User login
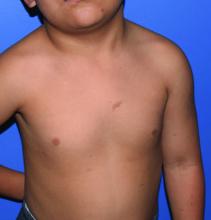
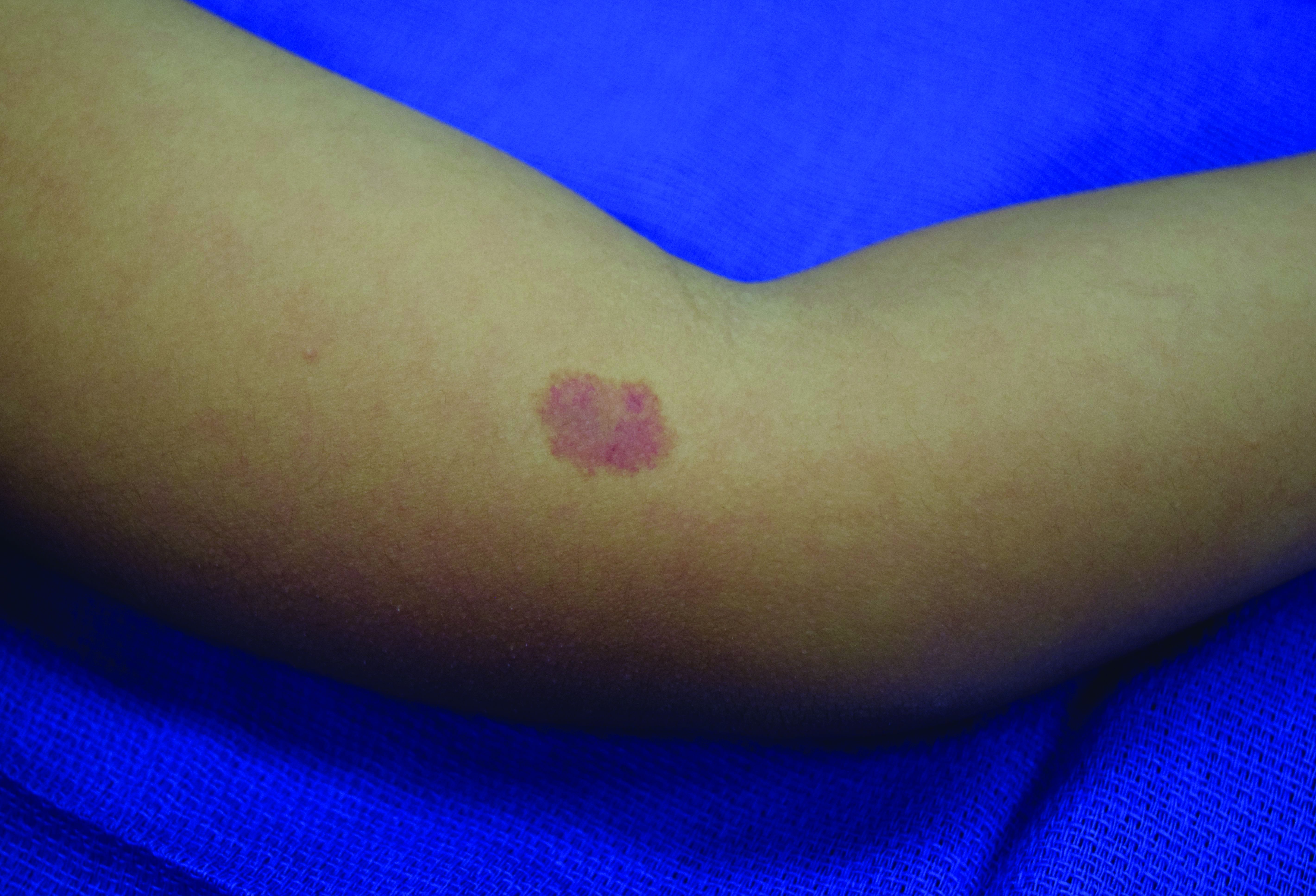
A 4-year-old presented to our pediatric dermatology clinic for evaluation of asymptomatic "brown spots."
Capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation syndrome
with or without arteriovenous malformations, as well as arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs). CM-AVM is an autosomal dominant disorder.1 CM-AVM type 1 is caused by mutations in the RASA1 gene, and CM-AVM type 2 is caused by mutations in the EPHB4 gene.2 Approximately 70% of patients with RASA1-associated CM-AVM syndrome and 80% of patients with EPHB4-associated CM-AVM syndrome have an affected parent, while the remainder have de novo variants.1
In patients with CM-AVM syndrome, CMs are often present at birth and more are typically acquired over time. CMs are characteristically 1-3 cm in diameter, round or oval, dull red or red-brown macules and patches with a blanched halo.3 Some CMs may be warm to touch indicating a possible underlying AVM or AVF.4 This can be confirmed by Doppler ultrasound, which would demonstrate increased arterial flow.4 CMs are most commonly located on the face and limbs and may present in isolation, but approximately one-third of patients have associated AVMs and AVFs.1,5 These high-flow vascular malformations may be present in skin, muscle, bone, brain, and/or spine and may be asymptomatic or lead to serious sequelae, including bleeding, congestive heart failure, and neurologic complications, such as migraine headaches, seizures, or even stroke.5 Symptoms from intracranial and spinal high-flow lesions usually present in early childhood and affect approximately 7% of patients.3
The diagnosis of CM-AVM should be suspected in an individual with numerous characteristic CMs and may be supported by the presence of AVMs and AVFs, family history of CM-AVM, and/or identification of RASA1 or EPHB4 mutation by molecular genetic testing.1,3 Although there are no consensus protocols for imaging CM-AVM patients, MRI of the brain and spine is recommended at diagnosis to identify underlying high-flow lesions.1 This may allow for early treatment before the development of symptoms.1 Any lesions identified on screening imaging may require regular surveillance, which is best determined by discussion with the radiologist.1 Although there are no reports of patients with negative results on screening imaging who later develop AVMs or AVFs, there should be a low threshold for repeat imaging in patients who develop new symptoms or physical exam findings.3,4
It has previously been suggested that the CMs in CM-AVM may actually represent early or small AVMs and pulsed-dye laser (PDL) treatment was not recommended because of concern for potential progression of lesions.4 However, a recent study demonstrated good response to PDL in patients with CM-AVM with no evidence of worsening or recurrence of lesions with long-term follow-up.6 Treatment of CMs that cause cosmetic concerns may be considered following discussion of risks and benefits with a dermatologist. Management of AVMs and AVFs requires a multidisciplinary team that, depending on location and symptoms of these features, may require the expertise of specialists such as neurosurgery, surgery, orthopedics, cardiology, and/or interventional radiology.1
Given the suspicion for CM-AVM in our patient, further workup was completed. A skin biopsy was consistent with CM. Genetic testing with the Vascular Malformations Panel, Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication revealed a pathogenic variant in the RASA1 gene and a variant of unknown clinical significance in the TEK gene. Parental genetic testing for the RASA1 mutation was negative, supporting a de novo mutation in the patient. CNS imaging showed a small developmental venous malformation in the brain that neurosurgery did not think was clinically significant. At the most recent follow-up at age 8 years, our patient had developed a few new small CMs but was otherwise well.
Dr. Leszczynska is trained in pediatrics and is the current dermatology research fellow at the University of Texas at Austin. Ms. Croce is a dermatology-trained pediatric nurse practitioner and PhD student at the University of Texas at Austin School of Nursing. Dr. Diaz is chief of pediatric dermatology at Dell Children’s Medical Center, Austin, assistant professor of pediatrics and medicine (dermatology), and dermatology residency associate program director at University of Texas at Austin . The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, is the editor of this column.
References
1. Bayrak-Toydemir P, Stevenson D. Capillary Malformation-Arteriovenous Malformation Syndrome. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al., eds. GeneReviews®. Seattle: University of Washington, Seattle; February 22, 2011.
2.Yu J et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017 Sep;34(5):e227-30.
3. Orme CM et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013 Jul-Aug;30(4):409-15.
4. Weitz NA et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Jan-Feb;32(1):76-84.
5. Revencu N et al. Hum Mutat. 2013 Dec;34(12):1632-41.
6. Iznardo H et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020 Mar;37(2):342-44.
Capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation syndrome
with or without arteriovenous malformations, as well as arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs). CM-AVM is an autosomal dominant disorder.1 CM-AVM type 1 is caused by mutations in the RASA1 gene, and CM-AVM type 2 is caused by mutations in the EPHB4 gene.2 Approximately 70% of patients with RASA1-associated CM-AVM syndrome and 80% of patients with EPHB4-associated CM-AVM syndrome have an affected parent, while the remainder have de novo variants.1
In patients with CM-AVM syndrome, CMs are often present at birth and more are typically acquired over time. CMs are characteristically 1-3 cm in diameter, round or oval, dull red or red-brown macules and patches with a blanched halo.3 Some CMs may be warm to touch indicating a possible underlying AVM or AVF.4 This can be confirmed by Doppler ultrasound, which would demonstrate increased arterial flow.4 CMs are most commonly located on the face and limbs and may present in isolation, but approximately one-third of patients have associated AVMs and AVFs.1,5 These high-flow vascular malformations may be present in skin, muscle, bone, brain, and/or spine and may be asymptomatic or lead to serious sequelae, including bleeding, congestive heart failure, and neurologic complications, such as migraine headaches, seizures, or even stroke.5 Symptoms from intracranial and spinal high-flow lesions usually present in early childhood and affect approximately 7% of patients.3
The diagnosis of CM-AVM should be suspected in an individual with numerous characteristic CMs and may be supported by the presence of AVMs and AVFs, family history of CM-AVM, and/or identification of RASA1 or EPHB4 mutation by molecular genetic testing.1,3 Although there are no consensus protocols for imaging CM-AVM patients, MRI of the brain and spine is recommended at diagnosis to identify underlying high-flow lesions.1 This may allow for early treatment before the development of symptoms.1 Any lesions identified on screening imaging may require regular surveillance, which is best determined by discussion with the radiologist.1 Although there are no reports of patients with negative results on screening imaging who later develop AVMs or AVFs, there should be a low threshold for repeat imaging in patients who develop new symptoms or physical exam findings.3,4
It has previously been suggested that the CMs in CM-AVM may actually represent early or small AVMs and pulsed-dye laser (PDL) treatment was not recommended because of concern for potential progression of lesions.4 However, a recent study demonstrated good response to PDL in patients with CM-AVM with no evidence of worsening or recurrence of lesions with long-term follow-up.6 Treatment of CMs that cause cosmetic concerns may be considered following discussion of risks and benefits with a dermatologist. Management of AVMs and AVFs requires a multidisciplinary team that, depending on location and symptoms of these features, may require the expertise of specialists such as neurosurgery, surgery, orthopedics, cardiology, and/or interventional radiology.1
Given the suspicion for CM-AVM in our patient, further workup was completed. A skin biopsy was consistent with CM. Genetic testing with the Vascular Malformations Panel, Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication revealed a pathogenic variant in the RASA1 gene and a variant of unknown clinical significance in the TEK gene. Parental genetic testing for the RASA1 mutation was negative, supporting a de novo mutation in the patient. CNS imaging showed a small developmental venous malformation in the brain that neurosurgery did not think was clinically significant. At the most recent follow-up at age 8 years, our patient had developed a few new small CMs but was otherwise well.
Dr. Leszczynska is trained in pediatrics and is the current dermatology research fellow at the University of Texas at Austin. Ms. Croce is a dermatology-trained pediatric nurse practitioner and PhD student at the University of Texas at Austin School of Nursing. Dr. Diaz is chief of pediatric dermatology at Dell Children’s Medical Center, Austin, assistant professor of pediatrics and medicine (dermatology), and dermatology residency associate program director at University of Texas at Austin . The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, is the editor of this column.
References
1. Bayrak-Toydemir P, Stevenson D. Capillary Malformation-Arteriovenous Malformation Syndrome. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al., eds. GeneReviews®. Seattle: University of Washington, Seattle; February 22, 2011.
2.Yu J et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017 Sep;34(5):e227-30.
3. Orme CM et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013 Jul-Aug;30(4):409-15.
4. Weitz NA et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Jan-Feb;32(1):76-84.
5. Revencu N et al. Hum Mutat. 2013 Dec;34(12):1632-41.
6. Iznardo H et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020 Mar;37(2):342-44.
Capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation syndrome
with or without arteriovenous malformations, as well as arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs). CM-AVM is an autosomal dominant disorder.1 CM-AVM type 1 is caused by mutations in the RASA1 gene, and CM-AVM type 2 is caused by mutations in the EPHB4 gene.2 Approximately 70% of patients with RASA1-associated CM-AVM syndrome and 80% of patients with EPHB4-associated CM-AVM syndrome have an affected parent, while the remainder have de novo variants.1
In patients with CM-AVM syndrome, CMs are often present at birth and more are typically acquired over time. CMs are characteristically 1-3 cm in diameter, round or oval, dull red or red-brown macules and patches with a blanched halo.3 Some CMs may be warm to touch indicating a possible underlying AVM or AVF.4 This can be confirmed by Doppler ultrasound, which would demonstrate increased arterial flow.4 CMs are most commonly located on the face and limbs and may present in isolation, but approximately one-third of patients have associated AVMs and AVFs.1,5 These high-flow vascular malformations may be present in skin, muscle, bone, brain, and/or spine and may be asymptomatic or lead to serious sequelae, including bleeding, congestive heart failure, and neurologic complications, such as migraine headaches, seizures, or even stroke.5 Symptoms from intracranial and spinal high-flow lesions usually present in early childhood and affect approximately 7% of patients.3
The diagnosis of CM-AVM should be suspected in an individual with numerous characteristic CMs and may be supported by the presence of AVMs and AVFs, family history of CM-AVM, and/or identification of RASA1 or EPHB4 mutation by molecular genetic testing.1,3 Although there are no consensus protocols for imaging CM-AVM patients, MRI of the brain and spine is recommended at diagnosis to identify underlying high-flow lesions.1 This may allow for early treatment before the development of symptoms.1 Any lesions identified on screening imaging may require regular surveillance, which is best determined by discussion with the radiologist.1 Although there are no reports of patients with negative results on screening imaging who later develop AVMs or AVFs, there should be a low threshold for repeat imaging in patients who develop new symptoms or physical exam findings.3,4
It has previously been suggested that the CMs in CM-AVM may actually represent early or small AVMs and pulsed-dye laser (PDL) treatment was not recommended because of concern for potential progression of lesions.4 However, a recent study demonstrated good response to PDL in patients with CM-AVM with no evidence of worsening or recurrence of lesions with long-term follow-up.6 Treatment of CMs that cause cosmetic concerns may be considered following discussion of risks and benefits with a dermatologist. Management of AVMs and AVFs requires a multidisciplinary team that, depending on location and symptoms of these features, may require the expertise of specialists such as neurosurgery, surgery, orthopedics, cardiology, and/or interventional radiology.1
Given the suspicion for CM-AVM in our patient, further workup was completed. A skin biopsy was consistent with CM. Genetic testing with the Vascular Malformations Panel, Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication revealed a pathogenic variant in the RASA1 gene and a variant of unknown clinical significance in the TEK gene. Parental genetic testing for the RASA1 mutation was negative, supporting a de novo mutation in the patient. CNS imaging showed a small developmental venous malformation in the brain that neurosurgery did not think was clinically significant. At the most recent follow-up at age 8 years, our patient had developed a few new small CMs but was otherwise well.
Dr. Leszczynska is trained in pediatrics and is the current dermatology research fellow at the University of Texas at Austin. Ms. Croce is a dermatology-trained pediatric nurse practitioner and PhD student at the University of Texas at Austin School of Nursing. Dr. Diaz is chief of pediatric dermatology at Dell Children’s Medical Center, Austin, assistant professor of pediatrics and medicine (dermatology), and dermatology residency associate program director at University of Texas at Austin . The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, is the editor of this column.
References
1. Bayrak-Toydemir P, Stevenson D. Capillary Malformation-Arteriovenous Malformation Syndrome. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al., eds. GeneReviews®. Seattle: University of Washington, Seattle; February 22, 2011.
2.Yu J et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017 Sep;34(5):e227-30.
3. Orme CM et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013 Jul-Aug;30(4):409-15.
4. Weitz NA et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Jan-Feb;32(1):76-84.
5. Revencu N et al. Hum Mutat. 2013 Dec;34(12):1632-41.
6. Iznardo H et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020 Mar;37(2):342-44.