0.91 (aged ≥ 70 years). However, PSA testing rates were significantly higher for the African American vs other races group at all ages (0.47 vs 0.46 tests per year, respectively, aged ≤ 39 years; 0.83 vs 0.77 tests per year, respectively, aged 40-54 years; 1.04 vs 1.00 tests per year, respectively, aged 55-69 years; and 1.08 vs 0.90 tests per year respectively, aged ≥ 70 years; P < .001) (Figure 2B).Of the cohort of 37,243 veterans, 28,396 (76.2%) had their post-SCI tests done at a single facility, 6770 (18.1%) at 2 locations, and 2077 (5.5%) at > 2 locations. Single-station group data were included in a subanalysis to determine the mean (SD) PSA testing rates, which for the 123 locations was 0.98 (0.36) tests per veteran per year (range, 0.2-3.0 tests per veteran per year).
Figure 3 shows a heat map of the US: each dot represents a specific VAMC and shows PSA testing rate variability between stations.To assess the impact of the 2012 USPSTF recommendations on PSA testing rates in veterans with SCI, mean PSA testing rates were calculated for 5 years before the recommendations (2007-2011) and compared with the average PSA testing rate for 5 years following the updated recommendations (2013-2017). The USPSTF updated its recommendation again in 2018 and acknowledged the potential benefit for PSA screening in certain patient populations.2,3 Surprisingly, and despite recommendations, the results show a significant increase in PSA testing rates in all age groups for all races (P < .001) (Figure 4).
For the entire population, the average PSA testing rates for 2007 to 2011 in tests per year were 0.39, 0.76, 1.03, and 0.89 for the ≤ 39 years, 40 to 54 years, 55 to 69 years, and ≥ 70 years age groups, respectively. Likewise, the average PSA testing rates for years 2013 to 2017 in tests per year were 0.75, 0.96, 1.13, and 0.98 for the ≤ 39 years, 40 to 54 years, 55 to 69 years, and ≥ 70 years age groups, respectively, with an increased rate of testing of 0.92, 0.26, 0.10, and 0.11, respectively, from years 2007-2011 to 2013-2017 (P < .001).