For whole health and AFHS, conversations about what matters are anchored in the veteran’s goals and preferences, especially those facing a significant health change (ie, a new diagnosis or treatment decision). 5,7 Together, the veteran’s goals and priorities serve as the foundation for developing person-centered care plans that often go beyond conventional medical treatments to address the physical, mental, emotional, and social aspects of health.
SYSTEM-WIDE DIRECTIVE
The WHS enhances AFHS discussions about what matters to veterans by adding a system-level lens for conceptualizing health care delivery by leveraging the 3 components of WHS: the “pathway,” well-being programs, and whole health clinical care.
The Pathway
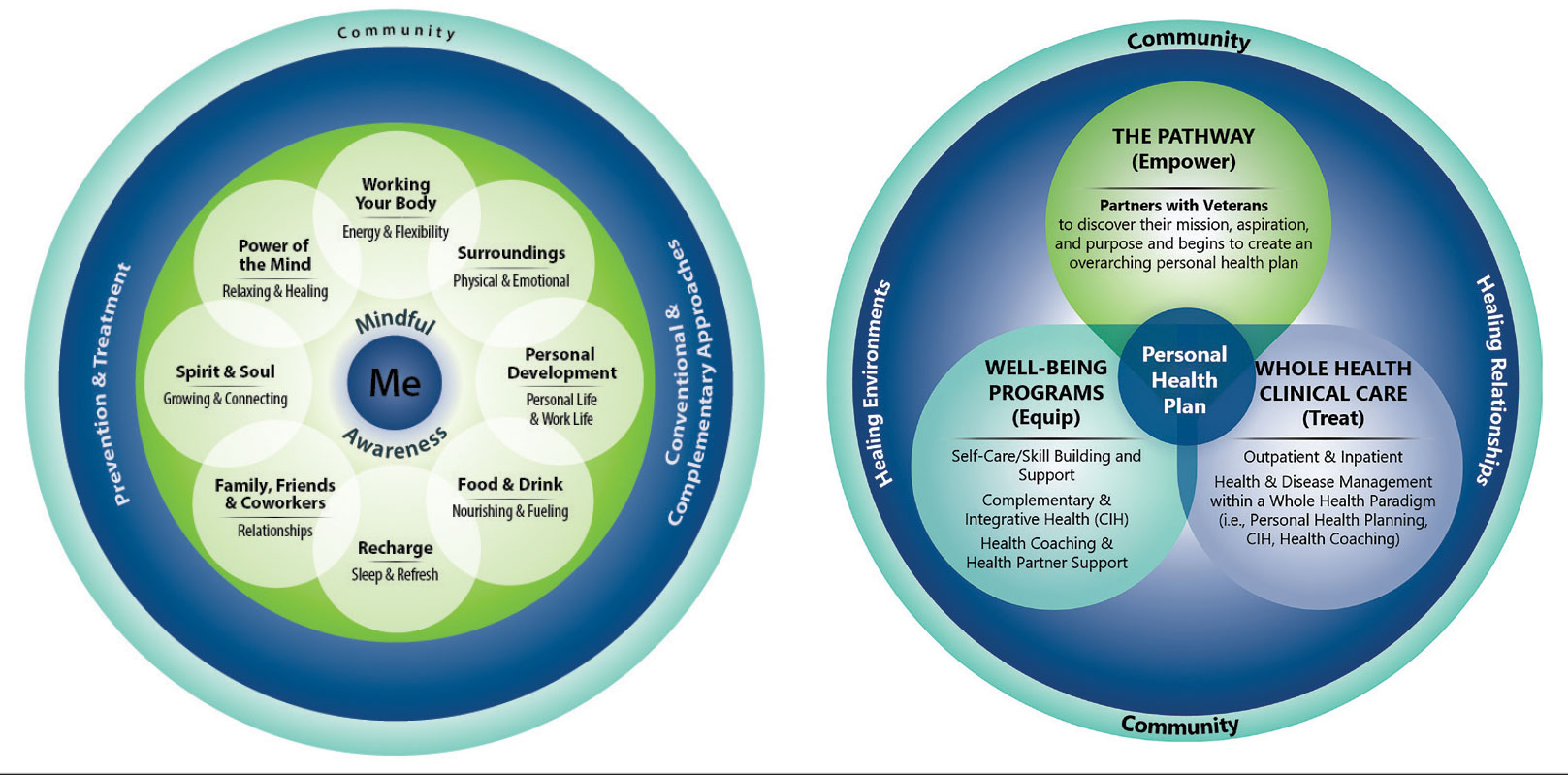
Discovering what matters, or the veteran’s “mission, aspiration, and purpose,” begins with the WHS pathway. When stepping into the pathway, veterans begin completing a personal health inventory, or “walking the circle of health,” which encourages self-reflection that focuses on components of their life that can influence health and well-being. 1,8 The circle of health offers a visual representation of the 4 most important aspects of health and well-being: First, “Me” at the center as an individual who is the expert on their life, values, goals, and priorities. Only the individual can know what really matters through mindful awareness and what works for their life. Second, self-care consists of 8 areas that impact health and wellbeing: working your body; surroundings; personal development; food and drink; recharge; family, friends, and coworkers; spirit and soul; and power of the mind. Third, professional care consists of prevention, conventional care, and complementary care. Finally, the community that supports the individual.
Well-Being Programs
VHA provides WHS programs that support veterans in building self-care skills and improving their quality of life, often through integrative care clinics that offer coaching and CIH therapies. For example, a veteran who prioritizes mobility when seeking care at an integrative care clinic will not only receive conventional medical treatment for their physical symptoms but may also be offered CIH therapies depending on their goals. The veteran may set a daily mobility goal with their care team that supports what matters, incorporating CIH approaches, such as yoga and tai chi into the care plan. 5 These holistic approaches for moving the body can help alleviate physical symptoms, reduce stress, improve mindful awareness, and provide opportunities for self-discovery and growth, thus promote overall well-being
Whole Health Clinical Care
AFHS and the 4Ms embody the clinical care component of the WHS. Because what matters is the driver of the 4Ms, every action taken by the care team supports wellbeing and quality of life by promoting independence, connection, and support, and addressing external factors, such as social determinants of health. At a minimum, well-being includes “functioning well: the experience of positive emotions such as happiness and contentment as well as the development of one’s potential, having some control over one’s life, having a sense of purpose, and experiencing positive relationships.” 9 From a system perspective, the VHA has begun to normalize focusing on what matters to veterans, using an interprofessional approach, one of the first steps to implementing AFHS.