Commentary
Meeting 21st Century Public Health Needs: Public Health Partnerships at the Uniformed Services University
The Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USU) was established by Congress in 1972 under the Uniformed...
Colin Smith and Paul Jung are officers in the Commissioned Corps of the US Public Health Service. Colin Smith is an Internal Medicine/ Psychiatry resident in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences and Department of Medicine at Duke University Hospital in Durham, North Carolina.
Correspondence: Colin Smith (colin.smith@ duke.edu)
Author Disclosures
The authors report no actual or potential conflicts of interest with regard to this article.
Disclaimer
The opinions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of Federal Practitioner, Frontline Medical Communications Inc., the US Government, or any of its agencies. This article may discuss unlabeled or investigational use of certain drugs. Please review the complete prescribing information for specific drugs or drug combinations—including indications, contraindications, warnings, and adverse effects—before administering pharmacologic therapy to patients.
Millennials, defined as those born between 1981 and 1996, currently comprise 15% of all active physicians in the US.1,2 A recent survey found that nearly 4 of 5 US millennial physicians have a desire for cross-sectional work in areas beyond patient care, such as academic research, health care consulting, entrepreneurship, and health care administration.3
For employers and educators, a better understanding of these preferences, through consideration of the unique education and skill set of the millennial physician workforce, may lead to more effective recruitment of young physicians and improved health systems, avoiding a mismatch between health care provider skills and available jobs that can be costly for both employers and employees.4
This article describes how US millennial physicians are choosing to cross-train (obtaining multiple degrees and/or completing combined medical residency training) throughout undergraduate, medical, and graduate medical education. We also outline ways in which the current physician marketplace may not match the skills of this population and suggest some ways that health care organizations could capitalize on this trend toward more cross-trained personnel in order to effectively recruit and retain the next generation of physicians.
The number of interdisciplinary undergraduate majors increased by almost 250% from 1975 to 2000.5 In 2010, nearly 20% of US college students graduated with 2 majors, representing a 70% increase in double majors between 2001 and 2011.6,7 One emerging category of interdisciplinary majors in US colleges is health humanities programs, which have quadrupled since 2000.8
Medical school applicants and matriculants reflect this trend. Whereas in 1994, only 19% of applicants to medical school held nonscience degrees, about one-third of applicants now hold such degrees.9,10 We have found no aggregated data on double majors entering US medical schools, but public class profiles suggest that medical school matriculants mirror their undergraduate counterparts in their tendency to hold double majors. In 2016, for example, 15% of the incoming class at the University of Michigan Medical School was composed of double majors, increasing to over 25% in 2017.11
Early dual-degree programs in undergraduate medical training were reserved for MD/PhD programs.12 Most US MD/PhD programs (90 out of 151) now offer doctorates in social sciences, humanities, or other nontraditional fields of graduate medical study, reflecting a shift in interests of those seeking dual-degree training in undergraduate medical education.13 While only 3 MD/PhD programs in the 1970s included trainees in the social sciences, 17 such programs exist today.14
Interest in dual-degree programs offering master’s level study has also increased over the past decade. In 2017, 87 medical schools offered programs for students to pursue a master of public health (MPH) and 41 offered master of science degrees in various fields, up from 52 and 37 institutions, respectively in 2006.15 The number of schools offering combined training in nonscience fields has also grown, with 63 institutions now offering a master of business administration (MBA), nearly double the number offered in 2006.15 At some institutions more than 20% of students are earning a master’s degree or doctorate in addition to their MD degree.16
The Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USU) was established by Congress in 1972 under the Uniformed...

Challenges facing rural recruitment include a lack of small-town residencies, the preferences of spouses, and the isolation that comes with...
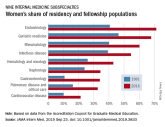
Women were more likely than men to report that they had never considered cardiology as a career choice.
Chief medical residents from the 3 affiliate residency training programs at VA Boston
Healthcare System developed a mission statement for the...
