User login
Teledermatology: A Postpandemic Update
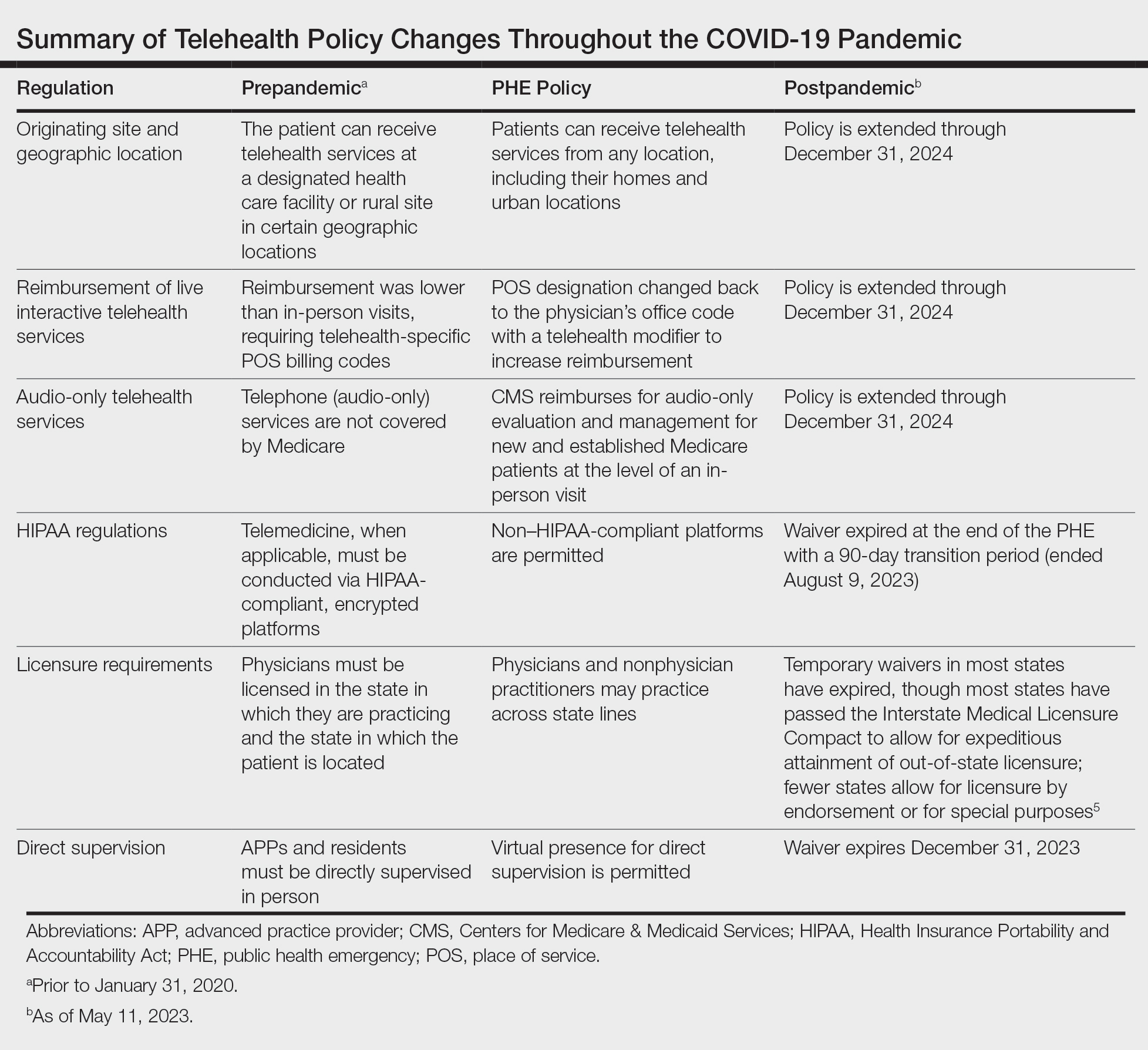
The rapid expansion of teledermatology in the United States due to the COVID-19 pandemic has been well documented, 1 but where do we stand now that health care and society as a whole are back to a new version of normal? It is important to consider why telemedicine was able to grow so quickly during that period—the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) unilaterally changed policies related to provision of services and reimbursement thereof due to the public health emergency (PHE), which was declared by the Department of Health and Human Services in January 2020 to provide increased access to care for patients. Under the PHE, reimbursement rates for virtual visits improved, providers could care for patients from their homes and across state lines, and the use of video platforms that were not Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act compliant was allowed. 2,3
The trajectory of teledermatology after the pandemic, however, remains unclear. In a survey assessing dermatologists’ perceptions of telemedicine (N=4356), 97% used telemedicine during the pandemic but only 58% reported that they intended to continue using teledermatology postpandemic,1 which is driven, at least in part, by the potential concern that dermatologists will again experience the same regulatory and logistical barriers that limited teledermatology utilization prepandemic.
What has changed in reimbursement for teledermatology since the PHE ended?
The PHE ended on May 11, 2023, and already video platforms that were used during the pandemic to provide telemedicine visits but are not Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act compliant are now forbidden,2 Medicare virtual check-in appointments can only be conducted with established patients,4 and medical licensing requirements have been reinstated in most states such that patients must be located in the state where the provider is licensed to practice medicine at the time of a virtual visit.3 Although the CMS was granted wide freedoms to waive and suspend certain rules, this was only in the context of the PHE, and any lasting changes must be established by Congress.
Reassuringly, recent legislation via the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2023, authorized an extension of many of the CMS telehealth flexibilities that were in place during the PHE through December 31, 2024 (Table),2 such as allowing access to telehealth services in any geographic area in the United States rather than only rural areas, allowing patients to stay in their homes for telehealth visits rather than traveling to an approved health care facility, and allowing the delivery of telemedicine via audio-only technology if a patient is unable to use both audio and video. As of now, the place of service (POS) designation for telehealth visits will not revert back to the former code (POS 02) but will remain at POS 11 with the telehealth modifier -95 so physicians will be reimbursed at the full level of a non-facility physician’s office rate.4 The CMS has indicated that there will be no change in the reimbursement policy until after December 31, 20234; however, the sense of uncertainty around what happens after this date has made it hard for organizations and practices to fully commit to teledermatology services without knowing what the long-term financial impact may be. Some organizations have already noted that they plan to continue supporting telemedicine after the CMS flexibilities expire. Accountable Care Organizations have the ability to offer services that allow participating practitioners to continue the use of telemedicine visits to expand access to care. Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program policies vary by state and private health insurance policies vary by individual plans, but it should be noted that commercial coverage for telemedicine visits was already strong prior to the pandemic.2
What medical licensing requirements are in place now for telehealth?
During the PHE, medical licensing requirements also were relaxed, enabling providers to deliver telemedicine service in states where they were not licensed.3 As the PHE orders ended, some states including New York discontinued cross-state licensing waivers altogether,6 whereas others have enacted legislation to make them permanent or extend them for brief periods of time.3,6 One potential solution is the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact (https://www.imlcc.org/), which includes 39 states as of October 2023. This program expedites the process for physicians already licensed in participating states to obtain their medical license in another participating state, though licensing fees are required for each state in which a physician wants to practice. Furthermore, some states such as North Dakota, Hawaii, and Virginia have licensure by endorsement policies, which enable licensed physicians with specific qualifications to provide telehealth services in the endorsing state. Other states such as Florida, New Jersey, Louisiana, Minnesota, Nevada, and New Mexico have special telehealth registries that allow physicians in good standing who are licensed in other states to deliver telehealth services to in-state residents barring they do not provide in-person, in-state services.6 Lastly, some states have temporary practice laws to allow existing patients who need medical attention while traveling out of state to see their home providers virtually or in person under certain circumstances for a limited period of time.3,5 In Hawaii and New Hampshire, physicians with out-of-state licenses can provide consultative services in some circumstances.5
What changes have been made to make it easier for patients to use telehealth?
As the legislation around telemedicine is shifting postpandemic, it is important to address additional logistical barriers to teledermatology on a larger scale if the discipline is to stay in practice. On November 15, 2021, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act provided $65 billion in funding for broadband to expand access to high-speed internet. Some of this money was allocated to the Affordable Connectivity Program, which provides eligible households with a discount on broadband service and internet-connected devices. Eligible patrons can qualify for a discount of up to $75 per month for internet service and a one-time discount up to $100 on a laptop, desktop computer, or tablet purchased through a participating provider.6 Although a step in the right direction, the effects of this program on telemedicine encounters remains to be proven. Additionally, these programs do not address educational barriers to understanding how to utilize telemedicine platforms or provide incentives for practitioners to offer telemedicine services.
Final Thoughts
The pandemic taught our specialty a great deal about how to utilize telemedicine. For many dermatologists a return to in-person business as usual could not come fast enough; however, many practices have continued to offer at least some teledermatology services. Although the PHE waivers have ended, the extension of numerous CMS flexibilities through the end of 2024 allows us more time to develop sustainable policies to support the long-term health of telemedicine as a whole, both to sustain practices and to expand access to care in dermatology. The favorable attitudes of both patients and physicians about teledermatology have been clearly documented,1,7 and we should continue to safely expand the use of this technology.
- Kennedy J, Arey S, Hopkins Z, et al. Dermatologist perceptions of teledermatology implementation and future use after COVID-19: demographics, barriers, and insights. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:595-597.
- US Department of Health and Human Services. HHS fact sheet: telehealth flexibilities and resources and the COVID-19 public health emergency. Published May 10, 2023. Accessed October 18, 2023. https://www.hhs.gov/aboutnews/2023/05/10/hhs-fact-sheet-telehealth-flexibilities-resources-covid-19-public-health-emergency.html
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Licensing across state lines. Updated May 11, 2023. Accessed October 25, 2023. https://telehealth.hhs.gov/licensure/licensing-across-state-lines
- American Academy of Dermatology. Teledermatology and the COVID-19 pandemic. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.aad.org/member/practice/telederm/covid-19
- American Medical Association. Licensure & Telehealth. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/issue-brief-licensure-telehealth.pdf
- Federal Communications Commission. Affordable Connectivity Program. Updated June 29, 2023. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.fcc.gov/affordable-connectivity-program
- Tensen E, van der Heijden JP, Jaspers MWM, et al. Two decades of teledermatology: current status and integration in national healthcare systems. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2016;5:96-104.
The rapid expansion of teledermatology in the United States due to the COVID-19 pandemic has been well documented, 1 but where do we stand now that health care and society as a whole are back to a new version of normal? It is important to consider why telemedicine was able to grow so quickly during that period—the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) unilaterally changed policies related to provision of services and reimbursement thereof due to the public health emergency (PHE), which was declared by the Department of Health and Human Services in January 2020 to provide increased access to care for patients. Under the PHE, reimbursement rates for virtual visits improved, providers could care for patients from their homes and across state lines, and the use of video platforms that were not Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act compliant was allowed. 2,3
The trajectory of teledermatology after the pandemic, however, remains unclear. In a survey assessing dermatologists’ perceptions of telemedicine (N=4356), 97% used telemedicine during the pandemic but only 58% reported that they intended to continue using teledermatology postpandemic,1 which is driven, at least in part, by the potential concern that dermatologists will again experience the same regulatory and logistical barriers that limited teledermatology utilization prepandemic.
What has changed in reimbursement for teledermatology since the PHE ended?
The PHE ended on May 11, 2023, and already video platforms that were used during the pandemic to provide telemedicine visits but are not Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act compliant are now forbidden,2 Medicare virtual check-in appointments can only be conducted with established patients,4 and medical licensing requirements have been reinstated in most states such that patients must be located in the state where the provider is licensed to practice medicine at the time of a virtual visit.3 Although the CMS was granted wide freedoms to waive and suspend certain rules, this was only in the context of the PHE, and any lasting changes must be established by Congress.
Reassuringly, recent legislation via the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2023, authorized an extension of many of the CMS telehealth flexibilities that were in place during the PHE through December 31, 2024 (Table),2 such as allowing access to telehealth services in any geographic area in the United States rather than only rural areas, allowing patients to stay in their homes for telehealth visits rather than traveling to an approved health care facility, and allowing the delivery of telemedicine via audio-only technology if a patient is unable to use both audio and video. As of now, the place of service (POS) designation for telehealth visits will not revert back to the former code (POS 02) but will remain at POS 11 with the telehealth modifier -95 so physicians will be reimbursed at the full level of a non-facility physician’s office rate.4 The CMS has indicated that there will be no change in the reimbursement policy until after December 31, 20234; however, the sense of uncertainty around what happens after this date has made it hard for organizations and practices to fully commit to teledermatology services without knowing what the long-term financial impact may be. Some organizations have already noted that they plan to continue supporting telemedicine after the CMS flexibilities expire. Accountable Care Organizations have the ability to offer services that allow participating practitioners to continue the use of telemedicine visits to expand access to care. Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program policies vary by state and private health insurance policies vary by individual plans, but it should be noted that commercial coverage for telemedicine visits was already strong prior to the pandemic.2

What medical licensing requirements are in place now for telehealth?
During the PHE, medical licensing requirements also were relaxed, enabling providers to deliver telemedicine service in states where they were not licensed.3 As the PHE orders ended, some states including New York discontinued cross-state licensing waivers altogether,6 whereas others have enacted legislation to make them permanent or extend them for brief periods of time.3,6 One potential solution is the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact (https://www.imlcc.org/), which includes 39 states as of October 2023. This program expedites the process for physicians already licensed in participating states to obtain their medical license in another participating state, though licensing fees are required for each state in which a physician wants to practice. Furthermore, some states such as North Dakota, Hawaii, and Virginia have licensure by endorsement policies, which enable licensed physicians with specific qualifications to provide telehealth services in the endorsing state. Other states such as Florida, New Jersey, Louisiana, Minnesota, Nevada, and New Mexico have special telehealth registries that allow physicians in good standing who are licensed in other states to deliver telehealth services to in-state residents barring they do not provide in-person, in-state services.6 Lastly, some states have temporary practice laws to allow existing patients who need medical attention while traveling out of state to see their home providers virtually or in person under certain circumstances for a limited period of time.3,5 In Hawaii and New Hampshire, physicians with out-of-state licenses can provide consultative services in some circumstances.5
What changes have been made to make it easier for patients to use telehealth?
As the legislation around telemedicine is shifting postpandemic, it is important to address additional logistical barriers to teledermatology on a larger scale if the discipline is to stay in practice. On November 15, 2021, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act provided $65 billion in funding for broadband to expand access to high-speed internet. Some of this money was allocated to the Affordable Connectivity Program, which provides eligible households with a discount on broadband service and internet-connected devices. Eligible patrons can qualify for a discount of up to $75 per month for internet service and a one-time discount up to $100 on a laptop, desktop computer, or tablet purchased through a participating provider.6 Although a step in the right direction, the effects of this program on telemedicine encounters remains to be proven. Additionally, these programs do not address educational barriers to understanding how to utilize telemedicine platforms or provide incentives for practitioners to offer telemedicine services.
Final Thoughts
The pandemic taught our specialty a great deal about how to utilize telemedicine. For many dermatologists a return to in-person business as usual could not come fast enough; however, many practices have continued to offer at least some teledermatology services. Although the PHE waivers have ended, the extension of numerous CMS flexibilities through the end of 2024 allows us more time to develop sustainable policies to support the long-term health of telemedicine as a whole, both to sustain practices and to expand access to care in dermatology. The favorable attitudes of both patients and physicians about teledermatology have been clearly documented,1,7 and we should continue to safely expand the use of this technology.
The rapid expansion of teledermatology in the United States due to the COVID-19 pandemic has been well documented, 1 but where do we stand now that health care and society as a whole are back to a new version of normal? It is important to consider why telemedicine was able to grow so quickly during that period—the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) unilaterally changed policies related to provision of services and reimbursement thereof due to the public health emergency (PHE), which was declared by the Department of Health and Human Services in January 2020 to provide increased access to care for patients. Under the PHE, reimbursement rates for virtual visits improved, providers could care for patients from their homes and across state lines, and the use of video platforms that were not Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act compliant was allowed. 2,3
The trajectory of teledermatology after the pandemic, however, remains unclear. In a survey assessing dermatologists’ perceptions of telemedicine (N=4356), 97% used telemedicine during the pandemic but only 58% reported that they intended to continue using teledermatology postpandemic,1 which is driven, at least in part, by the potential concern that dermatologists will again experience the same regulatory and logistical barriers that limited teledermatology utilization prepandemic.
What has changed in reimbursement for teledermatology since the PHE ended?
The PHE ended on May 11, 2023, and already video platforms that were used during the pandemic to provide telemedicine visits but are not Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act compliant are now forbidden,2 Medicare virtual check-in appointments can only be conducted with established patients,4 and medical licensing requirements have been reinstated in most states such that patients must be located in the state where the provider is licensed to practice medicine at the time of a virtual visit.3 Although the CMS was granted wide freedoms to waive and suspend certain rules, this was only in the context of the PHE, and any lasting changes must be established by Congress.
Reassuringly, recent legislation via the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2023, authorized an extension of many of the CMS telehealth flexibilities that were in place during the PHE through December 31, 2024 (Table),2 such as allowing access to telehealth services in any geographic area in the United States rather than only rural areas, allowing patients to stay in their homes for telehealth visits rather than traveling to an approved health care facility, and allowing the delivery of telemedicine via audio-only technology if a patient is unable to use both audio and video. As of now, the place of service (POS) designation for telehealth visits will not revert back to the former code (POS 02) but will remain at POS 11 with the telehealth modifier -95 so physicians will be reimbursed at the full level of a non-facility physician’s office rate.4 The CMS has indicated that there will be no change in the reimbursement policy until after December 31, 20234; however, the sense of uncertainty around what happens after this date has made it hard for organizations and practices to fully commit to teledermatology services without knowing what the long-term financial impact may be. Some organizations have already noted that they plan to continue supporting telemedicine after the CMS flexibilities expire. Accountable Care Organizations have the ability to offer services that allow participating practitioners to continue the use of telemedicine visits to expand access to care. Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program policies vary by state and private health insurance policies vary by individual plans, but it should be noted that commercial coverage for telemedicine visits was already strong prior to the pandemic.2

What medical licensing requirements are in place now for telehealth?
During the PHE, medical licensing requirements also were relaxed, enabling providers to deliver telemedicine service in states where they were not licensed.3 As the PHE orders ended, some states including New York discontinued cross-state licensing waivers altogether,6 whereas others have enacted legislation to make them permanent or extend them for brief periods of time.3,6 One potential solution is the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact (https://www.imlcc.org/), which includes 39 states as of October 2023. This program expedites the process for physicians already licensed in participating states to obtain their medical license in another participating state, though licensing fees are required for each state in which a physician wants to practice. Furthermore, some states such as North Dakota, Hawaii, and Virginia have licensure by endorsement policies, which enable licensed physicians with specific qualifications to provide telehealth services in the endorsing state. Other states such as Florida, New Jersey, Louisiana, Minnesota, Nevada, and New Mexico have special telehealth registries that allow physicians in good standing who are licensed in other states to deliver telehealth services to in-state residents barring they do not provide in-person, in-state services.6 Lastly, some states have temporary practice laws to allow existing patients who need medical attention while traveling out of state to see their home providers virtually or in person under certain circumstances for a limited period of time.3,5 In Hawaii and New Hampshire, physicians with out-of-state licenses can provide consultative services in some circumstances.5
What changes have been made to make it easier for patients to use telehealth?
As the legislation around telemedicine is shifting postpandemic, it is important to address additional logistical barriers to teledermatology on a larger scale if the discipline is to stay in practice. On November 15, 2021, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act provided $65 billion in funding for broadband to expand access to high-speed internet. Some of this money was allocated to the Affordable Connectivity Program, which provides eligible households with a discount on broadband service and internet-connected devices. Eligible patrons can qualify for a discount of up to $75 per month for internet service and a one-time discount up to $100 on a laptop, desktop computer, or tablet purchased through a participating provider.6 Although a step in the right direction, the effects of this program on telemedicine encounters remains to be proven. Additionally, these programs do not address educational barriers to understanding how to utilize telemedicine platforms or provide incentives for practitioners to offer telemedicine services.
Final Thoughts
The pandemic taught our specialty a great deal about how to utilize telemedicine. For many dermatologists a return to in-person business as usual could not come fast enough; however, many practices have continued to offer at least some teledermatology services. Although the PHE waivers have ended, the extension of numerous CMS flexibilities through the end of 2024 allows us more time to develop sustainable policies to support the long-term health of telemedicine as a whole, both to sustain practices and to expand access to care in dermatology. The favorable attitudes of both patients and physicians about teledermatology have been clearly documented,1,7 and we should continue to safely expand the use of this technology.
- Kennedy J, Arey S, Hopkins Z, et al. Dermatologist perceptions of teledermatology implementation and future use after COVID-19: demographics, barriers, and insights. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:595-597.
- US Department of Health and Human Services. HHS fact sheet: telehealth flexibilities and resources and the COVID-19 public health emergency. Published May 10, 2023. Accessed October 18, 2023. https://www.hhs.gov/aboutnews/2023/05/10/hhs-fact-sheet-telehealth-flexibilities-resources-covid-19-public-health-emergency.html
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Licensing across state lines. Updated May 11, 2023. Accessed October 25, 2023. https://telehealth.hhs.gov/licensure/licensing-across-state-lines
- American Academy of Dermatology. Teledermatology and the COVID-19 pandemic. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.aad.org/member/practice/telederm/covid-19
- American Medical Association. Licensure & Telehealth. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/issue-brief-licensure-telehealth.pdf
- Federal Communications Commission. Affordable Connectivity Program. Updated June 29, 2023. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.fcc.gov/affordable-connectivity-program
- Tensen E, van der Heijden JP, Jaspers MWM, et al. Two decades of teledermatology: current status and integration in national healthcare systems. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2016;5:96-104.
- Kennedy J, Arey S, Hopkins Z, et al. Dermatologist perceptions of teledermatology implementation and future use after COVID-19: demographics, barriers, and insights. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:595-597.
- US Department of Health and Human Services. HHS fact sheet: telehealth flexibilities and resources and the COVID-19 public health emergency. Published May 10, 2023. Accessed October 18, 2023. https://www.hhs.gov/aboutnews/2023/05/10/hhs-fact-sheet-telehealth-flexibilities-resources-covid-19-public-health-emergency.html
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Licensing across state lines. Updated May 11, 2023. Accessed October 25, 2023. https://telehealth.hhs.gov/licensure/licensing-across-state-lines
- American Academy of Dermatology. Teledermatology and the COVID-19 pandemic. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.aad.org/member/practice/telederm/covid-19
- American Medical Association. Licensure & Telehealth. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/issue-brief-licensure-telehealth.pdf
- Federal Communications Commission. Affordable Connectivity Program. Updated June 29, 2023. Accessed October 12, 2023. https://www.fcc.gov/affordable-connectivity-program
- Tensen E, van der Heijden JP, Jaspers MWM, et al. Two decades of teledermatology: current status and integration in national healthcare systems. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2016;5:96-104.
