User login
Periungual Papules in an Elderly Woman
The Diagnosis: Multicentric Reticulohistiocytosis
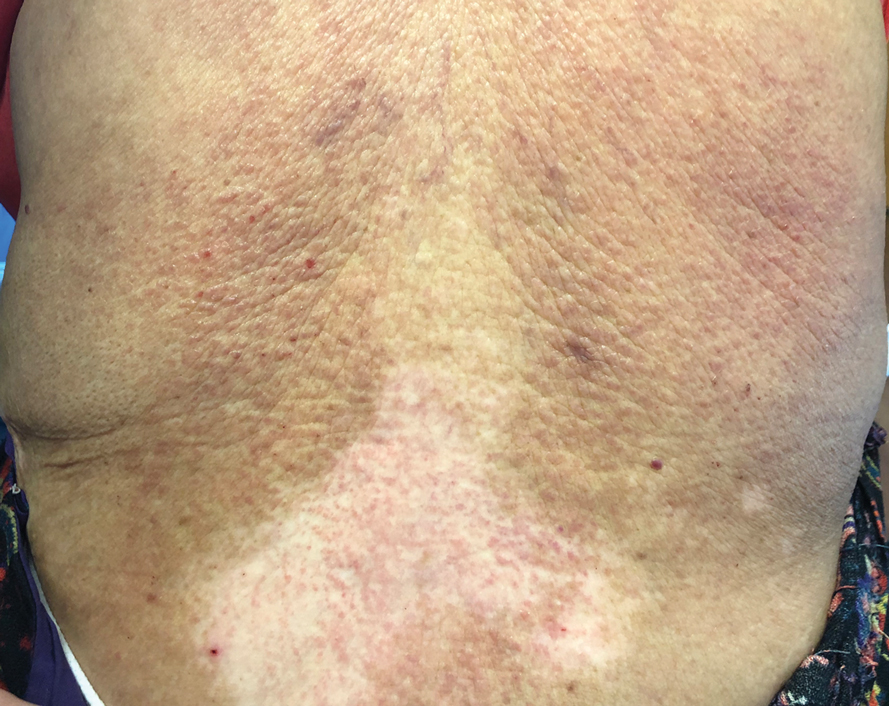
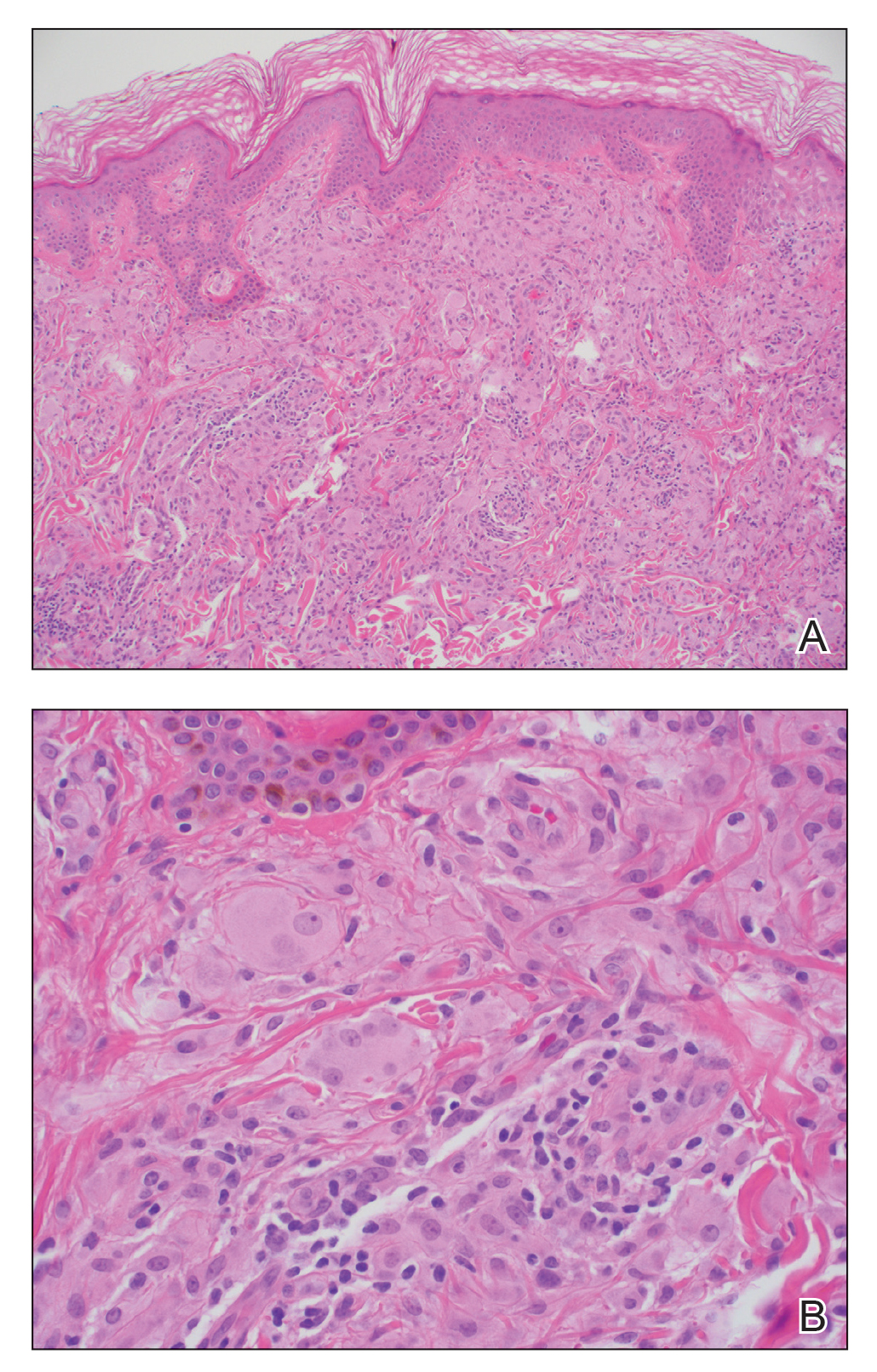
Te patient presented with pink papules coalescing into plaques on the upper chest and lower back (Figure 1) as well as a characteristic finding of periungual papules with a coral bead appearance. Histopathologic examination revealed a dense infiltrate of epithelioid histiocytes with amphophilic ground-glass cytoplasm in a nodular configuration (Figure 2). This pattern in conjunction with the clinical features seen in our patient was consistent with a diagnosis of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (MRH).1-3 The cutaneous symptoms were managed with triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily and oral hydroxyzine 10 mg 3 times daily as needed for itching with moderate improvement. She was referred to rheumatology for arthritis management, and the initial cancer screening was negative.
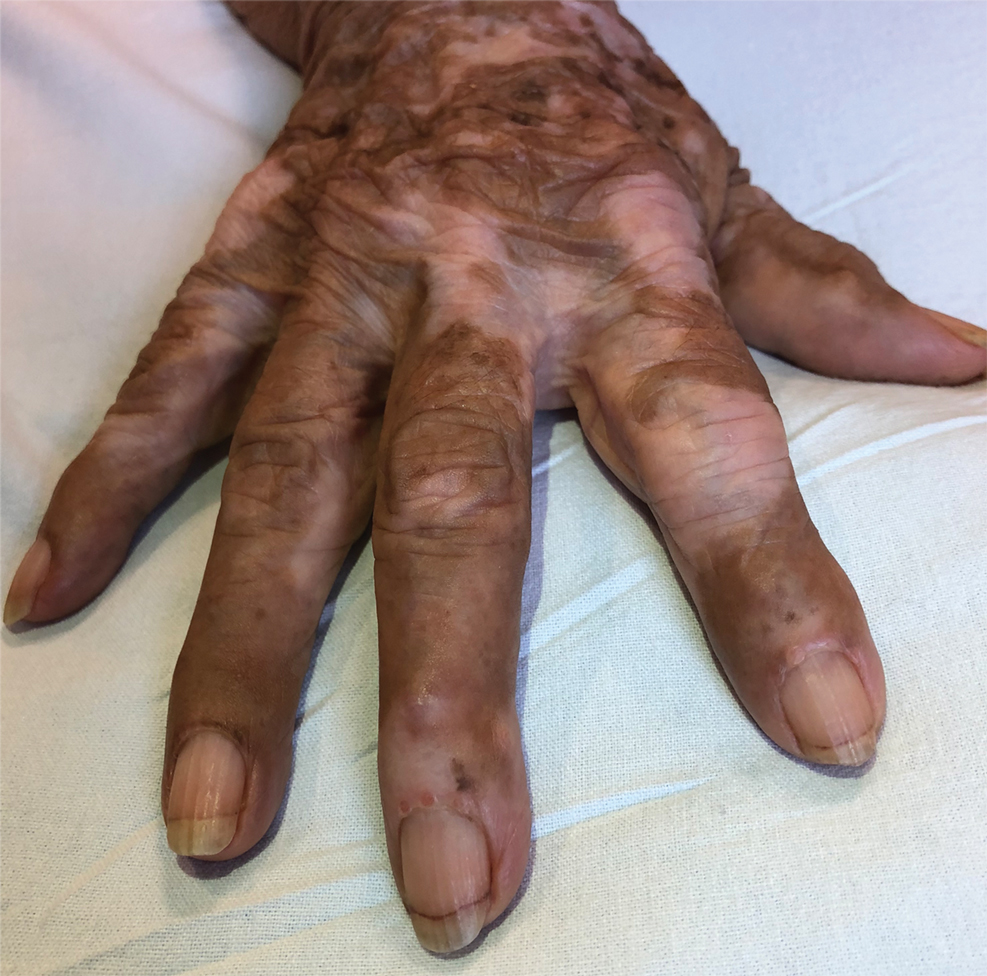
Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis is a rare granulomatous disease characterized by papulonodular cutaneous lesions and severe erosive arthritis. It has an insidious onset and most commonly affects middle-aged women.1 Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis typically presents as rounded pruritic papules or nodules that may be pink, red, or brown primarily affecting the face and distal upper extremities.1,3 Mucosal involvement occurs in more than half of patients and is characterized by multiple erythematous papules and nodules on the oral and nasopharyngeal mucosae that rarely can produce leonine facies.2 A hallmark feature of MRH is the presence of multiple shiny erythematous papules along the proximal and lateral nail folds that take on a coral bead appearance.1,3,4 Furthermore, nail changes such as atrophy, longitudinal ridging, brittleness, and hyperpigmentation can occur secondary to a synovial reaction that disturbs the nail matrix.4,5
Joint involvement precedes cutaneous involvement in most cases of MRH.1,5 Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis is associated with a symmetric destructive arthritis affecting the hands, knees, shoulders, and hips that often is associated with pain, stiffness, and swelling.1,3 The arthritis rapidly progresses in the early stages of the disease but then becomes less active over the subsequent 8 to 10 years.1 It has the potential to develop into arthritis mutilans, an end-stage form of arthritis also seen in psoriatic and rheumatoid arthritis that leads to severe joint deformity and debilitation.1,2
The etiology of MRH still is unknown, but it has an association with underlying malignancy in up to 25% of patients.6 Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis has been reported in the context of a wide variety of malignancies including melanoma; sarcoma; lymphoma; leukemia; and carcinomas of the breast, colon, and lung. In some cases, the diagnosis of MRH may even precede the diagnosis of cancer.3 Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis also may be associated with autoimmune conditions,3 as seen in our patient who had a history of both hypothyroidism and vitiligo.
Histopathologic examination is essential in distinguishing MRH from other autoimmune disorders associated with hand lesions, rash, and arthralgia. Erythema elevatum diutinum is associated with symmetric, violaceous, red or brown papules and plaques located on the extensor surfaces of the extremities and hands; however, histology reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis with a mixture of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and lymphocytes.7 Dermatomyositis may present with arthralgia, flattopped, erythematous (Gottron) papules localized over the proximal interphalangeal and distal interphalangeal joints, as well as proximal nail findings. The latter generally presents with periungual erythema associated with dilated capillary loops rather than the discrete orderly papules seen in MRH. Histologic examination of dermatomyositis shows mild epidermal atrophy, vacuolar changes in the basal keratinocyte layer, and a dermal perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate.8 Because MRH initially can present with joint symptoms and hand nodules, it may be confused with rheumatoid arthritis. However, rheumatoid arthritis typically is associated with severe osteopenia and tends to affect the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints rather than the distal interphalangeal joints that most often are affected in MRH.1 Histologic examination of rheumatoid nodules reveals palisading granulomas surrounding a central area of fibrinoid necrosis.9 Sarcoidosis is a multisystem disease that can present with cutaneous involvement including erythema nodosum, skin plaques, subcutaneous nodules, and papular eruptions in addition to joint lesions.10 Sarcoidosis most frequently involves the lungs, manifesting as diffuse interstitial lung disease with bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy. Furthermore, histologic examination of lesions demonstrates classic noncaseating granulomas containing epithelioid cells, multinucleated giant cells with inclusion bodies, and lymphocytes.11
A skin biopsy is required to establish the diagnosis of MRH. In general, patients with MRH and no underlying malignancy have a good prognosis and respond to anti-inflammatory therapies such as nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and corticosteroids. Other agents including methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, and tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors also have been effective in more severe cases.1,3,12 Finally, in addition to treating the cutaneous manifestations of MRH, it is important to screen patients for underlying malignancies and other autoimmune conditions.
- Tajirian AL, Malik MK, Robinson-Bostom L, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. Clin Dermatol. 2006;24:486-492.
- Gold RH, Metzger AL, Mirra JM, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (lipoid dermato-arthritis). an erosive polyarthritis with distinctive clinical, roentgenographic and pathologic features. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1975;124:610-624.
- Luz FB, Gaspar TAP, Kalil-Gaspar N, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2001;15:524-531.
- Barrow MV. The nails in multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. (lipoid dermato-arthritis). Arch Dermatol. 1967;95:200-201.
- Barrow MV, Holubar K. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. a review of 33 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 1969;48:287-305.
- Snow JL, Muller SA. Malignancy-associated multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: a clinical, histological and immunophenotypic study. Br J Dermatol. 1995;133:71-76.
- Yiannias JA, el-Azhary RA, Gibson LE. Erythema elevatum diutinum: a clinical and histopathologic study of 13 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26:38-44.
- Smith ES, Hallman JR, DeLuca AM, et al. Dermatomyositis: a clinicopathological study of 40 patients. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009; 31:61-67.
- Athanasou NA, Quinn J, Woods CG, et al. Immunohistology of rheumatoid nodules and rheumatoid synovium. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988;47:398-403.
- Yanardag H, Pamuk ON, Karayel T. Cutaneous involvement in sarcoidosis: analysis of the features in 170 patients. Respir Med. 2003;97:978-982.
- Ma Y, Gal A, Koss MN. The pathology of pulmonary sarcoidosis: update. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2007;24:150-161.
- Kovach BT, Calamia KT, Walsh JS, et al. Treatment of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis with etanercept. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:919-921.
The Diagnosis: Multicentric Reticulohistiocytosis
Te patient presented with pink papules coalescing into plaques on the upper chest and lower back (Figure 1) as well as a characteristic finding of periungual papules with a coral bead appearance. Histopathologic examination revealed a dense infiltrate of epithelioid histiocytes with amphophilic ground-glass cytoplasm in a nodular configuration (Figure 2). This pattern in conjunction with the clinical features seen in our patient was consistent with a diagnosis of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (MRH).1-3 The cutaneous symptoms were managed with triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily and oral hydroxyzine 10 mg 3 times daily as needed for itching with moderate improvement. She was referred to rheumatology for arthritis management, and the initial cancer screening was negative.
Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis is a rare granulomatous disease characterized by papulonodular cutaneous lesions and severe erosive arthritis. It has an insidious onset and most commonly affects middle-aged women.1 Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis typically presents as rounded pruritic papules or nodules that may be pink, red, or brown primarily affecting the face and distal upper extremities.1,3 Mucosal involvement occurs in more than half of patients and is characterized by multiple erythematous papules and nodules on the oral and nasopharyngeal mucosae that rarely can produce leonine facies.2 A hallmark feature of MRH is the presence of multiple shiny erythematous papules along the proximal and lateral nail folds that take on a coral bead appearance.1,3,4 Furthermore, nail changes such as atrophy, longitudinal ridging, brittleness, and hyperpigmentation can occur secondary to a synovial reaction that disturbs the nail matrix.4,5
Joint involvement precedes cutaneous involvement in most cases of MRH.1,5 Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis is associated with a symmetric destructive arthritis affecting the hands, knees, shoulders, and hips that often is associated with pain, stiffness, and swelling.1,3 The arthritis rapidly progresses in the early stages of the disease but then becomes less active over the subsequent 8 to 10 years.1 It has the potential to develop into arthritis mutilans, an end-stage form of arthritis also seen in psoriatic and rheumatoid arthritis that leads to severe joint deformity and debilitation.1,2
The etiology of MRH still is unknown, but it has an association with underlying malignancy in up to 25% of patients.6 Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis has been reported in the context of a wide variety of malignancies including melanoma; sarcoma; lymphoma; leukemia; and carcinomas of the breast, colon, and lung. In some cases, the diagnosis of MRH may even precede the diagnosis of cancer.3 Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis also may be associated with autoimmune conditions,3 as seen in our patient who had a history of both hypothyroidism and vitiligo.
Histopathologic examination is essential in distinguishing MRH from other autoimmune disorders associated with hand lesions, rash, and arthralgia. Erythema elevatum diutinum is associated with symmetric, violaceous, red or brown papules and plaques located on the extensor surfaces of the extremities and hands; however, histology reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis with a mixture of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and lymphocytes.7 Dermatomyositis may present with arthralgia, flattopped, erythematous (Gottron) papules localized over the proximal interphalangeal and distal interphalangeal joints, as well as proximal nail findings. The latter generally presents with periungual erythema associated with dilated capillary loops rather than the discrete orderly papules seen in MRH. Histologic examination of dermatomyositis shows mild epidermal atrophy, vacuolar changes in the basal keratinocyte layer, and a dermal perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate.8 Because MRH initially can present with joint symptoms and hand nodules, it may be confused with rheumatoid arthritis. However, rheumatoid arthritis typically is associated with severe osteopenia and tends to affect the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints rather than the distal interphalangeal joints that most often are affected in MRH.1 Histologic examination of rheumatoid nodules reveals palisading granulomas surrounding a central area of fibrinoid necrosis.9 Sarcoidosis is a multisystem disease that can present with cutaneous involvement including erythema nodosum, skin plaques, subcutaneous nodules, and papular eruptions in addition to joint lesions.10 Sarcoidosis most frequently involves the lungs, manifesting as diffuse interstitial lung disease with bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy. Furthermore, histologic examination of lesions demonstrates classic noncaseating granulomas containing epithelioid cells, multinucleated giant cells with inclusion bodies, and lymphocytes.11
A skin biopsy is required to establish the diagnosis of MRH. In general, patients with MRH and no underlying malignancy have a good prognosis and respond to anti-inflammatory therapies such as nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and corticosteroids. Other agents including methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, and tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors also have been effective in more severe cases.1,3,12 Finally, in addition to treating the cutaneous manifestations of MRH, it is important to screen patients for underlying malignancies and other autoimmune conditions.
The Diagnosis: Multicentric Reticulohistiocytosis
Te patient presented with pink papules coalescing into plaques on the upper chest and lower back (Figure 1) as well as a characteristic finding of periungual papules with a coral bead appearance. Histopathologic examination revealed a dense infiltrate of epithelioid histiocytes with amphophilic ground-glass cytoplasm in a nodular configuration (Figure 2). This pattern in conjunction with the clinical features seen in our patient was consistent with a diagnosis of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (MRH).1-3 The cutaneous symptoms were managed with triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily and oral hydroxyzine 10 mg 3 times daily as needed for itching with moderate improvement. She was referred to rheumatology for arthritis management, and the initial cancer screening was negative.
Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis is a rare granulomatous disease characterized by papulonodular cutaneous lesions and severe erosive arthritis. It has an insidious onset and most commonly affects middle-aged women.1 Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis typically presents as rounded pruritic papules or nodules that may be pink, red, or brown primarily affecting the face and distal upper extremities.1,3 Mucosal involvement occurs in more than half of patients and is characterized by multiple erythematous papules and nodules on the oral and nasopharyngeal mucosae that rarely can produce leonine facies.2 A hallmark feature of MRH is the presence of multiple shiny erythematous papules along the proximal and lateral nail folds that take on a coral bead appearance.1,3,4 Furthermore, nail changes such as atrophy, longitudinal ridging, brittleness, and hyperpigmentation can occur secondary to a synovial reaction that disturbs the nail matrix.4,5
Joint involvement precedes cutaneous involvement in most cases of MRH.1,5 Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis is associated with a symmetric destructive arthritis affecting the hands, knees, shoulders, and hips that often is associated with pain, stiffness, and swelling.1,3 The arthritis rapidly progresses in the early stages of the disease but then becomes less active over the subsequent 8 to 10 years.1 It has the potential to develop into arthritis mutilans, an end-stage form of arthritis also seen in psoriatic and rheumatoid arthritis that leads to severe joint deformity and debilitation.1,2
The etiology of MRH still is unknown, but it has an association with underlying malignancy in up to 25% of patients.6 Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis has been reported in the context of a wide variety of malignancies including melanoma; sarcoma; lymphoma; leukemia; and carcinomas of the breast, colon, and lung. In some cases, the diagnosis of MRH may even precede the diagnosis of cancer.3 Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis also may be associated with autoimmune conditions,3 as seen in our patient who had a history of both hypothyroidism and vitiligo.
Histopathologic examination is essential in distinguishing MRH from other autoimmune disorders associated with hand lesions, rash, and arthralgia. Erythema elevatum diutinum is associated with symmetric, violaceous, red or brown papules and plaques located on the extensor surfaces of the extremities and hands; however, histology reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis with a mixture of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and lymphocytes.7 Dermatomyositis may present with arthralgia, flattopped, erythematous (Gottron) papules localized over the proximal interphalangeal and distal interphalangeal joints, as well as proximal nail findings. The latter generally presents with periungual erythema associated with dilated capillary loops rather than the discrete orderly papules seen in MRH. Histologic examination of dermatomyositis shows mild epidermal atrophy, vacuolar changes in the basal keratinocyte layer, and a dermal perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate.8 Because MRH initially can present with joint symptoms and hand nodules, it may be confused with rheumatoid arthritis. However, rheumatoid arthritis typically is associated with severe osteopenia and tends to affect the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints rather than the distal interphalangeal joints that most often are affected in MRH.1 Histologic examination of rheumatoid nodules reveals palisading granulomas surrounding a central area of fibrinoid necrosis.9 Sarcoidosis is a multisystem disease that can present with cutaneous involvement including erythema nodosum, skin plaques, subcutaneous nodules, and papular eruptions in addition to joint lesions.10 Sarcoidosis most frequently involves the lungs, manifesting as diffuse interstitial lung disease with bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy. Furthermore, histologic examination of lesions demonstrates classic noncaseating granulomas containing epithelioid cells, multinucleated giant cells with inclusion bodies, and lymphocytes.11
A skin biopsy is required to establish the diagnosis of MRH. In general, patients with MRH and no underlying malignancy have a good prognosis and respond to anti-inflammatory therapies such as nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and corticosteroids. Other agents including methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, and tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors also have been effective in more severe cases.1,3,12 Finally, in addition to treating the cutaneous manifestations of MRH, it is important to screen patients for underlying malignancies and other autoimmune conditions.
- Tajirian AL, Malik MK, Robinson-Bostom L, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. Clin Dermatol. 2006;24:486-492.
- Gold RH, Metzger AL, Mirra JM, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (lipoid dermato-arthritis). an erosive polyarthritis with distinctive clinical, roentgenographic and pathologic features. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1975;124:610-624.
- Luz FB, Gaspar TAP, Kalil-Gaspar N, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2001;15:524-531.
- Barrow MV. The nails in multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. (lipoid dermato-arthritis). Arch Dermatol. 1967;95:200-201.
- Barrow MV, Holubar K. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. a review of 33 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 1969;48:287-305.
- Snow JL, Muller SA. Malignancy-associated multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: a clinical, histological and immunophenotypic study. Br J Dermatol. 1995;133:71-76.
- Yiannias JA, el-Azhary RA, Gibson LE. Erythema elevatum diutinum: a clinical and histopathologic study of 13 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26:38-44.
- Smith ES, Hallman JR, DeLuca AM, et al. Dermatomyositis: a clinicopathological study of 40 patients. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009; 31:61-67.
- Athanasou NA, Quinn J, Woods CG, et al. Immunohistology of rheumatoid nodules and rheumatoid synovium. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988;47:398-403.
- Yanardag H, Pamuk ON, Karayel T. Cutaneous involvement in sarcoidosis: analysis of the features in 170 patients. Respir Med. 2003;97:978-982.
- Ma Y, Gal A, Koss MN. The pathology of pulmonary sarcoidosis: update. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2007;24:150-161.
- Kovach BT, Calamia KT, Walsh JS, et al. Treatment of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis with etanercept. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:919-921.
- Tajirian AL, Malik MK, Robinson-Bostom L, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. Clin Dermatol. 2006;24:486-492.
- Gold RH, Metzger AL, Mirra JM, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (lipoid dermato-arthritis). an erosive polyarthritis with distinctive clinical, roentgenographic and pathologic features. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1975;124:610-624.
- Luz FB, Gaspar TAP, Kalil-Gaspar N, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2001;15:524-531.
- Barrow MV. The nails in multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. (lipoid dermato-arthritis). Arch Dermatol. 1967;95:200-201.
- Barrow MV, Holubar K. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. a review of 33 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 1969;48:287-305.
- Snow JL, Muller SA. Malignancy-associated multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: a clinical, histological and immunophenotypic study. Br J Dermatol. 1995;133:71-76.
- Yiannias JA, el-Azhary RA, Gibson LE. Erythema elevatum diutinum: a clinical and histopathologic study of 13 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26:38-44.
- Smith ES, Hallman JR, DeLuca AM, et al. Dermatomyositis: a clinicopathological study of 40 patients. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009; 31:61-67.
- Athanasou NA, Quinn J, Woods CG, et al. Immunohistology of rheumatoid nodules and rheumatoid synovium. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988;47:398-403.
- Yanardag H, Pamuk ON, Karayel T. Cutaneous involvement in sarcoidosis: analysis of the features in 170 patients. Respir Med. 2003;97:978-982.
- Ma Y, Gal A, Koss MN. The pathology of pulmonary sarcoidosis: update. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2007;24:150-161.
- Kovach BT, Calamia KT, Walsh JS, et al. Treatment of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis with etanercept. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:919-921.
A 79-year-old woman presented with pruritic papules and plaques on the chest, back, arms, hands, legs, and feet of 1 year’s duration. She reported a history of hypothyroidism, arthritis, and vitiligo but denied a history of cancer. Physical examination showed pink papules coalescing into plaques on the upper chest and lower back as well as lichenified plaques on the forearms and knees. Erythematous papules on the proximal nail folds of the right first and second digits also were noted. Multiple depigmented patches on the hands, wrists, arms, and lower back also were present, and deformities of the hands and bulbous-appearing knees were observed. Results from a complete blood cell count and blood chemistry analyses showed mild anemia but were otherwise normal. Radiography of the right knee showed degenerative changes and periarticular radiolucencies consistent with an inflammatory arthropathy. A 4-mm punch biopsy specimen from the back was obtained for histopathologic examination.
Graft-versus-host Disease Presenting Along Blaschko Lines: Cutaneous Mosaicism
To the Editor:
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is a common and serious complication seen most often with bone marrow transplantation and peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. With these therapies, functional lymphoid cells are transferred from an immunocompetent donor into a nongenetically identical recipient, or "host." Because of the allogeneic nature of these transplants, the transplanted lymphoid cells have a high potential to recognize and treat the host's cells as foreign, and the resultant clinical and pathologic picture is that of GVHD. The primary organ systems affected in this immune response are the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and hepatobiliary system.1,2 Cutaneous manifestations are by far the most common.3
Although notable gains have been made in elucidating the causes, risk factors, and mechanisms that result in the clinical picture of GVHD, gaps in our knowledge and understanding still exist. Our patient represents a unique case of unilateral GVHD occurring along Blaschko lines, which has important implications for both recognizing and understanding the pathogenesis of GVHD.
A 35-year-old woman was diagnosed with stage IV follicular lymphoma and received various chemotherapy regimens over the next 4 years. Unfortunately, her disease progressed despite treatment. At 39 years of age, she underwent a nonmyeloablative allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation from a single HLA-mismatched sibling. She was placed on prednisone and cyclosporine for immunosuppression. High-dose acyclovir prophylaxis also was initiated given her history of zoster affecting the right C3 dermatome. Successful engraftment was achieved, with molecular studies showing 100% of cells following transplantation were of donor origin. Restaging at 1 and 2 years following transplantation found her to be in complete remission.
At 2 years following transplantation, she began a slow taper of immunosuppressive medications. She was successfully weaned off prednisone and continued to gradually reduce the cyclosporine dose. Toward the end of the cyclosporine taper 3 months later, she developed a pruritic eruption on the left proximal arm.
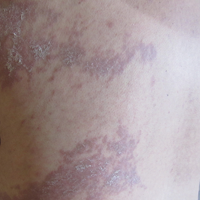
She was seen in a bone marrow transplant clinic 4 weeks after the rash developed. On examination, she had multiple, violaceous, lichenoid papules coalescing into linear bandlike plaques. One plaque extended along the left upper arm and 2 others encircled the left hemithorax, respecting the midline. She was treated empirically for zoster with valacyclovir 1 g 3 times daily based on the presumed dermatomal distribution of the eruption. Despite treatment, the rash progressed, and she developed fever. Eight days later, she was admitted with concern for disseminated zoster (Figure). Viral tissue cultures and polymerase chain reaction analysis of the lesions were negative for varicella-zoster virus and herpes simplex viruses 1 and 2. Biopsies of skin lesions on the arm and trunk were both consistent with GVHD.
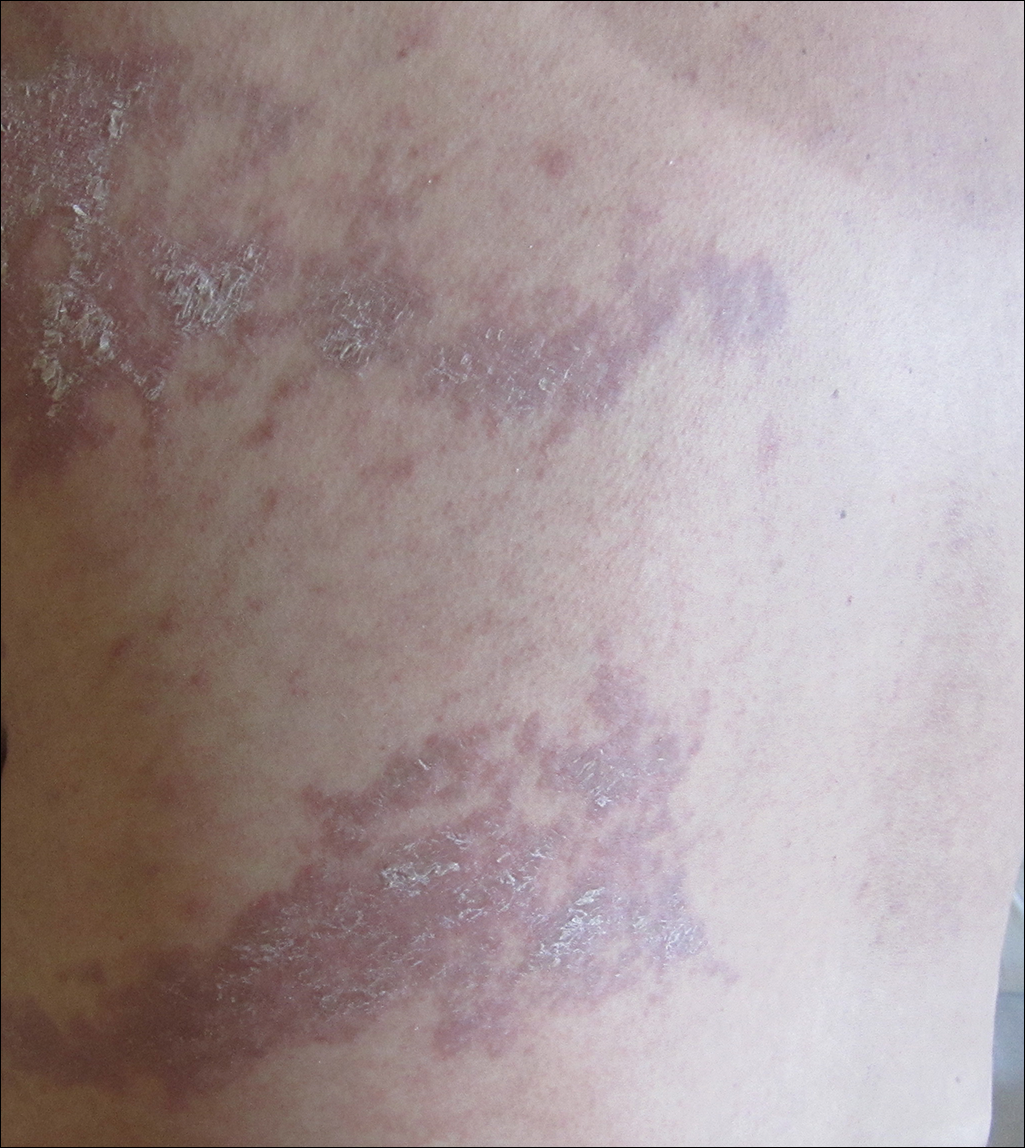
Given the clinical history, characteristic lesion morphology, and distinct linear distribution along with histopathological confirmation, a diagnosis of GVHD along Blaschko lines was made. Recognizing the cause to be immunogenic rather than infectious, immunosuppressive medications were started. In addition to increasing the prednisone and cyclosporine back to therapeutic levels, she received weekly methylprednisolone. With treatment, she showed gradual but marked improvement.
Six cases of linear GVHD have occurred as an isotopic response along dermatomes previously affected by varicella-zoster virus.4-8 These cases give credence to the idea that a cutaneous viral infection may alter the skin through unknown mechanisms, predisposing it to become affected by GVHD. Notably, this phenomenon occurred despite absence of a persistent viral genome when assessed using polymerase chain reaction analysis.4
An additional 3 cases of GVHD occurring in a dermatomal distribution without any prior infections in those areas have been reported.9,10 Of note, 2 of 3 patients did have episodes of zoster occur at other sites following transplantation and did not develop GVHD symptoms in any of those locations.9 Interestingly, controversy exists as to whether the distribution of these lesions was dermatomal or followed Blaschko lines.11
Two cases of linear GVHD have been reported in which lesions were identified as occurring along Blaschko lines.12,13 The lines of Blaschko, first described in 1901, correspond to cellular migration patterns during embryological development.14 Postzygotic mutations causing epidermal cell mosaicism may result in skin disorders occurring in segmental areas defined by the Blaschko lines.15-17 Accordingly, the Blaschko-linear pattern in GVHD suggests cellular mosaicism as the etiology in this case. Although the host's immune system develops immunotolerance to both cellular lineages during maturation, transplanted lymphoid cells from a nongenetically identical sibling may identify just one of the cell lines as nonself, producing a selective pattern of GVHD18 confined to the distribution of the genetically disparate cell line, which occurs along the lines of Blaschko in the skin. Candidate genes for mutations that would produce a mosaic following transplant GVHD include any of the 25 to 30 known minor histocompatibility antigens (or any of the several hundred yet to be found).19 Although well established for monogenic dominant disorders, in 2007 it was recognized that a postzygotic mutation can cause many complex polygenetic disorders, including GVHD, to manifest in a limited segmental pattern. This understanding, along with retrospective case review, has brought into question previously reported "dermatomal" or "zosteriform" presentations of GVHD, asserting that the linear patterns were misidentified and thus inappropriately attributed to a postviral response.20 Recognition of the Blaschko-linear distribution holds significance in both identifying lesion etiology and understanding disease pathogenesis and treatment.
Our patient illustrates a case of a Blaschko-linear GVHD. The distinctive pattern of her physical findings strongly favored epidermal cell mosaicism as the etiology of her disease. More than just a phenotypically unique case, it provided further insight into the complex etiology underlying GVHD and iterated the basic concepts of Blaschko lines and genetic alterations in development.
- Thomas ED, Storb R, Clift RA, et al. Bone-marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1975;292:895-902.
- Lee SJ, Vogelsang G, Flowers ME. Chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2003;9:215-233.
- Johnson ML, Farmer ER. Graft versus host reactions in dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;38:369-384.
- Baselga E, Drolet BA, Segura AD, et al. Dermatomal lichenoid chronic graft-vs-host disease following varicella-zoster infection despite absence of viral genome. J Cutan Pathol. 1996;23:576-581.
- Lacour JP, Sirvent N, Monpoux F, et al. Dermatomal chronic cutaneous graft versus host disease at the site of prior herpes zoster. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:587-589.
- Cordoba S, Fraga J, Bartolome B, et al. Giant cell lichenoid dermatitis within herpes zoster scars in a bone marrow recipient. J Cutan Pathol. 2000;27:255-257.
- Sanli H, Anadolu R, Arat M, et al. Dermatomal lichenoid graft-versus-host disease within herpes zoster scars. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:562-564.
- Martires KJ, Baird K, Citrin DE, et al. Localization of sclerotic-type chronic graft-versus-host disease to sites of skin injury: potential insight into the mechanism of isomorphic and isotopic responses. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:1081-1086.
- Freemer CS, Farmer ER, Corio RL, et al. Lichenoid chronic graft-vs-host disease occurring in a dermatomal distribution. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:70-72.
- Cohen PR, Hymes SR. Linear and dermatomal cutaneous graft-versus-host disease. South Med J. 1994;87:758-761.
- Reisfeld PL. Linear lichenoid graft-vs-host disease. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:1207-1208.
- Beers B, Kalish RS, Kaye VN, et al. Unilateral linear lichenoid eruption after bone marrow transplantation: an unmasking of tolerance to an abnormal keratinocyte clone? J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28(5, pt 2):888-892.
- Wilson BB, Lockman DW. Linear lichenoid graft-vs-host disease. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:1206-1207.
- Goldberg I, Sprecher E. Patterned disorders in dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2011;29:498-503.
- Colman SD, Rasmussen SA, Ho VT, et al. Somatic mosaicism in a patient with neurofibromatosis type 1. Am J Hum Genet. 1996;58:484-490.
- Munro CS, Wilkie AO. Epidermal mosaicism producing localised acne: somatic mutation in FGFR2. Lancet. 1998;352:704-705.
- Sakuntabhai A, Dhitavat J, Burge S, et al. Mosaicism for ATP2A2 mutations causes segmental Darier's disease. J Invest Dermatol. 2000;115:1144-1147.
- Dickinson AM, Wang XN, Sviland L, et al. In situ dissection of the graft-versus-host activities of cytotoxic T cells specific for minor histocompatibility antigens. Nat Med. 2002;8:410-414.
- Hansen JA, Chien JW, Warren EH, et al. Defining genetic risk for graft- versus-host disease and mortality following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Curr Opin Hematol. 2010;17:483-492.
- Happle R. Superimposed segmental manifestation of polygenic skin disorders. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:690-699.
To the Editor:
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is a common and serious complication seen most often with bone marrow transplantation and peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. With these therapies, functional lymphoid cells are transferred from an immunocompetent donor into a nongenetically identical recipient, or "host." Because of the allogeneic nature of these transplants, the transplanted lymphoid cells have a high potential to recognize and treat the host's cells as foreign, and the resultant clinical and pathologic picture is that of GVHD. The primary organ systems affected in this immune response are the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and hepatobiliary system.1,2 Cutaneous manifestations are by far the most common.3
Although notable gains have been made in elucidating the causes, risk factors, and mechanisms that result in the clinical picture of GVHD, gaps in our knowledge and understanding still exist. Our patient represents a unique case of unilateral GVHD occurring along Blaschko lines, which has important implications for both recognizing and understanding the pathogenesis of GVHD.
A 35-year-old woman was diagnosed with stage IV follicular lymphoma and received various chemotherapy regimens over the next 4 years. Unfortunately, her disease progressed despite treatment. At 39 years of age, she underwent a nonmyeloablative allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation from a single HLA-mismatched sibling. She was placed on prednisone and cyclosporine for immunosuppression. High-dose acyclovir prophylaxis also was initiated given her history of zoster affecting the right C3 dermatome. Successful engraftment was achieved, with molecular studies showing 100% of cells following transplantation were of donor origin. Restaging at 1 and 2 years following transplantation found her to be in complete remission.
At 2 years following transplantation, she began a slow taper of immunosuppressive medications. She was successfully weaned off prednisone and continued to gradually reduce the cyclosporine dose. Toward the end of the cyclosporine taper 3 months later, she developed a pruritic eruption on the left proximal arm.
She was seen in a bone marrow transplant clinic 4 weeks after the rash developed. On examination, she had multiple, violaceous, lichenoid papules coalescing into linear bandlike plaques. One plaque extended along the left upper arm and 2 others encircled the left hemithorax, respecting the midline. She was treated empirically for zoster with valacyclovir 1 g 3 times daily based on the presumed dermatomal distribution of the eruption. Despite treatment, the rash progressed, and she developed fever. Eight days later, she was admitted with concern for disseminated zoster (Figure). Viral tissue cultures and polymerase chain reaction analysis of the lesions were negative for varicella-zoster virus and herpes simplex viruses 1 and 2. Biopsies of skin lesions on the arm and trunk were both consistent with GVHD.

Given the clinical history, characteristic lesion morphology, and distinct linear distribution along with histopathological confirmation, a diagnosis of GVHD along Blaschko lines was made. Recognizing the cause to be immunogenic rather than infectious, immunosuppressive medications were started. In addition to increasing the prednisone and cyclosporine back to therapeutic levels, she received weekly methylprednisolone. With treatment, she showed gradual but marked improvement.
Six cases of linear GVHD have occurred as an isotopic response along dermatomes previously affected by varicella-zoster virus.4-8 These cases give credence to the idea that a cutaneous viral infection may alter the skin through unknown mechanisms, predisposing it to become affected by GVHD. Notably, this phenomenon occurred despite absence of a persistent viral genome when assessed using polymerase chain reaction analysis.4
An additional 3 cases of GVHD occurring in a dermatomal distribution without any prior infections in those areas have been reported.9,10 Of note, 2 of 3 patients did have episodes of zoster occur at other sites following transplantation and did not develop GVHD symptoms in any of those locations.9 Interestingly, controversy exists as to whether the distribution of these lesions was dermatomal or followed Blaschko lines.11
Two cases of linear GVHD have been reported in which lesions were identified as occurring along Blaschko lines.12,13 The lines of Blaschko, first described in 1901, correspond to cellular migration patterns during embryological development.14 Postzygotic mutations causing epidermal cell mosaicism may result in skin disorders occurring in segmental areas defined by the Blaschko lines.15-17 Accordingly, the Blaschko-linear pattern in GVHD suggests cellular mosaicism as the etiology in this case. Although the host's immune system develops immunotolerance to both cellular lineages during maturation, transplanted lymphoid cells from a nongenetically identical sibling may identify just one of the cell lines as nonself, producing a selective pattern of GVHD18 confined to the distribution of the genetically disparate cell line, which occurs along the lines of Blaschko in the skin. Candidate genes for mutations that would produce a mosaic following transplant GVHD include any of the 25 to 30 known minor histocompatibility antigens (or any of the several hundred yet to be found).19 Although well established for monogenic dominant disorders, in 2007 it was recognized that a postzygotic mutation can cause many complex polygenetic disorders, including GVHD, to manifest in a limited segmental pattern. This understanding, along with retrospective case review, has brought into question previously reported "dermatomal" or "zosteriform" presentations of GVHD, asserting that the linear patterns were misidentified and thus inappropriately attributed to a postviral response.20 Recognition of the Blaschko-linear distribution holds significance in both identifying lesion etiology and understanding disease pathogenesis and treatment.
Our patient illustrates a case of a Blaschko-linear GVHD. The distinctive pattern of her physical findings strongly favored epidermal cell mosaicism as the etiology of her disease. More than just a phenotypically unique case, it provided further insight into the complex etiology underlying GVHD and iterated the basic concepts of Blaschko lines and genetic alterations in development.
To the Editor:
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is a common and serious complication seen most often with bone marrow transplantation and peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. With these therapies, functional lymphoid cells are transferred from an immunocompetent donor into a nongenetically identical recipient, or "host." Because of the allogeneic nature of these transplants, the transplanted lymphoid cells have a high potential to recognize and treat the host's cells as foreign, and the resultant clinical and pathologic picture is that of GVHD. The primary organ systems affected in this immune response are the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and hepatobiliary system.1,2 Cutaneous manifestations are by far the most common.3
Although notable gains have been made in elucidating the causes, risk factors, and mechanisms that result in the clinical picture of GVHD, gaps in our knowledge and understanding still exist. Our patient represents a unique case of unilateral GVHD occurring along Blaschko lines, which has important implications for both recognizing and understanding the pathogenesis of GVHD.
A 35-year-old woman was diagnosed with stage IV follicular lymphoma and received various chemotherapy regimens over the next 4 years. Unfortunately, her disease progressed despite treatment. At 39 years of age, she underwent a nonmyeloablative allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation from a single HLA-mismatched sibling. She was placed on prednisone and cyclosporine for immunosuppression. High-dose acyclovir prophylaxis also was initiated given her history of zoster affecting the right C3 dermatome. Successful engraftment was achieved, with molecular studies showing 100% of cells following transplantation were of donor origin. Restaging at 1 and 2 years following transplantation found her to be in complete remission.
At 2 years following transplantation, she began a slow taper of immunosuppressive medications. She was successfully weaned off prednisone and continued to gradually reduce the cyclosporine dose. Toward the end of the cyclosporine taper 3 months later, she developed a pruritic eruption on the left proximal arm.
She was seen in a bone marrow transplant clinic 4 weeks after the rash developed. On examination, she had multiple, violaceous, lichenoid papules coalescing into linear bandlike plaques. One plaque extended along the left upper arm and 2 others encircled the left hemithorax, respecting the midline. She was treated empirically for zoster with valacyclovir 1 g 3 times daily based on the presumed dermatomal distribution of the eruption. Despite treatment, the rash progressed, and she developed fever. Eight days later, she was admitted with concern for disseminated zoster (Figure). Viral tissue cultures and polymerase chain reaction analysis of the lesions were negative for varicella-zoster virus and herpes simplex viruses 1 and 2. Biopsies of skin lesions on the arm and trunk were both consistent with GVHD.

Given the clinical history, characteristic lesion morphology, and distinct linear distribution along with histopathological confirmation, a diagnosis of GVHD along Blaschko lines was made. Recognizing the cause to be immunogenic rather than infectious, immunosuppressive medications were started. In addition to increasing the prednisone and cyclosporine back to therapeutic levels, she received weekly methylprednisolone. With treatment, she showed gradual but marked improvement.
Six cases of linear GVHD have occurred as an isotopic response along dermatomes previously affected by varicella-zoster virus.4-8 These cases give credence to the idea that a cutaneous viral infection may alter the skin through unknown mechanisms, predisposing it to become affected by GVHD. Notably, this phenomenon occurred despite absence of a persistent viral genome when assessed using polymerase chain reaction analysis.4
An additional 3 cases of GVHD occurring in a dermatomal distribution without any prior infections in those areas have been reported.9,10 Of note, 2 of 3 patients did have episodes of zoster occur at other sites following transplantation and did not develop GVHD symptoms in any of those locations.9 Interestingly, controversy exists as to whether the distribution of these lesions was dermatomal or followed Blaschko lines.11
Two cases of linear GVHD have been reported in which lesions were identified as occurring along Blaschko lines.12,13 The lines of Blaschko, first described in 1901, correspond to cellular migration patterns during embryological development.14 Postzygotic mutations causing epidermal cell mosaicism may result in skin disorders occurring in segmental areas defined by the Blaschko lines.15-17 Accordingly, the Blaschko-linear pattern in GVHD suggests cellular mosaicism as the etiology in this case. Although the host's immune system develops immunotolerance to both cellular lineages during maturation, transplanted lymphoid cells from a nongenetically identical sibling may identify just one of the cell lines as nonself, producing a selective pattern of GVHD18 confined to the distribution of the genetically disparate cell line, which occurs along the lines of Blaschko in the skin. Candidate genes for mutations that would produce a mosaic following transplant GVHD include any of the 25 to 30 known minor histocompatibility antigens (or any of the several hundred yet to be found).19 Although well established for monogenic dominant disorders, in 2007 it was recognized that a postzygotic mutation can cause many complex polygenetic disorders, including GVHD, to manifest in a limited segmental pattern. This understanding, along with retrospective case review, has brought into question previously reported "dermatomal" or "zosteriform" presentations of GVHD, asserting that the linear patterns were misidentified and thus inappropriately attributed to a postviral response.20 Recognition of the Blaschko-linear distribution holds significance in both identifying lesion etiology and understanding disease pathogenesis and treatment.
Our patient illustrates a case of a Blaschko-linear GVHD. The distinctive pattern of her physical findings strongly favored epidermal cell mosaicism as the etiology of her disease. More than just a phenotypically unique case, it provided further insight into the complex etiology underlying GVHD and iterated the basic concepts of Blaschko lines and genetic alterations in development.
- Thomas ED, Storb R, Clift RA, et al. Bone-marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1975;292:895-902.
- Lee SJ, Vogelsang G, Flowers ME. Chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2003;9:215-233.
- Johnson ML, Farmer ER. Graft versus host reactions in dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;38:369-384.
- Baselga E, Drolet BA, Segura AD, et al. Dermatomal lichenoid chronic graft-vs-host disease following varicella-zoster infection despite absence of viral genome. J Cutan Pathol. 1996;23:576-581.
- Lacour JP, Sirvent N, Monpoux F, et al. Dermatomal chronic cutaneous graft versus host disease at the site of prior herpes zoster. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:587-589.
- Cordoba S, Fraga J, Bartolome B, et al. Giant cell lichenoid dermatitis within herpes zoster scars in a bone marrow recipient. J Cutan Pathol. 2000;27:255-257.
- Sanli H, Anadolu R, Arat M, et al. Dermatomal lichenoid graft-versus-host disease within herpes zoster scars. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:562-564.
- Martires KJ, Baird K, Citrin DE, et al. Localization of sclerotic-type chronic graft-versus-host disease to sites of skin injury: potential insight into the mechanism of isomorphic and isotopic responses. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:1081-1086.
- Freemer CS, Farmer ER, Corio RL, et al. Lichenoid chronic graft-vs-host disease occurring in a dermatomal distribution. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:70-72.
- Cohen PR, Hymes SR. Linear and dermatomal cutaneous graft-versus-host disease. South Med J. 1994;87:758-761.
- Reisfeld PL. Linear lichenoid graft-vs-host disease. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:1207-1208.
- Beers B, Kalish RS, Kaye VN, et al. Unilateral linear lichenoid eruption after bone marrow transplantation: an unmasking of tolerance to an abnormal keratinocyte clone? J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28(5, pt 2):888-892.
- Wilson BB, Lockman DW. Linear lichenoid graft-vs-host disease. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:1206-1207.
- Goldberg I, Sprecher E. Patterned disorders in dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2011;29:498-503.
- Colman SD, Rasmussen SA, Ho VT, et al. Somatic mosaicism in a patient with neurofibromatosis type 1. Am J Hum Genet. 1996;58:484-490.
- Munro CS, Wilkie AO. Epidermal mosaicism producing localised acne: somatic mutation in FGFR2. Lancet. 1998;352:704-705.
- Sakuntabhai A, Dhitavat J, Burge S, et al. Mosaicism for ATP2A2 mutations causes segmental Darier's disease. J Invest Dermatol. 2000;115:1144-1147.
- Dickinson AM, Wang XN, Sviland L, et al. In situ dissection of the graft-versus-host activities of cytotoxic T cells specific for minor histocompatibility antigens. Nat Med. 2002;8:410-414.
- Hansen JA, Chien JW, Warren EH, et al. Defining genetic risk for graft- versus-host disease and mortality following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Curr Opin Hematol. 2010;17:483-492.
- Happle R. Superimposed segmental manifestation of polygenic skin disorders. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:690-699.
- Thomas ED, Storb R, Clift RA, et al. Bone-marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1975;292:895-902.
- Lee SJ, Vogelsang G, Flowers ME. Chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2003;9:215-233.
- Johnson ML, Farmer ER. Graft versus host reactions in dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;38:369-384.
- Baselga E, Drolet BA, Segura AD, et al. Dermatomal lichenoid chronic graft-vs-host disease following varicella-zoster infection despite absence of viral genome. J Cutan Pathol. 1996;23:576-581.
- Lacour JP, Sirvent N, Monpoux F, et al. Dermatomal chronic cutaneous graft versus host disease at the site of prior herpes zoster. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:587-589.
- Cordoba S, Fraga J, Bartolome B, et al. Giant cell lichenoid dermatitis within herpes zoster scars in a bone marrow recipient. J Cutan Pathol. 2000;27:255-257.
- Sanli H, Anadolu R, Arat M, et al. Dermatomal lichenoid graft-versus-host disease within herpes zoster scars. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:562-564.
- Martires KJ, Baird K, Citrin DE, et al. Localization of sclerotic-type chronic graft-versus-host disease to sites of skin injury: potential insight into the mechanism of isomorphic and isotopic responses. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:1081-1086.
- Freemer CS, Farmer ER, Corio RL, et al. Lichenoid chronic graft-vs-host disease occurring in a dermatomal distribution. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:70-72.
- Cohen PR, Hymes SR. Linear and dermatomal cutaneous graft-versus-host disease. South Med J. 1994;87:758-761.
- Reisfeld PL. Linear lichenoid graft-vs-host disease. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:1207-1208.
- Beers B, Kalish RS, Kaye VN, et al. Unilateral linear lichenoid eruption after bone marrow transplantation: an unmasking of tolerance to an abnormal keratinocyte clone? J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28(5, pt 2):888-892.
- Wilson BB, Lockman DW. Linear lichenoid graft-vs-host disease. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:1206-1207.
- Goldberg I, Sprecher E. Patterned disorders in dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2011;29:498-503.
- Colman SD, Rasmussen SA, Ho VT, et al. Somatic mosaicism in a patient with neurofibromatosis type 1. Am J Hum Genet. 1996;58:484-490.
- Munro CS, Wilkie AO. Epidermal mosaicism producing localised acne: somatic mutation in FGFR2. Lancet. 1998;352:704-705.
- Sakuntabhai A, Dhitavat J, Burge S, et al. Mosaicism for ATP2A2 mutations causes segmental Darier's disease. J Invest Dermatol. 2000;115:1144-1147.
- Dickinson AM, Wang XN, Sviland L, et al. In situ dissection of the graft-versus-host activities of cytotoxic T cells specific for minor histocompatibility antigens. Nat Med. 2002;8:410-414.
- Hansen JA, Chien JW, Warren EH, et al. Defining genetic risk for graft- versus-host disease and mortality following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Curr Opin Hematol. 2010;17:483-492.
- Happle R. Superimposed segmental manifestation of polygenic skin disorders. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:690-699.
Practice Points
- Recognizing the characteristic manners in which different linear dermatoses present can aid in correctly identifying disorders that most commonly present in either a dermatomal or Blaschko-linear-type distribution.
- A blaschkoid-type distribution is the result of cutaneous mosaicism that occurs during embryological development and therefore subsequently produces a unique phenotypical presentation for various genetically influenced skin disorders, including graft-versus-host disease.