User login
Engaging Veterans With Serious Mental Illness in Primary Care
People with serious mental illness (SMI) are at substantial risk for premature mortality, dying on average 10 to 20 years earlier than others.1 The reasons for this disparity are complex; however, the high prevalence of chronic disease and physical comorbidities in the SMI population have been identified as prominent factors.2 Engagement and reengagement in care, including primary care for medical comorbidities, can mitigate these mortality risks.2-4 Among veterans with SMI lost to follow-up care for more than 12 months, those not successfully reengaged in care were more likely to die compared with those reengaged in care.2,3
Given this evidence, health care systems, including the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), have looked to better engage these patients in care. These efforts have included mental health population health management, colocation of mental health with primary care, designation of primary care teams specializing in SMI, and integration of mental health and primary care services for patients experiencing homelessness.5-8
As part of a national approach to encourage locally driven quality improvement (QI), the VA compiles performance metrics for each facility, across a gamut of care settings, conditions, and veteran populations.9 Quarterly facility report cards, with longitudinal data and cross-facility comparisons, enable facilities to identify targets for QI and track improvement progress. One metric reports on the proportion of enrolled veterans with SMI who have primary care engagement, defined as having an assigned primary care practitioner (PCP) and a primary care visit in the prior 12 months.
In support of a QI initiative at the VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System (VAGLAHS), we sought to describe promising practices being utilized by VA facilities with higher levels of primary care engagement among their veterans with SMI populations.
Methods
We conducted semistructured telephone interviews with a purposeful sample of key informants at VA facilities with high levels of engagement in primary care among veterans with SMI. All project components were conducted by an interdisciplinary team, which included a medical anthropologist (JM), a mental health physician (PR), an internal medicine physician (KC), and other health services researchers (JB, AG). Because the primary objective of the project was QI, this project was designated as nonresearch by the VAGLAHS Institutional Review Board.
The VA Facility Complexity Model classifies facilities into 5 tiers: 1a (most complex), 1b, 1c, 2, and 3 (least complex), based on patient care volume, patient risk, complexity of clinical programs, and size of research and teaching programs. We sampled informants at VA facilities with complexity ratings of 1a or 1b with better than median scores for primary care engagement of veterans with SMI based on report cards from January 2019 to March 2019. To increase the likelihood of identifying lessons that can generalize to the VAGLAHS with its large population of veterans experiencing homelessness, we selected facilities serving populations consisting of more than 1000 veterans experiencing homelessness.
At each selected facility, we first aimed to interview mental health leaders responsible for quality measurement and improvement identified from a national VA database. We then used snowball sampling to identify other informants at these VA facilities who were knowledgeable about relevant processes. Potential interviewees were contacted via email.
Interviews
The interview guide was developed by the interdisciplinary team and based on published literature about strategies for engaging patients with SMI in care. Interview guide questions focused on local practice arrangements, panel management, population health practices, and quality measurement and improvement efforts for engaging veterans with SMI in primary care (Appendix). Interviews were conducted by telephone, from May 2019 through July 2019, by experienced qualitative interviewers (JM, JB). Interviewees were assured confidentiality of their responses.
Interview audio recordings were used to generate detailed notes (AG). Structured summaries were prepared from these notes, using a template based on the interview guide. We organized these summaries into matrices for analysis, grouping summarized points by interview domains to facilitate comparison across interviews.10-11 Our team reviewed and discussed the matrices, and iteratively identified and defined themes to identify the common engagement approaches and the nature of the connections between mental health and primary care. To ensure rigor, findings were checked by the senior qualitative lead (JM).
Results
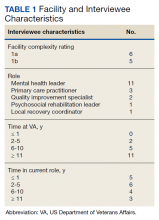
The median SMI engagement score—defined as the proportion of veterans with SMI who have had a primary care visit in the prior 12 months and who have an assigned PCP—was 75.6% across 1a and 1b VA facilities. We identified 16 VA facilities that had a median or higher score and more than 1000 enrolled veterans experiencing homelessness. From these16 facilities, we emailed 31 potential interviewees, 14 of whom were identified from a VA database and 17 referred by other interviewees. In total, we interviewed 18 key informants across 11 (69%) facilities, including chiefs of psychology and mental health services, PCPs with mental health expertise, QI specialists, a psychosocial rehabilitation leader, and a local recovery coordinator, who helps veterans with SMI access recovery-oriented services. Characteristics of the facilities and interviewees are shown in Table 1. Interviews lasted a mean 35 (range, 26-50) minutes.
Engagement Approaches
The strategies used to engage veterans with SMI were heterogenous, with no single strategy common across all facilities. However, we identified 2 categories of engagement approaches: targeted outreach and routine practices.
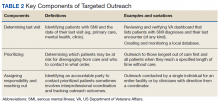
Targeted outreach strategies included deliberate, systematic approaches to reach veterans with SMI outside of regularly scheduled visits. These strategies were designed to be proactive, often prioritizing veterans at risk of disengaging from care. Designated VA care team members identified and reached out to veterans well before 12 months had passed since their prior visit (the VA definition of disengagement from care); visits included any care at VA, including, but not exclusively, primary care. Table 2 describes the key components of targeted outreach strategies: (1) identifying veterans’ last visit; (2) prioritizing which veterans to outreach to; and (3) assigning responsibility and reaching out. A key defining feature of targeted outreach is that veterans were identified and prioritized for outreach independent from any visits with mental health or other VA services.
In identifying veterans at risk for disengagement, a designated employee in mental health or primary care (eg, local recovery coordinator) reviewed a VA dashboard or locally developed report that identified veterans who have not engaged in care for several months. This process was repeated regularly. The designated employee either contacted those veterans directly or coordinated with other clinicians and support staff. When possible, a clinician or nurse with an existing relationship with the veteran would call them. If no such relationship existed, an administrative staff member made a cold call, sometimes accompanied by mailed outreach materials.
Routine practices were business-as-usual activities embedded in regular clinical workflows that facilitated engagement or reengagement of veterans with SMI in care. Of note, and in contrast to targeted outreach, these activities were tied to veteran visits with mental health practitioners. These practices were typically described as being at least as important as targeted outreach efforts. For example, during mental health visits, clinicians routinely checked the VA electronic health record to assess whether veterans had an assigned primary care team. If not, they would contact the primary care service to refer the patient for a primary care visit and assignment. If the patient already had a primary care team assigned, the mental health practitioner checked for recent primary care visits. If none were evident, the mental health practitioner might email the assigned PCP or contact them via instant message.
At some facilities, mental health support staff were able to directly schedule primary care appointments, which was identified as an important enabling factor in promoting mental health patient engagement in primary care. Some interviewees seemed to take for granted the idea that mental health practitioners would help engage patients in primary care—suggesting that these practices had perhaps become a cultural norm within their facility. However, some interviewees identified clear strategies for making these practices a consistent part of care—for example, by designing a protocol for initial mental health assessments to include a routine check for primary care engagement.
Mental Health/Primary Care Connections
Interviewees characterized the nature of the connections between mental health and primary care at their facilities. Nearly all interviewees described that their medical centers had extensive ties, formal and informal, between mental health and primary care.
Formal ties may include the reverse integration care model, in which primary care services are embedded in mental health settings. Interviewees at sites with programs based on this model noted that these programs enabled warm hand-offs from mental health to primary care and suggested that it can foster integration between primary care and mental health care for patients with SMI. However, the size, scope, and structure of these programs varied, sometimes serving a small proportion of a facility’s population of SMI patients. Other examples of formal ties included written agreements, establishing frequent, regular meetings between mental health and primary care leadership and front-line staff, and giving mental health clerks the ability to directly schedule primary care appointments.
Informal ties between mental health and primary care included communication and personal working relationships between mental health and PCPs, facilitated by mental health and primary care leaders working together in workgroups and other administrative activities. Some participants described a history of collaboration between mental health and primary care leaders yielding productive and trusting working relationships. Some interviewees described frequent direct communication between individual mental health practitioners and PCPs—either face-to-face or via secure messaging.
Discussion
VA facilities with high levels of primary care engagement among veterans with SMI used extensive engagement strategies, including a diverse array of targeted outreach and routine practices. In both approaches, intentional organizational structural and process decisions, as well as formal and informal ties between mental health and primary care, established and supported them. In addition, organizational cultural factors were especially relevant to routine practice strategies.
To enable targeted outreach, a bevy of organizational resources, both local and national were required. Large accountable care organizations and integrated delivery systems, like the VA, are often better able to create dashboards and other informational resources for population health management compared with smaller, less integrated health care systems. Though these resources are difficult to create in fragmented systems, comparable tools have been explored by multiple state health departments.12 Our findings suggest that these data tools, though resource intensive to develop, may enable facilities to be more methodical and reliable in conducting outreach to vulnerable patients.
In contrast to targeted outreach, routine practices depend less on population health management resources and more on cultural norms. Such norms are notoriously difficult to change, but intentional structural decisions like embedding primary care engagement in mental health protocols may signal that primary care engagement is an important and legitimate consideration for mental health care.13
We identified extensive and heterogenous connections between mental health and primary care in our sample of VA facilities with high engagement of patients with SMI in primary care. A growing body of literature on relational coordination studies the factors that contribute to organizational siloing and mechanisms for breaking down those silos so work can be coordinated across boundaries (eg, the organizational boundary between mental health and primary care).14 Coordinating care across these boundaries, through good relational coordination practices has been shown to improve outcomes in health care and other sectors. Notably, VA facilities in our sample had several of the defining characteristics of good relational coordination: relationships between mental health and primary care that include shared goals, shared knowledge, and mutual respect, all reinforced by frequent communication structured around problem solving.15 The relational coordination literature also offers a way to identify evidence-based interventions for facilitating relational coordination in places where it is lacking, for example, with information systems, boundary-spanning individuals, facility design, and formal conflict resolution.15 Future work might explore how relational coordination can be further used to optimize mental health and primary care connections to keep veterans with SMI engaged in care.
Our approach of interviewing informants in higher-performing facilities draws heavily on the idea of positive deviance, which holds that information on what works in health care is available from organizations that already are demonstrating “consistently exceptional performance.”16 This approach works best when high performance and organizational characteristics are observable for a large number of facilities, and when high-performing facilities are willing to share their strategies. These features allow investigators to identify promising practices and hypotheses that can then be empirically tested and compared. Such testing, including assessing for unintended consequences, is needed for the approaches we identified. Research is also needed to assess for factors that would promote the implementation of effective strategies.
Limitations
As a QI project seeking to identify promising practices, our interviews were limited to 18 key informants across 11 VA facilities with high engagement of care among veterans with SMI. No inferences can be made that these practices are directly related to this high level of engagement, nor the differential impact of different practices. Future work is needed to assess for these relationships. We also did not interview veterans to understand their perspectives on these strategies, which is an additional important topic for future work. In addition, these interviews were performed before the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. Further work is needed to understand how these strategies may have been modified in response to changes in practice. The shift to care from in-person to virtual services may have impacted both clinical interactions with veterans, as well as between clinicians.
Conclusions
Interviews with key informants demonstrate that while engaging and retaining veterans with SMI in primary care is vital, it also requires intentional and potentially resource-intensive practices, including targeted outreach and routine engagement strategies embedded into mental health visits. These promising practices can provide valuable insights for both VA and community health care systems providing care to patients with SMI.
Acknowledgments
We thank Gracielle J. Tan, MD for administrative assistance in preparing this manuscript.
1. Liu NH, Daumit GL, Dua T, et al. Excess mortality in persons with severe mental disorders: a multilevel intervention framework and priorities for clinical practice, policy and research agendas. World Psychiatry. 2017;16(1):30-40. doi:10.1002/wps.20384
2. Bowersox NW, Kilbourne AM, Abraham KM, et al. Cause-specific mortality among veterans with serious mental illness lost to follow-up. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2012;34(6):651-653. doi:10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2012.05.014
3. Davis CL, Kilbourne AM, Blow FC, et al. Reduced mortality among Department of Veterans Affairs patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder lost to follow-up and engaged in active outreach to return for care. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(suppl 1):S74-S79. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2011.300502
4. Copeland LA, Zeber JE, Wang CP, et al. Patterns of primary care and mortality among patients with schizophrenia or diabetes: a cluster analysis approach to the retrospective study of healthcare utilization. BMC Health Serv Res. 2009;9:127. doi:10.1186/1472-6963-9-127
5. Abraham KM, Mach J, Visnic S, McCarthy JF. Enhancing treatment reengagement for veterans with serious mental illness: evaluating the effectiveness of SMI re-engage. Psychiatr Serv. 2018;69(8):887-895. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201700407
6. Ward MC, Druss BG. Reverse integration initiatives for individuals with serious mental illness. Focus (Am Psychiatr Publ). 2017;15(3):271-278. doi:10.1176/appi.focus.20170011
7. Chang ET, Vinzon M, Cohen AN, Young AS. Effective models urgently needed to improve physical care for people with serious mental illnesses. Health Serv Insights. 2019;12:1178632919837628. Published 2019 Apr 2. doi:10.1177/1178632919837628
8. Gabrielian S, Gordon AJ, Gelberg L, et al. Primary care medical services for homeless veterans. Fed Pract. 2014;31(10):10-19.
9. Lemke S, Boden MT, Kearney LK, et al. Measurement-based management of mental health quality and access in VHA: SAIL mental health domain. Psychol Serv. 2017;14(1):1-12. doi:10.1037/ser0000097
10. Averill JB. Matrix analysis as a complementary analytic strategy in qualitative inquiry. Qual Health Res. 2002;12(6):855-866. doi:10.1177/104973230201200611
11. Zuchowski JL, Chrystal JG, Hamilton AB, et al. Coordinating care across health care systems for Veterans with gynecologic malignancies: a qualitative analysis. Med Care. 2017;55(suppl 1):S53-S60. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000737
12. Daumit GL, Stone EM, Kennedy-Hendricks A, Choksy S, Marsteller JA, McGinty EE. Care coordination and population health management strategies and challenges in a behavioral health home model. Med Care. 2019;57(1):79-84. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001023
13. Parmelli E, Flodgren G, Beyer F, et al. The effectiveness of strategies to change organisational culture to improve healthcare performance: a systematic review. Implement Sci. 2011;6(33):1-8. doi:10.1186/1748-5908-6-33
14. Bolton R, Logan C, Gittell JH. Revisiting relational coordination: a systematic review. J Appl Behav Sci. 2021;57(3):290-322. doi:10.1177/0021886321991597
15. Gittell JH, Godfrey M, Thistlethwaite J. Interprofessional collaborative practice and relational coordination: improving healthcare through relationships. J Interprof Care. 2013;27(3):210-13. doi:10.3109/13561820.2012.730564
16. Bradley EH, Curry LA, Ramanadhan S, Rowe L, Nembhard IM, Krumholz HM. Research in action: using positive deviance to improve quality of health care. Implement Sci. 2009;4:25. Published 2009 May 8. doi:10.1186/1748-5908-4-25
People with serious mental illness (SMI) are at substantial risk for premature mortality, dying on average 10 to 20 years earlier than others.1 The reasons for this disparity are complex; however, the high prevalence of chronic disease and physical comorbidities in the SMI population have been identified as prominent factors.2 Engagement and reengagement in care, including primary care for medical comorbidities, can mitigate these mortality risks.2-4 Among veterans with SMI lost to follow-up care for more than 12 months, those not successfully reengaged in care were more likely to die compared with those reengaged in care.2,3
Given this evidence, health care systems, including the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), have looked to better engage these patients in care. These efforts have included mental health population health management, colocation of mental health with primary care, designation of primary care teams specializing in SMI, and integration of mental health and primary care services for patients experiencing homelessness.5-8
As part of a national approach to encourage locally driven quality improvement (QI), the VA compiles performance metrics for each facility, across a gamut of care settings, conditions, and veteran populations.9 Quarterly facility report cards, with longitudinal data and cross-facility comparisons, enable facilities to identify targets for QI and track improvement progress. One metric reports on the proportion of enrolled veterans with SMI who have primary care engagement, defined as having an assigned primary care practitioner (PCP) and a primary care visit in the prior 12 months.
In support of a QI initiative at the VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System (VAGLAHS), we sought to describe promising practices being utilized by VA facilities with higher levels of primary care engagement among their veterans with SMI populations.
Methods
We conducted semistructured telephone interviews with a purposeful sample of key informants at VA facilities with high levels of engagement in primary care among veterans with SMI. All project components were conducted by an interdisciplinary team, which included a medical anthropologist (JM), a mental health physician (PR), an internal medicine physician (KC), and other health services researchers (JB, AG). Because the primary objective of the project was QI, this project was designated as nonresearch by the VAGLAHS Institutional Review Board.
The VA Facility Complexity Model classifies facilities into 5 tiers: 1a (most complex), 1b, 1c, 2, and 3 (least complex), based on patient care volume, patient risk, complexity of clinical programs, and size of research and teaching programs. We sampled informants at VA facilities with complexity ratings of 1a or 1b with better than median scores for primary care engagement of veterans with SMI based on report cards from January 2019 to March 2019. To increase the likelihood of identifying lessons that can generalize to the VAGLAHS with its large population of veterans experiencing homelessness, we selected facilities serving populations consisting of more than 1000 veterans experiencing homelessness.
At each selected facility, we first aimed to interview mental health leaders responsible for quality measurement and improvement identified from a national VA database. We then used snowball sampling to identify other informants at these VA facilities who were knowledgeable about relevant processes. Potential interviewees were contacted via email.
Interviews
The interview guide was developed by the interdisciplinary team and based on published literature about strategies for engaging patients with SMI in care. Interview guide questions focused on local practice arrangements, panel management, population health practices, and quality measurement and improvement efforts for engaging veterans with SMI in primary care (Appendix). Interviews were conducted by telephone, from May 2019 through July 2019, by experienced qualitative interviewers (JM, JB). Interviewees were assured confidentiality of their responses.
Interview audio recordings were used to generate detailed notes (AG). Structured summaries were prepared from these notes, using a template based on the interview guide. We organized these summaries into matrices for analysis, grouping summarized points by interview domains to facilitate comparison across interviews.10-11 Our team reviewed and discussed the matrices, and iteratively identified and defined themes to identify the common engagement approaches and the nature of the connections between mental health and primary care. To ensure rigor, findings were checked by the senior qualitative lead (JM).
Results
The median SMI engagement score—defined as the proportion of veterans with SMI who have had a primary care visit in the prior 12 months and who have an assigned PCP—was 75.6% across 1a and 1b VA facilities. We identified 16 VA facilities that had a median or higher score and more than 1000 enrolled veterans experiencing homelessness. From these16 facilities, we emailed 31 potential interviewees, 14 of whom were identified from a VA database and 17 referred by other interviewees. In total, we interviewed 18 key informants across 11 (69%) facilities, including chiefs of psychology and mental health services, PCPs with mental health expertise, QI specialists, a psychosocial rehabilitation leader, and a local recovery coordinator, who helps veterans with SMI access recovery-oriented services. Characteristics of the facilities and interviewees are shown in Table 1. Interviews lasted a mean 35 (range, 26-50) minutes.
Engagement Approaches
The strategies used to engage veterans with SMI were heterogenous, with no single strategy common across all facilities. However, we identified 2 categories of engagement approaches: targeted outreach and routine practices.
Targeted outreach strategies included deliberate, systematic approaches to reach veterans with SMI outside of regularly scheduled visits. These strategies were designed to be proactive, often prioritizing veterans at risk of disengaging from care. Designated VA care team members identified and reached out to veterans well before 12 months had passed since their prior visit (the VA definition of disengagement from care); visits included any care at VA, including, but not exclusively, primary care. Table 2 describes the key components of targeted outreach strategies: (1) identifying veterans’ last visit; (2) prioritizing which veterans to outreach to; and (3) assigning responsibility and reaching out. A key defining feature of targeted outreach is that veterans were identified and prioritized for outreach independent from any visits with mental health or other VA services.
In identifying veterans at risk for disengagement, a designated employee in mental health or primary care (eg, local recovery coordinator) reviewed a VA dashboard or locally developed report that identified veterans who have not engaged in care for several months. This process was repeated regularly. The designated employee either contacted those veterans directly or coordinated with other clinicians and support staff. When possible, a clinician or nurse with an existing relationship with the veteran would call them. If no such relationship existed, an administrative staff member made a cold call, sometimes accompanied by mailed outreach materials.
Routine practices were business-as-usual activities embedded in regular clinical workflows that facilitated engagement or reengagement of veterans with SMI in care. Of note, and in contrast to targeted outreach, these activities were tied to veteran visits with mental health practitioners. These practices were typically described as being at least as important as targeted outreach efforts. For example, during mental health visits, clinicians routinely checked the VA electronic health record to assess whether veterans had an assigned primary care team. If not, they would contact the primary care service to refer the patient for a primary care visit and assignment. If the patient already had a primary care team assigned, the mental health practitioner checked for recent primary care visits. If none were evident, the mental health practitioner might email the assigned PCP or contact them via instant message.
At some facilities, mental health support staff were able to directly schedule primary care appointments, which was identified as an important enabling factor in promoting mental health patient engagement in primary care. Some interviewees seemed to take for granted the idea that mental health practitioners would help engage patients in primary care—suggesting that these practices had perhaps become a cultural norm within their facility. However, some interviewees identified clear strategies for making these practices a consistent part of care—for example, by designing a protocol for initial mental health assessments to include a routine check for primary care engagement.
Mental Health/Primary Care Connections
Interviewees characterized the nature of the connections between mental health and primary care at their facilities. Nearly all interviewees described that their medical centers had extensive ties, formal and informal, between mental health and primary care.
Formal ties may include the reverse integration care model, in which primary care services are embedded in mental health settings. Interviewees at sites with programs based on this model noted that these programs enabled warm hand-offs from mental health to primary care and suggested that it can foster integration between primary care and mental health care for patients with SMI. However, the size, scope, and structure of these programs varied, sometimes serving a small proportion of a facility’s population of SMI patients. Other examples of formal ties included written agreements, establishing frequent, regular meetings between mental health and primary care leadership and front-line staff, and giving mental health clerks the ability to directly schedule primary care appointments.
Informal ties between mental health and primary care included communication and personal working relationships between mental health and PCPs, facilitated by mental health and primary care leaders working together in workgroups and other administrative activities. Some participants described a history of collaboration between mental health and primary care leaders yielding productive and trusting working relationships. Some interviewees described frequent direct communication between individual mental health practitioners and PCPs—either face-to-face or via secure messaging.
Discussion
VA facilities with high levels of primary care engagement among veterans with SMI used extensive engagement strategies, including a diverse array of targeted outreach and routine practices. In both approaches, intentional organizational structural and process decisions, as well as formal and informal ties between mental health and primary care, established and supported them. In addition, organizational cultural factors were especially relevant to routine practice strategies.
To enable targeted outreach, a bevy of organizational resources, both local and national were required. Large accountable care organizations and integrated delivery systems, like the VA, are often better able to create dashboards and other informational resources for population health management compared with smaller, less integrated health care systems. Though these resources are difficult to create in fragmented systems, comparable tools have been explored by multiple state health departments.12 Our findings suggest that these data tools, though resource intensive to develop, may enable facilities to be more methodical and reliable in conducting outreach to vulnerable patients.
In contrast to targeted outreach, routine practices depend less on population health management resources and more on cultural norms. Such norms are notoriously difficult to change, but intentional structural decisions like embedding primary care engagement in mental health protocols may signal that primary care engagement is an important and legitimate consideration for mental health care.13
We identified extensive and heterogenous connections between mental health and primary care in our sample of VA facilities with high engagement of patients with SMI in primary care. A growing body of literature on relational coordination studies the factors that contribute to organizational siloing and mechanisms for breaking down those silos so work can be coordinated across boundaries (eg, the organizational boundary between mental health and primary care).14 Coordinating care across these boundaries, through good relational coordination practices has been shown to improve outcomes in health care and other sectors. Notably, VA facilities in our sample had several of the defining characteristics of good relational coordination: relationships between mental health and primary care that include shared goals, shared knowledge, and mutual respect, all reinforced by frequent communication structured around problem solving.15 The relational coordination literature also offers a way to identify evidence-based interventions for facilitating relational coordination in places where it is lacking, for example, with information systems, boundary-spanning individuals, facility design, and formal conflict resolution.15 Future work might explore how relational coordination can be further used to optimize mental health and primary care connections to keep veterans with SMI engaged in care.
Our approach of interviewing informants in higher-performing facilities draws heavily on the idea of positive deviance, which holds that information on what works in health care is available from organizations that already are demonstrating “consistently exceptional performance.”16 This approach works best when high performance and organizational characteristics are observable for a large number of facilities, and when high-performing facilities are willing to share their strategies. These features allow investigators to identify promising practices and hypotheses that can then be empirically tested and compared. Such testing, including assessing for unintended consequences, is needed for the approaches we identified. Research is also needed to assess for factors that would promote the implementation of effective strategies.
Limitations
As a QI project seeking to identify promising practices, our interviews were limited to 18 key informants across 11 VA facilities with high engagement of care among veterans with SMI. No inferences can be made that these practices are directly related to this high level of engagement, nor the differential impact of different practices. Future work is needed to assess for these relationships. We also did not interview veterans to understand their perspectives on these strategies, which is an additional important topic for future work. In addition, these interviews were performed before the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. Further work is needed to understand how these strategies may have been modified in response to changes in practice. The shift to care from in-person to virtual services may have impacted both clinical interactions with veterans, as well as between clinicians.
Conclusions
Interviews with key informants demonstrate that while engaging and retaining veterans with SMI in primary care is vital, it also requires intentional and potentially resource-intensive practices, including targeted outreach and routine engagement strategies embedded into mental health visits. These promising practices can provide valuable insights for both VA and community health care systems providing care to patients with SMI.
Acknowledgments
We thank Gracielle J. Tan, MD for administrative assistance in preparing this manuscript.
People with serious mental illness (SMI) are at substantial risk for premature mortality, dying on average 10 to 20 years earlier than others.1 The reasons for this disparity are complex; however, the high prevalence of chronic disease and physical comorbidities in the SMI population have been identified as prominent factors.2 Engagement and reengagement in care, including primary care for medical comorbidities, can mitigate these mortality risks.2-4 Among veterans with SMI lost to follow-up care for more than 12 months, those not successfully reengaged in care were more likely to die compared with those reengaged in care.2,3
Given this evidence, health care systems, including the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), have looked to better engage these patients in care. These efforts have included mental health population health management, colocation of mental health with primary care, designation of primary care teams specializing in SMI, and integration of mental health and primary care services for patients experiencing homelessness.5-8
As part of a national approach to encourage locally driven quality improvement (QI), the VA compiles performance metrics for each facility, across a gamut of care settings, conditions, and veteran populations.9 Quarterly facility report cards, with longitudinal data and cross-facility comparisons, enable facilities to identify targets for QI and track improvement progress. One metric reports on the proportion of enrolled veterans with SMI who have primary care engagement, defined as having an assigned primary care practitioner (PCP) and a primary care visit in the prior 12 months.
In support of a QI initiative at the VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System (VAGLAHS), we sought to describe promising practices being utilized by VA facilities with higher levels of primary care engagement among their veterans with SMI populations.
Methods
We conducted semistructured telephone interviews with a purposeful sample of key informants at VA facilities with high levels of engagement in primary care among veterans with SMI. All project components were conducted by an interdisciplinary team, which included a medical anthropologist (JM), a mental health physician (PR), an internal medicine physician (KC), and other health services researchers (JB, AG). Because the primary objective of the project was QI, this project was designated as nonresearch by the VAGLAHS Institutional Review Board.
The VA Facility Complexity Model classifies facilities into 5 tiers: 1a (most complex), 1b, 1c, 2, and 3 (least complex), based on patient care volume, patient risk, complexity of clinical programs, and size of research and teaching programs. We sampled informants at VA facilities with complexity ratings of 1a or 1b with better than median scores for primary care engagement of veterans with SMI based on report cards from January 2019 to March 2019. To increase the likelihood of identifying lessons that can generalize to the VAGLAHS with its large population of veterans experiencing homelessness, we selected facilities serving populations consisting of more than 1000 veterans experiencing homelessness.
At each selected facility, we first aimed to interview mental health leaders responsible for quality measurement and improvement identified from a national VA database. We then used snowball sampling to identify other informants at these VA facilities who were knowledgeable about relevant processes. Potential interviewees were contacted via email.
Interviews
The interview guide was developed by the interdisciplinary team and based on published literature about strategies for engaging patients with SMI in care. Interview guide questions focused on local practice arrangements, panel management, population health practices, and quality measurement and improvement efforts for engaging veterans with SMI in primary care (Appendix). Interviews were conducted by telephone, from May 2019 through July 2019, by experienced qualitative interviewers (JM, JB). Interviewees were assured confidentiality of their responses.
Interview audio recordings were used to generate detailed notes (AG). Structured summaries were prepared from these notes, using a template based on the interview guide. We organized these summaries into matrices for analysis, grouping summarized points by interview domains to facilitate comparison across interviews.10-11 Our team reviewed and discussed the matrices, and iteratively identified and defined themes to identify the common engagement approaches and the nature of the connections between mental health and primary care. To ensure rigor, findings were checked by the senior qualitative lead (JM).
Results
The median SMI engagement score—defined as the proportion of veterans with SMI who have had a primary care visit in the prior 12 months and who have an assigned PCP—was 75.6% across 1a and 1b VA facilities. We identified 16 VA facilities that had a median or higher score and more than 1000 enrolled veterans experiencing homelessness. From these16 facilities, we emailed 31 potential interviewees, 14 of whom were identified from a VA database and 17 referred by other interviewees. In total, we interviewed 18 key informants across 11 (69%) facilities, including chiefs of psychology and mental health services, PCPs with mental health expertise, QI specialists, a psychosocial rehabilitation leader, and a local recovery coordinator, who helps veterans with SMI access recovery-oriented services. Characteristics of the facilities and interviewees are shown in Table 1. Interviews lasted a mean 35 (range, 26-50) minutes.
Engagement Approaches
The strategies used to engage veterans with SMI were heterogenous, with no single strategy common across all facilities. However, we identified 2 categories of engagement approaches: targeted outreach and routine practices.
Targeted outreach strategies included deliberate, systematic approaches to reach veterans with SMI outside of regularly scheduled visits. These strategies were designed to be proactive, often prioritizing veterans at risk of disengaging from care. Designated VA care team members identified and reached out to veterans well before 12 months had passed since their prior visit (the VA definition of disengagement from care); visits included any care at VA, including, but not exclusively, primary care. Table 2 describes the key components of targeted outreach strategies: (1) identifying veterans’ last visit; (2) prioritizing which veterans to outreach to; and (3) assigning responsibility and reaching out. A key defining feature of targeted outreach is that veterans were identified and prioritized for outreach independent from any visits with mental health or other VA services.
In identifying veterans at risk for disengagement, a designated employee in mental health or primary care (eg, local recovery coordinator) reviewed a VA dashboard or locally developed report that identified veterans who have not engaged in care for several months. This process was repeated regularly. The designated employee either contacted those veterans directly or coordinated with other clinicians and support staff. When possible, a clinician or nurse with an existing relationship with the veteran would call them. If no such relationship existed, an administrative staff member made a cold call, sometimes accompanied by mailed outreach materials.
Routine practices were business-as-usual activities embedded in regular clinical workflows that facilitated engagement or reengagement of veterans with SMI in care. Of note, and in contrast to targeted outreach, these activities were tied to veteran visits with mental health practitioners. These practices were typically described as being at least as important as targeted outreach efforts. For example, during mental health visits, clinicians routinely checked the VA electronic health record to assess whether veterans had an assigned primary care team. If not, they would contact the primary care service to refer the patient for a primary care visit and assignment. If the patient already had a primary care team assigned, the mental health practitioner checked for recent primary care visits. If none were evident, the mental health practitioner might email the assigned PCP or contact them via instant message.
At some facilities, mental health support staff were able to directly schedule primary care appointments, which was identified as an important enabling factor in promoting mental health patient engagement in primary care. Some interviewees seemed to take for granted the idea that mental health practitioners would help engage patients in primary care—suggesting that these practices had perhaps become a cultural norm within their facility. However, some interviewees identified clear strategies for making these practices a consistent part of care—for example, by designing a protocol for initial mental health assessments to include a routine check for primary care engagement.
Mental Health/Primary Care Connections
Interviewees characterized the nature of the connections between mental health and primary care at their facilities. Nearly all interviewees described that their medical centers had extensive ties, formal and informal, between mental health and primary care.
Formal ties may include the reverse integration care model, in which primary care services are embedded in mental health settings. Interviewees at sites with programs based on this model noted that these programs enabled warm hand-offs from mental health to primary care and suggested that it can foster integration between primary care and mental health care for patients with SMI. However, the size, scope, and structure of these programs varied, sometimes serving a small proportion of a facility’s population of SMI patients. Other examples of formal ties included written agreements, establishing frequent, regular meetings between mental health and primary care leadership and front-line staff, and giving mental health clerks the ability to directly schedule primary care appointments.
Informal ties between mental health and primary care included communication and personal working relationships between mental health and PCPs, facilitated by mental health and primary care leaders working together in workgroups and other administrative activities. Some participants described a history of collaboration between mental health and primary care leaders yielding productive and trusting working relationships. Some interviewees described frequent direct communication between individual mental health practitioners and PCPs—either face-to-face or via secure messaging.
Discussion
VA facilities with high levels of primary care engagement among veterans with SMI used extensive engagement strategies, including a diverse array of targeted outreach and routine practices. In both approaches, intentional organizational structural and process decisions, as well as formal and informal ties between mental health and primary care, established and supported them. In addition, organizational cultural factors were especially relevant to routine practice strategies.
To enable targeted outreach, a bevy of organizational resources, both local and national were required. Large accountable care organizations and integrated delivery systems, like the VA, are often better able to create dashboards and other informational resources for population health management compared with smaller, less integrated health care systems. Though these resources are difficult to create in fragmented systems, comparable tools have been explored by multiple state health departments.12 Our findings suggest that these data tools, though resource intensive to develop, may enable facilities to be more methodical and reliable in conducting outreach to vulnerable patients.
In contrast to targeted outreach, routine practices depend less on population health management resources and more on cultural norms. Such norms are notoriously difficult to change, but intentional structural decisions like embedding primary care engagement in mental health protocols may signal that primary care engagement is an important and legitimate consideration for mental health care.13
We identified extensive and heterogenous connections between mental health and primary care in our sample of VA facilities with high engagement of patients with SMI in primary care. A growing body of literature on relational coordination studies the factors that contribute to organizational siloing and mechanisms for breaking down those silos so work can be coordinated across boundaries (eg, the organizational boundary between mental health and primary care).14 Coordinating care across these boundaries, through good relational coordination practices has been shown to improve outcomes in health care and other sectors. Notably, VA facilities in our sample had several of the defining characteristics of good relational coordination: relationships between mental health and primary care that include shared goals, shared knowledge, and mutual respect, all reinforced by frequent communication structured around problem solving.15 The relational coordination literature also offers a way to identify evidence-based interventions for facilitating relational coordination in places where it is lacking, for example, with information systems, boundary-spanning individuals, facility design, and formal conflict resolution.15 Future work might explore how relational coordination can be further used to optimize mental health and primary care connections to keep veterans with SMI engaged in care.
Our approach of interviewing informants in higher-performing facilities draws heavily on the idea of positive deviance, which holds that information on what works in health care is available from organizations that already are demonstrating “consistently exceptional performance.”16 This approach works best when high performance and organizational characteristics are observable for a large number of facilities, and when high-performing facilities are willing to share their strategies. These features allow investigators to identify promising practices and hypotheses that can then be empirically tested and compared. Such testing, including assessing for unintended consequences, is needed for the approaches we identified. Research is also needed to assess for factors that would promote the implementation of effective strategies.
Limitations
As a QI project seeking to identify promising practices, our interviews were limited to 18 key informants across 11 VA facilities with high engagement of care among veterans with SMI. No inferences can be made that these practices are directly related to this high level of engagement, nor the differential impact of different practices. Future work is needed to assess for these relationships. We also did not interview veterans to understand their perspectives on these strategies, which is an additional important topic for future work. In addition, these interviews were performed before the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. Further work is needed to understand how these strategies may have been modified in response to changes in practice. The shift to care from in-person to virtual services may have impacted both clinical interactions with veterans, as well as between clinicians.
Conclusions
Interviews with key informants demonstrate that while engaging and retaining veterans with SMI in primary care is vital, it also requires intentional and potentially resource-intensive practices, including targeted outreach and routine engagement strategies embedded into mental health visits. These promising practices can provide valuable insights for both VA and community health care systems providing care to patients with SMI.
Acknowledgments
We thank Gracielle J. Tan, MD for administrative assistance in preparing this manuscript.
1. Liu NH, Daumit GL, Dua T, et al. Excess mortality in persons with severe mental disorders: a multilevel intervention framework and priorities for clinical practice, policy and research agendas. World Psychiatry. 2017;16(1):30-40. doi:10.1002/wps.20384
2. Bowersox NW, Kilbourne AM, Abraham KM, et al. Cause-specific mortality among veterans with serious mental illness lost to follow-up. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2012;34(6):651-653. doi:10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2012.05.014
3. Davis CL, Kilbourne AM, Blow FC, et al. Reduced mortality among Department of Veterans Affairs patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder lost to follow-up and engaged in active outreach to return for care. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(suppl 1):S74-S79. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2011.300502
4. Copeland LA, Zeber JE, Wang CP, et al. Patterns of primary care and mortality among patients with schizophrenia or diabetes: a cluster analysis approach to the retrospective study of healthcare utilization. BMC Health Serv Res. 2009;9:127. doi:10.1186/1472-6963-9-127
5. Abraham KM, Mach J, Visnic S, McCarthy JF. Enhancing treatment reengagement for veterans with serious mental illness: evaluating the effectiveness of SMI re-engage. Psychiatr Serv. 2018;69(8):887-895. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201700407
6. Ward MC, Druss BG. Reverse integration initiatives for individuals with serious mental illness. Focus (Am Psychiatr Publ). 2017;15(3):271-278. doi:10.1176/appi.focus.20170011
7. Chang ET, Vinzon M, Cohen AN, Young AS. Effective models urgently needed to improve physical care for people with serious mental illnesses. Health Serv Insights. 2019;12:1178632919837628. Published 2019 Apr 2. doi:10.1177/1178632919837628
8. Gabrielian S, Gordon AJ, Gelberg L, et al. Primary care medical services for homeless veterans. Fed Pract. 2014;31(10):10-19.
9. Lemke S, Boden MT, Kearney LK, et al. Measurement-based management of mental health quality and access in VHA: SAIL mental health domain. Psychol Serv. 2017;14(1):1-12. doi:10.1037/ser0000097
10. Averill JB. Matrix analysis as a complementary analytic strategy in qualitative inquiry. Qual Health Res. 2002;12(6):855-866. doi:10.1177/104973230201200611
11. Zuchowski JL, Chrystal JG, Hamilton AB, et al. Coordinating care across health care systems for Veterans with gynecologic malignancies: a qualitative analysis. Med Care. 2017;55(suppl 1):S53-S60. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000737
12. Daumit GL, Stone EM, Kennedy-Hendricks A, Choksy S, Marsteller JA, McGinty EE. Care coordination and population health management strategies and challenges in a behavioral health home model. Med Care. 2019;57(1):79-84. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001023
13. Parmelli E, Flodgren G, Beyer F, et al. The effectiveness of strategies to change organisational culture to improve healthcare performance: a systematic review. Implement Sci. 2011;6(33):1-8. doi:10.1186/1748-5908-6-33
14. Bolton R, Logan C, Gittell JH. Revisiting relational coordination: a systematic review. J Appl Behav Sci. 2021;57(3):290-322. doi:10.1177/0021886321991597
15. Gittell JH, Godfrey M, Thistlethwaite J. Interprofessional collaborative practice and relational coordination: improving healthcare through relationships. J Interprof Care. 2013;27(3):210-13. doi:10.3109/13561820.2012.730564
16. Bradley EH, Curry LA, Ramanadhan S, Rowe L, Nembhard IM, Krumholz HM. Research in action: using positive deviance to improve quality of health care. Implement Sci. 2009;4:25. Published 2009 May 8. doi:10.1186/1748-5908-4-25
1. Liu NH, Daumit GL, Dua T, et al. Excess mortality in persons with severe mental disorders: a multilevel intervention framework and priorities for clinical practice, policy and research agendas. World Psychiatry. 2017;16(1):30-40. doi:10.1002/wps.20384
2. Bowersox NW, Kilbourne AM, Abraham KM, et al. Cause-specific mortality among veterans with serious mental illness lost to follow-up. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2012;34(6):651-653. doi:10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2012.05.014
3. Davis CL, Kilbourne AM, Blow FC, et al. Reduced mortality among Department of Veterans Affairs patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder lost to follow-up and engaged in active outreach to return for care. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(suppl 1):S74-S79. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2011.300502
4. Copeland LA, Zeber JE, Wang CP, et al. Patterns of primary care and mortality among patients with schizophrenia or diabetes: a cluster analysis approach to the retrospective study of healthcare utilization. BMC Health Serv Res. 2009;9:127. doi:10.1186/1472-6963-9-127
5. Abraham KM, Mach J, Visnic S, McCarthy JF. Enhancing treatment reengagement for veterans with serious mental illness: evaluating the effectiveness of SMI re-engage. Psychiatr Serv. 2018;69(8):887-895. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201700407
6. Ward MC, Druss BG. Reverse integration initiatives for individuals with serious mental illness. Focus (Am Psychiatr Publ). 2017;15(3):271-278. doi:10.1176/appi.focus.20170011
7. Chang ET, Vinzon M, Cohen AN, Young AS. Effective models urgently needed to improve physical care for people with serious mental illnesses. Health Serv Insights. 2019;12:1178632919837628. Published 2019 Apr 2. doi:10.1177/1178632919837628
8. Gabrielian S, Gordon AJ, Gelberg L, et al. Primary care medical services for homeless veterans. Fed Pract. 2014;31(10):10-19.
9. Lemke S, Boden MT, Kearney LK, et al. Measurement-based management of mental health quality and access in VHA: SAIL mental health domain. Psychol Serv. 2017;14(1):1-12. doi:10.1037/ser0000097
10. Averill JB. Matrix analysis as a complementary analytic strategy in qualitative inquiry. Qual Health Res. 2002;12(6):855-866. doi:10.1177/104973230201200611
11. Zuchowski JL, Chrystal JG, Hamilton AB, et al. Coordinating care across health care systems for Veterans with gynecologic malignancies: a qualitative analysis. Med Care. 2017;55(suppl 1):S53-S60. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000737
12. Daumit GL, Stone EM, Kennedy-Hendricks A, Choksy S, Marsteller JA, McGinty EE. Care coordination and population health management strategies and challenges in a behavioral health home model. Med Care. 2019;57(1):79-84. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001023
13. Parmelli E, Flodgren G, Beyer F, et al. The effectiveness of strategies to change organisational culture to improve healthcare performance: a systematic review. Implement Sci. 2011;6(33):1-8. doi:10.1186/1748-5908-6-33
14. Bolton R, Logan C, Gittell JH. Revisiting relational coordination: a systematic review. J Appl Behav Sci. 2021;57(3):290-322. doi:10.1177/0021886321991597
15. Gittell JH, Godfrey M, Thistlethwaite J. Interprofessional collaborative practice and relational coordination: improving healthcare through relationships. J Interprof Care. 2013;27(3):210-13. doi:10.3109/13561820.2012.730564
16. Bradley EH, Curry LA, Ramanadhan S, Rowe L, Nembhard IM, Krumholz HM. Research in action: using positive deviance to improve quality of health care. Implement Sci. 2009;4:25. Published 2009 May 8. doi:10.1186/1748-5908-4-25