As the programs expand, AFHS teams can learn from whole health well-being programs and increase the capacity for self-care in older veterans. Learning about the key elements included in the circle of health helps clinicians understand each veteran’s perceived strengths and weaknesses to support their self-care. From there, teams can act on the 4Ms and connect older veterans with the most appropriate programs and services at their facility, ensuring continuum of care.
DOCUMENTATION
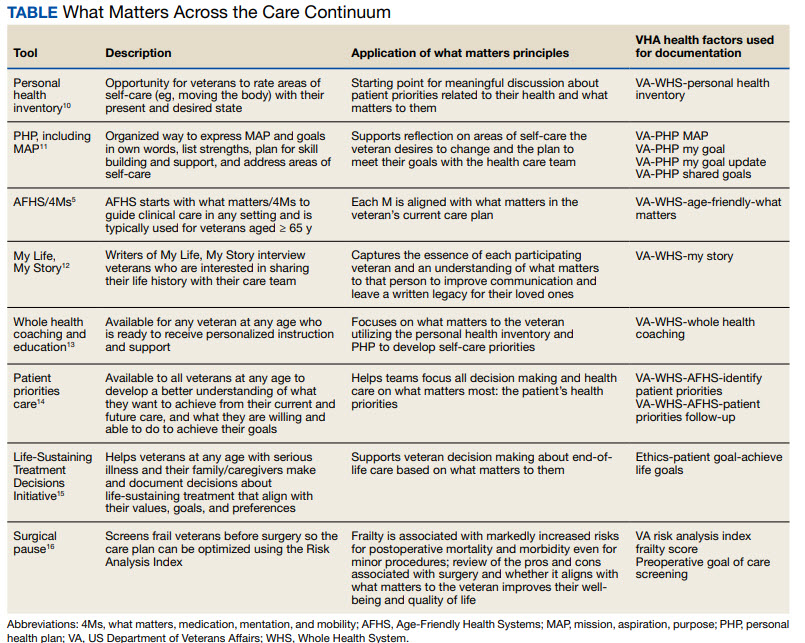
The VHA leverages several tools and evidence-based practices to assess and act on what matters for veterans of all ages (Table). 5,10-16 The VHA EHR and associated dashboards contain a wealth of information about whole health and AFHS implementation, scale up, and spread. A national AFHS 4Ms note template contains standardized data elements called health factors, which provide a mechanism for monitoring 4Ms care via its related dashboard. This template was developed by an interprofessional workgroup of VHA staff and underwent a thorough human factors engineering review and testing process prior to its release. Although teams continue to personalize care based on what matters to the veteran, data from the standardized 4Ms note template and dashboard provide a way to establish consistent, equitable care across multiple care settings. 17
Between January 2022 and December 2023, > 612,000 participants aged ≥ 65 years identified what matters to them through 1.35 million assessments. During that period, > 36,000 veterans aged ≥ 65 years participated in AFHS and had what matters conversations documented. A personalized health plan was completed by 585,270 veterans for a total of 1.1 million assessments.11 Whole health coaching has been documented for > 57,000 veterans with > 200,000 assessments completed. 13 In fiscal year 2023, a total of 1,802,131 veterans participated in whole health.
When teams share information about what matters to the veteran in a clinicianfacing format in the EHR, this helps ensure that the VHA honors veteran preferences throughout transitions of care and across all phases of health care. Although the EHR captures data on what matters, measurement of the overall impact on veteran and health system outcomes is essential. Further evaluation and ongoing education are needed to ensure clinicians are accurately and efficiently capturing the care provided by completing the appropriate EHR. Additional challenges include identifying ways to balance the documentation burden, while ensuring notes include valuable patient-centered information to guide care. EHR tools and templates have helped to unlock important insights on health care delivery in the VHA; however, health systems must consider how these clinical practices support the overall well-being of patients. How leaders empower frontline clinicians in any care setting to use these data to drive meaningful change is also important.
TRANSFORMING VHA CARE DELIVERY
In Achieving Whole Health: A New Approach for Veterans and the Nation , the National Academy of Science proposes a framework for the transformation of health care institutions to provide better whole health to veterans. 3 Transformation requires change in entire systems and leaders who mobilize people “for participation in the process of change, encouraging a sense of collective identity and collective efficacy, which in turn brings stronger feelings of self-worth and self-efficacy,” and an enhanced sense of meaningfulness in their work and lives. 18