User login
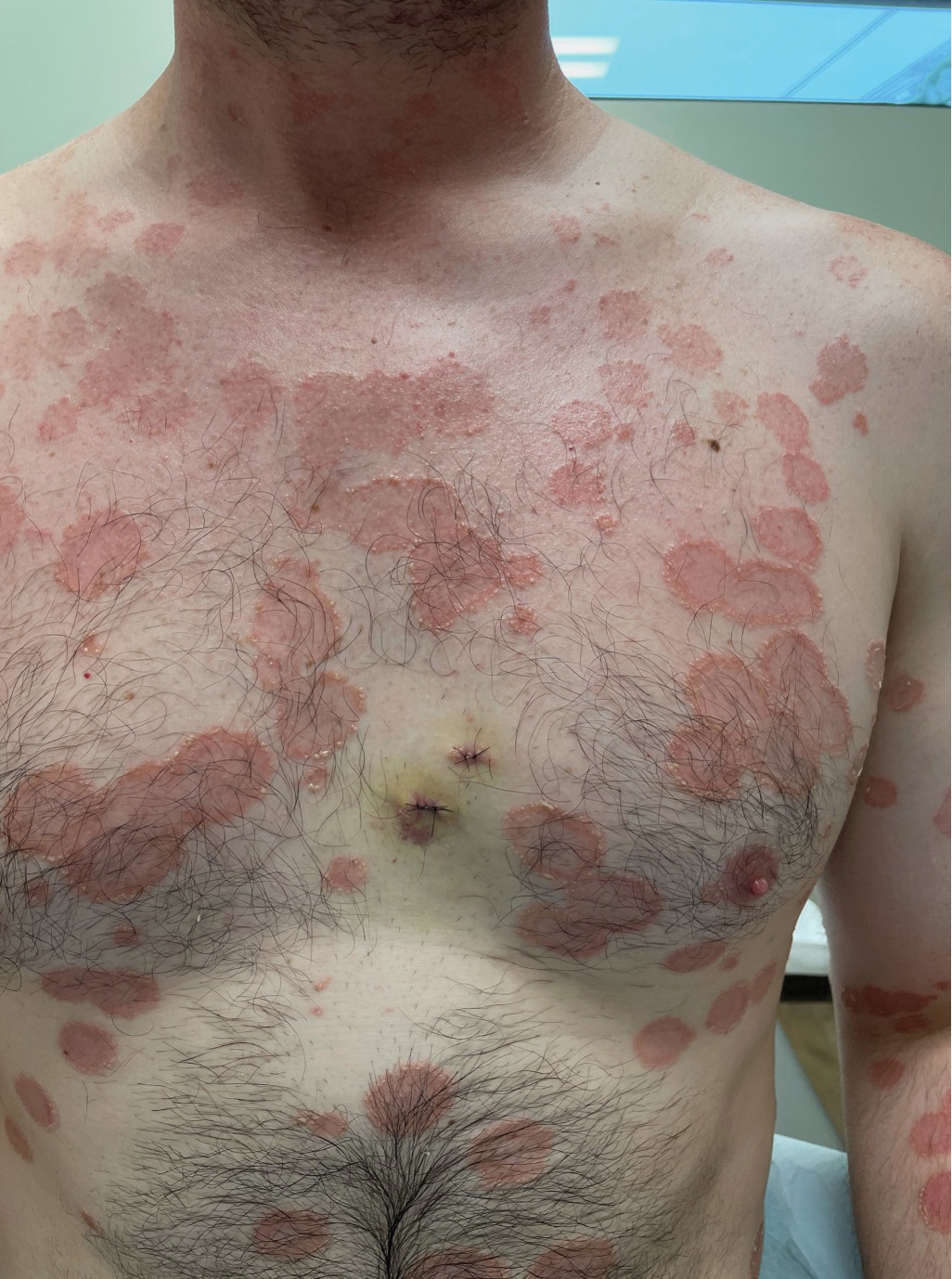
Painful and Pruritic Eruptions on the Entire Body
The Diagnosis: IgA Pemphigus
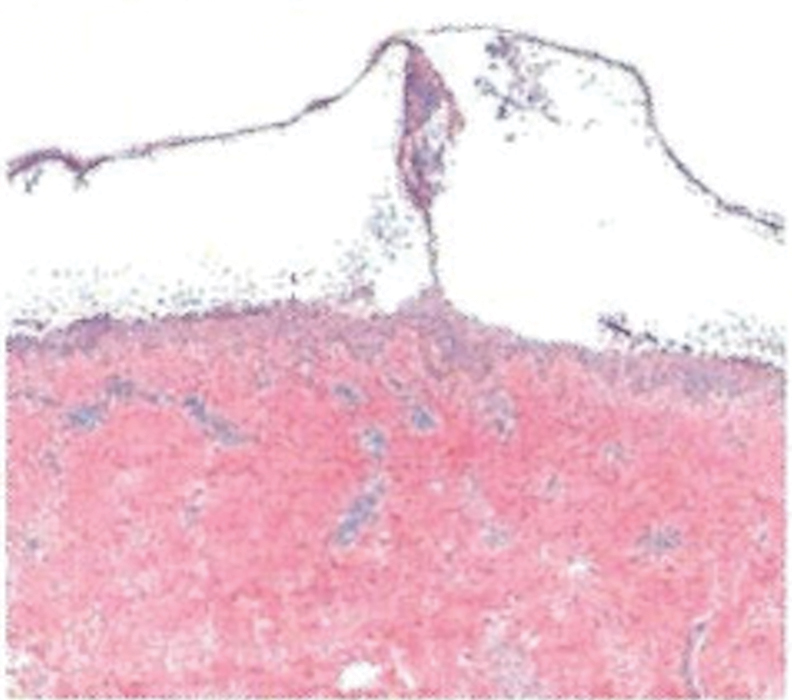
Histopathology revealed a neutrophilic pustule and vesicle formation underlying the corneal layer (Figure). Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) showed weak positive staining for IgA within the intercellular keratinocyte in the epithelial compartment and a negative pattern with IgG, IgM, C3, and fibrinogen. The patient received a 40-mg intralesional triamcinolone injection and was placed on an oral prednisone 50-mg taper within 5 days. The plaques, bullae, and pustules began to resolve, but the lesions returned 1 day later. Oral prednisone 10 mg daily was initiated for 1 month, which resulted in full resolution of the lesions.
IgA pemphigus is a rare autoimmune disorder characterized by the occurrence of painful pruritic blisters caused by circulating IgA antibodies, which react against keratinocyte cellular components responsible for mediating cell-to-cell adherence.1 The etiology of IgA pemphigus presently remains elusive, though it has been reported to occur concomitantly with several chronic malignancies and inflammatory conditions. Although its etiology is unknown, IgA pemphigus most commonly is treated with oral dapsone and corticosteroids.2
IgA pemphigus can be divided into 2 primary subtypes: subcorneal pustular dermatosis and intraepidermal neutrophilic dermatosis.1,3 The former is characterized by intercellular deposition of IgA that reacts to the glycoprotein desmocollin-1 in the upper layer of the epidermis. Intraepidermal neutrophilic dermatosis is distinguished by the presence of autoantibodies against the desmoglein members of the cadherin superfamily of proteins. Additionally, unlike subcorneal pustular dermatosis, intraepidermal neutrophilic dermatosis autoantibody reactivity occurs in the lower epidermis.4
The differential includes dermatitis herpetiformis, which is commonly seen on the elbows, knees, and buttocks, with DIF showing IgA deposition at the dermal papillae. Pemphigus foliaceus is distributed on the scalp, face, and trunk, with DIF showing IgG intercellular deposition. Pustular psoriasis presents as erythematous sterile pustules in a more localized annular pattern. Subcorneal pustular dermatosis (Sneddon-Wilkinson disease) has similar clinical and histological findings to IgA pemphigus; however, DIF is negative.
- Kridin K, Patel PM, Jones VA, et al. IgA pemphigus: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1386-1392.
- Moreno ACL, Santi CG, Gabbi TVB, et al. IgA pemphigus: case series with emphasis on therapeutic response. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:200-201.
- Niimi Y, Kawana S, Kusunoki T. IgA pemphigus: a case report and its characteristic clinical features compared with subcorneal pustular dermatosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:546-549.
- Aslanova M, Yarrarapu SNS, Zito PM. IgA pemphigus. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
The Diagnosis: IgA Pemphigus
Histopathology revealed a neutrophilic pustule and vesicle formation underlying the corneal layer (Figure). Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) showed weak positive staining for IgA within the intercellular keratinocyte in the epithelial compartment and a negative pattern with IgG, IgM, C3, and fibrinogen. The patient received a 40-mg intralesional triamcinolone injection and was placed on an oral prednisone 50-mg taper within 5 days. The plaques, bullae, and pustules began to resolve, but the lesions returned 1 day later. Oral prednisone 10 mg daily was initiated for 1 month, which resulted in full resolution of the lesions.

IgA pemphigus is a rare autoimmune disorder characterized by the occurrence of painful pruritic blisters caused by circulating IgA antibodies, which react against keratinocyte cellular components responsible for mediating cell-to-cell adherence.1 The etiology of IgA pemphigus presently remains elusive, though it has been reported to occur concomitantly with several chronic malignancies and inflammatory conditions. Although its etiology is unknown, IgA pemphigus most commonly is treated with oral dapsone and corticosteroids.2
IgA pemphigus can be divided into 2 primary subtypes: subcorneal pustular dermatosis and intraepidermal neutrophilic dermatosis.1,3 The former is characterized by intercellular deposition of IgA that reacts to the glycoprotein desmocollin-1 in the upper layer of the epidermis. Intraepidermal neutrophilic dermatosis is distinguished by the presence of autoantibodies against the desmoglein members of the cadherin superfamily of proteins. Additionally, unlike subcorneal pustular dermatosis, intraepidermal neutrophilic dermatosis autoantibody reactivity occurs in the lower epidermis.4
The differential includes dermatitis herpetiformis, which is commonly seen on the elbows, knees, and buttocks, with DIF showing IgA deposition at the dermal papillae. Pemphigus foliaceus is distributed on the scalp, face, and trunk, with DIF showing IgG intercellular deposition. Pustular psoriasis presents as erythematous sterile pustules in a more localized annular pattern. Subcorneal pustular dermatosis (Sneddon-Wilkinson disease) has similar clinical and histological findings to IgA pemphigus; however, DIF is negative.
The Diagnosis: IgA Pemphigus
Histopathology revealed a neutrophilic pustule and vesicle formation underlying the corneal layer (Figure). Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) showed weak positive staining for IgA within the intercellular keratinocyte in the epithelial compartment and a negative pattern with IgG, IgM, C3, and fibrinogen. The patient received a 40-mg intralesional triamcinolone injection and was placed on an oral prednisone 50-mg taper within 5 days. The plaques, bullae, and pustules began to resolve, but the lesions returned 1 day later. Oral prednisone 10 mg daily was initiated for 1 month, which resulted in full resolution of the lesions.

IgA pemphigus is a rare autoimmune disorder characterized by the occurrence of painful pruritic blisters caused by circulating IgA antibodies, which react against keratinocyte cellular components responsible for mediating cell-to-cell adherence.1 The etiology of IgA pemphigus presently remains elusive, though it has been reported to occur concomitantly with several chronic malignancies and inflammatory conditions. Although its etiology is unknown, IgA pemphigus most commonly is treated with oral dapsone and corticosteroids.2
IgA pemphigus can be divided into 2 primary subtypes: subcorneal pustular dermatosis and intraepidermal neutrophilic dermatosis.1,3 The former is characterized by intercellular deposition of IgA that reacts to the glycoprotein desmocollin-1 in the upper layer of the epidermis. Intraepidermal neutrophilic dermatosis is distinguished by the presence of autoantibodies against the desmoglein members of the cadherin superfamily of proteins. Additionally, unlike subcorneal pustular dermatosis, intraepidermal neutrophilic dermatosis autoantibody reactivity occurs in the lower epidermis.4
The differential includes dermatitis herpetiformis, which is commonly seen on the elbows, knees, and buttocks, with DIF showing IgA deposition at the dermal papillae. Pemphigus foliaceus is distributed on the scalp, face, and trunk, with DIF showing IgG intercellular deposition. Pustular psoriasis presents as erythematous sterile pustules in a more localized annular pattern. Subcorneal pustular dermatosis (Sneddon-Wilkinson disease) has similar clinical and histological findings to IgA pemphigus; however, DIF is negative.
- Kridin K, Patel PM, Jones VA, et al. IgA pemphigus: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1386-1392.
- Moreno ACL, Santi CG, Gabbi TVB, et al. IgA pemphigus: case series with emphasis on therapeutic response. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:200-201.
- Niimi Y, Kawana S, Kusunoki T. IgA pemphigus: a case report and its characteristic clinical features compared with subcorneal pustular dermatosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:546-549.
- Aslanova M, Yarrarapu SNS, Zito PM. IgA pemphigus. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
- Kridin K, Patel PM, Jones VA, et al. IgA pemphigus: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1386-1392.
- Moreno ACL, Santi CG, Gabbi TVB, et al. IgA pemphigus: case series with emphasis on therapeutic response. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:200-201.
- Niimi Y, Kawana S, Kusunoki T. IgA pemphigus: a case report and its characteristic clinical features compared with subcorneal pustular dermatosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:546-549.
- Aslanova M, Yarrarapu SNS, Zito PM. IgA pemphigus. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
A 36-year-old man presented with painful tender blisters and rashes on the entire body, including the ears and tongue. The rash began as a few pinpointed red dots on the abdomen, which subsequently increased in size and spread over the last week. He initially felt red and flushed and noticed new lesions appearing throughout the day. He did not attempt any specific treatment for these lesions. The patient tested positive for COVID-19 four months prior to the skin eruption. He denied systemic symptoms, smoking, or recent travel. He had no history of skin cancer, skin disorders, HIV, or hepatitis. He had no known medication allergies. Physical examination revealed multiple disseminated pustules on the ears, superficial ulcerations on the tongue, and blisters on the right lip. Few lesions were tender to the touch and drained clear fluid. Bacterial, viral, HIV, herpes, and rapid plasma reagin culture and laboratory screenings were negative. He was started on valaciclovir and cephalexin; however, no improvement was noticed. Punch biopsies were taken from the blisters on the chest and perilesional area.