User login
Early Treatment of Lyme Disease Prompted by Histopathologic Analysis of the Abdomen of an Engorged Tick
To the Editor:
Lyme disease is caused by spirochetes of the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato species complex and transmitted to humans by the bite of the Ixodes scapularis tick. It was first classified as a nationally notifiable disease in 1991, and the incidence has risen remarkably since then.1 More than 63,000 cases are reported annually to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; however, this number reflects severe underreporting, as the true incidence of the disease is projected to be closer to 476,000 cases per year.2 Additionally, 95% of US cases occur in the Northeast and upper Midwest.3 Given the pervasiveness of Lyme disease, early and reliable diagnostic methodology is critical, especially in cases in which the timeline of inoculation is unclear. We present a case of Lyme disease that was discovered during a routine dermatologic visit.
A 77-year-old White man with no relevant medical history presented to a dermatology clinic in west-central Virginia for a routine skin check. Physical examination revealed a well-appearing patient without overt skin abnormalities. However, on closer evaluation, a 0.2×0.1-cm engorged black I scapularis tick was visualized on the left lateral upper back. There was a surrounding zone of erythema that measured less than the 5-cm-diameter criterion for erythema migrans.1
Upon questioning, the patient reported that he was unaware of the tick and could not provide a timeline for inoculation. To ensure proper treatment, the tick was removed in the office and a specimen was sent for histopathology. The arthropod was formalin fixed and paraffin embedded, and it was examined using hematoxylin and eosin and Warthin-Starry stains. Histopathology of the specimen revealed a blood-engorged arthropod. Warthin-Starry stain of the abdomen of the tick highlighted tiny strandlike spirochetes within the gut that were compatible with B burgdorferi (Figure). This finding prompted treatment with a 3-week course of doxycycline. Following treatment, erythema resolved. The patient experienced no sequelae.
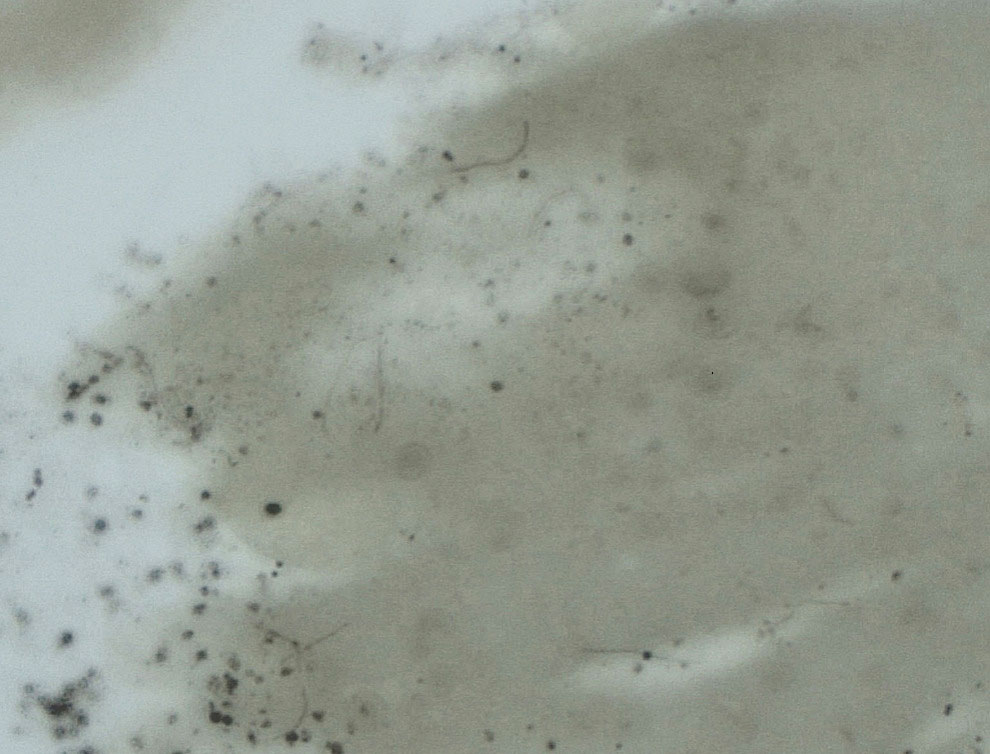
Lyme disease can cause a range of serious complications if left untreated, including arthritis, neurologic deficits, and heart block. During the early stages of disease, the sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic methods such as serologic testing are limited.4 The gold standard for the diagnosis of Lyme disease comprises culture and subsequent confirmation by polymerase chain reaction.1 However, cultivation of B burgdorferi is challenging.5 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends 2-tiered serologic antibody analysis, which has 27% sensitivity during the first week of cutaneous symptoms, and involves an enzyme-linked immunoassay followed by reflexive immunoblotting for positive or indeterminate cases.2,6 The precision of this method is limited by several variables; for example, seroconversion fails to occur in approximately 40% of cases, even after proven exposure to the spirochete.7 Furthermore, the sensitivity of the test is particularly low during the first 4 to 6 weeks of infection—before the body mounts a proper immune response; fewer than 50% of patients exhibit a positive response to the test at initial presentation.3
Clinical diagnosis of Lyme disease is possible, though the pathognomonic erythema migrans rash can be delayed for as long as 30 days and remains absent in 20% to 30% of patients.1 Prophylactic treatment can be offered to individuals who reside in a hyperendemic area and have a rash or have had an engorged Ixodes tick attached for longer than 36 hours.8
More definitive techniques for early diagnosis are needed to enable selective and accurate treatment. The standard of care for Lyme disease includes a 10-day course of doxycycline or a 14-day course of cefuroxime axetil or amoxicillin.9 Many patients tolerate treatment and achieve resolution of disease, but antibiotics are not benign, as some patients experience drug-related adverse effects such as photosensitivity, urticaria, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, esophagitis, hepatotoxicity, and the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction (fever, chills, rigors, nausea and vomiting, headache, tachycardia, hypotension, hyperventilation, flushing, myalgia, and exacerbation of lesions).10,11 In a group of 123 patients with Lyme disease, 30% treated with cefuroxime axetil and 32% treated with doxycycline had 1 or more drug-related adverse events.10 Additionally, avoidable antibiotic use is associated with increasing antibiotic resistance.12 Improved diagnostic accuracy would prevent unnecessary treatment. Galan and colleagues7 reported that Warthin-Starry staining of prepared sections of the abdomen of a tick allowed for detection of B burgdorferi with a sensitivity of 71% and specificity of 83%. This technique did not delay the final biopsy report and may be a promising adjunct to the diagnosis of early Lyme disease.7
Anecdotally, many patients who present with an attached and engorged tick are unaware of the timeline of their exposure. Histologic analysis of a removed tick could aid in early clinical decision-making—ie, when the diagnosis is unclear and treatment guidelines vary by region and circumstance. Improved sensitivity and specificity of diagnosis can prevent unnecessary antibiotic treatment, which is associated with adverse effects and escalation of antibiotic resistance.
- Borchers AT, Keen CL, Huntley AC, et al. Lyme disease: a rigorous review of diagnostic criteria and treatment. J Autoimmun. 2015;57:82-115. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2014.09.004
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Lyme disease: data and surveillance. February 14, 2024. Accessed March 5, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/datasurveillance/index.html
- Marques AR. Laboratory diagnosis of Lyme disease. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2015;29:295-307. doi:10.1016/j.idc.2015.02.005
- Bratton RL, Whiteside JW, Hovan MJ, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of Lyme disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83:566-571. doi:10.4065/83.5.566
- Berger B, Johnson R, Kodner C. Cultivation of Borrelia burgdorferi from human tick bite sites: a guide to the risk of infection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32(2 pt 1):184-187. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(95)90123-x
- Branda JA, Linskey K, Kim YA, et al. Two-tiered antibody testing for Lyme disease with use of 2 enzyme immunoassays, a whole-cell sonicate enzyme immunoassay followed by a VlsE C6 peptide enzyme immunoassay. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53:541-547. doi:10.1093/cid/cir464
- Galan A, Kupernik P, Cowper SE. Detection of Borrelia in Ixodes scapularis ticks by silver stain, immunohistochemical and direct immunofluorescent methods. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:473-477. doi:10.1111/cup.13143
- Nadelman RB, Nowakowski J, Fish D, et al; Prophylaxis with single-dose doxycycline for the prevention of Lyme disease after an Ixodes scapularis tick bite. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:79-84. doi:10.1056/NEJM200107123450201
- Lantos PM, Rumbaugh J, Bockenstedt LK, et al. Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), American Academy of Neurology (AAN), and American College of Rheumatology (ACR): 2020 guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of Lyme disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73:12-20. doi:10.1002/art.41562
- Nadelman RB, Luger SW, Frank E, et al. Comparison of cefuroxime axetil and doxycycline in the treatment of early Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1992;117:273-280. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-117-4-273
- Gresser U. Amoxicillin–clavulanic acid therapy may be associated with severe side effects—review of the literature. Eur J Med Res. 2001;6:139-149.
- Nathan C, Cars O. Antibiotic resistance—problems, progress, and prospects. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1761-1763. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1408040
To the Editor:
Lyme disease is caused by spirochetes of the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato species complex and transmitted to humans by the bite of the Ixodes scapularis tick. It was first classified as a nationally notifiable disease in 1991, and the incidence has risen remarkably since then.1 More than 63,000 cases are reported annually to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; however, this number reflects severe underreporting, as the true incidence of the disease is projected to be closer to 476,000 cases per year.2 Additionally, 95% of US cases occur in the Northeast and upper Midwest.3 Given the pervasiveness of Lyme disease, early and reliable diagnostic methodology is critical, especially in cases in which the timeline of inoculation is unclear. We present a case of Lyme disease that was discovered during a routine dermatologic visit.
A 77-year-old White man with no relevant medical history presented to a dermatology clinic in west-central Virginia for a routine skin check. Physical examination revealed a well-appearing patient without overt skin abnormalities. However, on closer evaluation, a 0.2×0.1-cm engorged black I scapularis tick was visualized on the left lateral upper back. There was a surrounding zone of erythema that measured less than the 5-cm-diameter criterion for erythema migrans.1
Upon questioning, the patient reported that he was unaware of the tick and could not provide a timeline for inoculation. To ensure proper treatment, the tick was removed in the office and a specimen was sent for histopathology. The arthropod was formalin fixed and paraffin embedded, and it was examined using hematoxylin and eosin and Warthin-Starry stains. Histopathology of the specimen revealed a blood-engorged arthropod. Warthin-Starry stain of the abdomen of the tick highlighted tiny strandlike spirochetes within the gut that were compatible with B burgdorferi (Figure). This finding prompted treatment with a 3-week course of doxycycline. Following treatment, erythema resolved. The patient experienced no sequelae.

Lyme disease can cause a range of serious complications if left untreated, including arthritis, neurologic deficits, and heart block. During the early stages of disease, the sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic methods such as serologic testing are limited.4 The gold standard for the diagnosis of Lyme disease comprises culture and subsequent confirmation by polymerase chain reaction.1 However, cultivation of B burgdorferi is challenging.5 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends 2-tiered serologic antibody analysis, which has 27% sensitivity during the first week of cutaneous symptoms, and involves an enzyme-linked immunoassay followed by reflexive immunoblotting for positive or indeterminate cases.2,6 The precision of this method is limited by several variables; for example, seroconversion fails to occur in approximately 40% of cases, even after proven exposure to the spirochete.7 Furthermore, the sensitivity of the test is particularly low during the first 4 to 6 weeks of infection—before the body mounts a proper immune response; fewer than 50% of patients exhibit a positive response to the test at initial presentation.3
Clinical diagnosis of Lyme disease is possible, though the pathognomonic erythema migrans rash can be delayed for as long as 30 days and remains absent in 20% to 30% of patients.1 Prophylactic treatment can be offered to individuals who reside in a hyperendemic area and have a rash or have had an engorged Ixodes tick attached for longer than 36 hours.8
More definitive techniques for early diagnosis are needed to enable selective and accurate treatment. The standard of care for Lyme disease includes a 10-day course of doxycycline or a 14-day course of cefuroxime axetil or amoxicillin.9 Many patients tolerate treatment and achieve resolution of disease, but antibiotics are not benign, as some patients experience drug-related adverse effects such as photosensitivity, urticaria, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, esophagitis, hepatotoxicity, and the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction (fever, chills, rigors, nausea and vomiting, headache, tachycardia, hypotension, hyperventilation, flushing, myalgia, and exacerbation of lesions).10,11 In a group of 123 patients with Lyme disease, 30% treated with cefuroxime axetil and 32% treated with doxycycline had 1 or more drug-related adverse events.10 Additionally, avoidable antibiotic use is associated with increasing antibiotic resistance.12 Improved diagnostic accuracy would prevent unnecessary treatment. Galan and colleagues7 reported that Warthin-Starry staining of prepared sections of the abdomen of a tick allowed for detection of B burgdorferi with a sensitivity of 71% and specificity of 83%. This technique did not delay the final biopsy report and may be a promising adjunct to the diagnosis of early Lyme disease.7
Anecdotally, many patients who present with an attached and engorged tick are unaware of the timeline of their exposure. Histologic analysis of a removed tick could aid in early clinical decision-making—ie, when the diagnosis is unclear and treatment guidelines vary by region and circumstance. Improved sensitivity and specificity of diagnosis can prevent unnecessary antibiotic treatment, which is associated with adverse effects and escalation of antibiotic resistance.
To the Editor:
Lyme disease is caused by spirochetes of the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato species complex and transmitted to humans by the bite of the Ixodes scapularis tick. It was first classified as a nationally notifiable disease in 1991, and the incidence has risen remarkably since then.1 More than 63,000 cases are reported annually to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; however, this number reflects severe underreporting, as the true incidence of the disease is projected to be closer to 476,000 cases per year.2 Additionally, 95% of US cases occur in the Northeast and upper Midwest.3 Given the pervasiveness of Lyme disease, early and reliable diagnostic methodology is critical, especially in cases in which the timeline of inoculation is unclear. We present a case of Lyme disease that was discovered during a routine dermatologic visit.
A 77-year-old White man with no relevant medical history presented to a dermatology clinic in west-central Virginia for a routine skin check. Physical examination revealed a well-appearing patient without overt skin abnormalities. However, on closer evaluation, a 0.2×0.1-cm engorged black I scapularis tick was visualized on the left lateral upper back. There was a surrounding zone of erythema that measured less than the 5-cm-diameter criterion for erythema migrans.1
Upon questioning, the patient reported that he was unaware of the tick and could not provide a timeline for inoculation. To ensure proper treatment, the tick was removed in the office and a specimen was sent for histopathology. The arthropod was formalin fixed and paraffin embedded, and it was examined using hematoxylin and eosin and Warthin-Starry stains. Histopathology of the specimen revealed a blood-engorged arthropod. Warthin-Starry stain of the abdomen of the tick highlighted tiny strandlike spirochetes within the gut that were compatible with B burgdorferi (Figure). This finding prompted treatment with a 3-week course of doxycycline. Following treatment, erythema resolved. The patient experienced no sequelae.

Lyme disease can cause a range of serious complications if left untreated, including arthritis, neurologic deficits, and heart block. During the early stages of disease, the sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic methods such as serologic testing are limited.4 The gold standard for the diagnosis of Lyme disease comprises culture and subsequent confirmation by polymerase chain reaction.1 However, cultivation of B burgdorferi is challenging.5 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends 2-tiered serologic antibody analysis, which has 27% sensitivity during the first week of cutaneous symptoms, and involves an enzyme-linked immunoassay followed by reflexive immunoblotting for positive or indeterminate cases.2,6 The precision of this method is limited by several variables; for example, seroconversion fails to occur in approximately 40% of cases, even after proven exposure to the spirochete.7 Furthermore, the sensitivity of the test is particularly low during the first 4 to 6 weeks of infection—before the body mounts a proper immune response; fewer than 50% of patients exhibit a positive response to the test at initial presentation.3
Clinical diagnosis of Lyme disease is possible, though the pathognomonic erythema migrans rash can be delayed for as long as 30 days and remains absent in 20% to 30% of patients.1 Prophylactic treatment can be offered to individuals who reside in a hyperendemic area and have a rash or have had an engorged Ixodes tick attached for longer than 36 hours.8
More definitive techniques for early diagnosis are needed to enable selective and accurate treatment. The standard of care for Lyme disease includes a 10-day course of doxycycline or a 14-day course of cefuroxime axetil or amoxicillin.9 Many patients tolerate treatment and achieve resolution of disease, but antibiotics are not benign, as some patients experience drug-related adverse effects such as photosensitivity, urticaria, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, esophagitis, hepatotoxicity, and the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction (fever, chills, rigors, nausea and vomiting, headache, tachycardia, hypotension, hyperventilation, flushing, myalgia, and exacerbation of lesions).10,11 In a group of 123 patients with Lyme disease, 30% treated with cefuroxime axetil and 32% treated with doxycycline had 1 or more drug-related adverse events.10 Additionally, avoidable antibiotic use is associated with increasing antibiotic resistance.12 Improved diagnostic accuracy would prevent unnecessary treatment. Galan and colleagues7 reported that Warthin-Starry staining of prepared sections of the abdomen of a tick allowed for detection of B burgdorferi with a sensitivity of 71% and specificity of 83%. This technique did not delay the final biopsy report and may be a promising adjunct to the diagnosis of early Lyme disease.7
Anecdotally, many patients who present with an attached and engorged tick are unaware of the timeline of their exposure. Histologic analysis of a removed tick could aid in early clinical decision-making—ie, when the diagnosis is unclear and treatment guidelines vary by region and circumstance. Improved sensitivity and specificity of diagnosis can prevent unnecessary antibiotic treatment, which is associated with adverse effects and escalation of antibiotic resistance.
- Borchers AT, Keen CL, Huntley AC, et al. Lyme disease: a rigorous review of diagnostic criteria and treatment. J Autoimmun. 2015;57:82-115. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2014.09.004
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Lyme disease: data and surveillance. February 14, 2024. Accessed March 5, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/datasurveillance/index.html
- Marques AR. Laboratory diagnosis of Lyme disease. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2015;29:295-307. doi:10.1016/j.idc.2015.02.005
- Bratton RL, Whiteside JW, Hovan MJ, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of Lyme disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83:566-571. doi:10.4065/83.5.566
- Berger B, Johnson R, Kodner C. Cultivation of Borrelia burgdorferi from human tick bite sites: a guide to the risk of infection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32(2 pt 1):184-187. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(95)90123-x
- Branda JA, Linskey K, Kim YA, et al. Two-tiered antibody testing for Lyme disease with use of 2 enzyme immunoassays, a whole-cell sonicate enzyme immunoassay followed by a VlsE C6 peptide enzyme immunoassay. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53:541-547. doi:10.1093/cid/cir464
- Galan A, Kupernik P, Cowper SE. Detection of Borrelia in Ixodes scapularis ticks by silver stain, immunohistochemical and direct immunofluorescent methods. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:473-477. doi:10.1111/cup.13143
- Nadelman RB, Nowakowski J, Fish D, et al; Prophylaxis with single-dose doxycycline for the prevention of Lyme disease after an Ixodes scapularis tick bite. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:79-84. doi:10.1056/NEJM200107123450201
- Lantos PM, Rumbaugh J, Bockenstedt LK, et al. Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), American Academy of Neurology (AAN), and American College of Rheumatology (ACR): 2020 guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of Lyme disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73:12-20. doi:10.1002/art.41562
- Nadelman RB, Luger SW, Frank E, et al. Comparison of cefuroxime axetil and doxycycline in the treatment of early Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1992;117:273-280. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-117-4-273
- Gresser U. Amoxicillin–clavulanic acid therapy may be associated with severe side effects—review of the literature. Eur J Med Res. 2001;6:139-149.
- Nathan C, Cars O. Antibiotic resistance—problems, progress, and prospects. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1761-1763. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1408040
- Borchers AT, Keen CL, Huntley AC, et al. Lyme disease: a rigorous review of diagnostic criteria and treatment. J Autoimmun. 2015;57:82-115. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2014.09.004
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Lyme disease: data and surveillance. February 14, 2024. Accessed March 5, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/datasurveillance/index.html
- Marques AR. Laboratory diagnosis of Lyme disease. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2015;29:295-307. doi:10.1016/j.idc.2015.02.005
- Bratton RL, Whiteside JW, Hovan MJ, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of Lyme disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83:566-571. doi:10.4065/83.5.566
- Berger B, Johnson R, Kodner C. Cultivation of Borrelia burgdorferi from human tick bite sites: a guide to the risk of infection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32(2 pt 1):184-187. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(95)90123-x
- Branda JA, Linskey K, Kim YA, et al. Two-tiered antibody testing for Lyme disease with use of 2 enzyme immunoassays, a whole-cell sonicate enzyme immunoassay followed by a VlsE C6 peptide enzyme immunoassay. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53:541-547. doi:10.1093/cid/cir464
- Galan A, Kupernik P, Cowper SE. Detection of Borrelia in Ixodes scapularis ticks by silver stain, immunohistochemical and direct immunofluorescent methods. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:473-477. doi:10.1111/cup.13143
- Nadelman RB, Nowakowski J, Fish D, et al; Prophylaxis with single-dose doxycycline for the prevention of Lyme disease after an Ixodes scapularis tick bite. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:79-84. doi:10.1056/NEJM200107123450201
- Lantos PM, Rumbaugh J, Bockenstedt LK, et al. Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), American Academy of Neurology (AAN), and American College of Rheumatology (ACR): 2020 guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of Lyme disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73:12-20. doi:10.1002/art.41562
- Nadelman RB, Luger SW, Frank E, et al. Comparison of cefuroxime axetil and doxycycline in the treatment of early Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1992;117:273-280. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-117-4-273
- Gresser U. Amoxicillin–clavulanic acid therapy may be associated with severe side effects—review of the literature. Eur J Med Res. 2001;6:139-149.
- Nathan C, Cars O. Antibiotic resistance—problems, progress, and prospects. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1761-1763. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1408040
PRACTICE POINTS
- Lyme disease is increasingly common in the United States.
- Lyme disease can cause debilitating sequelae if left untreated, including arthritis, neurologic deficits, and heart block.
- Diagnostic methods for identifying early Lyme disease have limited sensitivity and specificity, necessitating alternative strategies for making an accurate diagnosis and initiating treatment.
