User login
Discontinuing a long-acting injectable antipsychotic: What to consider
Mr. R, age 29, was diagnosed with schizophrenia 6 years ago. To manage his disorder, he has been receiving paliperidone palmitate long-acting injectable (LAI) 156 mg once a month for 2 years. Prior to maintenance with paliperidone palmitate, Mr. R was stabilized on oral paliperidone 9 mg/d. Though he was originally initiated on paliperidone palmitate due to nonadherence concerns, Mr. R has been adherent with each injection for 1 year.
At a recent visit, Mr. R says he wants to discontinue the injection because he is not interested in receiving an ongoing injectable medication and is not able to continue monthly clinic visits. He wants to take a daily oral antipsychotic again, despite the availability of longer-acting products.
A paucity of evidence exists regarding the discontinuation of LAI antipsychotics and the next steps that follow in treatment. There is neither a consensus nor recognized guidelines advising how and when to discontinue an LAI and restart an oral antipsychotic. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis evaluated different maintenance treatment strategies; however, switching from an LAI antipsychotic to an oral medication was not a focus.1 In this article, we outline a possible approach to discontinuing an LAI antipsychotic and restarting an oral formulation. Before discontinuing an LAI antipsychotic, clinicians should review with the patient the risks and benefits of switching medications, including the risk of decompensation and potential adverse effects.
Switching to an oral antipsychotic
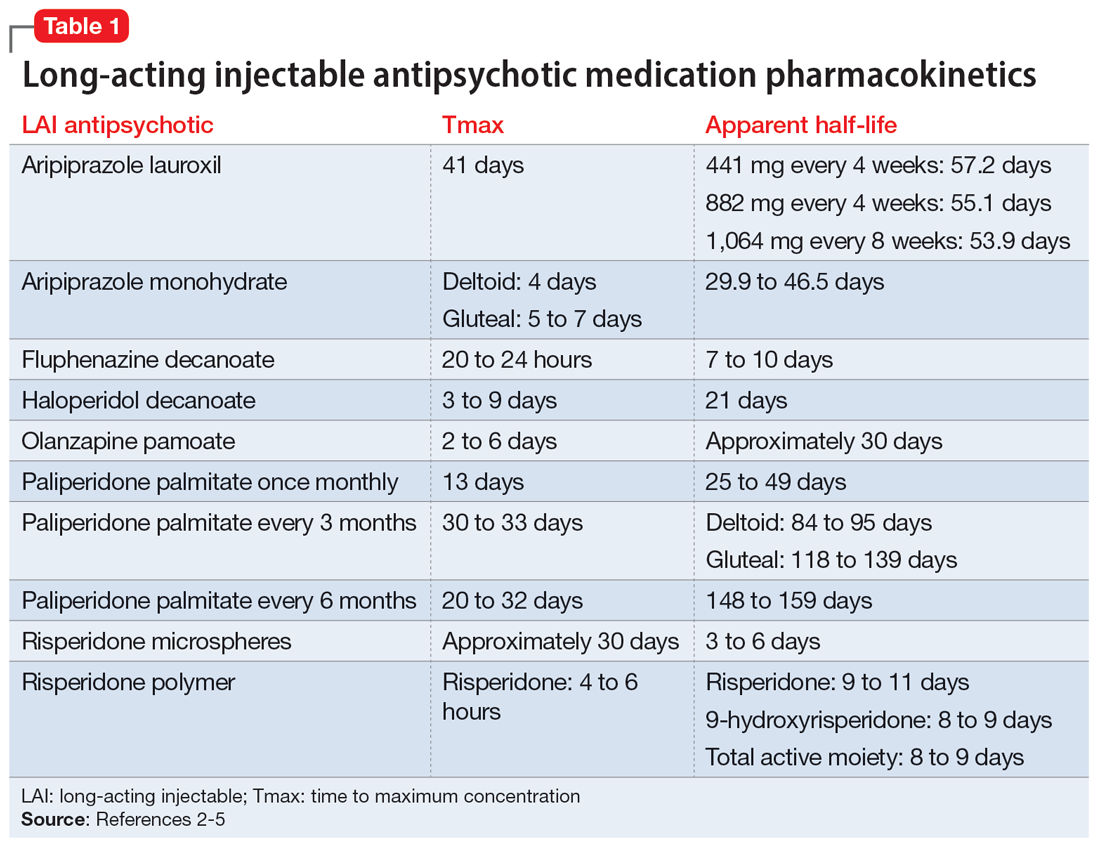
The first step in the discontinuation process is to determine whether the patient will continue the same oral medication as the LAI antipsychotic or if a different oral antipsychotic will be initiated. Next, determining when to initiate the oral medication requires several pieces of information, including the oral dose equivalent of the patient’s current LAI, the half-life of the LAI, and the release mechanism of the LAI (Table 1).2-5 To determine the appropriate time frame for restarting oral treatment, it is also vital to know the date of the last injection.
Based on the date of the next injection, the clinician will utilize the LAI’s half-life and its release mechanism to determine the appropriate time to start a new oral antipsychotic. Research demonstrates that in patients who have achieved steady state with a first-generation antipsychotic, plasma concentrations stay relatively consistent for 6 to 7 weeks after the last injection, which suggests oral medications may not need to be initiated until that time.6-9
For many second-generation LAI antipsychotics, oral medications may be initiated at the date of the next injection. Initiation of an oral antipsychotic may require more time between the last injection dose and the date of administration for oral medication due to the pharmacokinetic profile of risperidone microspheres. Once a patient is at steady state with risperidone microspheres, trough levels are not observed until 3 to 4 weeks after discontinuation.10
Previous pharmacokinetic model–based stimulations of active moiety plasma concentrations of risperidone microspheres demonstrate that 2 weeks after an injection of risperidone microspheres, the concentration of active moiety continued to approximate the steady-state concentration for 3 to 5 weeks.11 This is likely due to the product’s delay in release being 3 weeks from the time of injection to the last release phase. Of note, there was a rapid decline in the active moiety concentration; it reached nearly 0 by Week 5.11 The same pharmacokinetic model–based stimulation demonstrated a steady and slow decline of the concentration of active moiety of paliperidone palmitate after discontinuation of the LAI.11
Continue to: No guidance exists for...
No guidance exists for aripiprazole LAI medications; however, based on the pharmacokinetic data, administration of oral medications should be initiated at the date of next injection. Given the long half-life of aripiprazole, a cross-titration of the LAI with oral medication is reasonable.
Monitoring drug levels
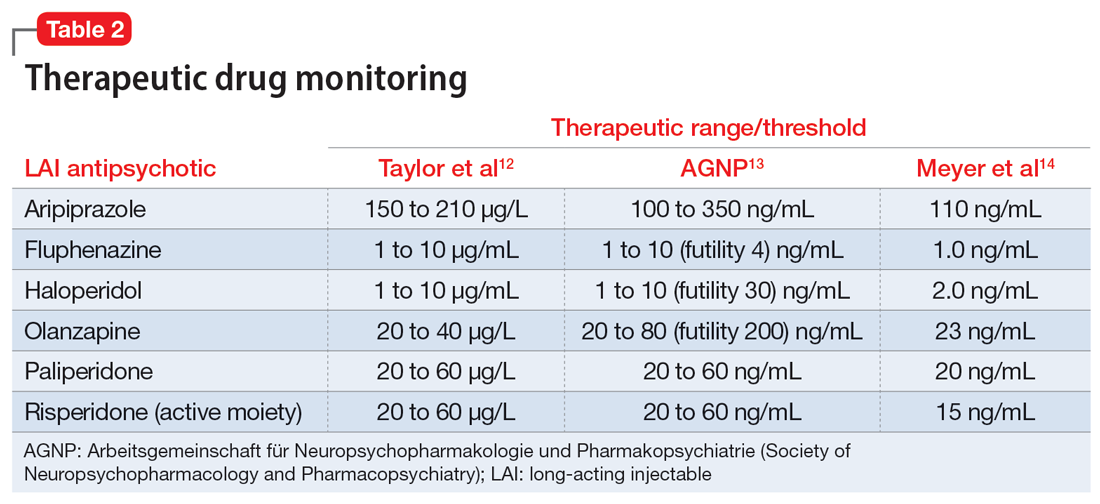
In addition to utilizing the pharmacokinetic data from LAI antipsychotics, therapeutic drug levels can be instrumental in determining the dose of oral medication to use and when to begin titration (Table 2).12-14 Obtaining a drug level on the date of the next injection can provide the clinician with data regarding the release of the medication specific to the patient. Based on the level and the current symptomatology, the clinician could choose to start the oral medication at a lower dose and titrate back to the LAI equivalent oral dose, or initiate the oral dose at the LAI equivalent oral dose. Continued therapeutic drug levels can aid in this determination.
No guidance exists on the appropriate discontinuation of LAI antipsychotics. Utilizing a medication’s half-life and release mechanism, as well as the patient’s previous medication history, date of last injection, and therapeutic drug levels, should be considered when determining the schedule for restarting an oral antipsychotic.
CASE CONTINUED
Based on the current dosing of paliperidone palmitate of 156 mg once a month, Mr. R likely requires 9 mg/d of oral paliperidone upon discontinuation of the LAI. On the date of the next injection, the clinician could decide to initiate a lower dose of paliperidone, such as to 3 mg/d or 6 mg/d, and increase the dose as tolerated over the next 10 to 14 days as the paliperidone palmitate is further metabolized. Additionally, the clinician may consider obtaining a therapeutic drug level to determine the current paliperidone level prior to initiating the oral medication. Each treatment option offers individual risks and benefits. The decision on when and how to initiate the oral medication will be based on the individual patient’s situation and history, as well as the comfort and discretion of the clinician. The clinician should arrange appropriate monitoring for potential increased symptomatology during the transition, and adverse effects should be assessed regularly until steady state is achieved with the targeted oral dose of medication.
Related Resources
- Parmentier BL. Second-generation long-acting injectable antipsychotics: a practical guide. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(3):24-32.
- Thippaiah SM, Fargason RE, Birur B. Switching antipsychotics: a guide to dose equivalents. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(4):13-14. doi:10.12788/cp.0103
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole lauroxil • Aristada
Aripiprazole monohydrate • Maintena
Haloperidol injection • Haldol decanoate
Olanzapine pamoate • Zyprexa Relprevv
Paliperidone • Invega
Paliperidone palmitate once monthly • Invega Sustenna
Paliperidone palmitate every 3 months • Invega Trinza
Paliperidone palmitate every 6 months • Invega Hafyera
Risperidone microspheres • Risperdal Consta
Risperidone polymer • Perseris
1. Ostuzzi G, Vita G, Bertolini F, et al. Continuing, reducing, switching, or stopping antipsychotics in individuals with schizophrenia-spectrum disorders who are clinically stable: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2022;9(8):614-624.
2. Correll CU, Kim E, Sliwa JK, et al. Pharmacokinetic characteristics of long-acting injectable antipsychotics for schizophrenia: an overview. CNS Drugs. 2021;35(1):39-59.
3. Spanarello S, La Ferla T. The pharmacokinetics of long-acting antipsychotic medications. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2014;9(3):310-317.
4. Meyer JM. Understanding depot antipsychotics: an illustrated guide to kinetics. CNS Spectr. 2013;18(Suppl 1):58-68.
5. Invega Hafyera [package insert]. Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2021.
6. Gitlin MJ, Midha KK, Fogelson D, et al. Persistence of fluphenazine in plasma after decanoate withdrawal. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1988;8(1):53-56.
7. Wistedt B, Jørgensen A, Wiles D. A depot neuroleptic withdrawal study. Plasma concentration of fluphenazine and flupenthixol and relapse frequency. Psychopharmacology. 1982;78(4):301-304.
8. Chang WH, Lin SK, Juang DJ, et al. Prolonged haloperidol and reduced haloperidol plasma concentrations after decanoate withdrawal. Schizophr Res. 1993;9(1):35-40.
9. Eklund K, Forsman A. Minimal effective dose and relapse—double-blind trial: haloperidol decanoate vs. placebo. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1991;1(Suppl 2):S7-S15.
10. Wilson WH. A visual guide to expected blood levels of long-acting injectable risperidone in clinical practice. J Psychiatry Pract. 2004;10(6):393-401.
11. Samtani MN, Sheehan JJ, Fu DJ, et al. Management of antipsychotic treatment discontinuation and interruptions using model-based simulations. Clin Pharmacol. 2012;4:25-40.
12. Taylor D, Barnes TRE, Young AH. The Maudsley Prescribing Guidelines in Psychiatry. 13th ed. Wiley-Blackwell; 2018.
13. Hiemke C, Bergemann N, Clement HW, et al. Consensus guidelines for therapeutic drug monitoring in neuropsychopharmacology: update 2017. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2018;51(1-2):9-62.
14. Meyer JM, Stahl SM. The Clinical Use of Antipsychotic Plasma Levels. Cambridge University Press; 2021.
Mr. R, age 29, was diagnosed with schizophrenia 6 years ago. To manage his disorder, he has been receiving paliperidone palmitate long-acting injectable (LAI) 156 mg once a month for 2 years. Prior to maintenance with paliperidone palmitate, Mr. R was stabilized on oral paliperidone 9 mg/d. Though he was originally initiated on paliperidone palmitate due to nonadherence concerns, Mr. R has been adherent with each injection for 1 year.
At a recent visit, Mr. R says he wants to discontinue the injection because he is not interested in receiving an ongoing injectable medication and is not able to continue monthly clinic visits. He wants to take a daily oral antipsychotic again, despite the availability of longer-acting products.
A paucity of evidence exists regarding the discontinuation of LAI antipsychotics and the next steps that follow in treatment. There is neither a consensus nor recognized guidelines advising how and when to discontinue an LAI and restart an oral antipsychotic. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis evaluated different maintenance treatment strategies; however, switching from an LAI antipsychotic to an oral medication was not a focus.1 In this article, we outline a possible approach to discontinuing an LAI antipsychotic and restarting an oral formulation. Before discontinuing an LAI antipsychotic, clinicians should review with the patient the risks and benefits of switching medications, including the risk of decompensation and potential adverse effects.
Switching to an oral antipsychotic
The first step in the discontinuation process is to determine whether the patient will continue the same oral medication as the LAI antipsychotic or if a different oral antipsychotic will be initiated. Next, determining when to initiate the oral medication requires several pieces of information, including the oral dose equivalent of the patient’s current LAI, the half-life of the LAI, and the release mechanism of the LAI (Table 1).2-5 To determine the appropriate time frame for restarting oral treatment, it is also vital to know the date of the last injection.

Based on the date of the next injection, the clinician will utilize the LAI’s half-life and its release mechanism to determine the appropriate time to start a new oral antipsychotic. Research demonstrates that in patients who have achieved steady state with a first-generation antipsychotic, plasma concentrations stay relatively consistent for 6 to 7 weeks after the last injection, which suggests oral medications may not need to be initiated until that time.6-9
For many second-generation LAI antipsychotics, oral medications may be initiated at the date of the next injection. Initiation of an oral antipsychotic may require more time between the last injection dose and the date of administration for oral medication due to the pharmacokinetic profile of risperidone microspheres. Once a patient is at steady state with risperidone microspheres, trough levels are not observed until 3 to 4 weeks after discontinuation.10
Previous pharmacokinetic model–based stimulations of active moiety plasma concentrations of risperidone microspheres demonstrate that 2 weeks after an injection of risperidone microspheres, the concentration of active moiety continued to approximate the steady-state concentration for 3 to 5 weeks.11 This is likely due to the product’s delay in release being 3 weeks from the time of injection to the last release phase. Of note, there was a rapid decline in the active moiety concentration; it reached nearly 0 by Week 5.11 The same pharmacokinetic model–based stimulation demonstrated a steady and slow decline of the concentration of active moiety of paliperidone palmitate after discontinuation of the LAI.11
Continue to: No guidance exists for...
No guidance exists for aripiprazole LAI medications; however, based on the pharmacokinetic data, administration of oral medications should be initiated at the date of next injection. Given the long half-life of aripiprazole, a cross-titration of the LAI with oral medication is reasonable.
Monitoring drug levels
In addition to utilizing the pharmacokinetic data from LAI antipsychotics, therapeutic drug levels can be instrumental in determining the dose of oral medication to use and when to begin titration (Table 2).12-14 Obtaining a drug level on the date of the next injection can provide the clinician with data regarding the release of the medication specific to the patient. Based on the level and the current symptomatology, the clinician could choose to start the oral medication at a lower dose and titrate back to the LAI equivalent oral dose, or initiate the oral dose at the LAI equivalent oral dose. Continued therapeutic drug levels can aid in this determination.

No guidance exists on the appropriate discontinuation of LAI antipsychotics. Utilizing a medication’s half-life and release mechanism, as well as the patient’s previous medication history, date of last injection, and therapeutic drug levels, should be considered when determining the schedule for restarting an oral antipsychotic.
CASE CONTINUED
Based on the current dosing of paliperidone palmitate of 156 mg once a month, Mr. R likely requires 9 mg/d of oral paliperidone upon discontinuation of the LAI. On the date of the next injection, the clinician could decide to initiate a lower dose of paliperidone, such as to 3 mg/d or 6 mg/d, and increase the dose as tolerated over the next 10 to 14 days as the paliperidone palmitate is further metabolized. Additionally, the clinician may consider obtaining a therapeutic drug level to determine the current paliperidone level prior to initiating the oral medication. Each treatment option offers individual risks and benefits. The decision on when and how to initiate the oral medication will be based on the individual patient’s situation and history, as well as the comfort and discretion of the clinician. The clinician should arrange appropriate monitoring for potential increased symptomatology during the transition, and adverse effects should be assessed regularly until steady state is achieved with the targeted oral dose of medication.
Related Resources
- Parmentier BL. Second-generation long-acting injectable antipsychotics: a practical guide. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(3):24-32.
- Thippaiah SM, Fargason RE, Birur B. Switching antipsychotics: a guide to dose equivalents. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(4):13-14. doi:10.12788/cp.0103
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole lauroxil • Aristada
Aripiprazole monohydrate • Maintena
Haloperidol injection • Haldol decanoate
Olanzapine pamoate • Zyprexa Relprevv
Paliperidone • Invega
Paliperidone palmitate once monthly • Invega Sustenna
Paliperidone palmitate every 3 months • Invega Trinza
Paliperidone palmitate every 6 months • Invega Hafyera
Risperidone microspheres • Risperdal Consta
Risperidone polymer • Perseris
Mr. R, age 29, was diagnosed with schizophrenia 6 years ago. To manage his disorder, he has been receiving paliperidone palmitate long-acting injectable (LAI) 156 mg once a month for 2 years. Prior to maintenance with paliperidone palmitate, Mr. R was stabilized on oral paliperidone 9 mg/d. Though he was originally initiated on paliperidone palmitate due to nonadherence concerns, Mr. R has been adherent with each injection for 1 year.
At a recent visit, Mr. R says he wants to discontinue the injection because he is not interested in receiving an ongoing injectable medication and is not able to continue monthly clinic visits. He wants to take a daily oral antipsychotic again, despite the availability of longer-acting products.
A paucity of evidence exists regarding the discontinuation of LAI antipsychotics and the next steps that follow in treatment. There is neither a consensus nor recognized guidelines advising how and when to discontinue an LAI and restart an oral antipsychotic. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis evaluated different maintenance treatment strategies; however, switching from an LAI antipsychotic to an oral medication was not a focus.1 In this article, we outline a possible approach to discontinuing an LAI antipsychotic and restarting an oral formulation. Before discontinuing an LAI antipsychotic, clinicians should review with the patient the risks and benefits of switching medications, including the risk of decompensation and potential adverse effects.
Switching to an oral antipsychotic
The first step in the discontinuation process is to determine whether the patient will continue the same oral medication as the LAI antipsychotic or if a different oral antipsychotic will be initiated. Next, determining when to initiate the oral medication requires several pieces of information, including the oral dose equivalent of the patient’s current LAI, the half-life of the LAI, and the release mechanism of the LAI (Table 1).2-5 To determine the appropriate time frame for restarting oral treatment, it is also vital to know the date of the last injection.

Based on the date of the next injection, the clinician will utilize the LAI’s half-life and its release mechanism to determine the appropriate time to start a new oral antipsychotic. Research demonstrates that in patients who have achieved steady state with a first-generation antipsychotic, plasma concentrations stay relatively consistent for 6 to 7 weeks after the last injection, which suggests oral medications may not need to be initiated until that time.6-9
For many second-generation LAI antipsychotics, oral medications may be initiated at the date of the next injection. Initiation of an oral antipsychotic may require more time between the last injection dose and the date of administration for oral medication due to the pharmacokinetic profile of risperidone microspheres. Once a patient is at steady state with risperidone microspheres, trough levels are not observed until 3 to 4 weeks after discontinuation.10
Previous pharmacokinetic model–based stimulations of active moiety plasma concentrations of risperidone microspheres demonstrate that 2 weeks after an injection of risperidone microspheres, the concentration of active moiety continued to approximate the steady-state concentration for 3 to 5 weeks.11 This is likely due to the product’s delay in release being 3 weeks from the time of injection to the last release phase. Of note, there was a rapid decline in the active moiety concentration; it reached nearly 0 by Week 5.11 The same pharmacokinetic model–based stimulation demonstrated a steady and slow decline of the concentration of active moiety of paliperidone palmitate after discontinuation of the LAI.11
Continue to: No guidance exists for...
No guidance exists for aripiprazole LAI medications; however, based on the pharmacokinetic data, administration of oral medications should be initiated at the date of next injection. Given the long half-life of aripiprazole, a cross-titration of the LAI with oral medication is reasonable.
Monitoring drug levels
In addition to utilizing the pharmacokinetic data from LAI antipsychotics, therapeutic drug levels can be instrumental in determining the dose of oral medication to use and when to begin titration (Table 2).12-14 Obtaining a drug level on the date of the next injection can provide the clinician with data regarding the release of the medication specific to the patient. Based on the level and the current symptomatology, the clinician could choose to start the oral medication at a lower dose and titrate back to the LAI equivalent oral dose, or initiate the oral dose at the LAI equivalent oral dose. Continued therapeutic drug levels can aid in this determination.

No guidance exists on the appropriate discontinuation of LAI antipsychotics. Utilizing a medication’s half-life and release mechanism, as well as the patient’s previous medication history, date of last injection, and therapeutic drug levels, should be considered when determining the schedule for restarting an oral antipsychotic.
CASE CONTINUED
Based on the current dosing of paliperidone palmitate of 156 mg once a month, Mr. R likely requires 9 mg/d of oral paliperidone upon discontinuation of the LAI. On the date of the next injection, the clinician could decide to initiate a lower dose of paliperidone, such as to 3 mg/d or 6 mg/d, and increase the dose as tolerated over the next 10 to 14 days as the paliperidone palmitate is further metabolized. Additionally, the clinician may consider obtaining a therapeutic drug level to determine the current paliperidone level prior to initiating the oral medication. Each treatment option offers individual risks and benefits. The decision on when and how to initiate the oral medication will be based on the individual patient’s situation and history, as well as the comfort and discretion of the clinician. The clinician should arrange appropriate monitoring for potential increased symptomatology during the transition, and adverse effects should be assessed regularly until steady state is achieved with the targeted oral dose of medication.
Related Resources
- Parmentier BL. Second-generation long-acting injectable antipsychotics: a practical guide. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(3):24-32.
- Thippaiah SM, Fargason RE, Birur B. Switching antipsychotics: a guide to dose equivalents. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(4):13-14. doi:10.12788/cp.0103
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole lauroxil • Aristada
Aripiprazole monohydrate • Maintena
Haloperidol injection • Haldol decanoate
Olanzapine pamoate • Zyprexa Relprevv
Paliperidone • Invega
Paliperidone palmitate once monthly • Invega Sustenna
Paliperidone palmitate every 3 months • Invega Trinza
Paliperidone palmitate every 6 months • Invega Hafyera
Risperidone microspheres • Risperdal Consta
Risperidone polymer • Perseris
1. Ostuzzi G, Vita G, Bertolini F, et al. Continuing, reducing, switching, or stopping antipsychotics in individuals with schizophrenia-spectrum disorders who are clinically stable: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2022;9(8):614-624.
2. Correll CU, Kim E, Sliwa JK, et al. Pharmacokinetic characteristics of long-acting injectable antipsychotics for schizophrenia: an overview. CNS Drugs. 2021;35(1):39-59.
3. Spanarello S, La Ferla T. The pharmacokinetics of long-acting antipsychotic medications. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2014;9(3):310-317.
4. Meyer JM. Understanding depot antipsychotics: an illustrated guide to kinetics. CNS Spectr. 2013;18(Suppl 1):58-68.
5. Invega Hafyera [package insert]. Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2021.
6. Gitlin MJ, Midha KK, Fogelson D, et al. Persistence of fluphenazine in plasma after decanoate withdrawal. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1988;8(1):53-56.
7. Wistedt B, Jørgensen A, Wiles D. A depot neuroleptic withdrawal study. Plasma concentration of fluphenazine and flupenthixol and relapse frequency. Psychopharmacology. 1982;78(4):301-304.
8. Chang WH, Lin SK, Juang DJ, et al. Prolonged haloperidol and reduced haloperidol plasma concentrations after decanoate withdrawal. Schizophr Res. 1993;9(1):35-40.
9. Eklund K, Forsman A. Minimal effective dose and relapse—double-blind trial: haloperidol decanoate vs. placebo. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1991;1(Suppl 2):S7-S15.
10. Wilson WH. A visual guide to expected blood levels of long-acting injectable risperidone in clinical practice. J Psychiatry Pract. 2004;10(6):393-401.
11. Samtani MN, Sheehan JJ, Fu DJ, et al. Management of antipsychotic treatment discontinuation and interruptions using model-based simulations. Clin Pharmacol. 2012;4:25-40.
12. Taylor D, Barnes TRE, Young AH. The Maudsley Prescribing Guidelines in Psychiatry. 13th ed. Wiley-Blackwell; 2018.
13. Hiemke C, Bergemann N, Clement HW, et al. Consensus guidelines for therapeutic drug monitoring in neuropsychopharmacology: update 2017. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2018;51(1-2):9-62.
14. Meyer JM, Stahl SM. The Clinical Use of Antipsychotic Plasma Levels. Cambridge University Press; 2021.
1. Ostuzzi G, Vita G, Bertolini F, et al. Continuing, reducing, switching, or stopping antipsychotics in individuals with schizophrenia-spectrum disorders who are clinically stable: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2022;9(8):614-624.
2. Correll CU, Kim E, Sliwa JK, et al. Pharmacokinetic characteristics of long-acting injectable antipsychotics for schizophrenia: an overview. CNS Drugs. 2021;35(1):39-59.
3. Spanarello S, La Ferla T. The pharmacokinetics of long-acting antipsychotic medications. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2014;9(3):310-317.
4. Meyer JM. Understanding depot antipsychotics: an illustrated guide to kinetics. CNS Spectr. 2013;18(Suppl 1):58-68.
5. Invega Hafyera [package insert]. Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2021.
6. Gitlin MJ, Midha KK, Fogelson D, et al. Persistence of fluphenazine in plasma after decanoate withdrawal. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1988;8(1):53-56.
7. Wistedt B, Jørgensen A, Wiles D. A depot neuroleptic withdrawal study. Plasma concentration of fluphenazine and flupenthixol and relapse frequency. Psychopharmacology. 1982;78(4):301-304.
8. Chang WH, Lin SK, Juang DJ, et al. Prolonged haloperidol and reduced haloperidol plasma concentrations after decanoate withdrawal. Schizophr Res. 1993;9(1):35-40.
9. Eklund K, Forsman A. Minimal effective dose and relapse—double-blind trial: haloperidol decanoate vs. placebo. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1991;1(Suppl 2):S7-S15.
10. Wilson WH. A visual guide to expected blood levels of long-acting injectable risperidone in clinical practice. J Psychiatry Pract. 2004;10(6):393-401.
11. Samtani MN, Sheehan JJ, Fu DJ, et al. Management of antipsychotic treatment discontinuation and interruptions using model-based simulations. Clin Pharmacol. 2012;4:25-40.
12. Taylor D, Barnes TRE, Young AH. The Maudsley Prescribing Guidelines in Psychiatry. 13th ed. Wiley-Blackwell; 2018.
13. Hiemke C, Bergemann N, Clement HW, et al. Consensus guidelines for therapeutic drug monitoring in neuropsychopharmacology: update 2017. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2018;51(1-2):9-62.
14. Meyer JM, Stahl SM. The Clinical Use of Antipsychotic Plasma Levels. Cambridge University Press; 2021.