Patients planning plastic surgery traditionally were instructed to stop anticoagulants and antiplatelet medications during the perioperative period to avoid bleeding, which could result in flap loss, pain, skin necrosis, and blood transfusions. In the veteran patient population, anticoagulants are prescribed for the prevention of limb- and life-threatening embolic and thrombotic events.1-3 As of June 2021, > 332,000 veterans were prescribed direct oral anticoagulants.1
In 2015, the Malcom Randall Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MRVAMC) in Gainesville, Florida, Plastic Surgery Service began instructing patients planning elective hand surgery to continue their prescription anticoagulants and antiplatelets during the perioperative period. This decision was prompted by a patient who needed carpal tunnel release surgery and was prescribed coumadin for repeated thrombosis of his dialysis grafts. Hand surgery literature at the time suggested allowing patients to continue their anticoagulants and antiplatelets through the perioperative period to avoid life- and limb-threatening events and wide fluctuations in blood anticoagulant levels.4-6 The MRVAMC Plastic Surgery Service chose to accept the risk of perioperative bleeding after shared decision making with the patients rather than risk a cardiac stent obstruction, pulmonary embolism, or embolic stroke in the at-risk patients.
The objective of this study was to determine the postoperative bleeding complication rate over a 7.5-year period in the veteran patients who did not interrupt their prescription blood thinners. This would assist the MRVAMC Plastic Surgery Service with providing data-driven informed consent and determine whether this protocol should continue.
Methods
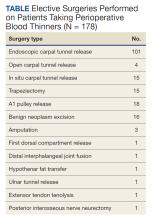
The North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System Research Committee and the University of Florida Institutional Review Board approved a retrospective chart review of elective hand cases performed by the MRVAMC Plastic Surgery Service from January 1, 2015, through June 30, 2022. Elective hand cases were identified based on the operation description and included nerve decompressions, tendon releases, trapeziectomy, small-joint fusion, neurectomy, elective amputations, and benign neoplasm removals (Table). Hand surgery included cubital tunnel releases (decompression of the ulnar nerve at the level of the elbow) because hand surgery fellowships, hand surgery training, and hand surgery practices traditionally include a high volume of cubital tunnel releases. We wanted this study to have real-world applications.
Patients’ histories and physicals were reviewed for prescription antithrombotics and for instructions not to interrupt these medications. Postoperative notes were reviewed for 30 days for evidence of postoperative bleeding complications.
The following prescription anticoagulants were included in the study: dabigatran, rivaroxaban, warfarin, edoxaban, and apixaban. In addition, the following prescription antiplatelets were included in the study: clopidogrel, aspirin/dipyridamole, prasugrel, cilostazol, and ticagrelor. Indications for the medications included a history of thromboembolic events, cardiac stents, cerebrovascular disease, atrial fibrillation, hypercoagulable states, and mechanical valves. Over-the-counter antiplatelet medications, such as aspirin and ibuprofen, were not included as a standalone medication for accuracy because patients taking those medications may not be captured in the electronic health record review.
Results
One hundred seventy-eight patients were identified for maintaining prescription blood thinners during their elective hand surgery. There was 1 major complication (0.6%) and 4 minor bleeding complications (2.2%). The major complication occurred when a patient had to return to surgery from the recovery room for emergent control of bleeding. The surgery was for an in situ cubital tunnel release. The patient, aged 48 years, was taking clopidogrel and aspirin and had a personal and family history of cardiovascular disease. The bleeding was controlled with bipolar cautery and Floseal, a topical haemostatic matrix made of bovine gelatin and human thrombin. The minor bleeding complications were treated in the clinic with compression, wound care, or expedited follow-up for reassurance. These included an in situ cubital tunnel release for a patient taking warfarin and aspirin, a digital inclusion cyst for a patient taking apixaban, an endoscopic carpal tunnel for a patient taking aspirin and clopidogrel, and an open carpal tunnel and ulnar tunnel release for a patient taking aspirin and clopidogrel. There were no thrombotic events during the study.
Discussion
Higher utilization of anticoagulation has been evidenced by a 30% increase in Medicare claims and a 277% increase in Medicaid anticoagulation claims between 2014 and 2019, driven by more prescriptions for direct oral anticoagulants such as apixaban and rivaroxaban.7 The MRVAMC Plastic Surgery Service began a protocol for managing perioperative anticoagulation in 2015 to avoid the risk of perioperative thrombotic events in veteran patients. Patients who choose elective hand surgery were instructed to continue their prescription blood thinners. Exceptions to this protocol were patients scheduled for a partial fasciectomy (for Dupuytren contracture) or cubital tunnel release with anterior ulnar nerve transposition. A hematoma would increase the risk for skin necrosis in the patients receiving a fasciectomy, resulting from the thin skin flaps and meticulous dissection to identify and protect the digital nerves. Worsening nerve dysfunction could result from hematoma compression and scarring in the ulnar nerve cases. If the risk of holding the blood thinner was felt to be unreasonably high, based on recommendations from the patients’ cardiologist or primary care doctor, we offered an in situ cubital tunnel release for the ulnar nerve patients.