User login
Transitioning patients with developmental disabilities to adult care
Some adults who have an intellectual or other developmental disability (IDD) require extensive subspecialty care; many, however, depend primarily on their family physician for the bulk of their health care. With that reliance in mind, this article provides (1) an overview of important services that family physicians can provide for their adult patients with IDD and (2) pragmatic clinical suggestions for tailoring that care. Note: We highlight only some high-impact areas of clinical focus; refer to the 2018 Canadian consensus guidelines for a comprehensive approach to optimizing primary care for this population.1
CASE
Laura S, a 24-year-old woman with Down syndrome, is visiting your clinic with her mother to establish care. Ms. S has several medical comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, repaired congenital heart disease, schizoaffective disorder, and hypothyroidism. She is under the care of multiple specialists, including a cardiologist and an endocrinologist. Her medications include the atypical antipsychotic risperidone, which was prescribed for her through the services of a community mental health center.
Ms. S is due for multiple preventive health screenings. She indicates that she feels nervous today talking about these screenings with a new physician.
First step in care: Proficiency in the lexicon of IDD
Three core concepts of IDD are impairment, disability, and handicap. According to the World Health Organization2:
- impairment “is any loss or abnormality of psychological, physiological, or anatomical structure or function.”
- disability “is any restriction or lack (resulting from an impairment) of ability to perform an activity in the manner or within the range considered normal for a human being.”
- handicap therefore “represents socialization of an impairment or disability, and as such it reflects the consequences for the individual—cultural, social, economic, and environmental—that stem from the presence of impairment and disability.”
Essential transition: Pediatric to adult health care
Health care transition (HCT) is the planned process of transferring care from a pediatric to an adult-based health care setting,3 comprising 3 phases:
- preparation
- transfer from pediatric to adult care
- integration into adult-based care.
Two critical components of a smooth HCT include initiating the transition early in adolescence and providing transition-support resources, which are often lacking, even in large, integrated health systems.4 Got Transition, created by the National Alliance to Advance Adolescent Health, outlines core elements of an organized HCT process (www.gottransition.org) specific to young adults with IDD, including young adults with autism spectrum disorder.5,6
Even young people who are served by a family physician and who intend to remain in that family practice as they age into adulthood require HCT services that include6:
- assessment of readiness to transition to adult care
- update of the medical history
- assessment and promotion of self-care skills
- consent discussions and optimized participation in decision-making
- transition of specialty care from pediatric to adult specialists.
Continue to: For an ideal HCT...
For an ideal HCT, full engagement of the patient, the medical home (physicians, nursing staff, and care coordinators), and the patient’s family (including the primary caregiver or guardian) is critical. In addition to preventive care visits and management of chronic disease, additional domains that require explicit attention in transitioning young people with IDD include health insurance, transportation, employment, and postsecondary education.
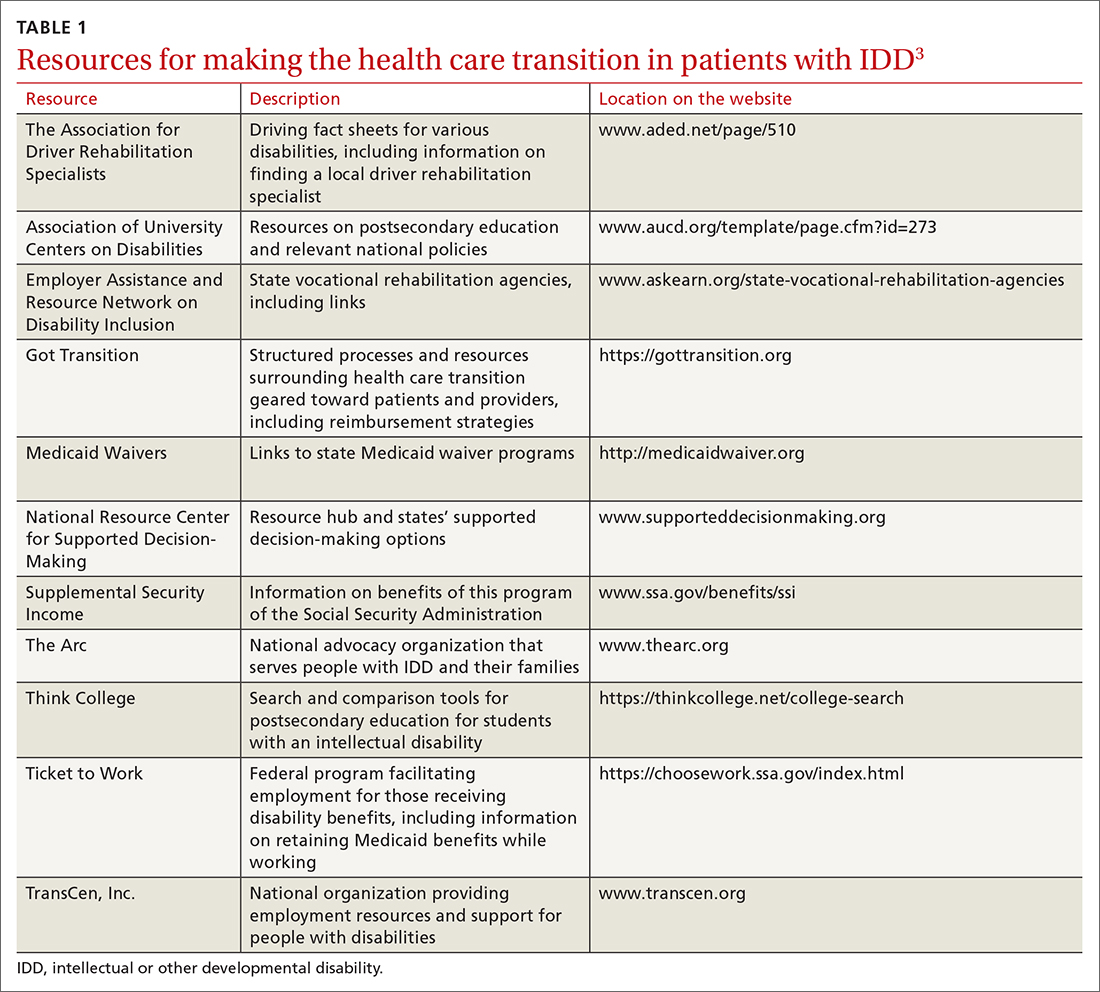
Young people who have special health care needs and receive high-quality HCT demonstrate improvements in adherence to care, disease-specific measures, quality of life, self-care skills, satisfaction with care, and health care utilization.7TABLE 13 lists resources identified by Berens and colleagues that are helpful in facilitating the transition.
Teach and practice disability etiquette
Societal prejudice harms people with IDD—leading to self-deprecation, alienation from the larger community, and isolation from others with IDD.8 To promote acceptance and inclusivity in residential communities, the workplace, recreational venues, and clinical settings, disability etiquette should be utilized—a set of guidelines on how to interact with patients with IDD. These include speaking to the patient directly, using clear language in an adult voice, and avoiding stereotypes about people with disabilities.9 The entire health care team, including all front-facing staff (receptionists and care and financial coordinators) and clinical staff (physicians, nurses, medical assistants), need to be educated in, and practice, disability etiquette.
Preparing for in-person visits. Pre-visit preparation, ideally by means of dialogue between health care staff and the patient or caregiver (or both), typically by telephone and in advance of the scheduled visit, is often critical for a successful first face-to-face encounter. (See “Pre-visit telephone questionnaire and script for a new adult patient with IDD,” page 287, which we developed for use in our office practice.) Outcomes of the pre-visit preparation should include identifying:
- words or actions that can trigger anxiety or panic
- de-escalation techniques, such as specific calming words and actions
- strategies for optimal communication, physical access, and physical examination.
SIDEBAR
Pre-visit telephone questionnaire and script for a new adult patient with IDD
Introduction
Hello! My name is ______________. I’m a nurse [or medical assistant] from [name of practice]. I understand that [name of patient] is coming to our office for an appointment on [date and time]. I am calling to prepare our health care team to make this first appointment successful for [name of patient] and you.
- How would [name of patient] prefer to be called?
- Who will be accompanying [name of patient] to the appointment? What parts of the appointment will that person remain for?
Describe what to expect, what the patient or caregiver should bring to the appointment, and how long the appointment will last.
- What makes [name of patient] anxious or fearful so that we might avoid doing that? Should we avoid bringing up certain topics? Should we avoid performing any procedures that are customary during a first appointment?
- Does [name of patient] have sensitivities—to light, sound, touch, etc—that we should be aware of?
Offer to have a room ready upon the patient’s arrival if remaining in the waiting area would cause too much anxiety.
- What helps calm [name of patient]? Are there some topics that put [name of patient] at ease?
- How does [name of patient] best communicate?
- Is there anything else the health care team might do to prepare for the appointment?
- Does [name of patient] need personal protective equipment, a wheelchair, oxygen, or other medical equipment upon arrival?
- What would make for a successful first appointment?
- What strategies or techniques have [name of patient’s] providers used in the past that have helped make health care visits successful?
- Is there anything else you want me to know that we haven’t talked about?
- Would it be helpful if I talked with [name of patient] now about their upcoming appointment?
Initial appointments should focus on building trust and rapport with the health care team and desensitizing the patient to the clinical environment.10 Examination techniques used with pediatric patients can be applied to this population: for example, demonstrating an examination maneuver first on the parent or caregiver; beginning the examination with the least invasive or anxiety-provoking components; and stating what you plan to do next—before you do it.
Continue to: Systematic health checks provide great value
Systematic health checks provide great value
A health check is a systematic and comprehensive health assessment that is provided annually to adults with IDD, and includes:
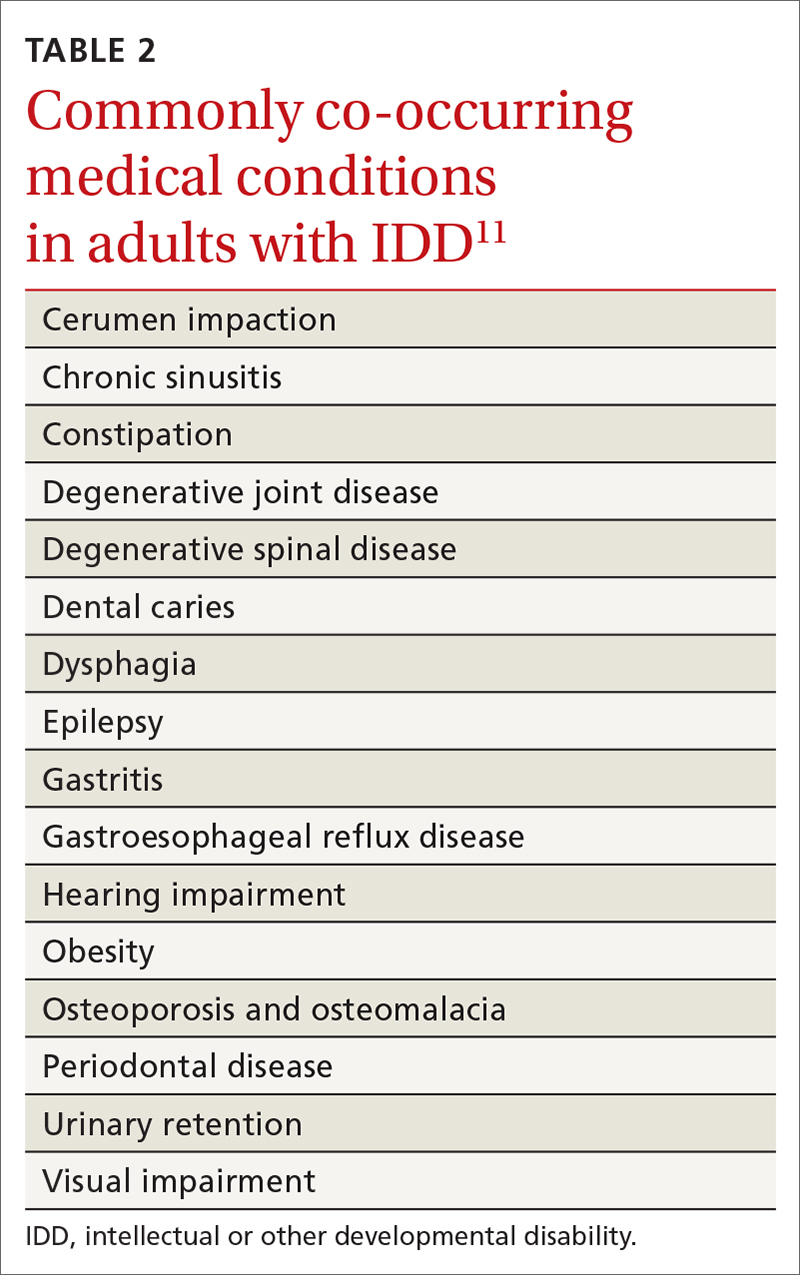
- specific review of signs and symptoms of health conditions that often co-occur in adults with IDD (TABLE 2Calibri11)
- screening for changes in adaptive functioning and secondary disability
- lifestyle counseling
- medication review and counseling
- immunization update
- discussion of caregiver concerns.
Regarding the last point: Many caregivers are the aging parents of the adult patient with IDD—people who have their own emerging health and support needs. You should initiate conversations about advanced planning for the needs of patients, which often involves engaging siblings and other family members to assume a greater role in caregiving.12
Benefits of the health check. A systematic review of 38 studies, comprising more than 5000 patients with IDD, found that health checks increased the detection of serious conditions, improved screening for sensory impairments, and increased the immunization rate.13 Although many patients with IDD generally understand the need for a periodic health examination, you can enhance their experience by better explaining the rationale for the health check; scheduling sufficient time for the appointment, based on the individual clinical situation; and discussing the value of laboratory testing and referrals to specialists.14
Tailoring preventive care
Many of the preventive services recommendations typically utilized by family physicians, such as guidelines from the US Preventive Services Task Force, have been developed for the general population at average risk of conditions of interest.15 Adults with IDD, depending on the cause of their developmental disability and their behavioral risk profile, might be at significantly higher (or lower) risk of cancer, heart disease, or other conditions than the general population. To address these differences, preventive care guidelines tailored to patients with certain developmental disabilities have been created, including guidelines specific to adults with Down syndrome, fragile X syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, Smith-Magenis syndrome, and 22q11.2 deletion (DiGeorge) syndrome.16
Clarifying the molecular genetic etiology of many developmental disabilities has led to more precise understandings about physical and behavioral health issues associated with specific developmental disabilities. For that reason, patients without a known cause for their IDD might benefit from referral to a geneticist—even in early or middle adulthood. Variables generally associated with a higher likelihood of an abnormal genetic test result include17:
- a family history of developmental disability
- a congenital malformation or dysmorphic features
- a dual diagnosis of developmental disability and co-occurring mental illness
- hypotonia
- severe or profound IDD.
Continue to: Successful implementation of preventive health screening tests...
Successful implementation of preventive health screening tests often requires ingenuity and the collective creativity of the patient, family members, staff, and family physician to allay fears and anxieties. Examples: Women who have been advised to undergo screening mammography might feel less anxious by undergoing tandem screening with their sister or mother, and colorectal cancer screening might be more easily accomplished using a fecal DNA test rather than by colonoscopy. Procedural desensitization strategies and preventive care instructional materials targeting people with IDD are posted on YouTube (for example, the “DD CARES Best Practices” series [see www.youtube.com/watch?v=EPJy4zvg4io]) and other websites.
Management of chronic disease
Evidence of health disparities in patients with IDD includes suboptimal management of chronic diseases, such as diabetes18 and hypertension,19 despite contact with a primary care physician. Nonadherence to a medication regimen might be more common in patients who live with their family or in a residential setting where there is a lower degree of supervision—that is, compared to a residence that maintains 24-hour staffing with daily nursing care and supervision. For a patient who is not so closely supervised, reviewing the medication refill history with the pharmacy, or using the so-called brown-bag technique of counting pill bottles brought to appointments, can ensure medication adherence.
CASE
As you interview Ms. S, you note that she is shy, avoids eye contact, and appears generally anxious. You calm her by noticing and complimenting her jewelry and fingernail polish. Ms. S smiles and talks about her favorite polish colors.
Her mother reports that, when Ms. S is stressed, she talks to herself alone in her bedroom. However, you do not observe evidence of schizoaffective disorder, and begin to wonder whether she needs to be taking risperidone.
Essentials of mental health care
It is estimated that one-third of adults with IDD have significant mental and behavioral health care needs.20 Patients with IDD suffer the same psychiatric disorders as the general population; some also engage in problematic behaviors, such as self-injurious actions, physical or verbal aggression (or both), property destruction, and resistance to caregiving assistance.
Continue to: Mental and behavioral health problems...
Mental and behavioral health problems can have a profound impact on the quality of life of patients with IDD, their peers, and their family and other caregivers. If untreated, these problems can lead to premature institutionalization, loss of employment or desired program participation, fractured social relationships, and caregiver withdrawal and burnout.
Initial evaluation of suspected mental and behavioral health problems begins with careful assessment for medical conditions that might be causing pain and distress, stereotypies, and other problematic behaviors. Common sources of pain and discomfort include dental and other oral disease, dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastritis, constipation, allergic disease, headache, musculoskeletal pathology, lower urinary tract disease, and gynecologic disorders.11 Identification and optimal treatment of medical conditions might not eliminate problematic behaviors but often decrease their frequency and intensity.
Psychoactive medications are prescribed for many patients with IDD. Many have behavioral adverse effects, such as akathisia, aggression, and disinhibition—leading to a prescribing cascade of psychoactive medication polypharmacy and escalating dosages.21 Antipsychotic medications are often initiated without a careful diagnosis, explicit outcome targets, or adequate clinical monitoring for effectiveness; in addition, they often lead to insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and massive weight gain.21 Even a family physician who is not the prescriber can perform an important advocacy role by critically reviewing psychoactive medications, documenting adverse effects, insisting on a clear therapeutic target, and calling for discontinuation of medications that appear to be ineffective.
Evaluation of mental and behavioral health problems requires a developmental perspective to interpret specific, observable behaviors with a proper clinical lens. For example, many patients with IDD engage in self-talk (soliloquizing) as a means of processing the world around them. This practice might escalate during a time of physical or psychological stress, and the unwary clinician might misinterpret this behavior as psychotic, leading to inappropriate prescribing of antipsychotic medication. Other psychotoform behaviors that, superficially, mimic but are typically not truly psychotic, include talk with or about imaginary friends and repetitive retelling of sometimes elaborate or grandiose tales or assertions. The failure of clinicians to recognize developmentally determined expressions of distress often leads to a misdiagnosis of schizophrenia or other psychotic illness and, consequently, inappropriate psychopharmacotherapy.
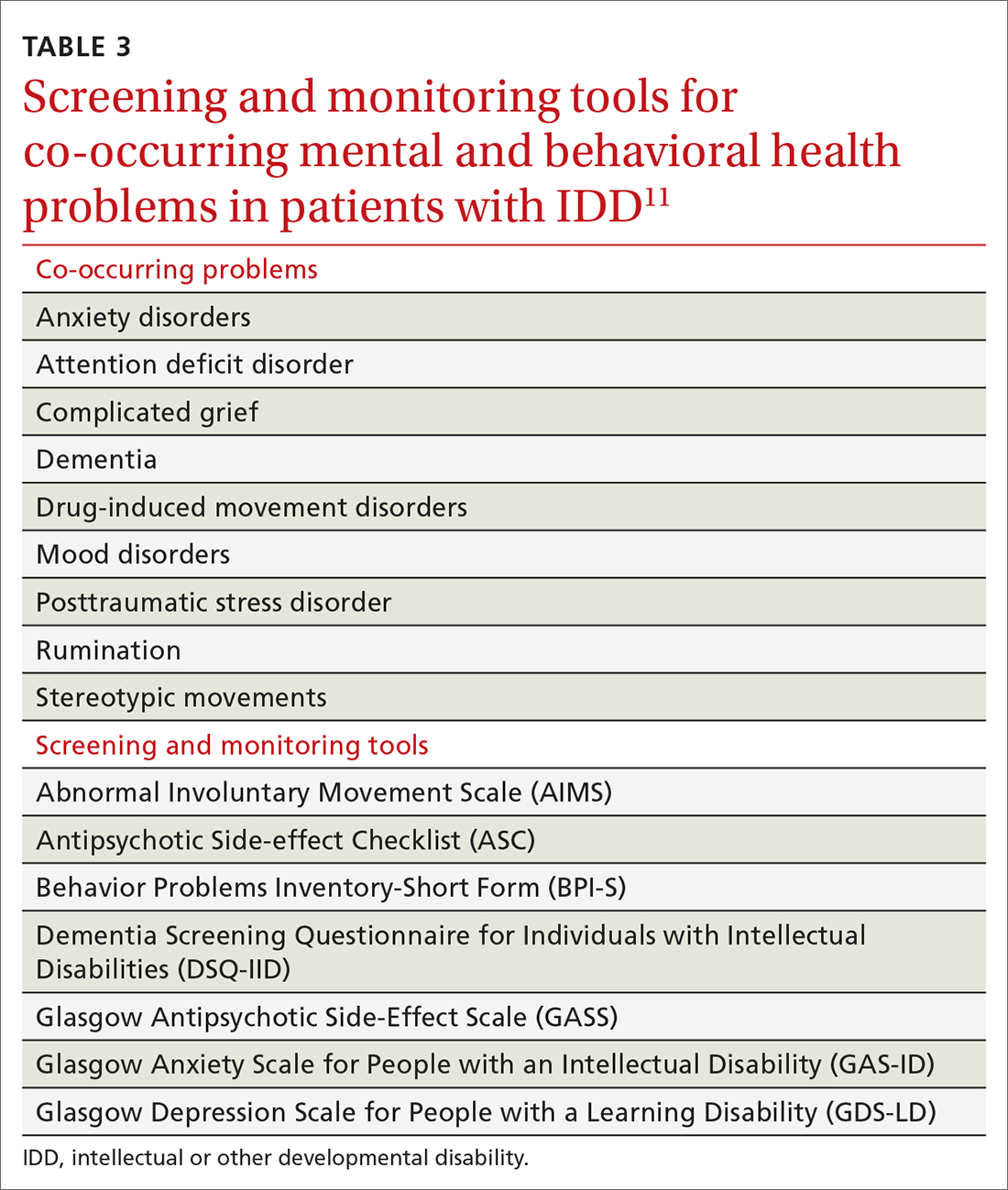
Family physicians, familiar with the use of psychiatric scales for diagnosis and treatment monitoring, should use similar scales that have been developed specifically for patients with IDD (TABLE 311). In addition, a psychiatric diagnosis manual, the Diagnostic Manual—Intellectual Disability 2, specific to people with IDD (and analogous to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition) provides modification of diagnostic criteria to account for patients who have difficulty articulating their internal emotional state and inner thoughts.22
Continue to: Problematic behaviors
Problematic behaviors that are not features of a bona fide psychiatric disorder are often best understood through functional behavioral analysis, which examines antecedents and consequences of problematic behaviors and identifies their predictable outcomes, such as gaining attention, avoiding a task, or securing a desired item. Rather than being given a prescription for psychoactive medication, many adult patients with IDD and problematic behaviors might be best served by having you order consultation with a certified behavior analyst. The analyst will conduct an evaluation and, along with family or residential staff and the patient, craft a behavioral support plan to address core drivers of the undesired behavior. Behavioral support plans might be enriched by multidisciplinary input from a speech and language pathologist, habilitation professionals, occupational and physical therapists, a neuropsychologist, and others.23
Resources to help you address the physical, mental, and behavioral health problems of these patients are available online through Vanderbilt Kennedy Center’s “Toolkit for primary care providers” (https://iddtoolkit.vkcsites.org).
CASE
During your examination, you review Ms. S’s vital signs, including body mass index (BMI). You calculate that she is morbidly obese—BMI, 37—in the setting of a known comorbidity, diabetes.
Ms. S tells you that she is interested in having a healthy lifestyle, but feels frustrated because she does not know how to make the necessary changes. You discuss with her how some medications, including risperidone, can promote weight gain, and that it is important for her mental health provider to carefully reassess whether she needs to continue the drug.
Weight management in a patient population that tends to be sedentary
Patients with IDD are more likely to live a sedentary lifestyle. Compared to adults who do not have IDD, adults with IDD—especially women and patients with Down syndrome—are reported to have a higher prevalence of obesity.24
Continue to: As in the general population...
As in the general population, the greatest success in weight management involves multidisciplinary treatment, including nutritional support, physical activity, behavioral changes, and close follow-up. The importance of such an approach was borne out by the findings of a randomized controlled trial in which a multicomponent intervention—an energy-reduced diet, physical activity, and behavioral sessions—delivered to participants or their caregivers during monthly visits produced clinically meaningful 6-month weight loss.25 Health-promoting behavioral interventions that rely on a dyadic strategy, such as peer health coaches (ie, people with IDD who have been trained as a health coach) or mentors (IDD staff trained as a health coach), might be more successful at changing health behaviors among patients with IDD than traditional office-based, individual patient education and counseling.26
Similarly, undesired weight loss demands careful evaluation and management because such loss can reflect a medically significant condition, such as gastroesophageal reflux, constipation, dysphagia, neglect, and cancer.27
Boosting the amount and effectiveness of physical activity
Young people with IDD participate in physical activity less often than their neurotypical peers; as a result, they tend to be less fit and have a higher prevalence of obesity.28 Based on a meta-analysis, interventions that focus on sport and movement skills training, such as soccer, basketball, and ball-throwing programs, might be more effective than general physical activity programs.28 In addition to year-round sports training and athletic competitions, Special Olympics conducts vital health screenings of athletes and supports community-based initiatives that address bias against patients with IDD, promote inclusion, and foster social relationships (www.specialolympics.org/our-work/inclusive-health?locale=en).
Emphasize regular activity. In adulthood, fewer than 10% of patients with IDD exercise regularly.21 According to the second edition of Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans,29 “all adults, with or without a disability, should get at least 150 minutes of aerobic physical activity a week. Activities can be broken down into smaller amounts, such as about 25 minutes a day every day.”30 Supplementation with muscle-strengthening activities (eg, yoga, weight training, and resistance-band training) provides further health benefit, such as improvement in posture and prevention of future injury.31 An ideal exercise program proposed by Tyler and Baker is based on a daily, “3-2-1” schedule (ie, of every hour of activity, 30 minutes should be of aerobic exercise; 20 minutes, of strength building; and 10 minutes, of flexibility).11 By participating in any type of physical activity, there is potential for considerable health benefit in reducing psychosocial stressors, improving mental health, counteracting metabolic syndromes, and, ultimately, reducing morbidity and mortality related to physical inactivity.
CASE
With permission from Ms. S, you send your progress notes by fax to her mental health provider at the community mental health center and request a call to discuss her case—in particular, to examine potential alternatives to risperidone. With Ms. S’s input, you also co-create an exercise prescription that includes a daily 20-minute walking program with her mother.
At the follow-up visit that is scheduled in 3 months, you anticipate adding a resistance component and balance activity to the exercise prescription to enrich Ms. S’s physical activity regimen.
CORRESPONDENCE
Carl V. Tyler Jr., MD, 14601 Detroit Avenue, Lakewood, OH, 44107; catyle@ccf.org
1. Sullivan WF, Diepstra H, Heng J, et al. Primary care of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: 2018 Canadian consensus guidelines. Can Fam Physician. 2018;64:254-279.
2. World Health Organization. International Classification of Impairments, Disabilities, and Handicaps: A Manual of Classification Relating to the Consequences of Disease. May 1980. Accessed May 27, 2021. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/41003/9241541261_eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
3. Berens J, Wozow C, Peacock C. Transition to adult care. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2020;31:159-170. doi:10.1016/j.pmr.2019.09.004
4. American Academy of Pediatrics; American Academy of Family Physicians; American College of Physicians; Transitions Clinical Report Authoring Group; Cooley WC, Sagerman PJ. Supporting the health care transition from adolescence to adulthood in the medical home. Pediatrics. 2011;128:182-200. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-0969
5. Dressler PB, Nguyen TK, Moody EJ, et al. Use of transition resources by primary care providers for youth with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2018;56:56-68. doi:10.1352/1934-9556-56.1.56
6. The National Alliance to Advance Adolescent Health. Six Core Elements of Health Care Transition.™ Got Transition website. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.gottransition.org
7. Schmidt A, Ilango SM, McManus MA, et al. Outcomes of pediatric to adult health care transition interventions: an updated systematic review. J Pediatr Nurs. 2020; 51:92-107. doi: 10.1016/j.pedn.2020.01.002
8. Keith JM, Bennetto L, Rogge RD. The relationship between contact and attitudes: reducing prejudice toward individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Res Dev Disabil. 2015;47:14-26. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2015.07.032
9. United Spinal Association. Disability Etiquette: Tips on Interacting With People With Disabilities. 2015. Accessed June 9, 2021. www.unitedspinal.org/pdf/DisabilityEtiquette.pdf
10. Nathawad R, Hanks C. Optimizing the office visit for adolescents with special health care needs. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2017;47:182-189. doi:10.1016/j.cppeds.2017.07.002
11. Tyler CV, Baker S. Intellectual Disabilities at Your Fingertips: A Health Care Resource. High Tide Press; 2009.
12. Williamson HJ, Perkins EA. Family caregivers of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: outcomes associated with U.S. services and supports. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2014;52:147-159. doi: 10.1352/1934-9556-52.2.147
13. Robertson J, Hatton C, Emerson E, et al. The impact of health checks for people with intellectual disabilities: an updated systematic review of evidence. Res Dev Disabil. 2014;35:2450-2462. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2014.06.007
14. Perry J, Felce D, Kerr M, et al. Contact with primary care: the experience of people with intellectual disabilities. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2014;27:200-211. doi: 10.1111/jar.12072
15. Recommendation topics. United States Preventive Services Task Force website. 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org
16. Developmental Disabilities Primary Care Initiative. Tools for the Primary Care of People with Developmental Disabilities. 1st ed. MUMS Guideline Clearinghouse; 2011.
17. Jang W, Kim Y, Han E, et al. Chromosomal microarray analysis as a first-tier clinical diagnostic test in patients with developmental delay/intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorders, and multiple congenital anomalies: a prospective multicenter study in Korea. Ann Lab Med. 2019;39:299-310. doi:10.3343/alm.2019.39.3.299
18. Shireman TI, Reichard A, Nazir N, et al. Quality of diabetes care for adults with developmental disabilities. Disabil Health J. 2010;3:179-185. doi:10.1016/j.dhjo.2009.10.004
19. Cyrus AC, Royer J, Carroll DD, et al. Anti-hypertensive medication use and actors related to adherence among adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Am J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2019;124:248-262. doi:10.1352/1944-7558-124.3.248
20. IDD/MI diagnosis. National Association for the Dually Diagnosed (NADD) website. 2019. Accessed May 27, 2021. https://thenadd.org/idd-mi-diagnosis
21. Matson JL, Mayville EA, Bielecki J, et al. Reliability of the Matson Evaluation of Drug Side Effects Scale (MEDS). Res Dev Disabil. 1998;19:501-506. doi:10.1016/s0891-4222(98)00021-3
22. Fletcher R, Barnhill J, Cooper SA. (2017). Diagnostic Manual-Intellectual Disability: A Textbook of Diagnosis of Mental Disorders in Persons with Intellectual Disability. 2nd ed. National Association for the Dually Diagnosed (NADD); 2017.
23. Marrus N, Hall L. Intellectual disability and language disorder. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2017;26:539-554. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2017.03.001
24. Rimmer JH, Yamaki K. Obesity and intellectual disability. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2006;12;22-7. doi: 10.1002/mrdd.20091
25. Ptomey LT, Saunders RR, Saunders M, et al. Weight management in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: a randomized controlled trial of two dietary approaches. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2018;31(suppl 1):82-96. doi:10.1111/jar.12348
26. Marks B, Sisirak J, Magallanes R, et al. Effectiveness of a HealthMessages peer-to-peer program for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2019;57:242-258. doi:10.1352/1934-9556-57.3.242
27. Escudé C. Clinical Pearls in IDD Health care. HRS, Inc; 2020.
28. Kapsal NJ, Dicke T, Morin AJS, et al. Effects of physical activity on the physical and psychosocial health of youth with intellectual disabilities: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Phys Act Health. 2019;16:1187-1195. doi:10.1123/jpah.2018-0675
29. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. 2nd ed. US Department of Health and Human Services; 2018. Accessed May 29, 2021. https://health.gov/sites/default/files/2019-09/Physical_Activity_Guidelines_2nd_edition.pdf
30. National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Physical activity for people with disability. September 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/disabilityandhealth/features/physical-activity-for-all.html
31. Introduction to strengthening exercises. National Center on Health, Physical Activity and Disability (NCHPAD). 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.nchpad.org/374/2096/Strengthening~Exercises
Some adults who have an intellectual or other developmental disability (IDD) require extensive subspecialty care; many, however, depend primarily on their family physician for the bulk of their health care. With that reliance in mind, this article provides (1) an overview of important services that family physicians can provide for their adult patients with IDD and (2) pragmatic clinical suggestions for tailoring that care. Note: We highlight only some high-impact areas of clinical focus; refer to the 2018 Canadian consensus guidelines for a comprehensive approach to optimizing primary care for this population.1
CASE
Laura S, a 24-year-old woman with Down syndrome, is visiting your clinic with her mother to establish care. Ms. S has several medical comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, repaired congenital heart disease, schizoaffective disorder, and hypothyroidism. She is under the care of multiple specialists, including a cardiologist and an endocrinologist. Her medications include the atypical antipsychotic risperidone, which was prescribed for her through the services of a community mental health center.
Ms. S is due for multiple preventive health screenings. She indicates that she feels nervous today talking about these screenings with a new physician.
First step in care: Proficiency in the lexicon of IDD
Three core concepts of IDD are impairment, disability, and handicap. According to the World Health Organization2:
- impairment “is any loss or abnormality of psychological, physiological, or anatomical structure or function.”
- disability “is any restriction or lack (resulting from an impairment) of ability to perform an activity in the manner or within the range considered normal for a human being.”
- handicap therefore “represents socialization of an impairment or disability, and as such it reflects the consequences for the individual—cultural, social, economic, and environmental—that stem from the presence of impairment and disability.”
Essential transition: Pediatric to adult health care
Health care transition (HCT) is the planned process of transferring care from a pediatric to an adult-based health care setting,3 comprising 3 phases:
- preparation
- transfer from pediatric to adult care
- integration into adult-based care.
Two critical components of a smooth HCT include initiating the transition early in adolescence and providing transition-support resources, which are often lacking, even in large, integrated health systems.4 Got Transition, created by the National Alliance to Advance Adolescent Health, outlines core elements of an organized HCT process (www.gottransition.org) specific to young adults with IDD, including young adults with autism spectrum disorder.5,6
Even young people who are served by a family physician and who intend to remain in that family practice as they age into adulthood require HCT services that include6:
- assessment of readiness to transition to adult care
- update of the medical history
- assessment and promotion of self-care skills
- consent discussions and optimized participation in decision-making
- transition of specialty care from pediatric to adult specialists.
Continue to: For an ideal HCT...
For an ideal HCT, full engagement of the patient, the medical home (physicians, nursing staff, and care coordinators), and the patient’s family (including the primary caregiver or guardian) is critical. In addition to preventive care visits and management of chronic disease, additional domains that require explicit attention in transitioning young people with IDD include health insurance, transportation, employment, and postsecondary education.
Young people who have special health care needs and receive high-quality HCT demonstrate improvements in adherence to care, disease-specific measures, quality of life, self-care skills, satisfaction with care, and health care utilization.7TABLE 13 lists resources identified by Berens and colleagues that are helpful in facilitating the transition.
Teach and practice disability etiquette
Societal prejudice harms people with IDD—leading to self-deprecation, alienation from the larger community, and isolation from others with IDD.8 To promote acceptance and inclusivity in residential communities, the workplace, recreational venues, and clinical settings, disability etiquette should be utilized—a set of guidelines on how to interact with patients with IDD. These include speaking to the patient directly, using clear language in an adult voice, and avoiding stereotypes about people with disabilities.9 The entire health care team, including all front-facing staff (receptionists and care and financial coordinators) and clinical staff (physicians, nurses, medical assistants), need to be educated in, and practice, disability etiquette.
Preparing for in-person visits. Pre-visit preparation, ideally by means of dialogue between health care staff and the patient or caregiver (or both), typically by telephone and in advance of the scheduled visit, is often critical for a successful first face-to-face encounter. (See “Pre-visit telephone questionnaire and script for a new adult patient with IDD,” page 287, which we developed for use in our office practice.) Outcomes of the pre-visit preparation should include identifying:
- words or actions that can trigger anxiety or panic
- de-escalation techniques, such as specific calming words and actions
- strategies for optimal communication, physical access, and physical examination.
SIDEBAR
Pre-visit telephone questionnaire and script for a new adult patient with IDD
Introduction
Hello! My name is ______________. I’m a nurse [or medical assistant] from [name of practice]. I understand that [name of patient] is coming to our office for an appointment on [date and time]. I am calling to prepare our health care team to make this first appointment successful for [name of patient] and you.
- How would [name of patient] prefer to be called?
- Who will be accompanying [name of patient] to the appointment? What parts of the appointment will that person remain for?
Describe what to expect, what the patient or caregiver should bring to the appointment, and how long the appointment will last.
- What makes [name of patient] anxious or fearful so that we might avoid doing that? Should we avoid bringing up certain topics? Should we avoid performing any procedures that are customary during a first appointment?
- Does [name of patient] have sensitivities—to light, sound, touch, etc—that we should be aware of?
Offer to have a room ready upon the patient’s arrival if remaining in the waiting area would cause too much anxiety.
- What helps calm [name of patient]? Are there some topics that put [name of patient] at ease?
- How does [name of patient] best communicate?
- Is there anything else the health care team might do to prepare for the appointment?
- Does [name of patient] need personal protective equipment, a wheelchair, oxygen, or other medical equipment upon arrival?
- What would make for a successful first appointment?
- What strategies or techniques have [name of patient’s] providers used in the past that have helped make health care visits successful?
- Is there anything else you want me to know that we haven’t talked about?
- Would it be helpful if I talked with [name of patient] now about their upcoming appointment?
Initial appointments should focus on building trust and rapport with the health care team and desensitizing the patient to the clinical environment.10 Examination techniques used with pediatric patients can be applied to this population: for example, demonstrating an examination maneuver first on the parent or caregiver; beginning the examination with the least invasive or anxiety-provoking components; and stating what you plan to do next—before you do it.
Continue to: Systematic health checks provide great value
Systematic health checks provide great value
A health check is a systematic and comprehensive health assessment that is provided annually to adults with IDD, and includes:
- specific review of signs and symptoms of health conditions that often co-occur in adults with IDD (TABLE 2Calibri11)
- screening for changes in adaptive functioning and secondary disability
- lifestyle counseling
- medication review and counseling
- immunization update
- discussion of caregiver concerns.
Regarding the last point: Many caregivers are the aging parents of the adult patient with IDD—people who have their own emerging health and support needs. You should initiate conversations about advanced planning for the needs of patients, which often involves engaging siblings and other family members to assume a greater role in caregiving.12
Benefits of the health check. A systematic review of 38 studies, comprising more than 5000 patients with IDD, found that health checks increased the detection of serious conditions, improved screening for sensory impairments, and increased the immunization rate.13 Although many patients with IDD generally understand the need for a periodic health examination, you can enhance their experience by better explaining the rationale for the health check; scheduling sufficient time for the appointment, based on the individual clinical situation; and discussing the value of laboratory testing and referrals to specialists.14
Tailoring preventive care
Many of the preventive services recommendations typically utilized by family physicians, such as guidelines from the US Preventive Services Task Force, have been developed for the general population at average risk of conditions of interest.15 Adults with IDD, depending on the cause of their developmental disability and their behavioral risk profile, might be at significantly higher (or lower) risk of cancer, heart disease, or other conditions than the general population. To address these differences, preventive care guidelines tailored to patients with certain developmental disabilities have been created, including guidelines specific to adults with Down syndrome, fragile X syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, Smith-Magenis syndrome, and 22q11.2 deletion (DiGeorge) syndrome.16
Clarifying the molecular genetic etiology of many developmental disabilities has led to more precise understandings about physical and behavioral health issues associated with specific developmental disabilities. For that reason, patients without a known cause for their IDD might benefit from referral to a geneticist—even in early or middle adulthood. Variables generally associated with a higher likelihood of an abnormal genetic test result include17:
- a family history of developmental disability
- a congenital malformation or dysmorphic features
- a dual diagnosis of developmental disability and co-occurring mental illness
- hypotonia
- severe or profound IDD.
Continue to: Successful implementation of preventive health screening tests...
Successful implementation of preventive health screening tests often requires ingenuity and the collective creativity of the patient, family members, staff, and family physician to allay fears and anxieties. Examples: Women who have been advised to undergo screening mammography might feel less anxious by undergoing tandem screening with their sister or mother, and colorectal cancer screening might be more easily accomplished using a fecal DNA test rather than by colonoscopy. Procedural desensitization strategies and preventive care instructional materials targeting people with IDD are posted on YouTube (for example, the “DD CARES Best Practices” series [see www.youtube.com/watch?v=EPJy4zvg4io]) and other websites.
Management of chronic disease
Evidence of health disparities in patients with IDD includes suboptimal management of chronic diseases, such as diabetes18 and hypertension,19 despite contact with a primary care physician. Nonadherence to a medication regimen might be more common in patients who live with their family or in a residential setting where there is a lower degree of supervision—that is, compared to a residence that maintains 24-hour staffing with daily nursing care and supervision. For a patient who is not so closely supervised, reviewing the medication refill history with the pharmacy, or using the so-called brown-bag technique of counting pill bottles brought to appointments, can ensure medication adherence.
CASE
As you interview Ms. S, you note that she is shy, avoids eye contact, and appears generally anxious. You calm her by noticing and complimenting her jewelry and fingernail polish. Ms. S smiles and talks about her favorite polish colors.
Her mother reports that, when Ms. S is stressed, she talks to herself alone in her bedroom. However, you do not observe evidence of schizoaffective disorder, and begin to wonder whether she needs to be taking risperidone.
Essentials of mental health care
It is estimated that one-third of adults with IDD have significant mental and behavioral health care needs.20 Patients with IDD suffer the same psychiatric disorders as the general population; some also engage in problematic behaviors, such as self-injurious actions, physical or verbal aggression (or both), property destruction, and resistance to caregiving assistance.
Continue to: Mental and behavioral health problems...
Mental and behavioral health problems can have a profound impact on the quality of life of patients with IDD, their peers, and their family and other caregivers. If untreated, these problems can lead to premature institutionalization, loss of employment or desired program participation, fractured social relationships, and caregiver withdrawal and burnout.
Initial evaluation of suspected mental and behavioral health problems begins with careful assessment for medical conditions that might be causing pain and distress, stereotypies, and other problematic behaviors. Common sources of pain and discomfort include dental and other oral disease, dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastritis, constipation, allergic disease, headache, musculoskeletal pathology, lower urinary tract disease, and gynecologic disorders.11 Identification and optimal treatment of medical conditions might not eliminate problematic behaviors but often decrease their frequency and intensity.
Psychoactive medications are prescribed for many patients with IDD. Many have behavioral adverse effects, such as akathisia, aggression, and disinhibition—leading to a prescribing cascade of psychoactive medication polypharmacy and escalating dosages.21 Antipsychotic medications are often initiated without a careful diagnosis, explicit outcome targets, or adequate clinical monitoring for effectiveness; in addition, they often lead to insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and massive weight gain.21 Even a family physician who is not the prescriber can perform an important advocacy role by critically reviewing psychoactive medications, documenting adverse effects, insisting on a clear therapeutic target, and calling for discontinuation of medications that appear to be ineffective.
Evaluation of mental and behavioral health problems requires a developmental perspective to interpret specific, observable behaviors with a proper clinical lens. For example, many patients with IDD engage in self-talk (soliloquizing) as a means of processing the world around them. This practice might escalate during a time of physical or psychological stress, and the unwary clinician might misinterpret this behavior as psychotic, leading to inappropriate prescribing of antipsychotic medication. Other psychotoform behaviors that, superficially, mimic but are typically not truly psychotic, include talk with or about imaginary friends and repetitive retelling of sometimes elaborate or grandiose tales or assertions. The failure of clinicians to recognize developmentally determined expressions of distress often leads to a misdiagnosis of schizophrenia or other psychotic illness and, consequently, inappropriate psychopharmacotherapy.
Family physicians, familiar with the use of psychiatric scales for diagnosis and treatment monitoring, should use similar scales that have been developed specifically for patients with IDD (TABLE 311). In addition, a psychiatric diagnosis manual, the Diagnostic Manual—Intellectual Disability 2, specific to people with IDD (and analogous to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition) provides modification of diagnostic criteria to account for patients who have difficulty articulating their internal emotional state and inner thoughts.22
Continue to: Problematic behaviors
Problematic behaviors that are not features of a bona fide psychiatric disorder are often best understood through functional behavioral analysis, which examines antecedents and consequences of problematic behaviors and identifies their predictable outcomes, such as gaining attention, avoiding a task, or securing a desired item. Rather than being given a prescription for psychoactive medication, many adult patients with IDD and problematic behaviors might be best served by having you order consultation with a certified behavior analyst. The analyst will conduct an evaluation and, along with family or residential staff and the patient, craft a behavioral support plan to address core drivers of the undesired behavior. Behavioral support plans might be enriched by multidisciplinary input from a speech and language pathologist, habilitation professionals, occupational and physical therapists, a neuropsychologist, and others.23
Resources to help you address the physical, mental, and behavioral health problems of these patients are available online through Vanderbilt Kennedy Center’s “Toolkit for primary care providers” (https://iddtoolkit.vkcsites.org).
CASE
During your examination, you review Ms. S’s vital signs, including body mass index (BMI). You calculate that she is morbidly obese—BMI, 37—in the setting of a known comorbidity, diabetes.
Ms. S tells you that she is interested in having a healthy lifestyle, but feels frustrated because she does not know how to make the necessary changes. You discuss with her how some medications, including risperidone, can promote weight gain, and that it is important for her mental health provider to carefully reassess whether she needs to continue the drug.
Weight management in a patient population that tends to be sedentary
Patients with IDD are more likely to live a sedentary lifestyle. Compared to adults who do not have IDD, adults with IDD—especially women and patients with Down syndrome—are reported to have a higher prevalence of obesity.24
Continue to: As in the general population...
As in the general population, the greatest success in weight management involves multidisciplinary treatment, including nutritional support, physical activity, behavioral changes, and close follow-up. The importance of such an approach was borne out by the findings of a randomized controlled trial in which a multicomponent intervention—an energy-reduced diet, physical activity, and behavioral sessions—delivered to participants or their caregivers during monthly visits produced clinically meaningful 6-month weight loss.25 Health-promoting behavioral interventions that rely on a dyadic strategy, such as peer health coaches (ie, people with IDD who have been trained as a health coach) or mentors (IDD staff trained as a health coach), might be more successful at changing health behaviors among patients with IDD than traditional office-based, individual patient education and counseling.26
Similarly, undesired weight loss demands careful evaluation and management because such loss can reflect a medically significant condition, such as gastroesophageal reflux, constipation, dysphagia, neglect, and cancer.27
Boosting the amount and effectiveness of physical activity
Young people with IDD participate in physical activity less often than their neurotypical peers; as a result, they tend to be less fit and have a higher prevalence of obesity.28 Based on a meta-analysis, interventions that focus on sport and movement skills training, such as soccer, basketball, and ball-throwing programs, might be more effective than general physical activity programs.28 In addition to year-round sports training and athletic competitions, Special Olympics conducts vital health screenings of athletes and supports community-based initiatives that address bias against patients with IDD, promote inclusion, and foster social relationships (www.specialolympics.org/our-work/inclusive-health?locale=en).
Emphasize regular activity. In adulthood, fewer than 10% of patients with IDD exercise regularly.21 According to the second edition of Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans,29 “all adults, with or without a disability, should get at least 150 minutes of aerobic physical activity a week. Activities can be broken down into smaller amounts, such as about 25 minutes a day every day.”30 Supplementation with muscle-strengthening activities (eg, yoga, weight training, and resistance-band training) provides further health benefit, such as improvement in posture and prevention of future injury.31 An ideal exercise program proposed by Tyler and Baker is based on a daily, “3-2-1” schedule (ie, of every hour of activity, 30 minutes should be of aerobic exercise; 20 minutes, of strength building; and 10 minutes, of flexibility).11 By participating in any type of physical activity, there is potential for considerable health benefit in reducing psychosocial stressors, improving mental health, counteracting metabolic syndromes, and, ultimately, reducing morbidity and mortality related to physical inactivity.
CASE
With permission from Ms. S, you send your progress notes by fax to her mental health provider at the community mental health center and request a call to discuss her case—in particular, to examine potential alternatives to risperidone. With Ms. S’s input, you also co-create an exercise prescription that includes a daily 20-minute walking program with her mother.
At the follow-up visit that is scheduled in 3 months, you anticipate adding a resistance component and balance activity to the exercise prescription to enrich Ms. S’s physical activity regimen.
CORRESPONDENCE
Carl V. Tyler Jr., MD, 14601 Detroit Avenue, Lakewood, OH, 44107; catyle@ccf.org
Some adults who have an intellectual or other developmental disability (IDD) require extensive subspecialty care; many, however, depend primarily on their family physician for the bulk of their health care. With that reliance in mind, this article provides (1) an overview of important services that family physicians can provide for their adult patients with IDD and (2) pragmatic clinical suggestions for tailoring that care. Note: We highlight only some high-impact areas of clinical focus; refer to the 2018 Canadian consensus guidelines for a comprehensive approach to optimizing primary care for this population.1
CASE
Laura S, a 24-year-old woman with Down syndrome, is visiting your clinic with her mother to establish care. Ms. S has several medical comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, repaired congenital heart disease, schizoaffective disorder, and hypothyroidism. She is under the care of multiple specialists, including a cardiologist and an endocrinologist. Her medications include the atypical antipsychotic risperidone, which was prescribed for her through the services of a community mental health center.
Ms. S is due for multiple preventive health screenings. She indicates that she feels nervous today talking about these screenings with a new physician.
First step in care: Proficiency in the lexicon of IDD
Three core concepts of IDD are impairment, disability, and handicap. According to the World Health Organization2:
- impairment “is any loss or abnormality of psychological, physiological, or anatomical structure or function.”
- disability “is any restriction or lack (resulting from an impairment) of ability to perform an activity in the manner or within the range considered normal for a human being.”
- handicap therefore “represents socialization of an impairment or disability, and as such it reflects the consequences for the individual—cultural, social, economic, and environmental—that stem from the presence of impairment and disability.”
Essential transition: Pediatric to adult health care
Health care transition (HCT) is the planned process of transferring care from a pediatric to an adult-based health care setting,3 comprising 3 phases:
- preparation
- transfer from pediatric to adult care
- integration into adult-based care.
Two critical components of a smooth HCT include initiating the transition early in adolescence and providing transition-support resources, which are often lacking, even in large, integrated health systems.4 Got Transition, created by the National Alliance to Advance Adolescent Health, outlines core elements of an organized HCT process (www.gottransition.org) specific to young adults with IDD, including young adults with autism spectrum disorder.5,6
Even young people who are served by a family physician and who intend to remain in that family practice as they age into adulthood require HCT services that include6:
- assessment of readiness to transition to adult care
- update of the medical history
- assessment and promotion of self-care skills
- consent discussions and optimized participation in decision-making
- transition of specialty care from pediatric to adult specialists.
Continue to: For an ideal HCT...
For an ideal HCT, full engagement of the patient, the medical home (physicians, nursing staff, and care coordinators), and the patient’s family (including the primary caregiver or guardian) is critical. In addition to preventive care visits and management of chronic disease, additional domains that require explicit attention in transitioning young people with IDD include health insurance, transportation, employment, and postsecondary education.
Young people who have special health care needs and receive high-quality HCT demonstrate improvements in adherence to care, disease-specific measures, quality of life, self-care skills, satisfaction with care, and health care utilization.7TABLE 13 lists resources identified by Berens and colleagues that are helpful in facilitating the transition.
Teach and practice disability etiquette
Societal prejudice harms people with IDD—leading to self-deprecation, alienation from the larger community, and isolation from others with IDD.8 To promote acceptance and inclusivity in residential communities, the workplace, recreational venues, and clinical settings, disability etiquette should be utilized—a set of guidelines on how to interact with patients with IDD. These include speaking to the patient directly, using clear language in an adult voice, and avoiding stereotypes about people with disabilities.9 The entire health care team, including all front-facing staff (receptionists and care and financial coordinators) and clinical staff (physicians, nurses, medical assistants), need to be educated in, and practice, disability etiquette.
Preparing for in-person visits. Pre-visit preparation, ideally by means of dialogue between health care staff and the patient or caregiver (or both), typically by telephone and in advance of the scheduled visit, is often critical for a successful first face-to-face encounter. (See “Pre-visit telephone questionnaire and script for a new adult patient with IDD,” page 287, which we developed for use in our office practice.) Outcomes of the pre-visit preparation should include identifying:
- words or actions that can trigger anxiety or panic
- de-escalation techniques, such as specific calming words and actions
- strategies for optimal communication, physical access, and physical examination.
SIDEBAR
Pre-visit telephone questionnaire and script for a new adult patient with IDD
Introduction
Hello! My name is ______________. I’m a nurse [or medical assistant] from [name of practice]. I understand that [name of patient] is coming to our office for an appointment on [date and time]. I am calling to prepare our health care team to make this first appointment successful for [name of patient] and you.
- How would [name of patient] prefer to be called?
- Who will be accompanying [name of patient] to the appointment? What parts of the appointment will that person remain for?
Describe what to expect, what the patient or caregiver should bring to the appointment, and how long the appointment will last.
- What makes [name of patient] anxious or fearful so that we might avoid doing that? Should we avoid bringing up certain topics? Should we avoid performing any procedures that are customary during a first appointment?
- Does [name of patient] have sensitivities—to light, sound, touch, etc—that we should be aware of?
Offer to have a room ready upon the patient’s arrival if remaining in the waiting area would cause too much anxiety.
- What helps calm [name of patient]? Are there some topics that put [name of patient] at ease?
- How does [name of patient] best communicate?
- Is there anything else the health care team might do to prepare for the appointment?
- Does [name of patient] need personal protective equipment, a wheelchair, oxygen, or other medical equipment upon arrival?
- What would make for a successful first appointment?
- What strategies or techniques have [name of patient’s] providers used in the past that have helped make health care visits successful?
- Is there anything else you want me to know that we haven’t talked about?
- Would it be helpful if I talked with [name of patient] now about their upcoming appointment?
Initial appointments should focus on building trust and rapport with the health care team and desensitizing the patient to the clinical environment.10 Examination techniques used with pediatric patients can be applied to this population: for example, demonstrating an examination maneuver first on the parent or caregiver; beginning the examination with the least invasive or anxiety-provoking components; and stating what you plan to do next—before you do it.
Continue to: Systematic health checks provide great value
Systematic health checks provide great value
A health check is a systematic and comprehensive health assessment that is provided annually to adults with IDD, and includes:
- specific review of signs and symptoms of health conditions that often co-occur in adults with IDD (TABLE 2Calibri11)
- screening for changes in adaptive functioning and secondary disability
- lifestyle counseling
- medication review and counseling
- immunization update
- discussion of caregiver concerns.
Regarding the last point: Many caregivers are the aging parents of the adult patient with IDD—people who have their own emerging health and support needs. You should initiate conversations about advanced planning for the needs of patients, which often involves engaging siblings and other family members to assume a greater role in caregiving.12
Benefits of the health check. A systematic review of 38 studies, comprising more than 5000 patients with IDD, found that health checks increased the detection of serious conditions, improved screening for sensory impairments, and increased the immunization rate.13 Although many patients with IDD generally understand the need for a periodic health examination, you can enhance their experience by better explaining the rationale for the health check; scheduling sufficient time for the appointment, based on the individual clinical situation; and discussing the value of laboratory testing and referrals to specialists.14
Tailoring preventive care
Many of the preventive services recommendations typically utilized by family physicians, such as guidelines from the US Preventive Services Task Force, have been developed for the general population at average risk of conditions of interest.15 Adults with IDD, depending on the cause of their developmental disability and their behavioral risk profile, might be at significantly higher (or lower) risk of cancer, heart disease, or other conditions than the general population. To address these differences, preventive care guidelines tailored to patients with certain developmental disabilities have been created, including guidelines specific to adults with Down syndrome, fragile X syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, Smith-Magenis syndrome, and 22q11.2 deletion (DiGeorge) syndrome.16
Clarifying the molecular genetic etiology of many developmental disabilities has led to more precise understandings about physical and behavioral health issues associated with specific developmental disabilities. For that reason, patients without a known cause for their IDD might benefit from referral to a geneticist—even in early or middle adulthood. Variables generally associated with a higher likelihood of an abnormal genetic test result include17:
- a family history of developmental disability
- a congenital malformation or dysmorphic features
- a dual diagnosis of developmental disability and co-occurring mental illness
- hypotonia
- severe or profound IDD.
Continue to: Successful implementation of preventive health screening tests...
Successful implementation of preventive health screening tests often requires ingenuity and the collective creativity of the patient, family members, staff, and family physician to allay fears and anxieties. Examples: Women who have been advised to undergo screening mammography might feel less anxious by undergoing tandem screening with their sister or mother, and colorectal cancer screening might be more easily accomplished using a fecal DNA test rather than by colonoscopy. Procedural desensitization strategies and preventive care instructional materials targeting people with IDD are posted on YouTube (for example, the “DD CARES Best Practices” series [see www.youtube.com/watch?v=EPJy4zvg4io]) and other websites.
Management of chronic disease
Evidence of health disparities in patients with IDD includes suboptimal management of chronic diseases, such as diabetes18 and hypertension,19 despite contact with a primary care physician. Nonadherence to a medication regimen might be more common in patients who live with their family or in a residential setting where there is a lower degree of supervision—that is, compared to a residence that maintains 24-hour staffing with daily nursing care and supervision. For a patient who is not so closely supervised, reviewing the medication refill history with the pharmacy, or using the so-called brown-bag technique of counting pill bottles brought to appointments, can ensure medication adherence.
CASE
As you interview Ms. S, you note that she is shy, avoids eye contact, and appears generally anxious. You calm her by noticing and complimenting her jewelry and fingernail polish. Ms. S smiles and talks about her favorite polish colors.
Her mother reports that, when Ms. S is stressed, she talks to herself alone in her bedroom. However, you do not observe evidence of schizoaffective disorder, and begin to wonder whether she needs to be taking risperidone.
Essentials of mental health care
It is estimated that one-third of adults with IDD have significant mental and behavioral health care needs.20 Patients with IDD suffer the same psychiatric disorders as the general population; some also engage in problematic behaviors, such as self-injurious actions, physical or verbal aggression (or both), property destruction, and resistance to caregiving assistance.
Continue to: Mental and behavioral health problems...
Mental and behavioral health problems can have a profound impact on the quality of life of patients with IDD, their peers, and their family and other caregivers. If untreated, these problems can lead to premature institutionalization, loss of employment or desired program participation, fractured social relationships, and caregiver withdrawal and burnout.
Initial evaluation of suspected mental and behavioral health problems begins with careful assessment for medical conditions that might be causing pain and distress, stereotypies, and other problematic behaviors. Common sources of pain and discomfort include dental and other oral disease, dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastritis, constipation, allergic disease, headache, musculoskeletal pathology, lower urinary tract disease, and gynecologic disorders.11 Identification and optimal treatment of medical conditions might not eliminate problematic behaviors but often decrease their frequency and intensity.
Psychoactive medications are prescribed for many patients with IDD. Many have behavioral adverse effects, such as akathisia, aggression, and disinhibition—leading to a prescribing cascade of psychoactive medication polypharmacy and escalating dosages.21 Antipsychotic medications are often initiated without a careful diagnosis, explicit outcome targets, or adequate clinical monitoring for effectiveness; in addition, they often lead to insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and massive weight gain.21 Even a family physician who is not the prescriber can perform an important advocacy role by critically reviewing psychoactive medications, documenting adverse effects, insisting on a clear therapeutic target, and calling for discontinuation of medications that appear to be ineffective.
Evaluation of mental and behavioral health problems requires a developmental perspective to interpret specific, observable behaviors with a proper clinical lens. For example, many patients with IDD engage in self-talk (soliloquizing) as a means of processing the world around them. This practice might escalate during a time of physical or psychological stress, and the unwary clinician might misinterpret this behavior as psychotic, leading to inappropriate prescribing of antipsychotic medication. Other psychotoform behaviors that, superficially, mimic but are typically not truly psychotic, include talk with or about imaginary friends and repetitive retelling of sometimes elaborate or grandiose tales or assertions. The failure of clinicians to recognize developmentally determined expressions of distress often leads to a misdiagnosis of schizophrenia or other psychotic illness and, consequently, inappropriate psychopharmacotherapy.
Family physicians, familiar with the use of psychiatric scales for diagnosis and treatment monitoring, should use similar scales that have been developed specifically for patients with IDD (TABLE 311). In addition, a psychiatric diagnosis manual, the Diagnostic Manual—Intellectual Disability 2, specific to people with IDD (and analogous to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition) provides modification of diagnostic criteria to account for patients who have difficulty articulating their internal emotional state and inner thoughts.22
Continue to: Problematic behaviors
Problematic behaviors that are not features of a bona fide psychiatric disorder are often best understood through functional behavioral analysis, which examines antecedents and consequences of problematic behaviors and identifies their predictable outcomes, such as gaining attention, avoiding a task, or securing a desired item. Rather than being given a prescription for psychoactive medication, many adult patients with IDD and problematic behaviors might be best served by having you order consultation with a certified behavior analyst. The analyst will conduct an evaluation and, along with family or residential staff and the patient, craft a behavioral support plan to address core drivers of the undesired behavior. Behavioral support plans might be enriched by multidisciplinary input from a speech and language pathologist, habilitation professionals, occupational and physical therapists, a neuropsychologist, and others.23
Resources to help you address the physical, mental, and behavioral health problems of these patients are available online through Vanderbilt Kennedy Center’s “Toolkit for primary care providers” (https://iddtoolkit.vkcsites.org).
CASE
During your examination, you review Ms. S’s vital signs, including body mass index (BMI). You calculate that she is morbidly obese—BMI, 37—in the setting of a known comorbidity, diabetes.
Ms. S tells you that she is interested in having a healthy lifestyle, but feels frustrated because she does not know how to make the necessary changes. You discuss with her how some medications, including risperidone, can promote weight gain, and that it is important for her mental health provider to carefully reassess whether she needs to continue the drug.
Weight management in a patient population that tends to be sedentary
Patients with IDD are more likely to live a sedentary lifestyle. Compared to adults who do not have IDD, adults with IDD—especially women and patients with Down syndrome—are reported to have a higher prevalence of obesity.24
Continue to: As in the general population...
As in the general population, the greatest success in weight management involves multidisciplinary treatment, including nutritional support, physical activity, behavioral changes, and close follow-up. The importance of such an approach was borne out by the findings of a randomized controlled trial in which a multicomponent intervention—an energy-reduced diet, physical activity, and behavioral sessions—delivered to participants or their caregivers during monthly visits produced clinically meaningful 6-month weight loss.25 Health-promoting behavioral interventions that rely on a dyadic strategy, such as peer health coaches (ie, people with IDD who have been trained as a health coach) or mentors (IDD staff trained as a health coach), might be more successful at changing health behaviors among patients with IDD than traditional office-based, individual patient education and counseling.26
Similarly, undesired weight loss demands careful evaluation and management because such loss can reflect a medically significant condition, such as gastroesophageal reflux, constipation, dysphagia, neglect, and cancer.27
Boosting the amount and effectiveness of physical activity
Young people with IDD participate in physical activity less often than their neurotypical peers; as a result, they tend to be less fit and have a higher prevalence of obesity.28 Based on a meta-analysis, interventions that focus on sport and movement skills training, such as soccer, basketball, and ball-throwing programs, might be more effective than general physical activity programs.28 In addition to year-round sports training and athletic competitions, Special Olympics conducts vital health screenings of athletes and supports community-based initiatives that address bias against patients with IDD, promote inclusion, and foster social relationships (www.specialolympics.org/our-work/inclusive-health?locale=en).
Emphasize regular activity. In adulthood, fewer than 10% of patients with IDD exercise regularly.21 According to the second edition of Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans,29 “all adults, with or without a disability, should get at least 150 minutes of aerobic physical activity a week. Activities can be broken down into smaller amounts, such as about 25 minutes a day every day.”30 Supplementation with muscle-strengthening activities (eg, yoga, weight training, and resistance-band training) provides further health benefit, such as improvement in posture and prevention of future injury.31 An ideal exercise program proposed by Tyler and Baker is based on a daily, “3-2-1” schedule (ie, of every hour of activity, 30 minutes should be of aerobic exercise; 20 minutes, of strength building; and 10 minutes, of flexibility).11 By participating in any type of physical activity, there is potential for considerable health benefit in reducing psychosocial stressors, improving mental health, counteracting metabolic syndromes, and, ultimately, reducing morbidity and mortality related to physical inactivity.
CASE
With permission from Ms. S, you send your progress notes by fax to her mental health provider at the community mental health center and request a call to discuss her case—in particular, to examine potential alternatives to risperidone. With Ms. S’s input, you also co-create an exercise prescription that includes a daily 20-minute walking program with her mother.
At the follow-up visit that is scheduled in 3 months, you anticipate adding a resistance component and balance activity to the exercise prescription to enrich Ms. S’s physical activity regimen.
CORRESPONDENCE
Carl V. Tyler Jr., MD, 14601 Detroit Avenue, Lakewood, OH, 44107; catyle@ccf.org
1. Sullivan WF, Diepstra H, Heng J, et al. Primary care of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: 2018 Canadian consensus guidelines. Can Fam Physician. 2018;64:254-279.
2. World Health Organization. International Classification of Impairments, Disabilities, and Handicaps: A Manual of Classification Relating to the Consequences of Disease. May 1980. Accessed May 27, 2021. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/41003/9241541261_eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
3. Berens J, Wozow C, Peacock C. Transition to adult care. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2020;31:159-170. doi:10.1016/j.pmr.2019.09.004
4. American Academy of Pediatrics; American Academy of Family Physicians; American College of Physicians; Transitions Clinical Report Authoring Group; Cooley WC, Sagerman PJ. Supporting the health care transition from adolescence to adulthood in the medical home. Pediatrics. 2011;128:182-200. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-0969
5. Dressler PB, Nguyen TK, Moody EJ, et al. Use of transition resources by primary care providers for youth with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2018;56:56-68. doi:10.1352/1934-9556-56.1.56
6. The National Alliance to Advance Adolescent Health. Six Core Elements of Health Care Transition.™ Got Transition website. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.gottransition.org
7. Schmidt A, Ilango SM, McManus MA, et al. Outcomes of pediatric to adult health care transition interventions: an updated systematic review. J Pediatr Nurs. 2020; 51:92-107. doi: 10.1016/j.pedn.2020.01.002
8. Keith JM, Bennetto L, Rogge RD. The relationship between contact and attitudes: reducing prejudice toward individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Res Dev Disabil. 2015;47:14-26. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2015.07.032
9. United Spinal Association. Disability Etiquette: Tips on Interacting With People With Disabilities. 2015. Accessed June 9, 2021. www.unitedspinal.org/pdf/DisabilityEtiquette.pdf
10. Nathawad R, Hanks C. Optimizing the office visit for adolescents with special health care needs. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2017;47:182-189. doi:10.1016/j.cppeds.2017.07.002
11. Tyler CV, Baker S. Intellectual Disabilities at Your Fingertips: A Health Care Resource. High Tide Press; 2009.
12. Williamson HJ, Perkins EA. Family caregivers of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: outcomes associated with U.S. services and supports. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2014;52:147-159. doi: 10.1352/1934-9556-52.2.147
13. Robertson J, Hatton C, Emerson E, et al. The impact of health checks for people with intellectual disabilities: an updated systematic review of evidence. Res Dev Disabil. 2014;35:2450-2462. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2014.06.007
14. Perry J, Felce D, Kerr M, et al. Contact with primary care: the experience of people with intellectual disabilities. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2014;27:200-211. doi: 10.1111/jar.12072
15. Recommendation topics. United States Preventive Services Task Force website. 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org
16. Developmental Disabilities Primary Care Initiative. Tools for the Primary Care of People with Developmental Disabilities. 1st ed. MUMS Guideline Clearinghouse; 2011.
17. Jang W, Kim Y, Han E, et al. Chromosomal microarray analysis as a first-tier clinical diagnostic test in patients with developmental delay/intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorders, and multiple congenital anomalies: a prospective multicenter study in Korea. Ann Lab Med. 2019;39:299-310. doi:10.3343/alm.2019.39.3.299
18. Shireman TI, Reichard A, Nazir N, et al. Quality of diabetes care for adults with developmental disabilities. Disabil Health J. 2010;3:179-185. doi:10.1016/j.dhjo.2009.10.004
19. Cyrus AC, Royer J, Carroll DD, et al. Anti-hypertensive medication use and actors related to adherence among adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Am J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2019;124:248-262. doi:10.1352/1944-7558-124.3.248
20. IDD/MI diagnosis. National Association for the Dually Diagnosed (NADD) website. 2019. Accessed May 27, 2021. https://thenadd.org/idd-mi-diagnosis
21. Matson JL, Mayville EA, Bielecki J, et al. Reliability of the Matson Evaluation of Drug Side Effects Scale (MEDS). Res Dev Disabil. 1998;19:501-506. doi:10.1016/s0891-4222(98)00021-3
22. Fletcher R, Barnhill J, Cooper SA. (2017). Diagnostic Manual-Intellectual Disability: A Textbook of Diagnosis of Mental Disorders in Persons with Intellectual Disability. 2nd ed. National Association for the Dually Diagnosed (NADD); 2017.
23. Marrus N, Hall L. Intellectual disability and language disorder. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2017;26:539-554. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2017.03.001
24. Rimmer JH, Yamaki K. Obesity and intellectual disability. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2006;12;22-7. doi: 10.1002/mrdd.20091
25. Ptomey LT, Saunders RR, Saunders M, et al. Weight management in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: a randomized controlled trial of two dietary approaches. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2018;31(suppl 1):82-96. doi:10.1111/jar.12348
26. Marks B, Sisirak J, Magallanes R, et al. Effectiveness of a HealthMessages peer-to-peer program for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2019;57:242-258. doi:10.1352/1934-9556-57.3.242
27. Escudé C. Clinical Pearls in IDD Health care. HRS, Inc; 2020.
28. Kapsal NJ, Dicke T, Morin AJS, et al. Effects of physical activity on the physical and psychosocial health of youth with intellectual disabilities: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Phys Act Health. 2019;16:1187-1195. doi:10.1123/jpah.2018-0675
29. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. 2nd ed. US Department of Health and Human Services; 2018. Accessed May 29, 2021. https://health.gov/sites/default/files/2019-09/Physical_Activity_Guidelines_2nd_edition.pdf
30. National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Physical activity for people with disability. September 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/disabilityandhealth/features/physical-activity-for-all.html
31. Introduction to strengthening exercises. National Center on Health, Physical Activity and Disability (NCHPAD). 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.nchpad.org/374/2096/Strengthening~Exercises
1. Sullivan WF, Diepstra H, Heng J, et al. Primary care of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: 2018 Canadian consensus guidelines. Can Fam Physician. 2018;64:254-279.
2. World Health Organization. International Classification of Impairments, Disabilities, and Handicaps: A Manual of Classification Relating to the Consequences of Disease. May 1980. Accessed May 27, 2021. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/41003/9241541261_eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
3. Berens J, Wozow C, Peacock C. Transition to adult care. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2020;31:159-170. doi:10.1016/j.pmr.2019.09.004
4. American Academy of Pediatrics; American Academy of Family Physicians; American College of Physicians; Transitions Clinical Report Authoring Group; Cooley WC, Sagerman PJ. Supporting the health care transition from adolescence to adulthood in the medical home. Pediatrics. 2011;128:182-200. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-0969
5. Dressler PB, Nguyen TK, Moody EJ, et al. Use of transition resources by primary care providers for youth with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2018;56:56-68. doi:10.1352/1934-9556-56.1.56
6. The National Alliance to Advance Adolescent Health. Six Core Elements of Health Care Transition.™ Got Transition website. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.gottransition.org
7. Schmidt A, Ilango SM, McManus MA, et al. Outcomes of pediatric to adult health care transition interventions: an updated systematic review. J Pediatr Nurs. 2020; 51:92-107. doi: 10.1016/j.pedn.2020.01.002
8. Keith JM, Bennetto L, Rogge RD. The relationship between contact and attitudes: reducing prejudice toward individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Res Dev Disabil. 2015;47:14-26. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2015.07.032
9. United Spinal Association. Disability Etiquette: Tips on Interacting With People With Disabilities. 2015. Accessed June 9, 2021. www.unitedspinal.org/pdf/DisabilityEtiquette.pdf
10. Nathawad R, Hanks C. Optimizing the office visit for adolescents with special health care needs. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2017;47:182-189. doi:10.1016/j.cppeds.2017.07.002
11. Tyler CV, Baker S. Intellectual Disabilities at Your Fingertips: A Health Care Resource. High Tide Press; 2009.
12. Williamson HJ, Perkins EA. Family caregivers of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: outcomes associated with U.S. services and supports. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2014;52:147-159. doi: 10.1352/1934-9556-52.2.147
13. Robertson J, Hatton C, Emerson E, et al. The impact of health checks for people with intellectual disabilities: an updated systematic review of evidence. Res Dev Disabil. 2014;35:2450-2462. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2014.06.007
14. Perry J, Felce D, Kerr M, et al. Contact with primary care: the experience of people with intellectual disabilities. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2014;27:200-211. doi: 10.1111/jar.12072
15. Recommendation topics. United States Preventive Services Task Force website. 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org
16. Developmental Disabilities Primary Care Initiative. Tools for the Primary Care of People with Developmental Disabilities. 1st ed. MUMS Guideline Clearinghouse; 2011.
17. Jang W, Kim Y, Han E, et al. Chromosomal microarray analysis as a first-tier clinical diagnostic test in patients with developmental delay/intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorders, and multiple congenital anomalies: a prospective multicenter study in Korea. Ann Lab Med. 2019;39:299-310. doi:10.3343/alm.2019.39.3.299
18. Shireman TI, Reichard A, Nazir N, et al. Quality of diabetes care for adults with developmental disabilities. Disabil Health J. 2010;3:179-185. doi:10.1016/j.dhjo.2009.10.004
19. Cyrus AC, Royer J, Carroll DD, et al. Anti-hypertensive medication use and actors related to adherence among adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Am J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2019;124:248-262. doi:10.1352/1944-7558-124.3.248
20. IDD/MI diagnosis. National Association for the Dually Diagnosed (NADD) website. 2019. Accessed May 27, 2021. https://thenadd.org/idd-mi-diagnosis
21. Matson JL, Mayville EA, Bielecki J, et al. Reliability of the Matson Evaluation of Drug Side Effects Scale (MEDS). Res Dev Disabil. 1998;19:501-506. doi:10.1016/s0891-4222(98)00021-3
22. Fletcher R, Barnhill J, Cooper SA. (2017). Diagnostic Manual-Intellectual Disability: A Textbook of Diagnosis of Mental Disorders in Persons with Intellectual Disability. 2nd ed. National Association for the Dually Diagnosed (NADD); 2017.
23. Marrus N, Hall L. Intellectual disability and language disorder. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2017;26:539-554. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2017.03.001
24. Rimmer JH, Yamaki K. Obesity and intellectual disability. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2006;12;22-7. doi: 10.1002/mrdd.20091
25. Ptomey LT, Saunders RR, Saunders M, et al. Weight management in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities: a randomized controlled trial of two dietary approaches. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2018;31(suppl 1):82-96. doi:10.1111/jar.12348
26. Marks B, Sisirak J, Magallanes R, et al. Effectiveness of a HealthMessages peer-to-peer program for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2019;57:242-258. doi:10.1352/1934-9556-57.3.242
27. Escudé C. Clinical Pearls in IDD Health care. HRS, Inc; 2020.
28. Kapsal NJ, Dicke T, Morin AJS, et al. Effects of physical activity on the physical and psychosocial health of youth with intellectual disabilities: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Phys Act Health. 2019;16:1187-1195. doi:10.1123/jpah.2018-0675
29. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. 2nd ed. US Department of Health and Human Services; 2018. Accessed May 29, 2021. https://health.gov/sites/default/files/2019-09/Physical_Activity_Guidelines_2nd_edition.pdf
30. National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Physical activity for people with disability. September 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/disabilityandhealth/features/physical-activity-for-all.html
31. Introduction to strengthening exercises. National Center on Health, Physical Activity and Disability (NCHPAD). 2020. Accessed May 27, 2021. www.nchpad.org/374/2096/Strengthening~Exercises
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
› Provide young people who have an intellectual or other developmental disability (IDD) with a defined, explicit process for making the transition into the adult health care system. A
› Conduct an annual comprehensive, systematic health assessment for patients who have IDD to improve detection of serious conditions and sensory impairments. A
› Encourage young people and adults with IDD to participate in regular physical activity to reduce psychosocial stressors and counteract metabolic syndromes. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series